Priora won't start, starter turns
| Possible malfunction | Diagnostics | Remedies |
| There is no gasoline in the tank | On the instrument panel the fuel level indicator is at zero. | Pour gasoline |
| Battery is low | The voltage at the battery terminals without load is less than 12V. When trying to start the car, a crashing sound is heard from under the hood. | Charge the battery or replace it with a new one |
| Oxidation of battery terminals or wire terminals, their fit is not tight | When you try to start the engine, the voltage in the on-board network drops much more than at the battery terminals. In this case, a crash may be heard under the hood. | Clean the contacts, lubricate them with petroleum jelly and tighten the terminals |
| Unreliable connection of electrical circuits of engine control and power supply systems | Check the connections of the connectors and the reliability of the contacts in the blocks. | Fix faulty wire connections |
| Increased resistance to rotation of the crankshaft (scores on the shafts, bearing shells, cylinder-piston parts, deformation of the shafts, frozen engine oil, jammed generator, jammed coolant pump) | The crankshaft turns slowly. If the engine is started in severe frost, and the engine was working properly the day before, then most likely the engine oil has frozen. If you hear extraneous noise when starting the engine, check the free rotation of the pump and generator pulleys. | Use the recommended engine oil. Repair the engine. Replace the pump and generator. |
| Malfunction in the ignition system | Check for spark. | Check the circuits and devices of the ignition system. Replace faulty system elements. |
| The high voltage wires are connected in the wrong order or the wire is disconnected | Inspect. | Connect the wires in the correct order |
| The timing belt is broken or the belt teeth are cut off | Open the front timing cover and check. | Replace timing belt |
| Disturbed valve timing | Check the marks on the crankshaft and camshaft pulleys. | Set the correct shaft position |
| Malfunction of the computer (brains), its circuits, crankshaft position sensor or coolant temperature | Check the supply of +12V to the ECU, the sensor circuit, and the absence of damage to the sensors themselves. | Replace ECU, sensors. |
| The idle air regulator (IAC) or its circuits are faulty | Check the idle air control. When starting the engine, lightly press the gas pedal. If the engine starts and stalls when you release the gas pedal, the sensor is faulty. | Replace sensor |
| The fuse is blown or the main relay of the control system is faulty | Check fuse and relay. | Eliminate the cause of the blown fuse. Replace fuse and relay |
| Fuse blown, fuel pump relay. Circuit, relay or pump is faulty. | When the ignition is turned on, there is no sound of the pump running. Check the fuse. Apply voltage to the pump from the battery. | Clean contacts, replace faulty circuits, replace fuse, pump and relay. |
| The fuel filter is dirty, the water in the fuel line is frozen, the fuel line is damaged | Check the pressure in the fuel rail and the condition of the fuel lines. | Replace the filter, blow out or replace the fuel lines. |
| Insufficient pressure in the fuel rail | Check the pressure in the fuel rail, the pump strainer and the condition of the fuel lines. | Clean the filter. Replace pump, fuel pressure regulator |
| Faulty injectors or their power supply circuits | Check the injector windings with an ohmmeter. Check the chains for breaks. | Replace injectors, replace chains |
| Air leak into the intake tract | Inspect the joints and fittings of the hoses and clamps. During start-up, turn off the vacuum brake booster and plug the receiver fitting. | Eliminate air leaks, replace vacuum booster |
If the Priora does not start well when hot
In this case, see the second table; in addition to the reasons described, also pay attention to:
- A pressure regulator that can discharge fuel through a membrane into the receiver.
- DPKV contacts, if the sensor has been changed, check that the poles are connected correctly.
- Faulty ignition module.
Let us remind you that in some cases the Priora does not start due to a faulty immobilizer or alarm system. In some cases, reflashing the engine ECU (electronic control unit) helps solve the problem of poor starting. And regular car maintenance will help eliminate problems of poor engine starting.
The spark disappeared on the 16-valve VAZ-2112 injector: causes and diagnostics
Many car enthusiasts have encountered the loss of spark on the 16-valve VAZ-2112 engine. What is this defect associated with? The first thing that suggests itself is the ignition. But, in this case, not everything is so simple, since the problem may lie deeper than it seems at first glance.
The video describes a situation when you lose a spark on the road and the car does not start:
If the light is on
Sometimes the injector fault light stays on until the engine warms up to 90 degrees, after which it stops flashing. This is usually observed in winter, when there is severe frost outside. And although the problem is not serious, it will have to be solved. It happens like this:
- Replace the injector sensor;
- Get the firmware installed at a car service center;
- Remove the battery terminals. Perhaps the light came on, but never went out.
