Circuit breakers
F1 (5A)
- License plate lamps
- Instrument lighting lamps
- External lighting indicator lamp in the instrument cluster
- Engine compartment lamp
- Additional brake signal lamp
- Left side marker lamps
F2 (7.5A)
- Low beam lamp (left headlight)
- Electric headlight corrector
- Corrector motor gearbox
F3 (7.5A)
- High beam lamp (left headlight)
- Indicator lamp for high beam headlights
F4 (10A)
Left fog lamp
F5 (30A)
- Power window relay
- Electric windows
F6 (15A)
- Before 2009:
Door lock control unit - After 2009:
Cigarette lighter
F7 (20A)
- Before 2009: Cigarette lighter
- Horn relay
- Sound signal
- Horn relay
F8
- Before 2009 (20A): Heated rear window relay (contacts)
- Rear window heating element
- Heated rear window relay
F9 (20A)
- Before 2009: Glove compartment lamp
- Windshield wiper relay
- Windshield wiper switch
- Windshield wiper motor
- Headlight wiper relay (contacts)
- Electric motors for headlight wipers
- Headlight washer motor
- Heated tailgate glass switch
F10 (20A)
- Before 2009:
Reserve - After 2009:
Electrical accessories remote control unit (door lock)
F11 (5A)
- Tail lamps
- Instrument lighting control
F12 (7.5A)
- Low beam lamp (right headlight)
- Corrector motor gearbox (right headlight)
F13 (10A)
High beam lamp (right headlight)
F14 (10A)
Right fog lamp
F15 (20A)
- Exterior mirror control unit
- Electric drives for exterior rear view mirrors
- Exterior mirror control unit
F16 (10A)
Relay-breaker for direction indicators and hazard warning lights (in hazard warning mode)
F17 (7.5A)
- Individual lighting lamp
- Immobilizer warning lamp
- Brake light bulbs
- Additional brake signal
- Interior lighting
F18 (25A)
- Before 2009: Reversing lamps
- Electric heater fan
- Windshield washer motor
- Heated rear window relay (coil)
- Rear window wiper relay
- Rear window wiper motor
- Rear window washer motor
- Door lock control unit
- Heater motor switch
F19 (10A)
- Before 2009: Relay interrupter for direction indicators and hazard warning lights (in turn signal mode)
- Instrument cluster (except engine management system malfunction warning lamp)
- Differential lock indicator lamp
- Starter relay
F20 (7.5A)
- Before 2009:
Rear fog lights - After 2009:
- Rear fog lights
Anti-theft system control unit (Since 2009)
Buzzer (Since 2009)
- Fog lamps in the rear lights
- Anti-theft system control unit (Since 2009)
- Buzzer (Since 2009)
K1
- Until 2009:
Relay for monitoring lamp health (jumpers are installed instead of relays) - After 2009:
Windshield wiper relay
K2
- Before 2009:
Windshield wiper relay - After 2009:
Relay-breaker for direction indicators and hazard warning lights
K3
- Before 2009:
Relay interrupter for direction indicators and hazard warning lights - After 2009:
Low beam relay
K4
- Before 2009:
Low beam relay - After 2009:
High beam relay
K5
- Before 2009:
High beam relay - After 2009:
Auxiliary Relay (Tailgate Defogger Relay Coil, Heater Fan, Windshield Wiper and Washer, Tailgate Wiper and Washer)
K6
- Before 2009:
Additional relay (Relieves ignition switch contacts) - After 2009:
Heated tailgate glass relay
K7
Heated tailgate glass relay
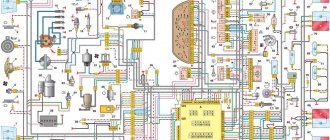
Designations of fuses and their purpose
To protect electrical circuits on cars, fuses are used, located in a special mounting block. On a Chevrolet Niva VAZ 2123, this block is located inside the instrument panel, to the left of the plastic steering column cover.
The placement of blocks in the cabin is the same for cars of all years of manufacture.
The main blocks of machines are divided into two types - before 2009 and after. These devices are not interchangeable. The blocks behind the glove box are identical in design.
On a 2005 car, you can easily install a block from a 2011 car. The designation of the fuse rating is marked on the body; on the assembly itself there is a number of the fuse link and a pictogram of the purpose.
