Independent suspension is the most popular type of suspension. It differs from others in that each wheel does not affect the others, and there is no rigid connection between the wheels. There are many types of independent suspension, but the most popular is the multi-link MacPherson strut. It differs from others in its good characteristics and relatively low cost.
Independent suspension
In modern brands of cars, the vibration damping device operates separately on each wheel. Colliding a car with an obstacle on one side, in principle, does not have a large impact on the body. The independent suspension works effectively, which means that vibration and shock from road irregularities are completely dampened.
The complex design of the device consists of a whole list of elements that coordinately participate in maintaining a stable position of the car body in motion.
You will have to spend money on maintenance and repair of independent suspension. This type of spring device is chosen for the sake of comfort and good handling of a truck or all-wheel drive vehicle. Popular on the independent list of many brands of passenger cars is the rear chassis of the MacPherson brand.
Independent suspension
Principle of operation
The operation of a car's suspension is based on the conversion of the impact energy arising from a wheel hitting an uneven road surface into the movement of elastic elements (for example, springs). In turn, the rigidity of the movement of elastic elements is controlled, accompanied and softened by the action of damping devices (for example, shock absorbers). As a result, thanks to the suspension, the impact force that is transmitted to the car body is reduced. This ensures smooth running. The best way to see the system in action is to use a video that clearly demonstrates all the elements of a car's suspension and how they interact. » alt=»»> Cars have suspensions that vary in stiffness. The stiffer the suspension, the more informative and efficient the car control. However, this seriously compromises comfort. And, on the contrary, the soft suspension is designed in such a way that it provides ease of use and sacrifices controllability (which cannot be allowed). That is why car manufacturers are striving to find their best option - a combination of safety and comfort.
Which is better - dependent or multi-link suspension?
The purpose of any spring device is to protect the car body from external impacts of road irregularities on the front and rear wheels. A multi-lever does this job well - a complex elastic structure. A dependent suspension is simpler and cheaper than a semi-independent one. But in modern cars this device is practically not used.
Different types of multi-link or semi-independent chassis of a car or truck have both advantages and disadvantages.
The advantage of semi-independent suspension is low weight, good handling and silent operation. This means tight grip on the road surface even at high speeds.
The advantages of a dependent front or rear suspension of a truck or passenger car are its simple, durable design and reliability.
Purpose
The purpose of the suspension is to make the ride safe, smooth, and protect the car from body roll (tilt) during acceleration, cornering and braking.
In fact, suspension elements solve several problems:
- Increases driving comfort. This is achieved by damping vibration, shocks, and impacts. The device “works” with the current forces of vibration and damping (transforms the effects into permissible vibrations), provides an elastic connection between the body and the wheels. A high-quality suspension allows you to achieve effective redistribution of the vehicle's vibration energy between the vehicle body and the wheelbase. Shock absorbers absorb this energy, turning it into heat. The more energy the shock absorber absorbs, the faster body vibrations will die out.
- They provide assistance during maneuvers, regulate (stabilize) the position of the body while driving, and provide resistance to trim - “nods” during braking. The stability of the car and its handling depend on the suspension. The vehicle's tires are in constant contact with the road surface.
- Minimizes wheel loads. Thanks to this, together with properly selected protectors, they improve traction.
- Optimizes the level of steering precision while driving. After all, the geometry of the position and movement of the wheels is under control.
Types of independent suspensions
The location and connection into the system of a whole list of damping device parts depends on the type of vehicle chassis. The main purpose is to dampen shocks, body vibrations and maintain directional stability.
List of types of independent front and rear suspensions:
- swing axle shafts;
- longitudinal, oblique and double wishbones;
- multi-lever.
According to the rating, an advantage was noted for the MacPherson chassis, which is usually found on the rear axles of many passenger car brands due to its good price-quality ratio. All independent suspensions differ in that they allow each wheel to react to obstacles separately.
Suspension with swing axles
In older domestic brands of cars, the chassis ensures that the wheel axis is vertical relative to the road. The axis itself appears to be divided into two halves. Each part is rigidly connected to the wheel hubs. The work of the damper in the device is performed by shock absorbers and spring blocks.
The axle shafts are connected on the inside by a hinge unit. On uneven roads, the track and camber of the front and rear discs have a large amplitude, which reduces safety.
Trailing arm suspension
An elastic device stabilizes the position of the body using springs or torsion bars. The design is often used on front-wheel drive vehicles. The trailing arms are attached to the body on one side and to the wheels of the car on the other.
