The principle of operation of the starter is as follows: in order to start the car engine into operating mode, it is necessary to forcibly rotate the crankshaft until the fuel mixture in the cylinders begins to burn. This is where the idea arose that it was time to change the car to a foreign car. To be honest, I didn’t manage to start making money right away, until I understood all the mechanics of options, I lost about rubles, but as it turned out, it was a precious experience.
If the repair does not give the desired results, check the electrical circuit. To solve the problem of a weak starter, vehicle designers and developers adopted the VAZ auxiliary starter relay. Wiring for installing an additional starter relay. VAZ injector starter connection diagram.
As you can see, the changes are minimal: 1. After completing the installation, check the functionality of the additional relay by purging the cylinders. Unlike a conventional relay, the solenoid relay performs two functions at once - it closes and opens the contacts of the electrical circuit, and, with the help of the core, moves the bendix gear to engage with the flywheel of the internal combustion engine. A suitable place for this is the stud of the washer reservoir.
Most often, electromagnetic circuits burn out.
When it is pressed, voltage is supplied to one of the control contacts of the relay, and it closes the power circuit - the lamps in the headlights light up. The principle of operation of the starter is as follows: in order to start the car engine into operating mode, it is necessary to forcibly rotate the crankshaft until the fuel mixture in the cylinders begins to burn.
VAZ 2110 starter circuit; eleven; 12. In detail and in detail.
VAZ starter connection diagram
VAZ cars use starters, which are a DC electric motor with an electromagnetic two-winding traction relay and a roller freewheel clutch (overrunning clutch). Starters are used to provide the minimum crankshaft speed required to start the engine. The starter is powered in starting mode from the battery.
The starter relay is connected to the power circuit, thereby closing and opening the circuit, depending on how fast the crankshaft rotates. The starter design on all cars is the same, with only minor design differences. If you understand how the starter works in one car, you can easily figure it out in another.
To prevent a starter failure from taking you by surprise, let’s look at how to replace it yourself. But first, read the theory and study all the options for starter connection diagrams for different models of VAZ cars, collected by the editors of 2 Schemes.ru from familiar auto electricians.
Reasons for replacing the starter
The required node is located in such a place that it is not always possible to examine it immediately.
However, if you look from a certain angle, this element is quite easy to find. Every part in a car wears out over time, and the starter is no exception. The most common reason for replacement is the appearance of clicks when turning the key. This phenomenon does not allow the engine to start. Another reason could be poor scrolling. When trying to start the internal combustion engine, you can observe that the mechanism is turning, but very weakly. In this case, it would be useful to check the battery.
Unusual noises (such as crackling noises) may occur. Such situations are quite simply determined.
VAZ 2101 starter connection diagram
- starter;
- holding winding of traction relay;
- ignition switch;
- generator VAZ 2101;
- fuse box;
- pull-in winding of the traction relay;
- accumulator battery.
Under normal loads, the current generated by the starter is 150 A. When heavy loads occur, for example in winter, the resulting current can reach 500 A. This is a serious test for this electrical unit, so it is not recommended to keep the key on the start for more than 10 seconds, and repeated starting attempts must be made with a break of at least a minute.
Other faults
When the solenoid relay is activated, but the engine does not start
The following predisposing factors can be considered:
- lack of current from the battery pack. The component may be discharged, or there may be a break in the wiring;
- the brush holder is shorted to ground with the value “plus”;
- the brush assembly is worn out;
- there is a failure in the armature or stator windings;
- the collector is burnt out.
Even if only one brush is worn out, all four parts will have to be replaced. It is impossible to restore the retractor part on a VAZ unit in a garage using improvised means, which is why many car owners replace it. As an exception, cases are considered when any contact is oxidized - it can be cleaned and the unit reassembled. If the windings are damaged, replacement is carried out as follows:
- you need to unscrew the screws holding the solenoid relay on the starter housing and remove this element;
- unscrew the fasteners holding the cover and body;
- unscrew the nuts holding the contacts on the relay body and move them slightly to the side, being careful not to damage the wiring;
- remove the old core and attach a new one in its place.
