How to check if the piston in the brake force regulator is soured, on 2109? And then the rear wheels don’t brake at all, but they use the handbrake
- The drum began to get warm after replacing the rear pads - 4 answers
- What causes friction to be heard on the rear wheel of a VAZ 2109? – 4 answers
- Only the right front wheel brakes - 3 answers
- How to eliminate braking after releasing the brakes? – 2 answers
- Which pads should not squeak? – 1 answer
About the rear brake force regulator, see here.
In short, you have a big gap there on the “sorcerer”. Once I had a “nine” and quickly dealt with the same “sore” as yours - I inserted a metal plate, that is, the gap on the “sorcerer” decreased and the rear wheels began to slow down.
Safety when driving a car is ensured by several systems, however, the main role is still assigned to the car's brake system. Timely braking saves you from traffic accidents, and the hand (parking) brake helps to secure the car on an inclined surface. It is these elements of the car that need to be given special attention. Timely diagnostics and repairs will help protect you and your car.
A properly functioning braking system is a guarantee of safety.
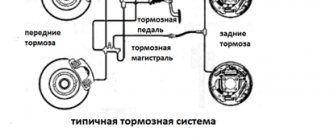
BRAKE SYSTEM DEVICE
Like any other mechanism in your car, the brake system consists of several elements that work together. The VAZ brake system is no exception. It is much simpler both in structure and functionality than in popular foreign cars, but it also deserves attention.
Its main elements are:
- Front wheel brake structures;
- Pipelines (both sides);
- Hydraulic drive main cylinder;
- Tank;
- An amplifier that has a vacuum structure;
- Braking mechanisms located on the rear wheels;
- Two pressure control levers;
- The hydraulic system also has a regulator that controls the pressure;
- Pedal;
- Hoses made of flexible material.
The system is designed so that if one of the circuits fails, the second will provide safe braking. This is done in order to make driving as safe as possible. The brake system of the VAZ 2115 works on the same principle.
The hand brake consists of:
- Lever with locking button;
- Cable in a protective sheath;
- Adjustment nuts;
- Equalizer;
- Locknuts;
- Protective cover.
The weak point of the handbrake is the cable . It requires constant attention. Its stretching or rupture can lead to disastrous consequences. It is also worth remembering that the pads are constantly worn out (especially with active use). It is important to pay attention to the brake force regulator of the VAZ 2113.
Diagram of the brake system of a front-wheel drive VAZ car (device)
These are the elements that make up the brake system of the VAZ 2114. Everything is quite simple, both in repair and in preventive maintenance. Any adjustments are also made without much effort. For example, you can adjust the handbrake in half an hour yourself, and adjusting the brake pressure regulator of the VAZ 2114 will not cause stupor even for a beginner. These are the key features of the domestic automobile industry - everything is easy and simple.
To be afraid or not
To begin with, I propose to understand the main points. Here it is important to distinguish when steam really poses a potential threat, that is, it indicates a malfunction, and when there is absolutely nothing to be afraid of.
If we are talking about absolutely safe and harmless smoke, then it should be white, have no odor and no traces of impurities. When the situation develops this way, we are talking about water vapor. Condensation has formed in the exhaust system, that is, a fairly large amount of moisture has accumulated. Now this water begins to actively evaporate due to gradual heating. It all turns into steam. It is in steam that this is important to remember. Because there is another concept. I'm talking about white smoke.
If we see such a picture when white smoke comes out of the exhaust, then it makes sense to suspect the engine or cooling system of some kind of malfunction.
During normal engine operation, the smoke coming out of the chimney should be transparent or close to it. However, on older cars and rather worn-out engines, the smoke becomes more toxic and dirtier.
What's the result?
If this element is present, then checking the catalyst for clogging will be your first priority.
Let's sum up the intermediate results. If white smoke is coming out of your car's exhaust pipe, this indicates high levels of moisture inside the exhaust system. It is important to pay close attention to this nuance. When the engine warms up, all the water should evaporate. Therefore, steam and condensate no longer come out of the pipe. But if the engine has warmed up and smoke continues to pour out, then this is an obvious sign of a problem. Something needs to be done. First, find out the reasons.
There are several possible reasons for this situation.
Let's look at them, and take a separate look at the features of diesel and gasoline internal combustion engines.
HOW TO ADJUST HYDRAULICS PRESSURE
As you know, hydraulic drives use fluids and pressure in the system instead of conventional mechanics, where any force is applied either directly or through transmission mechanisms. The key to clear hydraulic responsiveness is the presence of the required amount of brake fluid in the system and, of course, correctly adjusted pressure.
To properly adjust the pressure in the drive, you need to find an assistant. Doing this work alone is extremely inconvenient, and for the final test you will need an outside perspective.
