Being an integral element of the platform, the suspension of the Lada Largus has a reinforced design due to the rather massive bodies, both station wagon and van. Actually, both the front suspension subframe and the rear beam with separate localization of shock absorbers and springs are reinforced.
Lada Largus is essentially a replication of the original car model called Dacia Logan, which came out of the assembly line of Renault's Romanian subsidiary in 2006. And since 2012, after adaptation to the national characteristics of the Russian market, this super-compact model, intended for developing countries, received a rebranded version of Auto VAZ under the name Lada Largus FL.
The original, and subsequently the replication of this model, are based on the Renault family platform, namely the B0, which, according to some experts, was borrowed from Nissan.
Checking the Lada Largus chassis and transmission
Tools:
Notes:
We check the condition of the chassis and transmission every 15 thousand kilometers.
The parts of the chassis (wheels, suspension arms, anti-roll bar, front suspension subframe, rear suspension beam, shock absorbers and suspension springs) and transmission (front wheel drive shafts) must be free of deformations, cracks and other mechanical damage affecting the shape and strength of parts.
Checking the condition of wheel hub bearings
Alternately hanging the front and rear wheels (while the car must be securely fixed on stands), we check the condition of the wheel hub bearings.
Note:
Use only factory-made stands.
The wheel should rotate evenly by hand, without jamming or knocking.
Holding the wheel in a vertical plane, we alternately sharply pull the upper part of the wheel toward ourselves, and the lower part away from us, and vice versa.
We make sure there is no play (knock). If there is a knock on the front wheel, ask an assistant to press the brake pedal. If the knocking noise disappears, then the wheel bearing is faulty, and if the knocking noise remains, then the ball joint is most likely worn out.
The hub bearings of the front and rear wheels are not adjustable and must be replaced if there is play.
Checking the condition of the ball joint
1. To check the serviceability of the ball joint, insert a mounting blade between the steering knuckle eye (which includes the ball joint pin) and the suspension arm.
2. By pressing the lever away from the steering knuckle with a mounting blade, we monitor the movement of the ball joint housing relative to the steering knuckle eye.
If there is play in the connection, replace the ball joint.
3. We check the condition of the protective covers of the ball joints of the front suspension.
We replace ball joints with torn or cracked covers.
Checking the silent block of the front suspension arm
1. We alternately insert the mounting blade between the subframe and the end of the outer bushing of the silent block (on one side) and the subframe and the lever head (on the other side of the silent block).
2. We are trying to move the lever head along the axis of the bolt, first in one direction and then in the other.
If the lever head moves freely, without effort, it means that the silent block of the lever is badly worn or damaged and needs to be replaced. Ruptures, cracking and swelling of the rubber bushing of the silent block are unacceptable.
3. Similarly, we check the condition of the other silent block of the lever.
Checking the condition of the anti-roll bar cushions
1. We inspect the anti-roll bar cushions.
If ruptures, cracks or severe deformation are detected on the rubber cushions, they must be replaced.
2. Grasping the stabilizer bar with your hand near its attachment point to the lever, sharply swing the bar up and down.
If play is detected in the connection of the stabilizer bar with the front suspension arm, replace the rubber bushings of the screw securing the stabilizer bar to the arm.
Checking the condition of the silent block of the rear suspension beam arm
To check the condition of the silent block of the rear suspension beam lever, we insert a mounting spatula between the body bracket and the end of the outer hinge bushing and try to move the lever head along the axis of the bolt.
If ruptures or peeling of the rubber of the hinge are discovered, then replace the silent block.
Checking the condition of springs and shock absorbers
1. We check the condition of the springs and shock absorbers of the front suspension.
2. We check the condition of the springs and shock absorbers of the rear suspension.
The suspension springs must not be damaged. Tearing, cracking and severe deformation of rubber bushings, cushions and compression buffers of shock absorbers are unacceptable. Liquid leakage from shock absorbers is not allowed. A slight “fogging” of the shock absorber in its upper part, while maintaining the characteristics, is not a malfunction.