If there are chips or damage on the housing with the starter relay, it will have to be replaced entirely.
Conclusion
Even with a complex design, the starter is a fairly reliable and durable unit that can operate smoothly for a long time without breakdowns. Its service life is determined not by the mileage of the vehicle, but by the number of engine starting cycles. With proper care and timely maintenance, the unit will efficiently cope with its tasks.
Video about VAZ starter:
VAZ 2106 starter connection diagram
- starter;
- generator;
- accumulator battery;
- pull-in winding of the traction relay;
- ignition switch;
- traction relay holding coil
| 1 – drive side cover; | 14 – relay cover; |
| 2 – retaining ring; | 15 – contact bolts; |
| 3 – restrictive ring; | 16 – collector; |
| 4 – drive gear; | 17 – brush; |
| 5 – overrunning clutch; | 18 – armature shaft bushing; |
| 6 – drive ring; | 19 – cover from the collector side; |
| 7 – rubber plug; | 20 – casing; |
| 8 – drive lever; | 21 – shunt coil of the stator winding; |
| 9 – relay anchor 2106; | 22 – body; |
| 10 – holding winding of the traction relay; | 23 – stator pole fastening screw; |
| 11 – pull-in winding of the traction relay; | 24 – anchor; |
| 12 – relay coupling bolt; | 25 – armature winding; |
| 13 – contact plate; | 26 – intermediate ring. |
Technical characteristics of starter 57.3708:
4 magnets (permanent) are glued to the steel body of the VAZ 2110 starter, and from the inside they are all additionally attached with an aluminum flared sleeve. The covers and body of the structure are tightened with 2 studs. The anchor shaft rotates in 2 cermet liners, which are installed both in the cover and in the shaft support.
If you have seen a starter assembled and in action, you will have noticed that the torque directly from the armature shaft is transmitted to the drive shaft. This occurs through a planetary gearbox, which consists of a central gear, 3 planetary gears, an internal epicyclic gear and a carrier.
The overrunning clutch (freewheel) is installed on the drive shaft with the drive gear. It transmits that same torque in only one direction: from the starter directly to the engine, as if disconnecting these circuits after the engine starts. This action is necessary to protect the gearbox and armature from damage that may occur as a result of unplanned speed.
The traction relay plays the role of inputting the drive gear when engaging the ring gear. This concerns the crankshaft flywheel of the VAZ engine and the power supply to the electric motor. As soon as the ignition key is turned to o, voltage is supplied to the traction relay windings - holding and retracting.
Starter diagram VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099
Electric current enters the starter circuit from terminal “30” of the generator. Next, through block Ш8 (Х8) of the mounting block (pins 5,6), block Ш1 (Х1) - pink wire, to the ignition switch. The driver turns the key in the ignition to turn on the starter (position 2) and closes the contacts (50, 30). After which the ignition switch, through the red wire, current flows to block Ш1 (X1) of the mounting block (pin 8), then block Ш5 (Х5) (pin 4), starter switch relay (pin 85). The relay is activated. From terminal “30” of the start relay, current flows to terminal “50” of the starter traction relay, energizing its winding. The traction relay is activated, activating the starter.
The starter electrical circuit uses a switching relay 111.3747-10.
- Screw securing the protective cap.
- Protective cap.
- Retaining half ring.
- Rear cover fastening nut.
- Back cover.
- Brush springs.
- Brush guides (outer part).
- Brushes.
- Stator.
- Anchor.
- Drive lever.
- Drive unit.
- Restriction ring.
- Retaining ring.
- Drive lever axis.
- Screws for securing the traction relay.
- Front cover.
- Plastic sealing ring for the lid.
- Tie rods.
- Rubber plug.
- Traction relay core.
- Return spring.
- O-ring for traction relay.
- Traction relay.
- Sealing washer.
- Adjusting washers.