- And after removal, the injector will be overloaded.
The main reasons for the lack of spark
General view of the engine 10-12 series 16 valves
Not all motorists know the reasons for the loss of spark, much less methods for diagnosing and troubleshooting problems. So, it is worth identifying the main reasons, and then deciphering why exactly they become the cause. Finally, you need to consider ways to eliminate the defect. So, what reasons could cause the spark to disappear:
- Failure of the fuel pump.
- Spark plug.
- Ignition coil.
- High-voltage wires and their location.
- Gas distribution mechanism.
All the reasons have been found and it is worth moving on to the process of eliminating this malfunction.
Are you giving me a spark? Troubleshooting!
First of all, it’s worth noting that you don’t need to rush to check right away. As practice shows, there is a certain sequence of actions and malfunctions that could lead to loss of spark on a 16-valve engine.
Fuel pump
Fuel pump made by Bosch
Ignition is not the first reason for the ignition failure on a car. Before getting into the electrical part of the car, it’s worth delving into the mechanics, so to speak. Turn on the ignition and listen to see if the gasoline pump is working . If it is silent, then you need to check whether gasoline is entering the cylinders.
It is worth starting the diagnostic procedure by checking the fuses for serviceability. Of course, you can only view the one that is responsible for the fuel pump (in this case, when you turn on the ignition, the pump will not pump), but it is recommended to diagnose everything for integrity. If at least one fails, it must be replaced.
The fuses are located to the left of the steering wheel under the light mode switch
The 16-valve VAZ-2110 has no spark
Obvious reasons include malfunctions of the ignition coil, spark plugs, fuel pump, high-voltage wires and gas distribution mechanism.
Troubleshooting is carried out similarly to an 8-valve car. Candles are the first stage of testing. A visual inspection will help find flaws, after which they resort to checking the gaps and measuring the resistance.
Proven method: unscrew the spark plug, put on a high-voltage wire, install the base on the engine or body. After cranking the starter, a spark should form. Safety regulations must be followed.
Another reason may be hidden in the timing belt, namely, if the valve timing has gone astray due to improper installation of the timing disk. It is located on the crankshaft pulley and acts as a synchronizer.
It is quite possible to correct the situation if you change the installation of disks in accordance with the applied marks. The easiest way to find shortcomings is in working with high-voltage wires. However, it is necessary to understand that the engine will operate in strong vibration mode.
What could be the reason:
- The wire doesn't work. A complete replacement helps.
- Incorrect connection. Change the connection location.
conclusions
Loss of spark on a 16-valve VAZ-2112 may be a consequence of the failure of several vehicle components at once or each individually. But, if the operations indicated in the article did not help, then you should contact specialists at a car service center who will accurately identify the cause and eliminate it.
It is unlikely that several nodes will fail at once. This has not happened in my practice. Unless, of course, you hit the car properly.
The ignition coil rarely fails because it is initially reliable. But the spark plugs and fuel pump often fail.
Even if the timing phase is off, there should be a spark!
There will be a spark, but not at the right time when the air-fuel mixture arrives.
the article sucks. wrote the teapot. Moreover, the pump and the spark, and the timing belt. even with a broken timing belt there will be a spark. Kettle...boil somewhere else
What does the fuel pump and broken phases have to do with it? The author is in the furnace.
Wrote 100% who themselves have no idea what they are writing, if on the 12th engine if the spark disappears completely, then 80% is the module, and then 5% each of the crankshaft sensor, ignition switch, ECU and a break in the bus from the brain to the module or crankshaft all
Oh yes, I almost forgot the immobilizer and the signaling may be glitchy
I have a VAZ 2110 2001. First, the fuel pump failed, I found and eliminated the cause; the spark disappeared from the fuel pump; I can’t find the cause yet.
Still haven't found the spark?
I have the same problem. What helped in the end?
Guys, such garbage, no spark, no prior, crankshaft sensor called, coils too, they put another prior on mine and vice versa, I tried everything and it’s not there??
You write specifically for not all kinds of bullshit.
but there is a spark from the central one, that is, it goes to the distributor, but from the spark plug... oops! Everything was replaced with new ones, BREMI, and it’s still there!
Hello everyone, I have a 2112 16 valve, I turn the starter on the dashboard, all the lower indicators are blinking and the relay is knocking on the right side at the bottom, the car won’t start, I checked the spark and it hits every other time, can the module show off like that?
Exactly the same problem. Didn't find a solution?