The VAZ 2114 brake pressure regulator allows you to adjust the operation of the brakes to the required level. To do this you just need to do certain things:
- First you need to drive the car into the pit and rock its rear end. This will bring the suspension to the middle position, and this is exactly what needs to be achieved;
- Then slightly unscrew the front bolt on the VAZ brake pressure regulator mount;
- Using a screwdriver, make a small gap (2 mm) between the lever and the spring. For convenience, insert wire or whatever is at hand. A special protrusion on the lever allows you to move it to achieve the desired clearance;
- Tighten the previously loose bolt.
Now you need to check whether everything was done correctly. Accelerate to 35-40 km/h and brake. If the car does not drive away, then everything is done perfectly. In addition, you need to check the wheel locking sequence. Here you need a second person who will see how smoothly the brakes of the VAZ 2114 work. The whole point is that when working correctly, the front wheels should lock a little earlier than the rear ones. If this happens, then the system is set up with a bang.
If the front wheels lock later, the clearance must be increased. It is also possible that the rear wheels will be very late, in this case we reduce the gap. After completing all the work, securely tighten the regulator mount.
It is important to consider that all tests should not be carried out with flat tires. The result depends on this, and accordingly the brake system can be adjusted incorrectly. The tire pressure of the VAZ 2114 must meet the requirements specified in the vehicle documentation.
Operation diagram of the VAZ 2114 brake system
Real cases of malfunctions.
I noticed that when the engine is running, even to warm up, antifreeze presses through the plug. The fluid level also dropped, so I had to top it up periodically. I started looking for the problem. It turned out that the pump was at fault. Upon inspection, I saw that the timing belt protective cover was wet from the inside, and threads appeared on the block on the timing side. Thanks to the broken gasket of the water pump, the casing and block were splashed, and at high speeds after the engine warmed up, the coolant almost boiled and was thrown out through the valve. Since I took the car by hand, I didn’t bother to rebuild the pump - I installed a new one, now it doesn’t throw away and it’s dry.
Nikolay, Gazelle 4216:
There is a problem. Gazelle 4216, UMZ engine, new thermostat. When the engine warms up, everything is fine, it reaches operating temperature and the antifreeze begins to flow through the plug. The engine never overheated. I thought it was a crack in the head, but the oil level is normal, the antifreeze is clean, the fan works like a charm. Replacing the valve cover did not help. A thorough search for the cause at the service center showed that the gasket in the cylinder head had broken. The master said that the disease is known - it needs to be polished a little. It can be worse - often there are microcracks in the head, the beam should be changed immediately.
I noticed that coolant drips constantly appear around the plug and under the reservoir on the body. I read descriptions of faults on the Internet and started looking everywhere I could. I didn’t find it - everything is normal, but the streaks remain. I took the car to the service center.
The master enlightened me - it turns out that this is a common occurrence on this machine. When the pressure is released, especially when the engine is warm, the antifreeze flows out in an intense stream with splashing. As a result, some of the coolant splashes out. The process is repeated constantly when driving, splashes appear through the hole in the plug and numerous drips appear.
He solved the problem in literally 2 minutes - he inserted a piece of brake pipe into the hole where the fluid comes from and directed it to the bottom. I’ve been happy for a week now – everything is dry.
Alexey, VAZ 2107:
For several days, a distinct smell of antifreeze appeared in the cabin. An inspection under the hood showed that the reservoir was wet. I started to see what was happening. You add gas - the level is in place, at idle it steadily creeps up. I turned it off again and the antifreeze began to leave the container. I felt the pipes - they seemed to be in order. The service department said that the thermostat died. I changed it, but the antifreeze still rose into the reservoir at idle. I was puzzled, because I had just recently changed the pipes, the cooling radiator and heaters, the pump, the cylinder head gasket - I installed everything new.
It was not possible to resolve the issue on our own; we had to turn to specialists again. They were smart for almost a week (and it was in this service that they changed everything for me). It turned out that when they changed the cylinder head gasket, they did not pay attention to the surface; when tightening it, it was pressed through. They removed the head, sanded it, replaced the gasket with a new one, carefully installed it and tightened it - the problem was gone.
DEVICE OF BRAKE MECHANISMS
Many people wonder what is the difference between the brake mechanisms of the front wheels and the rear ones. The fact is that when braking, they are subject to different loads, and they do not operate synchronously. But this is not the main reason for the differences.
The front mechanisms consist of:
- Brake disc of classic design;
- Direction pads;
- Calipers;
- Directly the pads themselves;
- Cylinder;
- Piston;
- Seal rings;
- Protection casing;
- Direction finger;
- And its cover, which performs a protective function.
The design of the front brakes is a little simpler than the rear, however, this does not mean that they play a lesser role in braking. After all, these are the mechanisms that work first.
