Different cars, as a rule, are equipped with gasoline or diesel engines of different power, with different amounts of torque and, accordingly, different crankshaft speeds.
Also, regardless of the type of internal combustion engine, cars are equipped with different gearboxes. At the same time, for most gearboxes, such a concept as the main gear of a car is relevant. Next we will talk about what a final drive is and what it is needed for.
Design and principle of operation
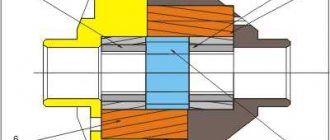
The principle of operation of the final drive is quite simple to understand. When the car is moving, torque is transmitted from the motor to the variable task box. After which, due to the main gear and differential, it is transmitted to the drive shafts. Accordingly, the main gear acts as a changing element. It changes the torque transmitted to the wheels and changes the speed of rotation of the wheels. The main characteristics of this gearbox include the gear ratio. The parameter reflects the ratio of the number of teeth of the driven gear to the driving gear. The larger the gear ratio, the faster the car will accelerate. However, in this case, the value of the maximum speed will inevitably decrease. The maximum speed is increased by reducing the gear ratio.
The main gear design is also quite simple. It consists of two gears of different sizes. It is subject to special requirements, including minimum noise and vibration levels during operation, minimum fuel consumption and high efficiency. The main gear must provide high traction and dynamic characteristics, be technologically advanced, reliable and undemanding in terms of maintenance.
This is interesting: Which engine runs on gas 66
Types and their applicability
The main characteristic of the main gears is the type of gears and the type of tooth engagement between them. The following types of gearboxes are used on cars:
- Cylindrical
- Conical
- Hypoid
- Worm
Types of main gears
Spur gears are used in the main gears of front-wheel drive cars. The absence of the need to change the direction of rotation allows the use of such a gearbox. The teeth on the gears are oblique or chevron.
The gear ratio for such gearboxes is in the range of 3.5-4.2. A larger gear ratio is not used, since this requires increasing the size of the gears, which is accompanied by an increase in the noise level of the transmission.
Bevel, hypoid and worm gears are used where it is necessary not only to change the gear ratio, but also to change the direction of rotation.
Bevel gearboxes are usually used on trucks. Their peculiarity comes down to the fact that the gear axes intersect, that is, they are on the same level. In such gears, oblique or curved teeth are used. This type of gearbox is not used in passenger cars due to its significant overall dimensions and increased noise.
On rear-wheel drive cars, a different type is most often used - hypoid. Its peculiarity is that the gear axes are shifted. Due to the location of the drive gear lower relative to the driven axis, it is possible to reduce the dimensions of the gearbox. Moreover, this type of transmission is characterized by increased resistance to loads, as well as smooth and silent operation.
Worm gears are the least common and are practically not used on cars. The main reason for this is the complexity and high cost of manufacturing the components.
Differential
The differential is a planetary mechanism designed to distribute torque between the drive axle shafts of a tractor or car and ensure rotation of the drive wheels at different frequencies when moving along a curve or uneven path. When turning or on an uneven path, the drive wheels move in arcs of different lengths. If both wheels were located on a common shaft, then their movement would be accompanied by slipping, tire wear and breakdowns. Therefore, the drive wheels are installed on separate shafts - axle shafts, connected by a differential.
Let us consider the operating principle of the differential according to the diagram shown in Figure a. Gears - satellite 7 (Figure a) is in mesh with racks 6 and 8 (in the actual design these are gears 6 and 8). A force P is applied to the axis 10 of gear 7, tending to move this gear upward.
If the resistance of racks 6 and 8 to movement by force P is the same, then equal forces P/2 act on their teeth and the racks move upward as a single unit with gear 7. However, when the resistance to movement of one of the racks, for example rack 6, will be greater than racks 8 , gear 7 begins to rotate around its axis and, rolling along rack 6, moves rack 8 up faster. In this case, the speed of movement of rack 8 increases as much as the speed of movement of rack 6 decreases. If the resistance to movement of rack 6 is increased so that it stops, then gear 7, rolling along it, will drag rack 8 up with it, and the speed of movement of rack 8 will be 2 times the speed of axis 10.