The suspension is easy to maintain and repair, but has one drawback: it does not cope well with body roll when cornering. The chassis does not allow you to maintain a constant wheelbase while moving.
Slanting wishbone suspension
In this damping device, the parts appear to be located at an angle to the wheel. Which means that the design effectively maintains the stability of the car body during any maneuvers. And maintains a constant wheel angle when cornering. But when hitting bumps and holes, the stability of the car decreases.
To neutralize the negative properties of suspension on oblique arms, torsion bars and springs are used. These elastic devices increase the stability of the car on uneven roads.
Double wishbone suspension
The design has a rigid attachment to the car body and works as an independent unit. This ensures controllability and good stability of the car on the road.
The levers in the independent front or rear suspension are located transversely and connected to the strut supports. On the front wheels, shock absorbers can rotate around a vertical axis. Elastic parts of the chassis - springs, pneumatic and hydraulic devices.
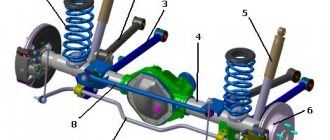
Multi-link suspension
This design is more often used in luxury cars on the rear axle. Many parts in the device better dampen multidirectional vibrations, thereby increasing the directional stability of the machine.
Multi-link suspension
The principle of a multi-link automobile suspension is the transverse arrangement of independently working parts. A special feature of the spring design is good smoothness and controllability, which also means silent operation when moving.
Technical nuances
Now let’s move on to the technical side of the issue and understand the design and structure of the dependent system, as well as its varieties. Similar types of pendants include the following:
- on longitudinal springs (spring);
- with guide arms (dependent spring);
- De Dion pendant.
The first option is one of the oldest. This structure consists of a bridge beam connecting two wheels, as well as two longitudinal springs on which it is attached.
The spring in this embodiment acts as a universal elastic element - it takes on loads in the vertical and transverse planes, and also dampens body vibrations. Of course, you cannot achieve high comfort from the operation of the suspension of such a system, and at high speeds, problems with controllability begin to appear.
A design with guide arms can be called more advanced and modern. There are a lot of design options in terms of the number of levers and their configuration - this includes a suspension with a Panhard rod, and with a Watt or Scott-Russell mechanism. Compared to spring systems, these systems have much better handling and cornering behavior. The main elastic element here is the spring, and the shock absorber helps it.
As for the De Dion pendant, there is one nuance. The fact is that this system cannot be called completely dependent due to the tricky arrangement of the elements, which is due to the fact that it was developed for the rear axle of rear-wheel drive cars. In it, the differential and the beam connecting the wheels are separated.
We recommend: List of necessary parts for interior renovation
The differential is rigidly connected to the car body, and rotation from it to the wheels is transmitted through swinging drive shafts. According to experts, the De Dion suspension is superior in many respects to the best examples of independent designs, and its only significant drawback is the price, which is why you can rarely see it, and even then mainly on sports cars.
Disadvantages and advantages of independent suspensions
The positive side of the spring design is the ability to adjust the chassis of a passenger car to maintain comfortable driving conditions. This means that the elastic elements create good contact on any road surface.
List of the main advantages of independent suspension:
- controllability in motion;
- smooth running of the machine;
- reduced roll when cornering;
- independent adjustment of the position of the front and rear wheels.
However, levers and beams, and other elements of the assembly quickly wear out during operation.
Here is a list of disadvantages of independent suspensions:
- complex design;
- expensive production and maintenance of the device;
- low maintainability due to many parts.
Therefore, complex spring structures are usually used in expensive brands of passenger cars.
Similarities and differences
Both pendants serve the same purpose. They are needed to make car travel safer and more comfortable.
In terms of design, what they have in common is that in both cases elastic elements, shock absorbers and guides are used. A striking example is the use of springs. Some actively mount air bags into springs to increase comfort.
But there are much more differences between them:
Application
As stated above, the design of independent suspension is complex. The unit consists of many parts. Due to an increase in the contact area of dependent moving parts, the reliability of the entire structure decreases. In this regard, multi-lever is rarely used in economy passenger cars. Independent suspension is often installed on the rear axle of crossovers and all-wheel drive SUVs.
The significance of the device is to ensure good grip on the road surface and stability of a car with front-wheel drive or all-wheel drive. At the same time, multi-link suspension on two axles can only be found in the list of modern luxury car brands.