There are no fuse markings on the main unit cover.
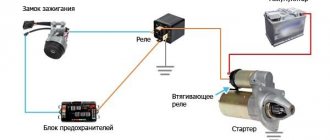
A typical fuel pump relay 75.3777-10 has 4 contacts, a coil with an armature, and a spring for opening the contact. When voltage is applied to the control contacts, the rod is drawn into the winding and another pair of contacts is closed. It turns off automatically as soon as the low-current connectors are de-energized.
Advantages of using relays in Niva Chevrolet cars:
- spontaneous leakage current in the on-board system is eliminated;
- reliable control of all electric motors;
- quick and guaranteed start of electrical mechanisms;
- Network overload protection.
Causes of electrical equipment malfunction
Let's look at the main reasons why electrical equipment may not work:
- Discharged or defective battery. Due to a damaged battery, the car engine can only be started “from the pusher”. A faulty battery can be determined by the low battery indicator on the dashboard lighting up. When troubleshooting, we recommend that you first check the external condition of the device - there should be no defects or damage that could cause electrolyte leakage. You also need to check the volume of the working solution inside the battery - the liquid should cover all the jars. If necessary, distilled water is added to the battery. The terminals are checked - sometimes the reason for the non-working state of the battery is the disconnection of contacts associated with vibration during shaking, as well as their oxidation.
- Damage to the generator unit. If the generator breaks down, it will not be able to keep the electrical equipment in working order. All devices will be powered by the battery until it eventually runs out. To troubleshoot, the generator will have to be dismantled and disassembled; damaged elements must be replaced.
- Voltage surges. There can be many reasons for this problem. Voltage surges often occur as a result of a regulator relay failure or the use of equipment that does not meet the operating specifications of the electrical circuit. For example, if you install a splitter in the cigarette lighter, this will lead to voltage surges and failure of the device.
- Burnout of safety elements. The devices are used to protect electrical appliances from overvoltage. When power surges occur, fuses are the first to fail. You cannot change parts for devices made by yourself. Sometimes car owners replace fuses with coins or jumpers made of wire. We do not recommend doing this to prevent overvoltage.
- Broken wires. Most often, this type of malfunction affects electrical circuits that are located in the area of moving parts of the body. The wires become kinked, making them unable to conduct electrical current.
- Failure of the equipment itself, for example, light bulbs in the headlights, radio, electric heater motor. Lighting sources must be replaced, and devices such as an electric motor or car radio can be repaired. It is better to entrust this procedure to qualified electricians.
- Leakage current. This problem occurs when the wire insulation is damaged. It is necessary to find the part of the electrical circuit where the insulating layer is broken and re-cover it with electrical tape.
- Damage to contacts or their oxidation. If problems appear in the operation of the equipment, check the contact elements on the wiring connectors. When they burn out, it is necessary to diagnose electrical circuits for the presence of voltage surges. If the contacts are oxidized, then you just need to clean them.
Lada 4×4 3D 2121 › Logbook › Electric fans 21214 in 2121
Just a short note about the installation. Inspired by an article on Niva-Fak and tired of constant boiling, I broke my piggy bank and went to the local car market, where I purchased: 1. Electric valves 21214 2. Tee for a sensor from a GAZelle 3. Sensor TM-108 87-92 degrees 4. Relay 711.3747-01 5. Fuse 30A 6. VAZ-2101 heater control button 7. Rubber radiator pads from VAZ-2108 2 pcs. So, part one is installation. In the article at the link, the guy writes that he barely inserted the valves into the face, raised the steering wheel, tightened it, sawed it off and installed it - DON’T DO THIS!
The valves rest with their lower legs against the holes in the muzzle, and with the upper rubber bands they press the radius against the top of the muzzle, and that’s it. Nothing warps or rubs, everything works PERFECTLY. And the sides on the upper elastic bands hint to me personally that this is how it should be, there is no need to cram in what cannot be squeezed in. At the same time, they unscrewed the native Carlson so that it would not take away the power from the already shaky Pihl. Also in the process, the gene belt was replaced, because it was slightly worn. The threesome with the sensor was cut into the lower pipe, it didn’t go in without a curse, but it went in.
The photo is not so great, but the car looks clearly better
Part two - connection. The diagram in the article, unlike the instructions, is more clear. Everything was connected according to it, only the wires on the button were swapped: ground with any other.