Drawing. Diagram of the differential and its locking mechanism: a - diagram of the differential operation; b - differential diagram with a locking mechanism; 1 - body; 2 — cam on the differential housing; 3 — differential lock mechanism fork; 4 - movable cam clutch; 5, 9 — axle shafts; 6, 8 — axle gears; 7 — satellite; 10 — satellite axis; 11 — driven bevel gear of the main gear.
Now let's look at a real differential circuit (Figure b). In the bosses of the housing 1, a satellite gear 7 is freely installed on the axis 10. The holes in the side bosses of the housing serve as supports for the axle shafts 5 and 9 with bevel semi-axial gears 6 and 8 mounted on them, meshed with the satellite gear 7. Rotation to the differential housing 1 is transmitted from the driven gear 11 main gear. If axle shafts 9 and 5 have the same resistance to rotation, then satellite 7, jammed by gears 6 and 8, is stationary on axis 10 and the entire system rotates as a single unit.
If the resistance to rotation of one axle shaft, for example, axle shaft 9, is greater than the resistance of axle shaft 5, then the satellite 7, turning on its axis, will slow down the rotation of gear 8 and speed up the rotation of gear 6, just as it was in the example with the movement of gear 7 and racks 6 and 8 (see figure a).
Changing the rotation speed of the axle shafts by the differential when the resistance on the wheels fluctuates reduces the tractor's maneuverability on moist or loose soil. In difficult soil conditions, it is better to turn off the differential to increase the traction of the wheels. For this purpose, tractors are equipped with differential locking mechanisms, very diverse in design.
Differential locking mechanisms
Differential locking mechanisms are divided into:
- forced
- automatic
- self-locking
And by drive type:
- mechanical
- hydraulic
Forced (mechanical) differential locking occurs when the movable cam clutch 4 (see Figure b), installed on the splines of the tractor axle shaft 5, engages with the cams 2 on the differential housing 1. In this case, the rotation speeds of the differential housing 7 and the axle shaft 5 will be the same, i.e. the differential will be locked.
The locking mechanism is activated by a pedal (or handle), and it is turned off by a pull-out spring when the force applied by the driver stops.
Automatic differential lock allows the driver not to expend any effort - the process of turning the mechanism on and off occurs automatically. Automatic differential locking is used on tractors MTZ-80, MTZ-82, T-150K, etc.
Principle of operation
General view of a hypoid final drive
The principle of operation of the final drive is quite simple: while the car is moving, torque from the engine is transmitted to the variable gearbox (Gearbox), and then, through the main gear and differential, to the drive shafts of the car. Thus, the final drive directly changes the torque that is transmitted to the wheels of the machine. Accordingly, through it the speed of rotation of the wheels also changes.
The main characteristic of this gearbox is the gear ratio. This parameter reflects the ratio of the number of teeth of the driven gear (connected to the wheels) to the drive gear (connected to the secondary shaft of the gearbox). The higher the gear ratio, the faster the car accelerates (more torque), but the maximum speed decreases. Reducing the gear ratio increases the maximum speed, while the car begins to accelerate more slowly. For each car model, the gear ratio is selected taking into account the characteristics of the engine, gearbox, wheel size, brake system, etc.
Transmission gears and the coolness of the car, how are they related?
Knowing the concept of gear ratio, as well as its effect on speed, acceleration dynamics and fuel efficiency, allows you to choose the optimal driving mode. This parameter is crucial for any car, regardless of its price and age. Few people know about this, but a competent analysis of the technical parameters before purchasing allows you to choose a car that ideally meets the owner’s needs. Let's consider the main aspects that need to be taken into account when choosing.
Advantages and disadvantages
- Cylindrical main gear. The maximum gear ratio is limited to 4.2. A further increase in the tooth ratio leads to a significant increase in the size of the mechanism, as well as an increase in the noise level.
- Hypoid main gear. This type is characterized by low tooth load and reduced noise level. In this case, due to the displacement in the meshing of the gears, sliding friction increases and efficiency decreases, but at the same time it becomes possible to lower the driveshaft as low as possible. Gear ratio for passenger cars – 3.5-4.5; for freight – 5-7;.
- Bevel main gear. Rarely used due to its large size and noise.