The amount of state duty for registering a trailer - payment procedure
- The wheels of the dependent system have a rigid connection, making them dependent on each other. The competitor's wheels work independently;
- Independent units have more unsprung masses, which is due to the absence of a bridge;
- Independent is more sensitive to wheels that do not meet the automaker's requirements;
- The likelihood of capsizing during a sharp turn or when falling into a hole on a car with independent auto suspension is less due to the lack of a rigid connection of the wheels.
As you can see, there really is a difference, and it is significant in many ways. What exactly to choose, everyone decides for themselves.
Double lever design
The car's double-wishbone independent suspension is also used on the front axle and differs from the previous design in the following ways:
- The shock absorber and spring do not form a single unit, although the first is built inside the second. The parts are attached separately - the strut to the body hinge, and the spring simply rests against the glass.
- An upper control arm has been added with a ball joint bolted to the steering knuckle. The length of the element is shorter than the lower arm, since it is attached to the side member from the inside of the wheel arch.
- The wheel is turned by the same steering rod, but due to two ball joints installed at the ends of the levers.
- The strut with the spring passes through the technological opening of the upper arm and is attached to the lower one. Accordingly, the elastic elements do not rotate together with the turning wheel, and there is no upper support bearing.
The rest of the suspension is identical to the MacPherson strut - there is a subframe at the bottom, connected to the arms on hinges and through a stabilizer bar. In some cases, the latter is not screwed to the front beam, but directly to the body parts.
Thanks to the design features, all dynamic and static loads are evenly distributed across all suspension elements - springs, shock absorbers, levers and stabilizer. As a result, the service life of the rack and other parts is significantly increased. The suspension is much “softer” and more reliable than McPherson, so it is successfully used on premium cars and SUVs.
Reference. The two-lever system was installed on all classic VAZ 2101–2107 models. Despite many other shortcomings, these old cars were considered quite comfortable to drive on our roads.
A 2-link suspension is understandably more expensive and more difficult to repair. But you have to “conjure” it less often, since the parts wear out evenly.
Single lever MacPherson system
This type of suspension is considered the cheapest and most practical. It is installed on the front axle of most budget passenger cars and consists of the following parts:
- subframe - a metal structure attached to the lower part of the body;
- transverse lower arms mounted on a subframe;
- the steering knuckle with the hub is attached to the lever by means of a ball joint;
- the role of the upper arm is played by the strut itself, assembled with a spring, resting with its upper end on the glass of the body spar;
- stabilizer connecting the wishbones;
- tie rod ends attached to the steering knuckles on hinges.
The principle of operation of the McPherson suspension is quite simple: a shock absorber installed inside the spring works together with it as the main damping element . The strut is able to rotate together with the steering knuckle due to the support bearing in the upper part. The lever holds the wheel from below, and rotation is carried out under the influence of a steering rod attached by a hinge to the knuckle. The car is protected from rolls by a stabilizer connected to the subframe and both levers.
Reference. The MacPherson struts are not strictly vertical, but are tilted back at a slight angle (the so-called caster angle).
The main advantages of this suspension are its compactness, low cost and the ability to easily connect CV joints from a transversely mounted motor to the wheels. An additional advantage is the large stroke, almost the entire length of the shock absorber opening, which protects body parts from suspension breakdowns.
Now about the cons:
- The support stand is subject to shock loads from the wheel and often fails. This is the weak point of the McPherson design.
- Due to the large stroke and movable fastening of the elastic element on the hinges, the camber of the front wheels changes significantly.
These disadvantages do not allow the installation of independent MacPherson suspension on heavy premium cars, SUVs and sports cars.
A little theory
Depending on its design, a car's suspension can be divided into two main categories: dependent or independent. In a dependent suspension on one axle, the wheels are rigidly interconnected; accordingly, the impact that falls on the left or right wheel will invariably affect the entire rigid beam and the second wheel on the axle. When passing uneven surfaces, the body will tilt or shudder, and if one wheel on the road surface is higher than the other, then in such a case the likelihood of the body tipping over increases.
The independent suspension does not have a rigid beam; accordingly, the wheels on the axle are not rigidly interconnected with each other, which can significantly increase comfort on board, improving the vehicle's handling. If one of the wheels hits an obstacle or falls into a hole, then due to the lack of interconnection, such impacts are not transmitted to the second wheel and the car body. This significantly improves the car's handling characteristics.