Result: the scheme works, but they hum - mother, don’t worry. for some reason you immediately feel like you’re on a Junkers
The sensor turned out to be too hot - according to the display meter, it turns on when the needle has already crept well over 90. The voltage at 2000 rpm with the valves on drops to 13 volts
Features of electrical equipment
The standard wiring on the VAZ 21213 differed from the circuit used on the VAZ 2121. In particular:
- The fuse box on the VAZ 21213 uses more modern “knife” fuses, for which the contact pad is modified;
- The power system uses EPHH - forced idle economizer, for which there is a separate harness with a block in the engine compartment wiring;
- The ignition system uses a non-contact circuit built on a microcontroller.
Differences in the engine compartment
The EPHH control unit is located in the engine compartment and is a plastic box with a connector for connecting a wiring harness to it. Its purpose is to ensure stable engine operation when coasting, including fuel economy.
Self-diagnosis capability
To make it easier to determine engine failure, car owners use a search algorithm based on the car manufacturer’s recommendations.
The manufacturer recommends using it first, and only then resorting to the help of another car:
- Use of known good parts;
- Easy start (“lighting up”), etc.
Conclusions: self-service of a car has long become the norm for our car owners. Moreover, video manuals with explanations of the work have become more accessible today, allowing you to avoid mistakes when troubleshooting the electrical network.
Differences in electrical circuits
Depending on the car model, electrical circuits may differ.
Index designations
What does the index in the model name indicate:
- 21213. This is a car equipped with a carburetor power unit. Engine volume is 1.7 liters. Cars with this index can be equipped with a 1.8-liter internal combustion engine.
- 21214 and 212140. These models use the same engine with the same volume, but the vehicle is equipped with a fuel injection system.
- 21215. This model of domestic cars was developed for export; mainly such cars were sold abroad. Unlike vehicles produced for the CIS countries, 21215 were equipped with diesel engines from the manufacturer Citroen.
- 21073. The main difference is the presence of an injection engine with injectors, but the same model can be equipped with Solex carburetor units. The difference in the electrical circuit also lies in the use of BSZ - non-contact ignition.
- 2131 and 21310. These models can be equipped with different engines, but their main difference from other Nivs is their extended five-door body.
The Nivovodstvo channel in its video showed how you can add additional mass to the electrical network of a Niva car.
Main differences
What is the difference between the electrical circuits of the old and new models in the models:
- In Niva 21213, a mounting block of fuses is installed, which use devices on legs. The working area of the unit has changed.
- The difference lies in the presence of an idle speed saving mechanism that is equipped with the power system. For its normal functioning, an additional plug with wires is located in the engine compartment.
- Using a contactless ignition system. The microcontroller is considered an important component of the BSZ.
- Different car models are equipped with different generator devices, it all depends on the type of power unit.
- Model 21214 is equipped with two radiator cooling fans. Because of this, the electrical circuit also has differences.
Electrical wiring of VAZ 21213: differences in the engine compartment and the possibility of self-diagnosis
Like any other domestic car, the VAZ 21213 is in most cases serviced by the hands of its owner. This is the specificity and even the mentality of our car enthusiasts, who, in addition to tools, also require a technical description of the main components and assemblies.
And the detailed wiring diagram of the Niva VAZ 21213 is just one of them, since in harsh operating conditions it is often necessary to restore the car in field conditions, because:
- VAZ 21213 is an off-road vehicle;
- Used by owners away from service stations and workshops;
- The life and safety of people (the owner and his family members) living far from large cities often depends on its technical condition.
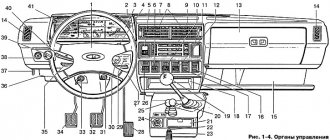
Dashboard
For subsequent modifications of the VAZ 2121, the instrument panel was thoroughly redesigned. In particular, the design and location of the warning lamps have changed, and new scales have appeared on the instrument panel indicators.
Conclusions: the owners of the VAZ 2121 car often serviced it themselves. And servicing electrical systems is impossible without original circuit diagrams. This was especially true for modernized versions, where changes were made to the operation scheme of components and assemblies.