- Worm main gear. This type of gear connection is practically not used due to the complexity of manufacturing and the high cost of production.
GP on rear wheel drive cars
Other types of final drives are installed on rear-wheel drive cars, since the engine and gearbox are parallel to the drive, and torque is supplied to the drive axle vertically.
Rear-wheel drive cars most often have a hypoid gear, which has the least load on the tooth and creates a minimum degree of noise. During operation, the efficiency decreases, since the displaced fastenings of the gear wheels increase the coefficient of friction during sliding.
On cars with a hypoid gearbox, the gear ratio is 3.5 - 5.4, on trucks 5 - 7. This gear differs from a cylindrical gear: the shaft axis does not intersect with the gear, because the shape allows the cardan to be lowered and the body clearance to be reduced, this leads to maximum vehicle stability.
If the car owner is not interested in the size and degree of noise, then a canonical type GP is used. Worm gears are installed very rarely, since their production is labor-intensive and expensive.
For normal functioning of rubbing elements and teeth, lubrication is required. Special oil is poured into the crankcase or rear axle. Its level must be monitored to ensure stable operation of machine elements.
Who's in charge here and why?
So, the main transmission of a car is a unit, without which the efforts of the engine and gearbox would be a waste of energy. Why? The fact is that it is she who is responsible for transmitting torque from the gearbox directly to the drive wheels.
In addition, rotation, as a rule, still needs to change direction - from longitudinal (along the axis of the car) to transverse in order to get to the wheels. And all this is performed, in fact, by one gear mechanism, also known as a gear reducer. In addition to everything, the gear ratios are selected in such a way as to increase the torque of the motor.
This is interesting: What is an adsorber in a car?
Basic faults
- failure of the differential bearing - in gearboxes, bearings are used to allow the differential to rotate. This is the most vulnerable part that operates under critical loads (speed, temperature changes). When the rollers or balls wear out, the bearing emits a hum, the volume of which increases in proportion to the speed of the vehicle. Neglecting timely replacement of the bearing threatens to jam the gears of the main pair, which subsequently leads to the replacement of the entire assembly, including satellites and axle shafts;
- activation of the GP teeth and satellites. The rubbing surfaces of parts are subject to wear; with every hundred thousand kilometers, the teeth of a pair wear out, and the gap between them increases, leading to increased vibration and hum. For this purpose, adjustment of the contact patch is provided by placing spacer washers;
- cutting off the teeth of the gearbox and satellites - occurs if you often drive away with slipping;
- licking of the splined part on the axle shafts and satellites - natural wear and tear according to the mileage of the car;
- turning the axle bushing leads to the fact that the car will stand still in any gear and the gearbox will rotate;
- oil leak - possibly as a result of increased pressure in the differential housing due to a clogged breather or due to a leak in the gearbox cover.
Purpose, design features
The main task of this element is to change the torque before applying it to the wheel drive. The gearbox does the same, but it has the ability to change gear ratios by engaging certain gears. Despite the presence of a gearbox in the design of the car, the torque output from it is small, and the rotation speed of the output shaft is high. If you transfer rotation directly to the drive wheels, the resulting load will “crush” the engine. In general, the car simply will not budge.
The final drive of the car provides increased torque and reduced rotation speed. But unlike a gearbox, its gear ratio is fixed.
This transmission on a passenger car is a conventional single-stage constant mesh gearbox, consisting of two gears of different diameters. The drive gear is small in size and is connected to the gearbox output shaft, that is, rotation is supplied to it. The driven gear is much larger in size and it supplies the resulting rotation to the drive shafts of the wheels.
The gear ratio is the ratio of the number of gear teeth in the gearbox. For passenger cars this parameter is in the range of 3.5-4.5, and for trucks it reaches 5-7.
The higher the gear ratio (the greater the number of teeth on the driven gear relative to the drive gear), the higher the torque supplied to the wheels. In this case, the tractive effort will be greater, but the maximum speed will be lower.
The main gear ratio is selected based on the performance indicators of the power plant, as well as other transmission components.
The final drive design directly depends on the design features of the car itself. This gearbox can be either a separate unit installed in its own housing (rear-wheel drive models) or be part of the gearbox design (cars with front-wheel drive).
