03/02/2022 4 128 Motor oils
Author: Victor
Thanks to engine oil, high-quality lubrication of all moving components and mechanisms of the machine’s power unit is ensured. Like any liquid, a lubricant can freeze and boil under certain conditions. What is the boiling point of motor oil and what you need to know about choosing and replacing a lubricant, we will tell you below.
[Hide]
Engine oil viscosity
The viscosity value of the liquid 0W20, 0W30, 5W30, 5W40, 10W40 or other lubricant is considered one of the main parameters. Lubricating fluid is used to reduce the amount of friction between the surfaces of mechanisms and components of a car’s power unit. Low lubricating properties and characteristics of the substance can lead to jamming, as well as accelerated wear and breakdown of the power unit as a whole.
Oils with a high or low flash point must have the following qualities:
- eliminating the possibility of friction between components and elements of the motor;
- unhindered passage of the substance through all lines of the lubrication system.
Oil manufacturers use special additives designed to improve temperature and viscosity parameters. Thanks to additives, motor fluid thins less when the engine warms up and becomes thicker in severe frost.
Substances characterized by low viscosity are found in almost all low-quality liquids. Because of this, the product burns out faster and evaporates on the internal walls of the engine. This contributes to accelerated lubricant consumption and a decrease in the temperature properties of the product.
Determination of viscosity by marking
The flash, boil and freezing point ranges are usually indicated on the engine fluid label. Also on the lubricant container there is detailed information regarding viscosity parameters in accordance with the SAE standard. This value is marked with numerical as well as letter designations, for example, 0W-30 or 10W-40. The letter W indicates winter performance. The numbers located on the sides indicate the operating parameters of the fluid for summer and winter. In the specified range, the manufacturer guarantees uninterrupted operation of the power unit.
Alexey Kambulov tested motor oils with heating, the results are shown in the video below.
Operating temperature range
The viscosity of the product depends not only on the composition of the substance, but also on the temperature over a wide operating range. This indicator is directly dependent on the temperature in the engine, as well as the air. In order for all components of the internal combustion engine to work smoothly, it is necessary to ensure the high-quality functioning of processes within normal limits.
When producing vehicles, the development company's engineers always calculate the viscosity parameters of the liquid. On average, the operating properties of the oil temperature vary in the region of -30 - +180 degrees, but much also depends on the design features of the engine engine and the environment.
Reasons for this problem
1. The main reason for this problem is the low quality of the lubricant used. If, in pursuit of cheaper oil, after some time problems arise with the car’s lubrication system, then this is not anything unexpected. After all, low-quality oil cannot cope with regular fluctuations in the temperature level inside the unit, thereby provoking it to evaporate and ignite. 2. Unfortunately, this situation can also arise when using high-quality material after it has aged. 3. The occurrence of a problem in the cooling system, such as a pump breakdown, a malfunction of the fan fluid coupling.
Good to know: Which motor oil is not counterfeited in Russia, list of the best
Why is high engine temperature dangerous?
Severe overheating of the motor will cause the unit to boil; this is much more dangerous than the lubricant hardening. With regular use of a car engine under these conditions, the viscosity parameters of the substance drop, as a result of which the internal combustion engine components cannot be properly lubricated. It should be taken into account that when overheated, motor fluid permanently loses the properties and performance characteristics specified by the manufacturer. At 125 degrees, the lubricant begins to evaporate, which helps reduce the volume of oil in the engine and leads to the need to add it regularly. Oil starvation will cause failure of the unit.
In his video, user Mikhail Autoinstructor talked about the causes of overheating, as well as ways to solve this problem.
Causes of excessive heating of engine oil
The operating temperature of Lukoil oil or any other product may change due to prolonged use of the fluid. Over time, the lubricant begins to age as a result of chemical reactions and oxidative processes that occur inside the internal combustion engine. This leads to the appearance of carbon deposits, varnishes, and sludge deposits in the unit. These processes occur faster during self-ignition or when the lubricant operates at elevated temperatures.
Soot is a solid substance resulting from the oxidation of a hydrocarbon. Such deposits may consist of lead, metal and other mechanical elements. The appearance of carbon deposits will lead to engine detonation and tripping, glow ignition, etc. As for varnishes, such deposits are oxidized films that create a sticky coating on rubbing working surfaces. As a result of exposure of the lubricant to high temperatures, boiling of varnishes, which contain oxygen, carbon, ash and hydrogen, can occur.