- Nuts that secure the hub;
- Actually, the hub itself;
- Tension springs (lower and upper);
- Brake pads;
- Directional springs;
- Wheel cylinder;
- Expansion bar;
- Handbrake lever finger;
- Handbrake lever;
- Mechanism casing.
Steam from the exhaust pipe on a warm engine: is it normal or dangerous?
Good day to all car enthusiasts! Winter. It's a wonderful time. It just so happens that most problems and breakdowns of cars happen during this period. Moreover, sometimes we may not even notice signs of emerging problems. For example, when steam comes out of the exhaust pipe on a warm engine.
Often motorists ignore these symptoms. And indeed, in winter there is nothing surprising in a couple. It's cold outside, very humid, hence the evaporation.
But white smoke, which is often called simply steam, is not always so harmless. After all, this can happen in the summer, and then there are even more questions.
What does the VAZ 2114 brake system consist of?
The brakes of the VAZ 2114 are a vital system of the car. These are not loud words and every driver will agree with this. Also, every driver knows that timely, high-quality repair of the VAZ 2114 brake system is the key to its trouble-free operation.
The brake system on the VAZ 2114 consists of two main parts:
- Wheel mechanisms - directly affect the elements rotating with the wheel and slow down its rotation.
- Drive – a system for transmitting force from the pressed pedal to the wheel mechanisms.
The “fourteenth” has a dual-circuit system with a hydraulic drive. This means that the force created by pressing the pedal creates fluid pressure (hydraulics) throughout the system. This same pressure forces the wheel cylinders to work. The concept of “dual-circuit” means that the pedal force is transmitted along two lines (circuits) independent of each other to pairs of wheels. The contours have a diagonal distribution: the rear right wheel works together with the front left one, and the rear left one works with the front right wheel. If one of the circuits fails, this solution allows you to maintain vehicle stability when braking, especially on slippery roads and when turning.
Important: the main condition for the system to work is its tightness. Therefore, it is extremely dangerous to operate a car with fluid leakage. It is also extremely dangerous for air to enter the system. According to its physical properties, air, when compressed, decreases in volume many times over, unlike liquid, which, when compressed, practically does not change its volume. When braking a car with a leaky system, the pedal may “fail” and the brakes of the VAZ 2114 will not work.
VAZ 2114 brake system diagram
The brake system diagram of the VAZ 2114 has a classic layout, similar to both VAZ models and cars of many world brands.
- Master brake cylinder.
- Metal pipes of the 1st circuit.
- Flexible hose for front mechanisms.
- Liquid reservoir.
- Vacuum brake booster.
- Metal pipes of the 2nd circuit.
- Rear wheel cylinders.
- Brake pressure regulator drive lever.
- Flexible hose for rear mechanisms.
- Pressure regulator.
- Pressure regulator bracket.
- Pedal.
Main brake cylinder VAZ 2114
General view of the brake master cylinder (MBC) under the hood of a car with a fluid reservoir and a vacuum booster.
The master brake cylinder creates pressure in the system, distributes it along the circuits and transmits it to the wheel cylinders. It consists of a two-section housing, inside which a piston moves, driven by a pedal. The fluid pressure created in the hydraulic structure is transmitted through circuits to the wheel mechanisms.
Clear downgrade problems
This is not entirely relevant to our question, but it’s worth mentioning. This needs to be checked first, and if you have not identified the reasons, then we will dig deeper. So, antifreeze may leak due to a leak in the system, let’s look at it point by point:
- Engine radiator leaked . Of course, this can be determined very quickly, just look at it and also look at the stains under the car; if it is leaky, there will be red, green or blue drops. Of course, you can try to solder or clamp the radiator tubes, but often the plastic component (sidewalls) is damaged, there is nothing you can do about it, you need to replace it.
- Heater radiator . Almost the same picture, only the interior heater is leaking, it is more difficult to diagnose, because the coolant will drip onto the seal (carpet) in the cabin. But the reasons for the determination are simple: if there is a smell of antifreeze in the cabin (sweet smell), but not outside. If the glass sweats even in dry weather, and there is an oily coating on the glass. Liquid leaving the tank means your heater radiator is covered, of course, if you remove the plastic (decorative) protection of the instrument panel, you will see that it is dripping somewhere. We do the same, either restore it, or if this is impossible, change it.
- Hoses . They wear out over time, because they expand each time (when the engine heats up) and contract (when it cools down), such work will sooner or later damage them, they will not be able to hold pressure and will rupture. Of course, there may be minimal damage, but it will leak constantly. It is useless to make hoses; it is better to replace them.
- Tubes _ The situation is the same as with hoses, they are metal and usually last a long time. But there are situations when they also occur.
- Thermostat and pump . These are two mechanisms that are designed to pump and regulate the flow of coolant; the housings are made of metal or plastic and they often leak, this happens from time to time. For replacement, they are practically not repaired.