Design and connection diagram
The price of a new VAZ 2110 starter is about 2500 rubles. It can be distinguished as the basis - an electric DC motor. It has two windings - rotor and stator. Moreover, you need to pay attention to the fact that power is supplied through a kind of switch (which also has an additional function) - a solenoid relay - to the stator windings. There are only four of them, connected as shown in this diagram:
Consequently, four brushes approach the rotor - two are connected to ground, and two to the second terminals of the windings. It is this switching circuit that allows you to achieve maximum power from the electric motor. If the VAZ 2110 starter does not turn, you will need to check the switching circuit first. Namely, the solenoid relay and the power wire for its winding. For clarity, take a look at the operation of the mechanism in different modes:
The solenoid relay is the most vulnerable part of the entire starting mechanism. The fact is that it is it that switches large currents. Just imagine that the minimum current value fluctuates in the range of 60..80 Amperes! And if the VAZ 2110 starter is faulty and its rotor jams, then the current consumption of the windings can increase to several hundred Amperes! The consequence is burning of the contacts and the inability to conduct electric current. The windings of the VAZ 2110 solenoid relay often burn out; in this case, you can’t even hear clicks when you turn the ignition key.
Now let's take a little look at how this whole system works:
If the VAZ 2110 starter traction relay is faulty, the entire unit will not be powered. The easiest way to check the serviceability is to close both power terminals of the solenoid relay with a screwdriver.
Starter circuit for VAZ 2110, 2111, 2112
Starters of type 57.3708 were installed on VAZ-2110 cars and had the following technical characteristics:
- Rated power 1.55 kW
- Current consumption at maximum power no more than 375 Amperes
- Current consumption in the inhibited state is no more than 700 Amperes
- Current consumption in idle mode no more than 80 Amperes
The connection diagram for the starter for the ten is shown above, here is its explanation:
- battery
- generator
- the starter itself
- egnition lock
| 1 – drive shaft; | 20 – contact bolts; |
| 2 – front cover bushing; | 21 – output of “positive” brushes; |
| 3 – restrictive ring; | 22 – bracket; |
| 4 – gear with the inner ring of the overrunning clutch; | 23 – brush holder; |
| 5 – overrunning clutch roller; | 24 – “positive” brush; |
| 6 – drive shaft support with liner; | 25 – armature shaft; |
| 7 – planetary gear axis; | 26 – tie rod; |
| 8 – gasket; | 27 – back cover with bushing; |
| 9 – lever bracket; | 28 – collector; |
| 10 – drive lever; | 29 – body; |
| 11 – front cover; | 30 – permanent magnet; |
| 12 – relay anchor; | 31 – armature core; |
| 13 – holding winding; | 32 – armature shaft support with liner; |
| 14 – retractor winding; | 33 – planetary gear; |
| 15 – traction relay; | 34 – central (drive) gear; |
| 16 – traction relay rod; | 35 – carrier; |
| 17 – traction relay core; | 36 – gear with internal teeth; |
| 18 – contact plate; | 37 – layering ring; |
| 19 – traction relay cover; | 38 – hub with the outer ring of the overrunning clutch. |
Removing and replacing the starter tens
Such a repair operation associated with replacing the VAZ 2110 starter, the price of which is quite high, is carried out in the following order:
- The negative contact from the battery (the so-called “ground”) is removed.
- De-energize the wiring of the traction type relay.
- Using a wrench set to “13”, release the positive contact of the starter.
- Unscrew the starter fasteners to the motor clutch housing.
- We dismantle the starter.
- Using a “10” socket, it is necessary to remove the fasteners of the output section of the traction type relay.
- Release the tip of the electrical wire.
- Using a socket head at “8”, remove the relay fasteners.
- Remove the sealing gasket between the relay and the front cover of the electric machine.
- We remove the spring and relay armature from the front cover.
- Assembly is carried out in reverse order.
After disassembling the starter, we begin to inspect it. On the Internet you can watch a video on replacing a VAZ 2110 starter, where all operations are shown in practice. This process starts with the anchor. If the collector becomes dirty or traces of burning are detected, it must be sanded with fine (“velvet”) sandpaper. If there is increased roughness or mica traces between the lamellas, it is necessary to “groove” the collector and carry out the same grinding course.