Charge the battery, everything will be fine
VAZ 21124 1.6 16kl engine 124 The cylinder head gasket in the 4th cylinder was broken. I dismantled it, cleaned everything, washed it properly, ground the valve, changed the gasket and reassembled it, and now, disappointingly, the engine does not start, there is a spark, there is also fuel. Ignition is normal. The motor sat disassembled for a month. Having rummaged around on your website, I found the reason for the installation, due to inattention, I mixed up the camshafts. Because of my carelessness, I had to re-open the engine and, as it turned out, the truth justified itself. I swapped the camshafts, fortunately the valves on my engine don’t bend. I cleaned the old sealant, degreased it, applied a new one, and assembled everything in the reverse order. And as a result, the engine also does not start, I was upset about my work, it seemed like I was doing everything according to the instructions. This time the reason was the lack of fuel and spark. I racked my brain and checked everything several times but to no avail. I had to resort to this site again, and still found the reason, I started the engine with an uninstalled generator drive pulley. Eliminated the cause, everything was fine, the engine started, everything is normal, thanks for the information
Why are the modules on 2112 16kl burning?
new spark plugs new ignition module marks are ok fuel pump hums no sparks no spark emobilizer switched off the signal to the engine is ringing the module is receiving power ground also the signal wires are intact from the hood to the engines reasons
Why there is no spark on the VAZ-2112 injector 16 valves: photo and video
Many car enthusiasts have encountered the loss of spark on the 16-valve VAZ-2112 engine. What is this defect associated with? The first thing that suggests itself is the ignition. But, in this case, not everything is so simple, since the problem may lie deeper than it seems at first glance.
The video describes a situation when you lose a spark on the road and the car does not start:
The main reasons for the lack of spark
General view of the engine 10-12 series 16 valves
Not all motorists know the reasons for the loss of spark, much less methods for diagnosing and troubleshooting problems. So, it is worth identifying the main reasons, and then deciphering why exactly they become the cause. Finally, you need to consider ways to eliminate the defect. So, what reasons could cause the spark to disappear:
All the reasons have been found and it is worth moving on to the process of eliminating this malfunction.
Are you giving me a spark? Troubleshooting!
First of all, it’s worth noting that you don’t need to rush to check right away. As practice shows, there is a certain sequence of actions and malfunctions that could lead to loss of spark on a 16-valve engine.
Diagnostics using ODB-2 scanner
Since there are quite a few reasons for the lack of a spark, it is first recommended to carry out a comprehensive diagnosis of the car. A quick way to do this is to use an ODBII scanner.
The main feature of Scan Tool Pro is the diagnosis of not only the engine, but also other components of the car (gearbox, abs, transmission, air conditioning system, etc.). The device works with all models of the domestic automobile industry (since 1993 for gasoline cars and 1996 for diesel cars) and was created specifically for the CIS market - it shows error codes with their interpretation in Russian. The scanner also displays the operation of all available sensors in real time, the vehicle’s VIN, its actual mileage and much more.
There is no spark, we check the functionality of the components. Algorithm for finding a spark on spark plugs and ignition coil
When the spark is lost, you will, of course, never start the car, and in such a situation, first of all, you need to check the ignition system.
The vehicle's ignition system plays a key role in its operation. If in case of many other malfunctions the car can be taken under its own power to the service station, then in case of problems with the ignition it is unlikely that it will be possible to start the engine at all.
How to check the spark
Checking the spark on a spark plug can be done in several ways:
- Check for ground (the spark plug body is pressed against the engine and the spark is analyzed when the starter rotates).
- Checking the spark plug with a multimeter (you can determine the breakdown of the spark plug).
- Diagnostics with a tester based on a piezoelectric element (the testing principle is similar to the ground breakdown method; the presence of a spark is determined and is used mainly on fuel-injected cars).
The main reasons why there is no spark
- problem with spark plugs (flooded or faulty);
- breakdown of high-voltage wires or loss of contact;
- the reason is the crankshaft sensor (requires checking with a multimeter);
- malfunction in the ignition module;
- failure of the ignition coil;
- problem in the switch;
- Distributor malfunction (burned contacts, loss of clearance);
- poor ground wire contact;
- failure or malfunction of the ECU;
No spark injector
You need to be very careful when checking the spark on fuel-injected cars (especially for foreign cars - you can burn the electronic unit).
It is recommended to use a spark gap to understand at what stage there is no spark on the spark plugs (no spark from the distributor, no spark from the coil, or directly from the spark plug itself). If there is no spark in all cylinders at the same time, there may be several culprits:
- controller;
- entire module;
- coil or center wire.