Maintenance of wiring VAZ 21214 and other Niva models injector and carburetor: electrical diagram
Every modern car today is equipped with an electrical part. The electrical diagram of the VAZ 21214 Niva injector allows, if necessary, to find all the elements included in the on-board network, which is especially important when faults occur in the wiring. Everything a driver needs to know about electrics in domestic SUVs is described in this article.
Detailed electrical diagram of Niva
The wiring diagram may vary slightly depending on the design features of the vehicle.
First, let's look at the index notation:
- VAZ 21213. This index designates a vehicle equipped with a carburetor. The volume of the power unit is 1.7 liters.
- 21214. In VAZ 21214 cars, the scheme involves the use of a similar engine with the same volume. The only difference is that the car is equipped with a fuel injection system.
- There is another model with the index 21213. In VAZ 21213 cars, the electrical circuit includes the same elements, only depending on the year of manufacture, the car can be equipped with a 1.8 liter engine.
- Version 21073. The SUV is equipped with either an injection engine with nozzles or a Solex carburetor engine. One of the features of these cars is a contactless ignition circuit.
- 21215. These SUVs were originally produced for export, so these cars are difficult to find on our roads. It is worth noting that they were equipped with Citroen diesel engines.
At the beginning of the article there is a diagram of the VAZ electrical equipment using the example of the Niva 2121 model. If you are the owner of version 2131 or any other, then there will be a difference in the circuit diagram, but not fundamentally. If we are talking about carburetor engines, then in this case the battery charging circuit, as well as the ignition, will not be protected (video author - Nail Poroshin).
Features of electrical equipment
The electrical circuit of the VAZ model 21213 has certain differences with the model 2121, in particular:
- 21213 vehicles use more modernized foot fuses in the fuse box. Of course, the use of such devices led to the fact that the block site also became different.
- The power supply system of these vehicles additionally includes an idle speed saving device. For this option to work properly, another connector with wiring was added in the engine compartment.
- Another difference is that these cars use a non-contact ignition circuit, the main element of which is a microcontroller.
It should be noted that differences in the Niva circuit may lie both in the generator units and in the electrics themselves.
Differences in generators
In any case, the differences in the wiring diagram of the models will primarily depend on the power unit - carburetor or injection.
The main differences in carburetors:
- models 21213 use the generator unit model 371.3701;
- in the engines of models 21214, the manufacturer decided to install a more powerful generator device; it is marked with the numbers 9412.3701 (video author - Sergei Chekhonin).
And although these generators are different, they have certain similarities in design. In any case, it is a synchronous AC device. In addition, these units have a built-in rectifier and output voltage regulation mechanism.
Wiring differences
If we talk directly about wiring, then depending on the car model, it may also have differences. It should be noted that these differences greatly simplify do-it-yourself maintenance and repair of the system. As for injection modifications of SUVs specifically, in this case the system is equipped with three outputs intended for installing electronic ignition.
In addition, 21214 cars use two ventilating devices that perform the function of cooling the radiator assembly. Accordingly, due to the use of additional fans, the wiring also underwent, albeit not significant, differences. Of course, they are not fundamental.
We study the electrical wiring of the Niva car and learn how to service it
Many articles have been written about how functional the Niva car turned out to be. Moreover, this car is considered one of the best creations of the domestic automobile industry, so we could not ignore such an issue as its electrical circuit. You will learn more about the features of the electrical equipment of the VAZ 21214 Niva injector below.
Operating principle
The cooling system of VAZ Niva models does not come into contact with the atmosphere in operating condition, and therefore requires pressure. The coolant is antifreeze with a freezing point of 40 degrees Celsius. The composition of the solution is water and ethylene glycol. The total volume of the cooling circuit is 10.7 liters. Antifreeze can boil after a temperature of +110 degrees Celsius.
The main functional unit in the system is the thermostatic valve, which distributes the coolant flow depending on the engine temperature. The thermostat, controlled by a temperature-sensitive sensor, regulates the direction of movement of antifreeze. A simplified work flow looks like this:
In summer and during transition periods in models with an injector, the movement of the cooler is limited by a special tap. The Niva Chevrolet model does not have such a blocker, so the heating is turned off by directing the air flow past the heat exchanger.
About standard engine protection
The Niva is designed primarily for off-road driving or very bad roads. This leads to regular landings “on the belly”, hitting the ground and stones. The standard crankcase protection for Niva 21214 is a curved metal plate 2-3 mm thick. Several fins and holes are provided for additional engine cooling.