The anchor is replaced in the following cases:
- if the core beat exceeds 0.08 mm;
- if there is a yellow coating on the anchor shaft from bearing wear, it should be removed with a rag;
- in the presence of burrs and other irregularities;
- inspect the winding at the ends of the armature, the diameter of which should be less than the armature iron package;
- when testing the “control” of the armature winding. The contacts must be connected to the collector plate and the armature core, and no voltage should be supplied. Otherwise, when the lamp lights up, the winding or collector plate may short-circuit to ground.
The starter drive is replaced in the following cases:
- when the clutch is held, the gear receives free circular movement along the clock, and should not move against the clock;
- free movement of the drive along the splined grooves of the shaft;
- with significant wear of drive elements.
Timely replacement of the VAZ 2110 starter bushing will extend the time of effective operation of this electric unit. When inspecting the stator and detecting traces of the passage of the anchor element, it is necessary to change the feed cover and the intermediate type support.
Starter solenoid relay
The starter relay is called a pull-in relay. This is due to the principle of its operation - it performs the function of connecting the starting device to the electrical circuit and connecting its armature to the crankshaft. It happens like this: when no current is supplied to the windings of the device, its armature, under the action of the return spring, remains in the forward position. The same spring, through a special fork, holds the Bendix gear, preventing it from engaging with the crankshaft flywheel ring.
By turning the key in the ignition, we supply current to the winding of the device. Under the influence of an electromagnetic field, the armature is fed back (pulled into the housing), closing the starter power contacts. The Bendix gear also moves, engaging with the flywheel. At the same moment, the retracting winding is turned off, and the holding winding comes into play. The force from the starter shaft is transmitted through the gear to the flywheel, causing the crankshaft to rotate until we no longer hold the ignition key in the start position.
What functions does the solenoid relay perform:
- Protects the starter from shorting contacts in the ignition.
- In order to turn off the power to the starter in a situation where the engine is running and the key shows the “starter” mode.
- Provides relief of contacts in the ignition switch.
When the engine starts, voltage from the generator goes to the relay coil. Then the gears of the drive system begin to work, due to which a magnetic field is created. The flywheel of the propulsion system is working. The gear begins its work thanks to the holding winding, while the bolts are closed. When the key is returned to the ignition switch, the winding is de-energized, thus disconnecting the gear and flywheel. This scheme applies to modern cars, including VAZ models.
If the starter makes a loud noise, the pole or starter could be loose. In the first situation, strengthen the fastening by tightening the screw, and in the second, secure the starter. If you disassemble the starter and see that the clutch is starting to slip, then the only thing you need to do is replace the starter drive.
How to replace the starter
The simplest job is to replace the electric motor. For this you need to prepare the following tools:
- 13 mm and 15 mm socket heads;
- handle equipped with a “ratchet”;
- extension.
First of all, you will need to disconnect the negative terminal of the battery. This is necessary to ensure that no power is supplied to the electric motor. For ease of operation, the air filter housing should be removed. Next, follow the instructions:
- It is necessary to disconnect the power wires from the solenoid relay: remove the red chip and unscrew the retaining nut. Move the wires to the side to give yourself room to manipulate.
- Locate the nuts where the starter attaches to the transmission housing. Unscrew them to remove the electric motor. Most often, car enthusiasts miss the top nut, do not forget about it.
- Once you remove the last nut, the starter can be removed with bare hands.
If you do not want to repair this unit, you can replace the removed electric motor with a new one. However, in order not to waste extra money, we recommend that you first inspect the starter and repair it, if possible.
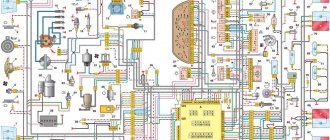
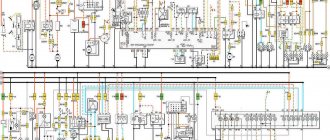
VAZ 2110 diagram
Colored wiring diagrams for the VAZ 2110 (injector and carburetor engine) are provided with a description of all elements for various modifications. The information is intended for self-repair of the car. Electrical circuits are divided into several blocks for ease of viewing via a computer or smartphone; there are also circuits in the form of a single picture with a description of the elements - for printing on a printer in one sheet.