The entire checking procedure should begin with the integrity of the fuses, the condition of the ground contacts and contacts on high-voltage wires.
If there is no spark from the ignition coil, then the reason may be hidden in many places. First of all, you need to check the high voltage wire, which must be in perfect condition and without damage to the insulation. Otherwise, the wire needs to be replaced.
No spark, check spark plugs
If the problem is not solved, then check the spark plugs. The spark plug contacts must be clean. The fact that there is no spark may be caused by dirty spark plug contacts. It is best to replace the spark plugs, but you can also clean the contacts. But before changing the spark plugs, check whether the discharge reaches the spark plugs themselves.
To do this, remove the spark plug wire and bring it to the car body at a distance of 0.5 cm. Turn the starter several times and see if there is a spark between the wire and the body. The spark should be white with a slight blue tint.
If it is absent or present, but with a different shade, we can say that the spark plugs are fine, and the problem is in the heart of the car’s ignition system - the coil.
How to check spark on ignition coil
To see if the coil is working at all, pull the wire from the breaker distributor that comes from the coil. The same test is carried out with it as with the spark plug wires, namely, they bring the wire to a distance of 0.5 cm and turn the starter. Now, regardless of the result, we can accurately talk about the cause of the breakdown.
If there is a spark, then the problem is in the distributor-chopper; if there is no spark, then the ignition coil is faulty.
In the first case, you need to check the contacts in the distributor-breaker for oxidation, insulation damage, and also check the serviceability of the rotor. If there is no spark due to it, the rotor must be replaced.
Checking the ignition coil
Checking the ignition coil also involves inspecting the integrity of the windings for physical damage, as well as burnt spots, which indicate a short circuit in the coil. In these cases, the coil either needs to be repaired or replaced.
No spark VAZ (injector, 8 valves)
The other day, out of the blue, the car (Kalina 1.6, 8 valves) began to shake terribly. Diagnostics showed misfires in cylinders 1 and 4. After a little checking (see how to check correctly here), I came to the conclusion that there was no spark . And only in cylinders 1-4.
Next, in order to find out the reason for the loss of spark, I will go in order.
The first thing to check is the spark plugs. The spark plug looked normal, so I didn’t have much hope that replacing it would fix the situation. And so it happened - the new spark plug still refused to produce a spark.
The second is checking high-voltage wires. They are checked with a conventional multimeter in resistance measurement mode. The resistance should be within 15 kOhm. The wires also turned out to be fine.
Third, and probably most important, is the ignition coil. She, like no one else, is responsible for the spark. Its operability is also checked with a multimeter in continuity and resistance measurement mode. First you need to check the resistance between pins 1-4 and 2-3. It should be about 4 kOhm. If the tester shows infinity, then the coil is broken and must be completely replaced. Next, check the resistance between pins 1a and 1b. There shouldn't be a break here. And the last thing is to check the central contact for breakdown to the housing. The tester should show infinity.
My reel passed the test perfectly. It seems that all the main parts are working properly, so why is there no spark? After digging a little on the Internet, I realized that I still need to check the circuit from the ECU to the coil itself.
A 3-pin chip is placed on the ignition coil, therefore you need to check these 3 wires. The central contact is +12V, which is constantly supplied when the ignition is on. The extreme contacts - 1a and 1b - provide a control signal (negative) at the moment when a spark is needed. How can all this be checked? Very simple - using a regular light bulb.
You need a lamp with a power of 1-2 W or an LED with an additional resistance of 500-700 Ohms.
We connect the lamp to the central terminal and contact 1a and ask a partner to crank the engine a little (first remove the fuel pump fuse and relieve the pressure in the rail). When cranking the starter, the lamp should flash. The same procedure must be done with pin 1b - the lamp should also blink.
When I turned on the ignition, the lamp started to light up, just constantly on (pin 1b and central). This means that the control wire has a short to ground somewhere or that the transistor (VT1) in the ECU is broken. To find out, we need to find the ECU, disconnect the wiring harness from it, find the wires we need (1b) and test them for integrity.
Having found the contact diagram, I found out that contact 1b goes to pin 5 of the ECU, 1a goes to pin 2, 3 goes to ground of the ignition circuit. I rang them for integrity - they were all intact. I called ground and everything is fine too. Therefore, you need to check the transistor in the controller itself.
My car has a January 7.2 controller. Inside there are 2 transistors that pass control signals to pins 1a and 1b of the ignition coil. So one of these transistors was broken, i.e. was constantly in the open position.