Checking the condition of the protective covers of the outer and inner joints of the front wheel drives
Alternately rotating and turning the front wheels, we inspect the protective covers of the outer and inner joints of the front wheel drives, and check the reliability of their fastening with clamps.
Covers that are cracked, torn or have lost elasticity must be replaced.
Checking the condition of the wheel drive inner joint seals
We check that there is no oil leakage from the gearbox through the seals of the internal joints of the wheel drives. If there is a leak, replace the seals.
The article is missing:
Source
Replacing shock absorbing struts
It is necessary to change the Lada Largus shock absorber when a factory defect is detected or when a certain mileage has been covered. Unscheduled work is carried out in the presence of obvious defects or leakage of technical fluid. And also, in case of loss of their performance.
Carrying out technical work is preceded by diagnostics, and the tightening of the bolts securing the shock absorbers to the levers is also checked.
Removing shock absorber struts
Let's find out the algorithm for dismantling actions:
- The vehicle must be placed on a lift. It is possible to carry out dismantling activities in the inspection pit. In this case, you need to put the car in first gear and put stops under the front wheels.
- If the car is designed for 5 passengers, as is the case with the R90 model, you need to move the lining of the rear wheel arches to the side. Having opened the luggage compartment door, we remove the rear seats of the third row, if we are talking about a station wagon.
- Remove the trim from the rear arches and remove the lower mounting bolts. Remove the trim frame.
- Remove the rubber cap from the shock absorber.
- Next, you can see the nut that holds the rod. She is also being filmed.
- Then the rubber cushion is removed.
- The fastening bolts are removed.
- The shock absorber is removed.
- The compression buffer and protection cover are removed from the rod.
- They must subsequently be separated.
- The protective cap is dismantled.
- If there are worn out and/or damaged parts, remove them.
After this, the shock absorber is placed vertically. The rod lowers and extends until it stops. In this case, there should be no extraneous noise, knocking or failure.
If the above points occur, the shock-absorbing structure changes. It is also dismantled if deformation of the rod is detected and/or the integrity of the threaded connection is compromised
When checking, pay attention to the degree of compression of the spring
Similar to the procedure described, the second shock-absorbing device is dismantled and replaced.
It remains to consider the issue of installing a new kit, which is what we will do.
Shock absorber installation
Installation of the rear shock-absorbing structure is carried out in reverse order.
So, as we have already said, installation is carried out in the reverse order:
- You need to install a new nut that secures the shock absorber rod.
- It is advisable to change the shock absorber mounting bolt connecting it to the rear suspension.
- The following is placed on the rod: a washer, a hinge bushing, and a lower cushion.
- We install the shock absorber in the rear wheel arch of the car.
- We connect it to the lever of the rear suspension structure.
- The rod fits into the mounting hole of the wheel arch.
- The upper hinge pad, control washer and new fastening nut are put on the rod. The tightening torque of the nut is 14 Nm (1.4 kgf.m).
Don't forget to put the plugs where the new elements are attached to the rear wheel arches.
The above operations in the specified sequence are acceptable for working with the second shock-absorbing structure.
We put the wheels in place. We fasten the arch trim, storage compartment, fastening parts and brackets for the side and rear armrests.
We lower the car to the ground. And only now we tighten the bolts securing the shock absorbers to the arms of the rear suspension structure.
The tightening torque of the bolts is 105 Nm (10.5 kgf.m. We work with a replaceable head No. 21.
We repair the Lada Largus suspension ourselves
The suspension of the Lada Largus ensures comfortable movement. It is recognized by many motorists as unkillable. This is especially true on domestic roads. This detail is completely borrowed from Renault Logan. It is energy-intensive, soft and reliable. But sometimes problems arise with it. You can solve them yourself.
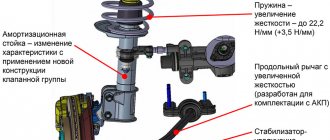
Design and characteristics of suspensions
The front suspension is a simple, comfortable and inexpensive MacPherson strut design, but with some modifications. It is mounted on a subframe. The front arms are attached to it. At the ends of the levers there is a ball joint, through which the lever is connected to the steering knuckle. Vibrations are dampened by shock absorber struts with coil springs. To avoid lateral rolls, a torsion stabilizer is installed.