The presence of a varnish coating impairs the heat transfer of the cylinders and pistons of the internal combustion engine, which leads to rapid overheating of the structural elements of the engine. The piston rings and grooves suffer the most from the effects of varnish; due to coking, these components can become stuck. Coke is formed in the engine due to the chemical reaction of carbon deposits with varnish. Precipitation in the form of sludge is a mixture of oxidation products with emulsion deposits. Their formation contributes to a decrease in the quality of the fluid and disruption of the mode of use of the vehicle as a whole.
The main reason for heating the oil is its low quality, if you do not take into account mechanical problems with the internal combustion engine.
Motor oil neutralization numbers
Below is a list of abbreviations:
- TBN. Indicates the total alkaline parameter of the liquid. Using this indicator, you can determine the amount of acid that is required to neutralize the alkaline elements contained in one gram of the product. The parameter is measured in mg KOH. The TBN value determines the number of weak and strong alkaline elements that make up the base of the liquid.
- TAN. Total Base Number. This value determines the amount of potassium hydroxide that will be required to neutralize the free acids present in one gram of liquid. The operating parameter expresses the number of acidic elements contained in the lubricant.
- SBN. Alkaline index for identifying strong acids. This value determines the volume of acid that is needed to neutralize the strong alkaline components present in one gram of lubricant. As a rule, we are talking about unlimited alkalis, but in practice this happens quite rarely.
- SAN. A parameter for strong acids that determines the volume of alkaline elements required to neutralize them.
From Roman Romanov's video you can learn about the main reasons for overheating of a car engine.
Boiling temperature
When the automobile power unit warms up to normal, the viscosity of the mineral or synthetic product should decrease to a certain value. If this does not happen, under heavy loads this will not affect the functionality of the motor in any way. Temperature parameters will increase slightly, and the viscosity will decrease to normal over time. This will not cause rapid wear of a diesel or gasoline engine, provided that the lubricant does not boil. With moderate overheating, the pistons may melt a little, but it is advisable to do more detailed diagnostics if smoke appears from the engine compartment.
Prolonged boiling of the lubricant will cause the cylinder head to become distorted, traces of defects and cracks to appear on it, which can lead to the valve seat “flying out”. Increased fluid temperature can destroy the cylinder head gasket. The inter-ring partitions, oil seals and other components of the internal combustion engine will deteriorate, which can lead to lubricant leakage. Due to severe overheating of the engine, the pistons of the internal combustion engine melt and burn out, as a result of which molten aluminum settles on the walls of the engine cylinders. This will lead to the fact that the stroke of the pistons will be more difficult, the elements will wear out much faster.
Motor fluid overheats under the influence of elevated temperatures and loses its lubricating properties. The moving components of the internal combustion engine break down, and wear products begin to stick to the crankshaft. As a result of high load under the influence of the piston, the crankshaft may break into two parts. In addition, the piston components will puncture the cylinder head wall. This will lead to complete breakdown of the unit and the need for a major overhaul. The boiling point of motor oil is usually 250 degrees.
Flash point
The combustion temperature is determined by heating the lubricant in an open container. To record the state of the liquid, specialists hold a lit wick over a crucible or equipment where the lubricant is heated. The lubricant temperature parameter should change and increase by no more than two degrees within one minute. In this case, the liquid should not only flare up, but also ignite. At lower temperatures, the viscosity of the lubricant increases.
The temperature at which oil burns depends on the manufacturer. On average, according to GOST, flammability and spontaneous combustion of motor fluid occurs at a temperature of 250-260 degrees, and smoke and bubbles may appear in the engine unit. Fire is one of the most serious problems for an engine. If the liquid burns and ignites, the engine may explode. Of course, no amount of major repairs will solve this problem if the car explodes. This is especially dangerous for the driver and passengers, since the explosion can lead not only to serious injuries, but also death.
Igor Kushnir provided a video that shows the result of contact of motor fluid with oxygen - ignition of the product.