How to check the transistor for serviceability? It has 3 pins - 2 of which are soldered. It is necessary to ring each outer terminal with the central one. In both cases, the tester should not beep. The contacts must not be closed.
Now all that’s left to do is to unsolder the broken transistor (its marking is gb10nb37lz), solder a new one in its place and rejoice at the spark that appears.
Story
The ignition system in Lada cars has changed over generations. Earlier cars with carburetor fuel injection used a distributor ignition system, which is quite unreliable and required manual adjustment and frequent maintenance.
The distributor was replaced with the advent of injection engines by a modular ignition system; a spark in such a system was produced by a module consisting of two coils. This system began to use a crankshaft position sensor, which helped the engine control unit determine the top dead center and compression stroke of the fuel-air mixture.
Possible errors in VAZ injectors
Codes can indicate malfunctions of any parts and components in the car. Most often this is due to sensors. Temperature sensors are especially affected - they overheat. Car enthusiasts also complain about the injectors. Problems arise due to breaks in the circuit. As a result, they cannot respond on time. This also includes a popular breakdown on the VAZ-2110 - no spark. The 8 valve injector cannot start normally because of this.
Now about engine-related errors. The most common one is overheating. The spark plugs also overheat, causing the spark to disappear. As a result, the motor does not show any signs of life. Next we should consider the valves. These parts may become too dirty, causing them to close completely.
Ignition system
Such a system is a collection of parts that are involved in the process of spark formation in the engine. A spark in an internal combustion engine is necessary to ignite the fuel mixture in the combustion chamber. If the engine loses spark, its operation stops completely.
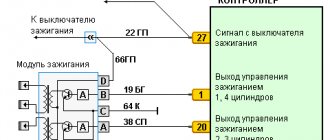
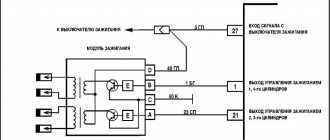
The Priora ignition system includes the following elements:
- Ignition coil;
- Spark plug;
- Crankshaft position sensor;
These three parts are responsible for the formation of a spark in the Priora engine; failure of one of them entails the loss of spark in a particular cylinder.
Let's look at each part of the car's ignition system in more detail to understand their purpose in more detail.
Spark plug
Spark plugs are used in all gasoline-powered vehicles. It screws into the cylinder head and creates a spark in the combustion chamber, which is necessary to ignite the fuel mixture.
The spark plug is a part with a threaded part that is screwed into the cylinder head; an electrode is placed inside the threaded part that generates a spark. Since the spark plug operates under high voltage, a special insulator is used in the spark plug to prevent breakdown and leakage of voltage.
Ignition coil
As described above, the Priora already uses an individual ignition coil. Such a coil is installed on each cylinder and is responsible for supplying a spark to a specific cylinder. The transition to IKZ made it possible to increase engine power while saving fuel.
The ignition coil is a part in which there are two windings, primary and secondary. A voltage of 12V is supplied to the primary winding, and a voltage of almost 40,000 Volts is generated on the secondary winding. This voltage is necessary for reliable spark formation in the combustion chamber.
Crankshaft position sensor
This sensor is necessary to determine the top dead center of the internal combustion engine, that is, when the compression stroke occurs in the engine, it is necessary to supply a spark in the combustion chamber. This sensor understands when the piston is at the top and sends a signal to the ECU, which in turn sends a signal to the IKZ to form a spark in this cylinder. This is how the fuel-air mixture ignites in a specific cylinder.
This sensor is installed next to the crankshaft pulley and reads readings from it. There are marks on the crankshaft pulley that the DPKV reads and thereby determines TDC.
It should be noted that a breakdown of this sensor or a break in its power supply leads to a loss of spark in the internal combustion engine and the inability to start it.
Signs of faulty spark plugs
The Check Engine Light can also be a sign of faulty spark plugs.
If the spark plugs do not work correctly, for example, they periodically miss a spark or do not create the required voltage discharge, problems arise in the engine due to insufficient fuel combustion.
As a result of this, the driver notices the following changes in engine operation:
- Reduced engine power and at the same time increased fuel consumption.
- Dips in power when pressing hard on the gas.
- Engine stops at high speeds.
- Long engine start.
- Uneven engine operation, even during quiet driving.
- Engine tripping.
It is important to note that some of the symptoms listed only appear under specific conditions. However, their absence does not indicate the normal condition of the spark plugs. A worn-out spark plug may be just one of the signs.