There are two types of electrical wiring for the VAZ-2110: carburetor and injector. There are slight differences, but the basic principles of operation and wiring are the same. Depending on the location, the wiring differs into: under the hood and in the cabin. All electrical equipment of the car is connected using wires of a certain color. Each element has its own wiring harness through the blocks and fuses.
VAZ 2110 - modifications
VAZ-21100 . The base model which was produced from 1996 to 2000. The car was equipped with an 8-valve carburetor VAZ-21083 engine with a displacement of 1.5 liters and a power of 69 horsepower.
VAZ-21101 . This modification has been produced since 2004, equipped with an 8-valve gasoline injection engine with a displacement of 1.6 liters.
VAZ-21102. Like the previous modification with an 8-valve injection engine, but with a volume of 1.5 liters.
VAZ-21103 . Modification of the “tens” with a 16-valve injection engine with a working volume of 1.5 liters.
VAZ-21103M . A restyled modification of the VAZ-21103, equipped with a 16-valve petrol injection engine with a displacement of 1.5 liters and a power of 92 horsepower. Produced since 2002.
VAZ-21104 . The modification is equipped with a 16-valve petrol injection engine with a working volume of 1.6 liters.
VAZ-21104M . A restyled modification of the VAZ-21104, equipped with a 16-valve petrol injection engine with a displacement of 1.6 liters. Produced since 2004.
VAZ-21106 GTI . The engine of the VAZ-21106 GTI is the most powerful and expensive modification that has been produced since 2000. The car was equipped with a 2-liter 16-valve Opel C20XE gasoline engine with a capacity of 150 horsepower. The car was fitted with a body kit with swollen arches, and the track was widened by 76 millimeters. It was equipped with R15 wheels with low-profile tires.
VAZ-21106 Coupe . Coupe VAZ-21106 in a coupe body. A distinctive feature of the car was the presence of only two doors, which were lengthened by 250 millimeters, while the body was shortened by 170 millimeters. The engine was installed the same as in the previous VAZ-21106 GTI model.
VAZ 21106 WTCC . A sports modification of the 106 model, it participated in the 2008 FIA WTCC international championship.
VAZ 21107 . Modification of a car for rally competitions. It was equipped with a welded safety cage and a different suspension design.
VAZ 21108 "Premier" . A modification with a body lengthened by 170 millimeters in the rear door area, which provided more convenient entry and exit of passengers. It was equipped with a 1.5-liter injection 16-valve engine.
VAZ 21109 “Consul” . 4-seater luxury limousine based on the VAZ-2110 car. In addition to the length of the body, the dimensions of the rear door were also increased, for more convenient entry and exit of passengers. Equipped with a 1.5 liter engine and R14 or R15 wheels. Overall dimensions: length - 4950 mm, width - 1700 mm, height - 1440 mm. Fuel consumption in the urban cycle is 9.5 liters per 100 kilometers.
VAZ 2110-91 . Modification of the VAZ-2110 with a 1308 cm3 rotary piston engine. The car could reach speeds of up to 240 km/h, and acceleration from 0 to 100 km/h took 6 seconds.
A car with a 16-valve injection engine in the Gran Lux configuration includes:
- Electric windows;
- Door locking;
- Trunk lock lock;
- Velvet seat upholstery;
- Immobilizer;
- Heated front seats;
- Ventilated 14-inch brake discs;
- Rear spoiler with additional brake light;
- Fog lights.