As for some all-wheel drive cars, they may use a different layout. If in such a car the location of the power plant is transverse, then the main gear of the front axle is included in the design of the gearbox, and the rear axle is located in a separate housing. In a car with a longitudinal layout, the main gears on both axles are separated from the gearbox and transfer case.
In models with a separate main gear, this gearbox performs one more task - it changes the angle of rotation by 90 degrees. That is, the gearbox output shaft and wheel drive shafts are perpendicular.
In front-wheel drive models, where the main gear is included in the gearbox design, these shafts are parallel, since there is no need to change the direction angle.
A number of trucks use two-stage gearboxes. It is noteworthy that their design can be different, but the most widespread is the so-called spaced layout, which uses one central gearbox and two wheeled (on-board) gearboxes. This design allows you to significantly increase the torque and, accordingly, the traction force on the wheels.
Drive cars
The peculiarity of the gearbox is that it evenly divides the rotation between both drive shafts. For straight-line motion, this condition is normal. But when cornering, the wheels of the same axle travel different distances, so it is necessary to change the rotation speed of each of them. This is the job of the differential used in the transmission design (it is installed on the driven gear). As a result, the main gear supplies rotation to the drive shafts not directly, but through the differential.
Primary requirements. Modern tendencies
The main gears are subject to many requirements, the main ones being:
- Reliability;
- Minimal maintenance required;
- High efficiency indicators;
- Smooth and silent;
- Minimum possible overall dimensions.
Naturally, there is no ideal option, so designers have to look for compromises when choosing the type of final drive.
It is not yet possible to abandon the use of final drives in transmission designs, so all developments are aimed at increasing performance indicators.
It is noteworthy that changing the operating parameters of the gearbox is one of the main types of transmission tuning. By installing gears with a changed gear ratio, you can significantly influence the dynamics of the car, maximum speed, fuel consumption, load on the gearbox and power unit.
Finally, it is worth mentioning the design features of dual-clutch robotic gearboxes, which also affects the final drive design. In such gearboxes, paired and unpaired gears are separated, so there are two secondary shafts at the output. And each of them transmits rotation to its own drive gear of the main gear. That is, in such gearboxes there are two driving gears, and only one driven gear.
DSG gearbox diagram
This design feature allows you to make the gear ratio on the gearbox variable. To do this, only drive gears with different numbers of teeth are used. For example, when using a number of unpaired gears, to increase traction, a gear is used that provides a larger gear ratio, and the gear of a paired row has a lower value of this parameter.
Types of main gear by type of gear connection
If we divide the types of main gears, then we can distinguish:
- cylindrical;
- conical;
- worm;
- hypoid;
Cylindrical final drives are used in front-wheel drive passenger cars with a transverse engine and gearbox. Its gear ratio is in the range of 3.5-4.2.
Spur gears can be spur, helical or chevron. The cylindrical gear has a high efficiency (at least 0.98) but it reduces ground clearance and is quite noisy.
- The bevel final drive is used on rear-wheel drive light and medium-duty vehicles with a longitudinal arrangement of the internal combustion engine, where overall dimensions do not matter.
The axes of the gears and the wheels of such a transmission intersect. These gears use straight, oblique or curved (spiral) teeth. Noise reduction is achieved by using an oblique or spiral tooth. The efficiency of the final drive with a spiral tooth reaches 0.97-0.98.
- The worm main gear can be either with a lower or an upper worm arrangement. The gear ratio of such a main gear is in the range from 4 to 5.
Compared to other types of gears, the worm gear is more compact and less noisy, but has a low efficiency of 0.9 - 0.92. Currently, it is rarely used due to the complexity of production and the high cost of materials.
- Hypoid final drive is one of the popular types of gear connection. This transmission is a kind of compromise between a bevel and a worm final drive.
The transmission is used on rear-wheel drive cars and trucks. The axes of the gears and the wheels of the hypoid gear do not intersect, but are crossed. The transmission itself can be either with a lower or an upper offset.
A bottom offset final drive allows the driveline to be positioned lower. Consequently, the center of gravity of the car also shifts, increasing its stability when driving.