Volatility
Car owners may encounter problems with fluid evaporation; this is usually due to low quality oil and non-compliance with the operating conditions of the power unit. With increased fluidity of the lubricant, the level of the substance in the engine decreases. Some will go to soot and deposits. At a reduced level, the car engine will operate in conditions of oil starvation. This will lead to an increase in the load on rubbing components and parts, which may result in the problem of rapid wear of spare parts. Ultimately, the performance of the power unit will deteriorate and it will break down as a whole.
Evaporation of lubricant usually occurs at a temperature of 250 degrees. To determine the volatility value, the Nok method is used. Its essence is to heat one liter of lubricant for an hour at a temperature of 250 degrees. If during this time about 800 grams of liquid remain, this indicates that the volatility value is 20%, since 200 grams have evaporated. According to ACEA standards, this parameter should be no more than 15% for products corresponding to class A1/B1. For liquids of classification A3/B3, A3/B4, A5/B5, C1-C3, E4, E6, E7 and E9, the volatility value should be no more than 13%. As for C4 standard oils, the volatility parameter should be no higher than 11%.
Flashes
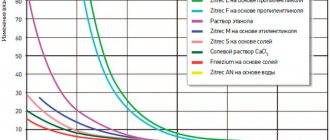
The flash point of a liquid determines the threshold at which a substance will ignite. It will always be 20-30 degrees less than the ignition temperature of the lubricant; it all depends on the manufacturer and the manufacturing technology of the product. The technical parameters of the oil can be found in the tables below. A lubricant flash will cause serious problems, including fire. If you use overheated oil for a long time, it will catch fire.
Table of correspondence of technical parameters of oils of different classes
Table of technical characteristics of 5W-40 class lubricant
Total Base Number (TBN)
During engine operation, chemical and physical processes take place in it, as a result of which fuel molecules are oxidized, oxide is formed, and it has an extremely negative effect on the metal parts of the engine, forms sludge, settles on parts, some chemical components of the oxide participate in corrosion processes, destroy rubber seals. To neutralize the resulting acid, chemically active additives are added to the oil. By itself, refined mineral oil is chemically neutral.
To increase the alkalinity of the oil, special additives are added to it - detergents; they partially neutralize the resulting acid and break it down into small fractions, preventing the formation of sludge. Alkalinity decreases with mileage; the longer the mileage, the lower the alkaline number and the higher the acid number. When there is a small gap left before they “meet”, the oil loses its ability to wash and neutralize and becomes unusable. Therefore, oils with a high alkaline number are considered the best and most effective.
In modern oils, the alkali level ranges from 5 to 14 mgKOH/g. A good indicator for gasoline engines is 7-8 mgKOH/g, for diesel engines from 9 - in a diesel engine the conditions for oil are more difficult, the temperature is higher, there is more sulfur in the fuel. It is considered safe to use oil up to a TBN value of up to 50% of that of fresh oil. With the advent of gasoline with low sulfur content, this figure has decreased slightly; sulfur is one of the main enemies of oil, contributing to its oxidation. The critical indicator for changing the oil is when the alkaline number is compared with the acid number.
Different methods are used to determine the base number in fresh and used oil. For fresh oil GOST 30050 or ASTM D 2896, for processing GOST 11362 or ASTM D 4739. Each method “sees” alkalis of different types, but sometimes companies use GOST 30050 or ASTM D 2896 for analysis and processing, this is due to internal manufacturer's policy.
Determining the quality of oil by alkaline number is twofold. On the one hand, oil with a low number will burn out faster and will lose its ability to wash away sludge. On the other hand, enriching the additive composition reduces the base number, that is, oils with a rich additive package may have a low base number. Therefore, some cheap oils with a high alkaline number may simply have a poor additive package.
The influence of low temperatures on engine starting stability
When purchasing a lubricant, you need to familiarize yourself with the winter parameters of the fluid, since they determine the quality of starting the internal combustion engine in the cold season. If you are using a 5W-40 class lubricant, then subtract 35 from the number 5 (this is a constant number for all types of oils). We get -30 - this is the minimum temperature at which the lubricant can start the engine without problems.
Low temperature parameters
It is necessary to take into account not only the ambient temperature, but also the power unit, since the operation of the engine is determined by the vehicle’s mileage and loads.
There are low-temperature properties of the working fluid, which include:
- Pumpability. This parameter means a state in which the substance is pumped without problems through the channels of the lubrication system.