If in old VAZ models the lever was changed separately from the ball joint, then on Largus the ball joints are changed simultaneously with the lower lever, as on Renault Logan. Largus also differs in that the stabilizer is secured to a lever located below. Due to the simplicity of the design and maintainability, you can find faults yourself at home.
The main part of the rear suspension is a semi-independent beam, in the cavity of which there is a stabilizer, rigidly connected to the lower arms. The rear shock absorbers are attached to the lever at their lower end; its springs rest against the lever bracket through a gasket. The difference between the largus suspension is that the shock absorber and spring are separate parts that are not combined into a single unit. Each lever is attached to the body using silent blocks. The rear suspension is a reliable unit; it rarely breaks, but is easy to repair.
Diagnostics and signs of suspension malfunctions
One of the advantages of the Lada Largus is its reliable and durable suspension. But despite this, over time the elements wear out. If proper maintenance is carried out in a timely manner, faults are identified and corrected, you can extend the life of the suspension and prevent failure of its parts.
The subframe is the main element of the front suspension, so timely diagnostics will avoid problems with the chassis and unit failure. The levers, rear part of the engine and exhaust system cushions are mounted on it. Subframe malfunctions should be looked for in the places where the hanging elements are attached. Typical symptoms of malfunctions are a knocking sound in the front suspension, and wheel alignment changes.
Functional load of Lada Largus suspensions
Front suspension
One of the main tasks of this element of the chassis is to ensure smooth movement. When the front wheel encounters an uneven road, the body continues its movement along the previously traversed trajectory, “damping” all vibrations.
Its design is much more complex than the rear variation, since it provides the ability to change the position of the front wheels, thereby providing effective control of movement in all directions. This is justified by a number of design features that are subject to additional loads.
It is worth noting that the front part of the Lada Largus, like any other car, is heavier than the rear, because the weighty units of the power and chassis are concentrated there. Undoubtedly, this causes a large load, which contributes to its rapid wear. Thus, the condition of the front suspension is directly related to the safety of driving the car.
Rear suspension
As a rule, the rear suspension of the Lada Largus is much simpler than the front: the wheels of the same name are not required to change the angle of rotation, and their orientation is focused only on vertical movement. But, despite this, the condition of this unit is also related to the safety of movement and the corresponding level of comfort.
In relation to it, semi-dependent and dependent varieties are considered. In the first case, the suspension consists of two levers fixed between the body and the wheels, which provides optimal kinematics. The dependent suspension is connected by a rear axle beam, which is attached to the body by trailing arms.
Analogs of rear shock absorbers
As for analogues of largus. We do not have exact data (sizes). Therefore, we will not mislead you. But, we authoritatively declare that on the spare parts market you can choose the necessary goods from global manufacturers and products from Russian companies. Here are some of them:
- The products of the manufacturer Monroe are of interest. You can order directly and save money.
- Sachs products are considered softer.
- Among the domestic manufacturers, one can single out the Russian one, which produces several lines. The “Comfort” kit has won the greatest popularity among Largus owners. They have an acceptable price/quality ratio. Many people like the kit, although they complain about excessive rigidity. The best absorption of road surface irregularities occurs at a speed of 50 km/h.
Malfunctions and ways to eliminate them
During its operation, the suspension can cause not only all sorts of sounds in the form of knocks and squeaks, but also direct problems with the steering. If this part behaves suspiciously, it should be immediately fully diagnosed.
Noise and knocking while driving
The main reasons for the suspension failure of the Lada Largus are related to uneven roads. For example, a knocking sound in the front suspension of a Lada Largus begins after the car falls into a hole or hits a bump.
In addition, the inexperience of the car owner is not the last circumstance that leads to repair of the chassis. Having noticed a pothole belatedly, the brake pedal is pressed, which only increases the load several times and aggravates the situation.