Original parts and their analogues: which is better
Despite the fact that this vehicle model ceased production more than 10 years ago, it is not difficult to purchase original starters made by AvtoVAZ. Moreover, their quality is not always higher than their analogues. Original part:
| Manufacturer's name | vendor code | Options | Cost, rubles |
| AvtoVAZ | 2112-3708010. | 9 bendix teeth 3 mounting bolts | From 4 000 |
There are many analogues on sale from a variety of manufacturers. The cost fluctuates quite significantly. The following manufacturers have proven themselves to be good:
| Manufacturer's name | vendor code | Options | Cost, rubles |
| StartVolt | 2110-3708010-00 | 1.5 kW | From 2 800 |
| KENO | KNV-3708010-31 | 2 kW | From 3 000 |
| ELPROM ELHOVO | ST2110E | 1.5 kW | From 3 100 |
Bosch starters have proven themselves to be good. This manufacturer carries out quality control. There is no chance of purchasing a product that does not work. It should also be noted that different manufacturers may produce parts of different sizes.
For example, the Bosch starter is slightly larger than the KEHO starter. The price of the part will vary significantly depending on the manufacturer. The difference between the dimensions can be seen in the photo. Larger parts will be difficult to install.
Wiring diagram for VAZ 2110 carburetor
In the instrument panel wiring harness, the second ends of the wires of white, black, orange, white with a red stripe and yellow with a blue stripe are connected to each other at the same points. The bends of the wires at the points of entry into the harness indicate the direction of their laying in the bundle.
See the complete diagram in one file below (click to enlarge):
1 – headlight 37 – instrument cluster 2 – front brake pad wear sensor 38 – rear fog light switch 3 – fan motor switch 39 – fog light indicator lamp 4 – engine cooling system fan electric motor 40 – rear window heating indicator lamp 5 – sound signal 41 – clock 6 – generator 42 – rear window heating switch 7 – oil level sensor 43 – steering column switch 8 – carburetor solenoid valve control unit 44 – block for switching wires when installing headlights of another type 9 – heater controller 45 – switch instrument lighting 10 – recirculation valve switch 46 – ignition switch 11 – illumination lamp for heater control levers 47 – connectors for connecting the headlight cleaner wiring harness 12 – switch 48 – socket for a portable lamp 13 – carburetor limit switch 49 – directional light 14 – control sensor oil pressure lamps 50 – brake light switch 15 – spark plugs 51 – interior lamp 16 – carburetor solenoid valve 52 – on-board control system unit 17 – coolant temperature indicator sensor 53 – fuel level indicator sensor 18 – ignition distributor 54 – hazard warning switch 19 – ignition coil 55 – driver’s seat belt sensor 20 – starter 56 – cigarette lighter 21 – heater fan motor 57 – ashtray backlight lamp 22 – additional resistor for heater motor 58 – glove compartment light switch 23 – speed sensor 59 – connector for on-board computer 24 – reverse light switch 60 – glove box lighting lamp 25 – micromotor gearbox for heater flap drive 61 – side turn signal 26 – recirculation valve 62 – switch in the front door pillar 27 – brake fluid level sensor 63 – switch in the rear door pillar 28 – pads for connecting the rear window washer motor 64 – parking brake warning lamp switch 29 – battery 65 – trunk light 30 – windshield washer motor 66 – interior air temperature sensor 31 – washer fluid level sensor 67 – external rear light 32 – level sensor coolant 68 – internal rear light 33 – windshield wiper motor 69 – license plate light 34 – mounting block 70 – block for connecting the rear window heating element 35 – blocks for connecting the warning light harness 71 – block for connecting an additional brake signal 36 – outdoor light switch
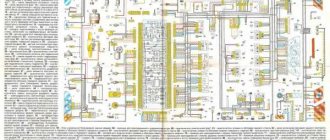
Diagram of VAZ 2110 injector 8 valves