Experienced motorists also know that similar signs of malfunction can signal other problems. The problem may be in the ignition coil, high-voltage wiring, power system and other systems that keep the engine running. Therefore, when faced with one or more symptoms, you need to correctly diagnose the ignition unit.
Misfires on Priora
There may be no spark at the Prior due to a breakdown of the sensor, coil, spark plug or ECU. Failures that lead to loss of spark are quite easy to solve, with the exception of a breakdown in the ECU.
If the spark on a Priora disappears on all 4 cylinders, this indicates a breakdown of the crankshaft sensor in 80% of cases, in the remaining 20% the ECU may fail.
If there is no spark on one of the cylinders, then there may be several reasons - a spark plug, a coil or a transistor in the ECU.
Consider each of the reasons in more detail.
Spark plug
Quite often, low-quality spark plugs can fail after several hundred kilometers or even immediately after installation. It is recommended to purchase only high-quality spark plugs.
Which spark plugs are best for Priora can be read in our article.
You can check the serviceability of the spark plug on a special stand or by trying to replace it with a new one or by installing a suspicious spark plug in the working cylinder.
Ignition coil
Problems with the coil appear practically the same as with spark plugs. One of the windings in it may break or break through the insulation, which causes the coil to malfunction. IKZ Prioras cannot be repaired and if they break down they are replaced with a new one.
You can check the serviceability of the coil by replacing it with a coil of another cylinder or using a special diagnostic device ELM 327.
You can read how to check the coil here.
Crankshaft position sensor
DPKV is installed in a place that is subject to both mechanical and temperature influences. Since the sensor works on the principle of a magnet, and its sensitive part tends to magnetize chips. The formation of chips on the sensor will negatively affect the reading from the crankshaft pulley, which can lead to the inability to determine TDC and, consequently, to loss of spark.
The sensor's power circuit is located close to the exhaust manifold, which heats up to enormous temperatures. Because of this, the DPKV wiring is exposed to high temperatures, which leads to the destruction of the insulation and screen of the wire, and this has a bad effect on the transmission of information to the ECU and can cause a loss of spark.
Misfire in a VAZ Priora cylinder, signs, causes
Unstable engine operation and shaking at idle, loss of power and increased fuel consumption, the appearance of a “Check” error on the instrument panel, jerking of the car and other troubles can be caused by a misfire in the engine cylinder.
There is nothing wrong with this, because if the engine runs but does not pull, it means that not everything is so critical.
Next, we will talk about how to properly diagnose a car and identify the cause of the malfunction.
Main causes of misfire
There can be many reasons for the problem; even professional mechanics spend more than one hour to identify its source.
The main reasons for misfire in cylinders 1, 2, 3, 4 can be:
- The ignition coil or module has failed;
- Inoperative fuel injector, clogged due to low-quality gasoline;
- Incorrect spark plug gap, which can lead to poor sparking;
- The spark plugs are flooded or carbon deposits have formed on them;
- Breakage of high-voltage wires, increased resistance (non-standard ones are installed), oiliness of contact points;
- A high-voltage wire has fallen off (often happens on Lada Kalina and Granta);
- On an 8-valve engine, the timing belt may jump (during replacement, an error was made due to marks or as a result of excessive wear);
- On a 16-valve engine, the hydraulic compensators are not working correctly;
- Air leak (can be anywhere);
- The compression in the engine cylinders has dropped or is different (applies to cars with high mileage);
- Low pressure in the fuel rail as a result of reduced fuel pump performance.
Diagnostics using a computer
If your car is equipped with a modern control unit, then this greatly simplifies troubleshooting; otherwise, you will have to use time-tested old-fashioned methods.
By connecting the computer to the car, you can find out in which cylinder, 1, 2, 3 or 4, and for what reason there are misfires, for example, the ignition coil or one of the injectors has failed.
But in any case, before going to a car service center, you need to check the condition of the spark plugs, injectors, high-voltage wires, how the exhaust system works, and whether there is smoke from the exhaust pipe.
Many car owners cannot afford instruments for car diagnostics, these include scanners (software and portable), motor testers, oscilloscopes, gas analyzers and other devices, and you need to be able to use them, read error codes, and so on. Although if you look into it, there is nothing complicated there.
The scanner is connected to a special connector, which can be located in different places in each car model, but it has one function: diagnostics.
Next, error codes are read from the control unit and decrypted.