The problem may be faulty shock absorbers, worn ball joints, loose fastening bolts, or lack of lubrication. If worn parts need to be replaced, this should be done immediately. When a malfunction of the suspension is associated with the fixing force or lack of lubricant, tightening them and appropriate lubrication will correct the situation.
If there is noise or knocking in the rear suspension, in addition to rubber seals and torque rods, attention should be paid to the condition of the exhaust pipe. A detailed analysis of the entire mechanism allows you to accurately determine the cause of the breakdown and eliminate it in a timely manner.
Departure of a vehicle from straight-line motion
Most often this is due to different tire pressures, incorrect wheel alignment or incorrect bearing clearance. These problems are resolved by checking and adjusting the characteristics to suit normal operation.
In some cases, even disassembling the suspension using specialized equipment is required. For example, if the front suspension arm of a Lada Largus is severely deformed, then the entire axle will need to be replaced.
It is worth noting that tire defects may not be immediately noticeable, so you should swap the wheels of the front of the car. If the direction of care changes, then the problem is in the condition of the rubber. When the loss of strength of one of the springs is to blame, it will immediately compress, affecting the visual tilt of the car body.
Installation of wheels with a larger radius
Largus comes standard with 15R wheels. Many motorists choose the 16 or 17 radius option instead of the one proposed by the factory. Additionally, this makes the car's exterior more attractive. However, this option also has a significant drawback, namely the unstable position of the car when driving, as well as malfunctions in the ABS system and some related sensors.
Installation of spacers
The most budget option (and popular) is to install special spacers, which are sold at any auto parts store. The only thing that is required from the car owner is the removal of the suspension struts. The parts themselves are unified and suitable for many VAZ cars. Spacers are installed between the rack and the body bowls (as an option - between the beam and the rack).
Replacing strut parts
One of the best methods for increasing ground clearance is to install stiffer springs and longer shock absorbers. As a rule, such racks are approximately 20 mm longer than standard devices. In combination with reinforced springs, they are able to significantly increase ground clearance, and the car does not sag all the way when transporting the maximum permissible weight of cargo. The only drawback is the higher price of such kits.
Repairing the suspension yourself and increasing the ground clearance on the Lada Largus is easy to do if you have at least minimal car repair skills. If you have never done this before, it is still recommended to carefully study the instructions. And if you are unsure of your own abilities, it is better to turn to qualified car service specialists.
We recommend reading:
- Lada Largus car data
- Tips for installing and operating roof rails on Largus
- Universal and original DRLs for Lada Largus
- Methods for attaching a spare tire on Largus
- The principle of operation of LPG on the Lada Largus: which gas is better?
- Alternator belt Lada Largus - types and replacement on different types of engines
How to check ball joints on Largus
We check the condition of the chassis and transmission every 15 thousand kilometers. The parts of the chassis (wheels, suspension arms, anti-roll bar, front suspension subframe, rear suspension beam, shock absorbers and suspension springs) and transmission (front wheel drive shafts) must be free of deformations, cracks and other mechanical damage affecting the shape and strength of parts. Alternately hanging the front and rear wheels (while the car must be securely fixed on stands), we check the condition of the wheel hub bearings.
Holding the wheel in a vertical plane, we alternately sharply pull the upper part of the wheel toward ourselves, and the lower part away from us, and vice versa. We make sure there is no play (knock). If there is a knock on the front wheel, ask an assistant to press the brake pedal. If the knocking noise disappears, then the wheel bearing is faulty, and if the knocking noise remains, then the ball joint is most likely worn out. The hub bearings of the front and rear wheels are not adjustable and must be replaced if there is play. To check the serviceability of the ball joint, insert a mounting blade between the steering knuckle eye (which includes the ball joint pin) and the suspension arm.
By pressing the lever away from the steering knuckle with a mounting blade, we monitor the movement of the ball joint housing relative to the steering knuckle eye. If there is play in the connection, replace the ball joint.
We check the condition of the protective covers of the front suspension ball joints. We replace ball joints with torn or cracked covers. To check the silent block of the front suspension arm...