In reality, according to reviews from most drivers, when driving on real off-road or deep snow, the ventilation clogs instantly. If you do not clean it regularly, then after a while a dense layer of mud will form between the crankcase and the protection. It leads to additional heating of the engine. In addition, the factory protective plate will save the maximum from soft ground. It can only withstand a blow against a large stone.
Therefore, it is strongly recommended to replace the standard crankcase protection with a professional one from a store or make it yourself. Some models consist of one element, others - of two (1 plate for the engine, 2nd for the gearbox and underbody). There are three materials for making parts, each of which has its own characteristics:
- Iron or steel. Factory version of the tread, which actually does not fulfill its purpose during aggressive off-road driving. It is cheap, but is present under the crankcase purely nominally.
- Aluminum (duralumin). The plate is 4-5 mm thick, but at the same time significantly lighter than its iron counterpart. The material does not rust and is practically not subject to corrosion; it does an excellent job of cooling and protecting the engine. A significant disadvantage is that the cost is almost 2 times higher than factory models.
- Composite The material provides maximum “armor”, not much heavier than duralumin plates. The main problem is the price (the average price tag is 8,000 rubles).
Nuances of moving a generator
The disadvantage of domestic Niva SUVs is the location of the generator unit - at the bottom of the engine compartment. It constantly gets contaminated when driving off-road, and coolant constantly drips. The problem is solved by moving the generator upstairs (the author of the video is SARTANETS).
To transfer, you will need a set of keys, a bracket, mounting bolts, and a V-belt. You can make a generator transfer bracket with your own hands according to the drawing below.
Drawing of a homemade bracket
Sequence of actions during transfer:
- We dismantle the propeller, pump and remove the belt.
- By unscrewing the standard bracket, you can remove the generator.
- We cut off the bead around the side of the cylinder head and on the cylinder block.
- Then you should unscrew the two bolts and two studs.
- Next, the assembly is installed on a new bracket and final assembly is performed.
1. Schematic illustration of unscrewing the fastening material
2. Car with the belt removed
3. The unit is in a new location
Thus, moving the generator unit upstairs is not difficult.
How to replace fuses and relays of a VAZ-2121 car
Most of the vehicle's electrical circuits are protected by fuses. Electric motors of gear motors (windshield wipers, tailgate glass, headlights - if installed) are protected by automatic reusable bimetallic fuses.
The power supply circuit of the injection system (VAZ-21214 engine) is protected by a fuse-link made of wire with a conductor of reduced cross-section (1 mm 2 ). The battery charging, ignition (VAZ-21213 engine), engine starting, and the “generator – ignition switch – fuse box” circuits are not protected. Powerful consumers (starter, headlights, electric motors for cooling system fans, electric fuel pump, etc.) are connected via a relay. The fuses are grouped in two fuse blocks located on the left under the instrument panel. The fuse ratings and the circuits they protect are shown in the table. The injection system fuses (VAZ-21214 engine) are located in a separate block on the left side panel under the instrument panel. A 30 A fuse protects the power supply circuit for the electric radiator fans, and three 15 A fuses protect the electric fuel pump, the control unit (constant power input) and the injection system main relay circuits, respectively.
Circuits protected by fuses
Protected circuits (current)
Heater fan motor. Relay (winding) for headlight cleaners and electric motors for headlight cleaners in all brush positions except the initial one. Relay (coil) for turning on the heated glass of the tailgate. Electric motors for the tailgate glass cleaner and washer. Windshield washer motor
Windshield wiper relay and motor. Turn signal lamps and relay-interrupter for turn signals and hazard warning lights (in turn signal mode). Turn signal indicator lamp. Rear lights (reversing lamps). Generator field winding (when starting the engine) and battery charge indicator lamp*. Differential lock warning lamp. Relay breaker and warning lamp for the parking brake system. Warning lamp for insufficient brake fluid level. Oil pressure warning lamp. Coolant temperature gauge. Fuel level indicator with reserve indicator lamp. Tachometer 3 (8 A) Left headlight (high beam). High beam warning lamp
Right headlight (high beam)
Left headlight (low beam)
Right headlight (low beam)
Left front lamp (side light). Right rear light (side light). License plate lights. Side light warning lamp
Right front lamp (side light). Left rear light (side light). Instrument cluster lighting lamps. Illumination panel for heater control levers. Cigarette lighter lamps. Switch illumination lamps
Direction indicators and relay-interrupter for direction indicators and hazard warning lights in hazard warning mode. Rear window heating element and relay (contacts) for its activation
Sound signal. Plug socket for portable lamp. Interior lighting lamps. Tail lights (brake lights)
Rear lights (fog light). Electric motors of headlight cleaners at the moment of start-up and at the moments when the brushes pass the initial position. Relays (contacts) for headlight cleaners. Headlight washer motor
* On cars produced before 1996, a voltmeter was installed in the instrument cluster instead of a warning lamp, which was also protected by fuse No. 2.