- The expansion tank cap and the tank itself. The cap is a valve ; after a certain mileage it also fails; if it does not hold pressure, then antifreeze from the expansion tank can splash out when warming up. The tank itself may also burst, because it is made of plastic; if the lid is faulty, it may rupture. For replacement.
These are obvious reasons, they are worth checking first - ALWAYS! It often happens that the driver searches and cannot find it, but antifreeze (antifreeze) goes into, say, the stove and then into the passenger compartment, which is quite difficult to immediately determine. Park the car in a dry area or in a garage, if possible, and observe, if there are stains the color of your coolant, then this is definitely a leak, look for it!
Front brake mechanism
The design of the front brake mechanism on the VAZ 2114
The front brake mechanism consists of the following components:
- Brake disk. Directly connected to the wheel hub and rotates with it. Slowing down the rotation and stopping the disk leads to the slowing down and stopping of the wheel.
- Pad guide. Serves as a holder for the pads and a base for the guide pins.
- Caliper. It combines the pads, cylinder, and piston into a single unit and ensures uniform transmission of force from both pads to the disc.
- Brake pads. They directly act on the disc, squeezing it on both sides and slowing down the movement.
- Cylinder. A sealed cavity in which the piston moves.
- Piston. Under the influence of hydraulic fluid pressure, the pad is pressed against the disc. Thanks to the “floating clamp” system, the second block is pressed simultaneously. This ensures uniform wear of their linings and discs and guarantees effective braking.
- Seal ring. Prevents fluid leakage and ensures system tightness
- A cover to protect the guide pin from dirt, allowing for unhindered movement of the pads.
- Guide finger. Allows the pads to move evenly and adhere to the disc with their entire plane.
- Protective cover. Protects the disc from road dirt.
The front wheels are equipped with disc brakes. They automatically adjust the clearance from the pad to the disc. The caliper and cylinder form a floating caliper, which creates the same even force on both pads. This ensures uniform wear of the linings. To monitor their wear, there is an indicator on the inner block.
Finding the cause of pedal failure
The most common reason, which accounts for up to 70% of cases of brake pedal failure while the engine is running, is airing of the system, that is, atmospheric air entering the pipelines and lines through which the brake fluid moves. This, in turn, may be caused by the following factors:
- Low fluid level in the compensating tank - when the brake fluid level drops below the minimum mark, the vacuum created by the system elements begins to draw air in.
- Severe mechanical wear of the pads and working surfaces when the fluid level is close to the minimum - in combination, these phenomena lead to airing due to the pistons traveling too deep in the brake cylinders.
- Incorrect choice of brake fluid - a discrepancy between the fluid class, operating conditions and design features of the system can cause destruction of seals and cuffs, and the formation of viscous clots - “thrombi”.
- Boiling of the liquid - occurs when the system is severely overheated, for example, during prolonged aggressive driving in the hot season. Causes sudden and severe pedal failure due to changes in the physical properties of the substance.
- Depressurization is the occurrence of breakdowns, breaks, leaks in system elements and places and contacts through which brake fluid flows out and air gets in.
In addition, pedal failure is often associated with a rupture of the vacuum booster diaphragm. This type of malfunction is easy to diagnose - it only appears when the internal combustion engine is running, and the brake fluid level does not change while the pedal is depressed. This is explained by the fact that a torn diaphragm is not able to create the required vacuum in the amplifier chamber even with full pedal travel.
If the pedal does not fall completely, but moves jerkily, going through some areas easily, and others with considerable effort, we can conclude that the pads or caliper are not installed correctly or are poorly secured. However, do not forget that the first two to three hundred kilometers after their installation may also be due to the natural break-in of parts.
Heater radiator repair
Usually, if mechanical damage is detected, the stove radiator is replaced with a new one. However, some car owners try to repair cracks and holes using soldering. A copper radiator is quite easy to solder, and it is much easier to restore than an aluminum one. To repair an aluminum heat exchanger, you will need special flux and tinning solder, as well as a powerful soldering iron. The damaged area is first cleaned of dirt and degreased. Then flux and solder are applied to it with a soldering iron. After soldering, it is recommended to check the radiator under pressure to make sure there are no leaks.
The brake failed at full speed: what to do?
First, try pressing the pedal sharply several times: perhaps its functionality will be partially restored. Next, assess the situation and identify a place where you can gradually turn. Then tighten the handbrake (don't do it too hard) and start shifting (if you have a manual transmission) to a lower gear. At the same time, when the lever is in “neutral”, press the accelerator (perform “re-throw”) to “prepare” the gearbox gears for emergency operation. As a last resort, choose the lesser of two “evils” - it is better to run into some obstacle near the road (roadside bushes are a good option) than to collide with a car.