Compared to bevel gears, hypoid gears are smoother, quieter, and smaller in size. It is used on passenger cars with a gear ratio of 3.5-4.5, and on trucks instead of a double main gear with a gear ratio of 5-7. In this case, the efficiency of the hypoid transmission is 0.96-0.97.
With all its advantages, the hypoid transmission has one drawback - the jamming threshold when the car reverses (exceeding the rated speed). For this reason, the driver needs to take special care when selecting the speed of reversing.
Classification of final drives
By the number of pairs of gears
- Single - has only one pair of gears: driven and driven.
- Double - has two pairs of gears. Divided into double central or double spaced. The double central one is located only in the drive axle, and the double spaced one is also located in the hub of the drive wheels. It is used in trucks, as they require a higher gear ratio.
Single and double final drive
By type of gear connection
- Cylindrical. Used on front-wheel drive vehicles in which the engine and gearbox are transversely located. This type of connection uses gears with herringbone and helical teeth.
- Conical. Used on those rear-wheel drive cars in which the size of the mechanisms is not important and there are no restrictions on the noise level.
- Hypoid is the most popular type of gear connection for rear-wheel drive vehicles.
- Worm gear is practically not used in the design of car transmissions.
Cylindrical final drive
By layout
- Placed in the gearbox or power unit. On front-wheel drive vehicles, the main gear is located directly in the gearbox housing.
- Placed separately from the checkpoint. In rear-wheel drive vehicles, the main pair of gears is located in the drive axle housing along with the differential.
Note that in all-wheel drive vehicles, the location of the main pair of gears depends on the type of drive.
Bevel final drive
Types of car transmissions
The type of transmission system depends on the energy source and the method of transmitting torque from the internal combustion engine to the wheels of the vehicle. Automakers produce vehicles with several types of transmissions:
- mechanical;
- hydromechanical;
- electrical;
- hybrid.
Mechanical
The most common type of power transmission, present in all cars with a manual gearbox and clutch unit. The rotation of the crankshaft is transmitted through the clutch discs to the gearbox and other transmission units.
Hydromechanical
It is gaining popularity due to the widespread use of automatic transmissions in new car models. Mechanical rotation is transformed into fluid (oil) movement in the torque converter, a more advanced clutch replacement. The transmission of torque through the transformer is smoother.
Electric
Used in electric cars and cars with hybrid power plants. In the first case, electricity from the battery powers an electric motor that rotates the wheels. Autohybrids are equipped with two types of power plants: internal combustion engines, electric motors, and batteries. Some car models use an internal combustion engine only after accelerating to a certain speed; up to this point, the wheels are turned by electric current. Some solutions allow you to constantly move with the help of electric motors, using a low-power gasoline engine only to recharge the batteries.
Where is?
We seem to have figured out the purpose of the car’s main gear; now it would be nice to find it. Doing this can be a difficult task, because the location of this unit can be different and depends on the type of machine drive and the imagination of the development engineers.
Fortunately, the flight of thoughts here is limited by the number of axes. So, for example, if we have front-wheel drive, then in this case the main gear of the car should be looked for in the gearbox along with the differential, in vehicles with rear drive wheels - directly in the rear axle. If all four are leading, then choose one of the above options.
The most common signs of transmission failure
The most difficult transmission element to repair is the gearbox. The car owner should be wary of:
- difficulties when changing gears, crunching, creaking, other extraneous sounds when moving the lever to another position;
- it is impossible to engage the gear;
- a strong smell of engine oil appears in the cabin;
- rustling, knocking noises when the gear shift lever is in neutral.
An oil leak from the gearbox is a serious reason to immediately contact a specialist. Lack of lubrication can completely damage the mechanism.
Damage to the cable or a “weak” clutch pedal can lead to “sticking” of the clutch. When you press the pedal, the discs will not be able to separate, and you will not be able to change the speed. At the same time, an unpleasant grinding sound is heard.
Gear ratios (row)
Gear ratios are the gears of each gear, which also have their own size.
Gear ratios characterize the speed characteristics of a car in a particular gear. In a standard VAZ, the following numbers are used:
| Gearbox ratios: | |
| I | 3,636 |
| II | 1,95 |
| III | 1,357 |
| IV | 0,941 |
| V | 0,784 |
| reverse | 3,53 |
The characteristics shown above are just with standard gear ratios.