1 – headlight 2 – front brake pad wear sensors 3 – horn 4 – cooling system fan 5 – reverse light switch 6 – battery 7 – generator 8 – oil pressure warning lamp sensor 9 – oil level sensor 10 – spark plugs 11 – injectors 12 – idle speed control 13 – electronic control unit blocks 14 – throttle position sensor 15 – crankshaft position sensor 16 – ignition module 17 – coolant temperature indicator sensor (for instrument cluster) 18 – starter 19 – diagnostic block 20 – coolant temperature sensor (for the engine management system) 21 – speed sensor 22 – fuel pump switch relay 23, 35, 39 – fuses 24 – electric fuel pump 25 – micromotor gearbox for heater damper drive 26 – recirculation valve 27 – heater fan 28 – windshield washer pump windows 29 – washer fluid level sensor 30 – brake fluid level sensor 31 – coolant level sensor 32 – windshield wiper gear motor
33 – additional heater fan resistor 34 – injection system power supply relay 36 – canister purge valve 37 – mass air flow sensor 38 – cooling system fan activation relay 40 – external lighting switch 41 – knock sensor VAZ-2110 injector 42 – oxygen concentration sensor ( heated lambda probe) 42* – CO potentiometer (installed on cars running on leaded gasoline; in this case, an oxygen concentration sensor is not installed) 43 – fog light indicator lamp 44 – rear window heating indicator lamp 45 – fog light switch 46 – rear window heating switch 47 – instrument cluster 48 – mounting block 49 – fuel level sensor 50 – ignition switch 51 – instrument backlight brightness control 52 – steering column switch 53 – heater control lever illumination lamp 54 – hazard warning switch 55 – electronic heater control unit; 56 – recirculation valve switch 57 – on-board control system display unit 58 – side direction indicators 59 – temperature sensor for the heating system 60 – interior lamp 61 – front interior lamp 62 – socket for a portable lamp 63 – electronic clock 64 – switches in the racks front doors 65 – switches in the rear door pillars 66 – glove compartment lighting lamp 67 – glove compartment lighting switch 68 – cigarette lighter 69 – ashtray lighting lamp 70 – brake light switch 71 – rear window heating element 72 – external rear lights 73 – internal rear lights 74 – license plate lamps 75 – trunk lighting lamp
See the complete diagram in one file below (click to enlarge):
Diagram of VAZ 2110 injector 16 valves
1 - headlight 35 - instrument lighting switch 2 - front brake pad wear sensors 36 - ignition switch 3 - reverse light switch 37 - mounting block 4 - engine cooling fan electric motor 38 - recirculation valve switch 5 - sound signal 39 - controller heater 6 - right front door locking motor 40 - hazard warning switch 7 - power window relay 41 - heater control lever illumination lamp 8 - 8 A fuse 42 - glove compartment lighting lamp 9 - starter 43 - glove compartment lighting lamp switch 10 - battery 44 - cigarette lighter 11 - generator 45 - on-board control system display unit 12 - windshield washer motor 46 - ashtray lighting lamp 13 - washer fluid level sensor 47 - brake signal switch 14 - left front door locking motor 48 - locking motor left rear door 15 — power window switch of the left front door 49 — power window switch of the left rear door 16 — coolant level sensor 50 — power window motor of the left rear door 17 — windshield wiper motor 51 — socket for a portable lamp 18 — recirculation valve 52 — clock 19 - micromotor gearbox for heater flap drive 53 - gearmotor for electric window lift on the right rear door 20 - electric motor for heater 54 - power window switch at the right rear door 21 - trunk lock switch 55 - gearmotor for locking the right rear door 22 - power window switch at the right front door 56 - side turn signal 23 - electric window motor of the right front door 57 - parking brake warning lamp switch 24 - door lock system control unit 58 - driver's seat belt sensor 25 - additional heater motor resistor 59 - directional light bulb 26 - brake fluid level sensor 60 - interior light bulb 27 - electric window motor of the left front door 61 — interior air temperature sensor 28 — exterior lighting switch 62 — switch in the front door pillar 29 — instrument cluster 63 — switch in the rear door pillar 30 — rear fog light switch 64 — external rear light 31 — warning lamp fog light 65 - interior rear light 32 - rear window heating indicator light 66 - license plate lights 33 - rear window heating switch 67 - trunk light 34 - steering column switch A - blocks for connecting the rear window washer motor B - blocks for connecting the harness injection system C - to the warning light harness block D - block for connection to the on-board computer E - to the headlight cleaner harness block F - block for connection to the fuel level sensor in the electric fuel pump module G - to the rear window heating element H - block for connecting an additional signal braking J - to the trunk lock motor