Car diagrams
Share with friends: You may also be interested. The photo below shows the wiring diagram of a VAZ with a classic carburetor power unit. Only after this can you resort to the possibility of easier car starting
They are also characterized by the presence of a built-in rectifier, as well as an output voltage regulator, which is important. Spark plug. For example, in the case of a carburetor, the electrical circuit for charging the battery and ignition system is not protected, unlike injectors. Features of electrical equipment Differences in generators It was already mentioned that the VAZ wiring diagram had some differences, primarily associated with the installed power unit
It should also be noted that the versions are equipped with two fans designed to cool the radiator. When the engine is not running, all consumers are powered by the battery, and after the engine is started - by an alternating current generator with a built-in rectifier and electronic voltage regulator. Rear window washer motor. In particular, versions with fuel injection required a more powerful generator, therefore: A model generator was installed on the VAZ. The ignition system in these cars is contactless. In addition, if you want to improve your SUV, for example, by installing a modern audio system or changing the interior lighting, then it would also be useful to learn about the circuit designations. Before installing a new fuse to replace the blown one, find out and eliminate the cause of the blown.
The second version of the NIVA 21213 scheme
Lamp switches located in the door pillars. Three lever switch. Ignition switch.
The order of conditional numbering of plugs in the blocks: a - windshield wipers, headlights and tailgate glass, windshield wiper relay breaker; b — ignition distributor sensor; c — relay-interrupter for alarm and direction indicators; g - switch; d — three-lever switch; e — alarm switch; g — relay for turning on the rear fog light; h — rear lights numbering of terminals in order from top to bottom; and — instrument clusters. Carburetor solenoid valve. Three lever switch.
Switch for the carburetor choke warning lamp. As for the ignition system, it has become contactless. Front lights. The price of an SUV was higher than passenger models, but this did not stop buyers seeking freedom of movement. How to connect an alarm
Chevrolet Niva spare parts stores in Moscow
You can select the part you are interested in for Chevrolet NIVA Chevrolet NIVA cars and order and purchase spare parts in Moscow online, as well as install them in one of our service centers according to the standards of an official dealer
Specify the make, model and VIN number of the car for a more accurate selection of spare parts or select it from the garage.
Indicate the catalog numbers of spare parts or simply write down which spare parts you need in a list, and our specialist will select the correct numbers, check prices and availability.
Pay for your order online or in our offices upon receipt. Pick it up at a car dealership convenient for you in Moscow.
Heater fan for VAZ 2121
The interior of the VAZ 2121 Niva has never been called warm, especially in severe frosts. Many people fight this problem using various liquids for complete prevention of the entire heating system, while alcohol and glycerin are used in the liquid for a better effect. This is necessary because some parts on the Niva car are installed and designed very poorly. It is necessary to eliminate all cracks or gaps using sealant or foam rubber. The interior of a NIVA car must first of all be warm and not allow moisture to pass through, because the VAZ 2121 is a car for extreme conditions. You need to know how the nozzles are located, where the air comes from to the windshield. Some car enthusiasts plug up the air ducts that are used to blow the side windows. Naturally, one can argue with such an option, but sealing the air duct, which is installed in the middle of the entire dashboard, is a very bad idea. The air intake, which is installed on the front of the car, takes only 2/3 of the grille on the hood itself. In this case, the air flow is divided into two parts.