For example, VAZ 2110, 2114, 2115, Lada Kalina, Priora, Granta cars have the following error codes that are characteristic of misfire:
- P0300 - a large number of misfires;
- P0301, P0302, P0303, P0304 – misfires in cylinders 1, 2, 3 and 4, respectively;
- P0300 - a large number of misfires in a random order;
- P0301, P0302, P0303, P0304 – misfires were detected in 1, 2, 3 and 4, respectively;
- P0363 – see point 4 + fuel supply to problem cylinders is stopped;
- P1301, P1302, P1303, P1304 – respectively, misfires dangerous for the catalytic converter were detected in cylinders 1, 2, 3, 4;
- P0300, P0301, P0302, P0303, P0304 – detection of misfires affecting the toxicity of exhaust gases;
- P0363, P1301, P1302, P1303, P1304 – the same as in point 7, but affecting the catalyst;
- P0351, P0352, P0353, P0354 – open circuit in the ignition coil in the control circuit 1 (1-4), 2 (2-3), 3, 4;
- P2301 P2303 P2305 P2307 - short to on-board network in the coil in the control circuit of cylinders 1 (1-4), 2 (2-3), 3, 4;
- P0201, P0202, P0203, P0204 – respectively, open circuit for controlling injectors 1,2,3,4;
- P0261, P0264, P0267, P0270 - short circuit of the injector control wires to the body, respectively, in the 1st, 2nd, 3rd, 4th center;
- P0262, P0265, P0268, P0271 – the same as point 12, but only to the on-board network;
- P1500 – electric fuel pump relay, wire break.
POPULAR WITH READERS: Is it worth warming up an injection engine?
Read more about how to diagnose a car using a laptop.
Diagnostics of VAZ 2109, 2110, 2114, 2115, Kalina, Priora, Granta
Let's look at misfires using the example of the VAZ 2109, 2110, 2114, 2115, Kalina, Priora, Granta models.
The computer generated error P0303 (misfire in 3rd crank).
First you need to understand how the ignition coil works. It consists of two small coils, pins 1 and 4 are connected to the first, and pins 2 and 3 to the second.
Those. during operation, voltage is simultaneously supplied to the first and fourth cylinders or to the second and third.
We have misfires in cylinder 3. Remove the wires from 2 and 3 and swap them.
Start the engine and see if the error has moved to cylinder 2, then the problem is most likely in the high-voltage wires or in the coil itself, and they need to be checked first.
High-voltage wires are tested by checking their resistance. To do this you need a regular multimeter.
Set the resistance measurement mode to 20 kOhm.
In our case, we check the third wire. If the device shows numbers within the range of 3.5 - 10 kOhm, then the wire resistance is considered normal, otherwise it changes.
Next we check the coil. For this you also need a multimeter.
We measure the resistance between 1 and 4 and 2 and 3 coil terminals. Readings of 10 kOhm, or around this figure, are considered standard.
Important. During testing, the tester should not show 1. This means that there is an open circuit in the circuit and the coil is faulty.
Next we check the resistance between each terminal and ground. In this case, on the contrary, the multimeter should show 1 (infinity).
If resistance is shown at one of the terminals, it means that its insulation is damaged and it is connecting to ground. Accordingly, the required voltage will not be supplied to form a spark.
Next, we check the resistance between the central terminal of the ignition coil and the housing (ground). It should also be equal to infinity, i.e. 1.
Now it remains to check the resistance between the extreme terminals. To do this, set a different measurement range on the device - 200 Ohms.
A resistance of 2 ohms is considered normal (+-). There should be no break between the extreme terminals.
Next, check the condition of the contacts on the coil itself and on the wires; they tend to oxidize over time, especially if your region of residence has a humid climate.
If the error remains in cylinder 3, but the coil and high-voltage wires are in good condition, we check the spark plug.
The easiest option is to remove the spark plug from the working cylinder and swap them.
If the error then transferred to another cylinder, then most likely the issue is in the spark plug.
If nothing has changed and the error remains, then check the injectors.
In this case, you also need a multimeter. Disconnect the wires from the injector, in our case from cylinder 3, and measure the resistance, it should be about 13 ohms.
Next, check the injector power supply circuit. Also, the injector may become clogged and not supply the required amount of fuel, which can cause misfires. Therefore, you will have to clean the injectors.
If after all the above checks the misfires have not disappeared, you need to check the valve clearances.
The valves should not be tightly clamped, as this will lead to their incomplete closing, and this, in turn, will lead to a decrease in compression and compression ratio in the cylinders and this will cause misfires. Also, if you press too hard, the valve may burn out.
Especially the condition of the valves should be paid to owners of cars with LPG, since the combustion temperature of gas there is slightly higher than gasoline and therefore the thermal clearances of the valves in this case should be slightly larger, i.e. not 0.2, but 0.25 mm. And where is 0.3, then 0.35 mm (for the above models).