... we alternately insert the mounting blade between the subframe and the end of the outer bushing of the silent block (on one side) and the subframe and the lever head (on the other side of the silent block) ... ... and try to move the lever head along the axis of the bolt, first into one, and then into the other side. If the lever head moves freely, without effort, it means that the silent block of the lever is badly worn or damaged and needs to be replaced. Ruptures, cracking and swelling of the rubber bushing of the silent block are unacceptable. Similarly, we check the condition of the other silent block of the lever.
We inspect the anti-roll bar cushions. If ruptures, cracks or severe deformation are detected on the rubber cushions, they must be replaced. Grasping the stabilizer bar with your hand near its attachment point to the lever...
...sharply swing the barbell up and down. If play is detected in the connection of the stabilizer bar with the front suspension arm, replace the rubber bushings of the screw securing the stabilizer bar to the arm. To check the condition of the silent block of the rear suspension beam arm...
...insert the mounting blade between the body bracket and the end of the outer joint bushing and try to move the lever head along the axis of the bolt. If ruptures or peeling of the rubber of the hinge are discovered, then replace the silent block. Checking the condition of the springs and shock absorbers...
...and rear suspension. The suspension springs must not be damaged. Tearing, cracking and severe deformation of rubber bushings, cushions and compression buffers of shock absorbers are unacceptable. Liquid leakage from shock absorbers is not allowed. A slight “fogging” of the shock absorber in its upper part, while maintaining the characteristics, is not a malfunction. Alternately rotating and turning the front wheels...
...we inspect the protective covers of the outer... ...and inner joints of the front wheel drives, checking the reliability of their fastening with clamps. Covers that are cracked, torn or have lost elasticity must be replaced. We check that there is no oil leakage from the gearbox through the seals of the internal joints of the wheel drives. If there is a leak, replace the seals.
As you know, the front wheels of the Lada Largus, like any car, provide movement on the road and allow you to maneuver. Of course, their position imposes a number of requirements in terms of handling, the compliance of which is ensured by the suspension with ball joints. The latter may have a number of malfunctions that require timely diagnosis and search for methods to eliminate them.
The ball joint looks like a cone-shaped pin with a spherical tip
The Largus ball joint is a part of the suspension that connects its arm to the steered wheel. It helps rotate the hubs in horizontal and vertical positions. Moreover, the part itself has the shape of a cone with a spherical tip, which simultaneously rotates and swings.
Replacing shock absorbing struts
It is necessary to change the Lada Largus shock absorber when a factory defect is detected or when a certain mileage has been covered. Unscheduled work is carried out in the presence of obvious defects or leakage of technical fluid. And also, in case of loss of their performance.
Carrying out technical work is preceded by diagnostics, and the tightening of the bolts securing the shock absorbers to the levers is also checked.
Removing shock absorber struts
Let's find out the algorithm for dismantling actions:
- The vehicle must be placed on a lift. It is possible to carry out dismantling activities in the inspection pit. In this case, you need to put the car in first gear and put stops under the front wheels.
- If the car is designed for 5 passengers, as is the case with the R90 model, you need to move the lining of the rear wheel arches to the side. Having opened the luggage compartment door, we remove the rear seats of the third row, if we are talking about a station wagon.
- Remove the trim from the rear arches and remove the lower mounting bolts. Remove the trim frame.
- Remove the rubber cap from the shock absorber.
- Next, you can see the nut that holds the rod. She is also being filmed.
- Then the rubber cushion is removed.
- The fastening bolts are removed.
- The shock absorber is removed.
- The compression buffer and protection cover are removed from the rod.
- They must subsequently be separated.
- The protective cap is dismantled.
- If there are worn out and/or damaged parts, remove them.
After this, the shock absorber is placed vertically. The rod lowers and extends until it stops. In this case, there should be no extraneous noise, knocking or failure.
If the above points occur, the shock-absorbing structure changes. It is also dismantled if deformation of the rod is detected and/or the integrity of the threaded connection is compromised
When checking, pay attention to the degree of compression of the spring
Similar to the procedure described, the second shock-absorbing device is dismantled and replaced.