Only 1/3 of the flow passes into the smaller part, in the case where there is very little air resistance. As a result, only 1/3 of the grille needs to be sealed and this is done with tape. If possible, it is best to replace the standard fan with brass bearings with a fan with ball bearings. Such additional work will not have a strong effect on improving heat flow, but the noise level will still decrease. You also need to carefully inspect the entire coolant supply system. Sometimes you come across small faucets with a reduced flow area. Precipitates from low-quality coolant are created in the radiator and, as a result, air pockets are created. You should also check the thermostat.
Standard car insulation is unimpressive and many people remove it over time. All insulation can be re-done to a high standard. But, back to the topic of replacing the fan on a VAZ 2121. First you need to disconnect the battery ground. First you need to remove the panel that secures the radio, then you need to unscrew the nut that secures the breaker relay for the turn signals and hazard warning lights. Next, you need to remove the negative wire of the heater fan from the stud. On this pin you can find two more negative wires. We pull out the rod from under the spring clamp, which is located on the right side of the fan casing. Using a screwdriver, carefully disconnect the spring clips that secure the fan casing. Remove the casing, guide casing and the fan itself. You also need to disconnect all the fan wires from the additional resistor, after which we remove the fan from the casing. We carefully remove the rubber motor mountings and the lock washer to the side. We remove the fan impeller and at this stage the process of removing the heater fan on the VAZ 2121 can be considered complete. Reassemble and install the fan in reverse order. Many also recommend replacing the additional fan resistor. To do this, you need to disconnect the negative battery again, remove the fan direction casing, disconnect the wire tips from the terminals of the additional resistor, remove the two spring washers, pull out the resistor and replace it.
Features of replacing the ignition switch
First of all, it is important to make sure that the problem is in the lock. Therefore, the spark plugs, distributor and ignition coil are inspected.
Often these parts of the internal combustion engine become the reason for failures of correct operation. If breakdowns in them are excluded, then the ignition switch (IZ) should be replaced. Removal order:
- Disconnect battery.
- Remove the steering column.
- Mark the wires going to the 3Z contact area. Using a flat-head screwdriver, unscrew the bolts securing the switch to the steering column (left and right).
- Insert the key into position 0. By pressing the screwdriver, press the lock slightly through the hole (do not touch the key).
- Lightly pull the 3Z towards you and dismantle it. The ignition switch Niva 21213 is switched off according to the wiring diagram (the contact part is changed if required). To do this, be sure to remove the retaining ring with a screwdriver.
- Remove the key, install the contact part so that the wide protrusions of the body and the parts coincide.
- The remaining parts are assembled in the reverse order.
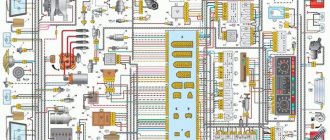
Engine control system VAZ-21214
Connection diagram of the VAZ-21214 engine management system with central fuel injection under US-83 toxicity standards with controller 21214-1411010 (EFI-4 type) on VAZ-21214 vehicles: 1 - “CHECK ENGINE” control lamp; 2 — instrument cluster (fragments); 3 — electric fans of the engine cooling system*; 4 — electric heater of the intake pipe; 5 — air temperature sensor; 6 — absolute pressure sensor; 7 — coolant temperature sensor; 8 — block connected to the throttle position sensor; 9 — central fuel injection unit; 10 — block connected to the idle speed regulator; 11 — block connected to the nozzle; 12 — diagnostic block; 13 - controller; 14 — knock sensor; 15 — speed sensor; 16 — oxygen concentration sensor; 17 - adsorber; 18 — battery; 19 - main relay; 20 — fuse block of the engine control system; 21 — relay for turning on the electric fuel pump; 22 — relay for turning on the electric fan*; 23 — relay for turning on the electric heater of the inlet pipe; 24 — electric heater protection fuse; 25 — starter activation relay; 26 — ignition relay; 27 — main car fuse box (fragment); 28 — spark plugs; 29 — tachometer; 30 — electric fuel pump with fuel level sensor; 31 — ignition module; 32 — crankshaft position sensor; 33 - courtesy light switch, located on the driver's door pillar; 34 — control unit of the automobile anti-theft system**; 35 — status indicator of the car anti-theft system**; A - wire going to plug “50” of the ignition switch; B - wire going to plug “15” of the ignition switch; B - wire going to terminal “30” of the generator; G - rear wiring harness wires connected to the fuel level indicator; D - rear wiring harness wire connected to switch 33.