- Product rotation. This value indicates the dynamic characteristics of the viscosity of lubricants, as well as the temperature at which the lubricant becomes most liquid. In this state, starting the engine will be easier. The cranking temperature is always 5 degrees higher than the pumping temperature.
User Vlas Prudov made a video in which he talked about choosing a high-quality fluid for a machine engine.
Freezing
The value of the pour point is determined by the loss of mobility and fluidity properties of the liquid. When the viscosity parameters increase sharply, this leads to the beginning of the wax crystallization process. Oil operating at low temperatures will be less mobile. The lubricant hardens, which leads to an increase in ductility as a result of the release of hydrocarbon substances. The pour point of the motor fluid corresponds to the minimum circulation parameter. If the oil begins to solidify, starting the engine is possible, but it will be very difficult.
Solidification temperature
The solidification temperature is 3-5 degrees lower than solidification. When it gets very cold, the fluid base becomes harder, making it impossible for it to pass through the channels of the lubrication system. Accordingly, the driver will not be able to start the power unit. This problem is more pressing for residents of northern regions, who fill their cars with oils that do not meet the viscosity class for use in such conditions.
What to do when the grease boils
- The car engine will immediately turn off.
- Minimize the load on the power unit by reducing speed.
- Turn on the car furnace for the maximum possible airflow, which will allow you to effectively and quickly remove superheated air from the working part of the car engine.
- If there is such an opportunity, then it is advisable to drive along a coasting road to quickly cool the engine compartment.
- After stopping the car completely, you need to wait at least 5 minutes and only then turn off the engine.
Video “Testing motor oils?”
User Denis MECHANIC tested different brands of fluids in his video and talked about the test results.
Do you have any questions? Specialists and readers of the AUTODVIG website will help you ask a question
Was this article helpful?
Thank you for your opinion!
The article was useful. Please share the information with your friends.
Yes (100.00%)
No
X
Please write what is wrong and leave recommendations on the article
Cancel reply
Rate this article: ( 5 votes, average: 5.00 out of 5)
Discuss the article:
Sulfur content
The amount of sulfur in fresh oil is determined as a mass fraction, that is, as a percentage. This indicator depends on the nature of the oil from which the base was prepared and on the quality of its purification. Modern refining methods make it possible to create oils with low sulfur content.
Based on the amount of sulfur in the analysis, you can determine the degree of base purification and the additive package used - calcium sulfonates or calcium salicylates. In the first case, sulfur will be up to 0.400%, in the second 0.200-0.260%. If sulfur is more than 0.500%, this most often indicates that the base contains mineral oil of the first group, most often found in semi-synthetics with high viscosity.
Oxidation inhibitors
(antioxidant additives). During operation, the engine oil is constantly exposed to high temperatures, atmospheric oxygen and nitrogen oxides, which causes its oxidation, destruction of additives and thickening. Antioxidant additives slow down the oxidation of oils and the inevitable subsequent formation of corrosive deposits. The principle of their action is a chemical reaction at high temperatures with products that cause oxidation of the oil. They are divided into inhibitor additives, which work in the general volume of oil, and thermal-oxidative additives, which perform their functions in the working layer on heated surfaces.
Total.
So to speak, the conclusions from the article in brief:
- Characteristic is a quantitative expression of a particular property of the oil. You can measure it and compare it with other oils.
- Viscosity - winter, characterizes the ability of the oil to ensure engine starting in cold weather (dynamic viscosity) and working (NOT summer) (kinematic viscosity), tells us about the quality of engine lubrication. Thicker is better. Viscosity index is the change in viscosity with temperature. The number is larger - the change is smaller - better.
- Ash content is bad for catalysts and particulate filters in diesel engines; the alkalinity number means the oil’s resource for neutralizing acids.
- The pour point, like the flash point (and density), has no practical significance, but allows you to draw some conclusions about the composition of the oil.
Ash content
Sulfate ash is formed during the combustion of lubricant. Base oils are refined and virtually ash-free, but additives introduce unwanted impurities such as magnesium, calcium, phosphorus, zinc and others. During the combustion of substances, deposits form on the surface of engine parts, which contribute to premature ignition of the fuel mixture, that is, they increase detonation. Ash also contaminates exhaust catalytic converters and particulate filters. Accordingly, the lower the indicator, the less deposits on the parts.