It remains to consider the issue of installing a new kit, which is what we will do.
Shock absorber installation
Installation of the rear shock-absorbing structure is carried out in reverse order.
So, as we have already said, installation is carried out in the reverse order:
- You need to install a new nut that secures the shock absorber rod.
- It is advisable to change the shock absorber mounting bolt connecting it to the rear suspension.
- The following is placed on the rod: a washer, a hinge bushing, and a lower cushion.
- We install the shock absorber in the rear wheel arch of the car.
- We connect it to the lever of the rear suspension structure.
- The rod fits into the mounting hole of the wheel arch.
- The upper hinge pad, control washer and new fastening nut are put on the rod. The tightening torque of the nut is 14 Nm (1.4 kgf.m).
Don't forget to put the plugs where the new elements are attached to the rear wheel arches.
The above operations in the specified sequence are acceptable for working with the second shock-absorbing structure.
We put the wheels in place. We fasten the arch trim, storage compartment, fastening parts and brackets for the side and rear armrests.
We lower the car to the ground. And only now we tighten the bolts securing the shock absorbers to the arms of the rear suspension structure.
The tightening torque of the bolts is 105 Nm (10.5 kgf.m. We work with a replaceable head No. 21.
Features of operation
Based on its direct purpose, this suspension part is operated in a fairly harsh mode. After all, the main load of the body and all its components is on the insignificant surface of the ball. If we add to this the weight of passengers and possible cargo, poor-quality road surface, then it increases many times, which provokes wear of the ball joints and failure of the entire suspension.
The most important nuance of operation is that it is almost impossible to check their characteristics after installation on a vehicle. This is due to the fact that very often parts simply break at the joint junction, that is, where they come into contact with the lever. In addition, if the ball is not suitable for Largus, then, naturally, it will not achieve the unambiguous trust of the master - it is simply impossible to check.
As practice shows, it is impossible to predict the moment of failure of the above-mentioned supports even for a highly qualified craftsman. During diagnostics, he can simply pay attention to parts that pose a potential safety hazard.
Causes of failure
Among the main reasons for the malfunction of the ball joint is the wear of surfaces touching each other, increasing the gap between the body and the pin. As a result of this, the last part begins not only to rotate, but also to practically fall out.
If this level of wear is too strong and the entire load in Largus is distributed unevenly on the two ball joints, then this leads to the pins being pulled out of the housings. The consequence of this is the impossibility of supporting the wheels and, accordingly, the car falling onto the asphalt.
In addition, the natural wear and tear of parts can be “loaded” with obsolete materials. Due to the increase in dynamic load and considerable speed of movement, they are simply not able to perform their functions.
Analogs of rear shock absorbers
As for analogues of largus. We do not have exact data (sizes). Therefore, we will not mislead you. But, we authoritatively declare that on the spare parts market you can choose the necessary goods from global manufacturers and products from Russian companies. Here are some of them:
- The products of the manufacturer Monroe are of interest. You can order directly and save money.
- Sachs products are considered softer.
- Among the domestic manufacturers, one can single out the Russian one, which produces several lines. The “Comfort” kit has won the greatest popularity among Largus owners. They have an acceptable price/quality ratio. Many people like the kit, although they complain about excessive rigidity. The best absorption of road surface irregularities occurs at a speed of 50 km/h.
Diagnostics of ball joints
Of course, it is almost impossible to accurately determine the wear pattern of a ball joint without disassembling it. Of course, if the signs listed above are felt, then everything becomes more or less clear. However, a significant breakdown cannot be determined without analysis.
Diagnostics, as well as replacing the ball joint on the Lada Largus, should be carried out at a car service center. This is due to the fact that unsatisfactory results of checking this part during a comprehensive diagnosis of the suspension can cause wear of the step bearing or shock absorber struts, which cannot be replaced without qualified assistance.
Troubleshooting solutions
After carrying out a visual inspection, which has made it possible to determine the causes of sounds uncharacteristic of the car, you should proceed to dismantling the failed elements. Although sometimes they can be quite successfully repaired.