The order of conditional numbering of plugs in the blocks: a - controller; b — control unit of the automobile anti-theft system; c — indicator of the state of the automobile anti-theft system; g — speed sensor; d — central fuel injection unit; e — electric fuel pump and oxygen concentration sensor; g — ignition module; h - absolute pressure sensor.
Connection diagram of the VAZ-21214 engine management system with distributed fuel injection under Euro-2 toxicity standards with controller 2123-1411020-10 (type MP 7.0) on VAZ-21214 vehicles: 1 - control lamp of the engine management system; 2 — instrument cluster (fragments); 3 — electric fans of the engine cooling system; 4 — courtesy light switch, located on the driver’s door pillar; 5 — status indicator of the car anti-theft system; 6 — control unit of the automobile anti-theft system; 7-coolant temperature sensor; 8 — air flow sensor; 9 — throttle assembly; 10 — block connected to the throttle position sensor; 11 — block connected to the idle speed regulator; 12 - controller; 13 — oxygen concentration sensor; 14 — knock sensor; 15 — crankshaft position sensor; 16 — speed sensor; 17 - adsorber; 18 — battery; 19 - main relay; 20 — diagnostic block; 21 — fuse block of the engine control system; 22 — relay for turning on the electric fuel pump; 23 — relay for turning on electric fans; 24 — main car fuse box (fragment); 25 — block connected to the additional wiring harness*; 26 — ignition module; 27 - tachometer; 28 — electric fuel pump with fuel level sensor; 29 — nozzles; 30 — spark plugs; A - rear wiring harness wire connected to switch 4; B - wires connected to plug “1” of fuse block 24 (one wire goes to plug “15” of the ignition switch, and the other to plug “85” of the ignition relay); B - rear wiring harness wires connected to the fuel level indicator.
The order of conditional numbering of plugs in the blocks: a - controller; b — control unit of the automobile anti-theft system; c – air flow sensor; g — speed sensor; d — indicator of the state of the automobile anti-theft system; e — electric fuel pump and oxygen concentration sensor; g - throttle pipe; h — ignition module.
Download all schemes in high quality, you need to log in to the site
Let us remind you that you will find detailed instructions for repairing the Niva SUV in this section.
Schemes on Niva with injection engine
The fundamental difference between a carburetor electrical circuit and an injection circuit is the use of an improved power unit control system.
Diagram of the engine control system of the injection Niva
Let's look at the interactive diagram of the EMS injector with 8 valves:
- Adsorber purge device.
- Throttle mechanism.
- A controller that determines the temperature regime of the engine; its readings are based on the temperature of the coolant in the cooling system.
- Radiator ventilator located to the right of the engine.
- The same fan, only installed to the left of the power unit.
- The ignition system coil is located in the engine compartment.
- Spark plugs with connected high-voltage wires.
- Air flow controller supplied to form the combustible mixture.
- Crankshaft position controller. If it fails, the engine will not start.
- Wiring harness connected to the oxygen concentration controller.
- Oxygen control controller.
- Camshaft timing regulator or camshaft sensor.
- Knock controller. Affects idle speed.
- Harness connected to the injector connection wiring.
- Directly the system injectors themselves.
- Designation of the gas pedal located in the cabin.
- A harness with wiring connected to the control panel.
- Main relay.
- Protective element of the right ventilation device.
- A similar component protects the left fan circuit.
- A relay that ensures the operating condition of the fuel pump circuit. If it breaks, the pumping device will not be able to operate, making it impossible to start the engine.
- Safety element responsible for the pump.
- Connector to which the fuel pump in the module is connected.
- Diagnostic connector is used to troubleshoot various vehicle systems.
- Plug connecting electrical wiring to ground.
- Mounting block with safety elements that ensure the operating condition of the power unit control system.
- The connector to which the electrical wiring of the APS operating status indicator lamp is connected.
- Connector with connected wiring of the communication coil of the same system.
- The control module of the car alarm, with its help the anti-theft device is configured.
- A connector with a connected wiring block coming from the diagnostic oxygen concentration controller.
- Diagnostic controller.
- Central motor control module. These car models use Bosch 17.9.7 ECUs.
There is also a symbol A in the diagram - in this place the wiring harness passes from the engine compartment into the car interior.