BMW x5 e53 engine m54 3.0 USA
If we talk about foreign cars, they also have special error codes indicating misfires.
Let's look at the error codes using the example of a BMW x5 e53 motor M54 3.0 USA (if the country of manufacture is different, the codes may differ).
As a rule, these errors are associated with problems with mixture formation, sparking and decreased compression:
- Problems with the ignition coil - errors 101, 202, 303, respectively, cylinders 2, 4, 6;
- Injector circuits – errors 505, 606, short circuit, open circuit;
- Injector - codes 2216, 2317, 2418, 3321, respectively, refer to cylinders 3, 6, 4, 5;
- Malfunction of the idle air control valve - 271V;
- Ignition coil - errors 291D, 301E, 311F - 1, 3, 5 ts.
- Problems with the camshaft position sensor - error code 6541;
- Fuel pump relay - error code 6945;
- Problems in the ignition system - 210D2;
- Failure of the idle air control valve as a result of its mechanical damage - 211D3;
- Poor quality fuel mixture - 227E3 for cylinders 1, 2, 3 and 228E4 for 4, 5, 6.
- Cylinder misfires - 238EE in the first, 239EF in the second, 240F0 in the third, 241F1 in the fourth, 242F2 in the fifth, 243F3 in the sixth;
- Weak flow in the air mixing system - 245F5 cylinders 1, 2 and 3. Error code 246F6 - 4, 5 and 6 cylinders.
Also, the reasons for misfire in a BMW x5 e53 M54 engine can be:
- Air leakage, for example, the throttle corrugation or other suction points are torn;
- The mass air flow sensor has failed;
- Incorrect operation of hydraulic compensators;
- Timing chain stretching and ignition timing deviation;
- The high-voltage coil of one of the cylinders has failed (rearrange it to check);
- The problem is in the flow meter, remove the terminal block from it and see how the engine works;
- If the BMW x5 e53 has misfires after 3000 rpm, then check the DIS (DISA - installed inside the intake manifold, designed to suck in the fuel mixture through separate pipelines);
- A failed membrane is responsible for the mixture of gasoline and air;
- Other reasons.
Diagnostics without a computer
If you do not have a scanner, and most likely this is the case, and there is no desire to contact a car service, then the causes of misfire can be identified using the so-called old-fashioned methods.
Candles.
They need to be checked first; they must be dry without soot and oil.
If the spark plug is flooded, then ignition will not occur in this cylinder, and if it does, it will be misfired. The spark plug gap must be correct.
High voltage wires.
A common situation is that the wire just fell off. Also, the wires may be broken, damaged, or oily.
Remove the cap and conduct an external inspection of the wires, especially their contacts, to see if they are oxidized.
Check the resistance of the wires; read how to do this above. The resistance should be no higher than 10 kOhm and no lower than 3.5 kOhm. Replace the wires if necessary.
Ignition module or coil.
Everything is done simply with the car running; one by one, remove the high-voltage wire from the coil and observe what happens to the engine.
If nothing changes, then most likely the problem is not her. Also check the coil resistance as described above.
Injectors.
Also remove them one by one and check for clogging, clean if necessary. Check the resistance, read above how to do this, we won’t repeat it.
Timing belt.
When replacing it, a mistake could have been made by several marks; also check its condition; due to stretching, the belt could have jumped several teeth.
Air leak.
This could also be the cause of a misfire. You need to check everything from the air filter to the injectors.
On the injectors, pay attention to the rubber seals, which dry out over time and begin to leak air. Check the manifold gasket.
Other reasons, impaired compression, valve condition, etc. described above.
But I would like to note that using a scanner or oscilloscope significantly speeds up the search for the cause of a misfire, and in some cases it is impossible to do without these devices.
no spark in cylinders 2 and 4
- Megatheronosaurus
- Group: Users
- Posts: 6,964
- nineman
- Group: Users
- Posts: 155
- Megatheronosaurus
- Group: Users
- Posts: 6,964
I saw how the controller works on a Zhiguli car. I believe in any miracles.
They brought me the controller already removed, we disassembled it with a torx screwdriver and saw what the problem was.
- nineman
- Group: Users
- Posts: 155
- Megatheronosaurus
- Group: Users
- Posts: 6,964
- nineman
- Group: Users
- Posts: 155
Well, the controller was removed from the working car, I started it myself, turned it off, removed the controller and put it on mine, I started it and two cylinders did not work.