The standard range on the 2114 is far from ideal: First gear is too short – second gear is too long. Due to this, there is a sharp drop in dynamics when switching from first to second. Not only is there a failure, but when switching sharply, the second gear synchronizer slowly dies.
Therefore, there are sports series where the gap between 1st and 2nd is removed, and not only: sports series are selected according to the type of engine: it can just be a good city engine, or a sports one, or tailored for 402-meter racing. There are also “turbo” gears - designed for a turbo engine.
How is the GP structured?
What does the main gear consist of:
- bevel gear;
- bevel wheel.
The gear is the driving part (the thrust from the gearbox and the engine is attached to it), and the wheel is the driven element (it receives the thrust from the gear and transmits it at an angle of 90°).
Gears are made with teeth in the form of a spiral, because of this their hardness and number increase. At the same time, they are meshed, and the gears operate smoothly and without noise.
In addition to a bevel gear transmission with axes that intersect each other, the machine uses a hypoid transmission. Here the teeth have a certain design and the axis of a small bevel gear. It is shifted downward relative to the center of the largest gear by a certain distance.
This allows you to place the driveshaft lower and reduce the height of the convex upper part of the tunnel for positioning the shaft on the underbody, thereby increasing the area of the car interior.
It becomes possible to slightly reduce the center of gravity of the machine and increase its stability. Hypoid transmission has significant smoothness, high tooth strength and wear resistance.
Required care
Any gears of the main gear and self-block need lubrication and maintenance. Despite the fact that all elements of the GP and self-block look like powerful pieces of hardware, they still have their own durability resource. Because of this, advice regarding sudden starts and braking, rough clutch engagement and other vehicle loads remain relevant today.
All rubbing elements and gear teeth must be lubricated regularly. Because of this, special oil is poured into the crankcase, the level of which must be checked occasionally.
The oil in which the gears operate can leak through weak connections and worn-out seals.
If there is any doubt about the occurrence of any malfunction in the transmission, it is necessary to raise the drive wheel of the machine using a jack. Start the motor and gear to rotate the wheel. Look at all the rotating parts, listen for any strange or suspicious noise.
Then you should jack up the other wheel. If there is significant noise, vibration or oil droplets, you must contact a car service center.
Gearbox maintenance and troubleshooting
Below are links to articles that can help you find the information you need.
- What kind of oil to pour into the gearbox? Types of oils, viscosity, oil service life.
- How to remove/replace the gearbox? Step-by-step instructions for removing the gearbox.
- The gearshift lever is rattling, what should I do? We get rid of the rattling of the gearbox handle at 2.5-4 rpm.
- How to replace a malso in a gearbox? Step-by-step instructions for changing the oil in the box.
- How to check the oil level? About where the dipstick is on the box and how to check the level.
- How to replace the reverse sensor (RDS)? The reversing lights do not light up - most likely the sensor has failed. Detailed instructions for replacing the sensor.
- Reverse gear does not engage. What to do? The reasons for this problem and what can be done about it.
- Second gear crunches. The reasons for this problem and what can be done about it.
We hope you found answers to your questions.
How does the service work?
Gearbox maintenance is rarely done; usually everything is limited to changing the oil. At a mileage of over 150,000 km, the bearing may need to be adjusted, as well as the contact patch between the driven and drive gears. When changing the oil, it is extremely important to clean the cavity from wear products (small chips), as well as dirt. It is not necessary to use flushes for the axle gearbox; it is enough to use 2 liters of diesel fuel and let the unit run at low speeds.
Tips on how to extend the performance of the GP and differential:
- change the oil in a timely manner, and if your driving style is more sporty, the car endures high loads (driving at high speed, transporting cargo);
- When changing the oil manufacturer or changing the viscosity, flush the gearbox;
- When driving over 200,000 km, it is recommended to use additives. Why is an additive needed? Molybdenum disulfide, contained in the additive, reduces friction of parts, as a result of which the temperature decreases, the oil retains its properties longer. Remember that if the main pair is heavily worn, there is no point in using an additive;
- Avoid starting with slipping.