If, during the diagnosis of a new type of ball joint, looseness of the bolts securing the stabilizer bar was identified, then they need to be tightened.
When the above-mentioned part has to be replaced, especially together with the lever, it is considered an expensive pleasure. That is why today the services of restorers involved in their comprehensive repair are in great demand. Two technologies are used here:
If there is excessive or insufficient resistance to turning the ball joint pin of the front suspension arm, it can only be eliminated by completely replacing it.
Conclusion
To ensure that the entire list of “symptoms” indicating serious malfunctions of ball joints does not affect the vehicle, comprehensive diagnostics of the suspension should be carried out in a timely manner. If you regularly monitor all its elements, you can not only save money, but also prevent adverse consequences for the car and its owner.
Wear of suspension elements is usually characterized by the appearance of a knocking sound in the front of the car when driving over small uneven surfaces. It is difficult for an inexperienced motorist to determine by the sound which part has “gone bad” and requires replacement. But you can diagnose the problem yourself if you figure out how to check the ball joint. After all, it is its breakdown that leads to the wheel coming off and an inevitable accident. The wear of other elements - stabilizer seals, silent blocks and bearings is not so critical and allows you to operate the car for some time.
Analogs of rear shock absorbers
As for analogues of largus. We do not have exact data (sizes). Therefore, we will not mislead you. But, we authoritatively declare that on the spare parts market you can choose the necessary goods from global manufacturers and products from Russian companies. Here are some of them:
- The products of the manufacturer Monroe are of interest. You can order directly and save money.
- Sachs products are considered softer.
- Among the domestic manufacturers, one can single out the Russian one, which produces several lines. The “Comfort” kit has won the greatest popularity among Largus owners. They have an acceptable price/quality ratio. Many people like the kit, although they complain about excessive rigidity. The best absorption of road surface irregularities occurs at a speed of 50 km/h.
The role of support in the suspension and the consequences of failure
The part is a ball pin with a thread at the end, enclosed inside a metal housing. So that it can rotate, a sleeve made of hard plastic (usually fluoroplastic) is installed between the ball and the body. The pin is screwed with a nut to the steering knuckle of the wheel hub, and the part itself is bolted to the suspension arm. To prevent dirt from getting inside the hinge, it is protected on the open side with a rubber or silicone boot.
Note: in some car models, the ball joints are integral with the levers and are also replaced together.
The task of the element is to provide a hinged attachment of the hub to the lever so that it can rotate . That is, the support bears the load from the weight of the car, impacts from the wheel and the impact of friction when turning. Now it becomes clear what the risk of malfunctioning this important part is. First of all, the plastic sleeve wears out, causing the ball to begin to dangle inside the body. If measures are not taken, then on a strong bump the ball pin will pop out of the body, and the wheel will come off along with the hub.
Despite the fact that after separation the ball hub is held on a stand or on a second lever, the wheel becomes uncontrollable. The consequences are unpredictable and depend on the speed of movement at the time of the breakdown. That is why it is important to monitor the condition of these elements and respond in a timely manner to extraneous sounds coming from the chassis. If the first signs of a malfunction of the ball joint appear, it is advisable to check it and clarify the diagnosis in order to replace it with a new one in time.
Symptoms and causes of element wear
While driving, a worn ball joint manifests itself as follows:
If you find one of these signs, you should contact a service station for diagnostics or check the functionality of the parts yourself and without a lift. The service life of ball joints on cars made in Russia, China and Korea is in the range of 20-50 thousand km. Higher quality parts of European and Japanese foreign cars can last up to 150 thousand kilometers. It is necessary to focus on these intervals when troubleshooting .
Contrary to popular belief, the behavior of a car with worn joints when driving on a flat road changes little. The deviation from a straight line and the lateral abrasion of the rubber are so small that an inexperienced driver will not notice the changes, unless the ball joint becomes completely loose. A clear sign is a distinct knocking sound.
Torn boots are one of the main reasons for premature failure of ball joints. You will maximize their service life if you notice defects in the protective covers in time and replace them.