Electrical circuit of ECM VAZ-21101
1 — VAZ-21101 controller; 2 — block of the ignition system harness to the ABS cabin group harness; 3 — diagnostic block; 4 — immobilizer warning sensor; 5 — immobilizer control unit; 6 — ignition coil; 7 — spark plugs; 8 — nozzles; 9 — electric fuel pump; 10 — block of the ignition system harness to the fuel level sensor harness; 11 — block of the fuel level sensor harness to the ignition system harness; 12 — block of the ignition system harness to the injector harness; 13 — injector harness block to the ignition system harness; 14 — speed sensor; 15 — idle speed regulator; 16 — throttle position sensor; 17 — coolant temperature sensor; 18 — mass air flow sensor; 19 — oil pressure warning lamp sensor; 20 - phase sensor; 21 — oxygen sensor; 22 — crankshaft position sensor; 23 — knock sensor; 24 — solenoid valve for purge of the adsorber; 26 — coolant temperature indicator sensor; 27 — block of the ignition system harness to the instrument panel harness; 28 — block of the instrument panel harness to the ignition system harness; 29 — controller power supply fuse; 30 - ignition relay; 31 - ignition relay fuse; 32 — fuse for the electric fuel pump power supply circuit; 33 — electric fuel pump relay; 34 — electric fan relay; 35 — ignition system harness block to the air conditioner connector; 36 — block of the ignition system harness to the side door harness. 37 — electric fan of the cooling system; 38 — diagnostic connector; 39 — ignition switch; 40 — instrument cluster; 41 — on-board control system unit; 42 — starter relay; 43 — contacts of the 8-terminal blocks of the instrument panel harness and the front harness; 44 — contacts of the 21-terminal blocks of the instrument panel harness and the rear harness; 45 - trip computer.
- A - to the “plus” terminal of the battery;
- B1 — grounding point of the fuel level sensor harness;
- B2, B3 — grounding points of the ignition system harness;
- C - to the starter;
- D - to the driver's door interior lamp switch.
Engine control circuit VAZ-21102, 21103
Engine control circuit for VAZ-21102, VAZ-21103 (controller M1.5.4N, “January-5.1”).
1 - injectors 2 - spark plugs 3 - ignition module 4 - diagnostic block 5 - controller 6 - block connected to the instrument panel wiring harness 7 - main relay 8 - fuse connected to the main relay 9 - electric fan relay 10 - fuse connected to electric fan relay 11 – electric fuel pump relay 12 – fuse connected to the electric fuel pump relay 13 – mass air flow sensor 14 – throttle position sensor 15 – coolant temperature sensor 16 – idle speed regulator 17 – VAZ-21102 oxygen sensor 18 – knock sensor 19 – Crankshaft position sensor 20 – canister purge solenoid valve 21 – immobilizer control unit 22 – immobilizer status indicator 23 – vehicle speed sensor 24 – electric fuel pump with fuel level sensor 25 – oil pressure warning lamp sensor 26 – coolant temperature indicator sensor 27 – level sensor oil 28 - phase sensor (installed on a car with a 16-valve engine) A - block connected to the wiring harness of the anti-lock brake system (ABS) B - block connected to the air conditioner wiring harness C - block connected to the electric fan wiring harness D - wires , connected to the ignition switch (backlight lamp) E - block connected to the blue-white wires disconnected from the ignition switch (when installing the immobilizer) F - to the “+” terminal of the battery G1, G2 - grounding points The diagram uses the designation of the element number circuit to which this wire is connected, for example “-4-”. In some cases, in addition to the designation of the element number, it is given through an oblique fraction and the contact number, for example “-5/15-”. The diagram does not show the connection points of the pink-black, red and green with a red stripe wires.
Pinout of 8-pin connector
- power supply
- speed sensor (electric speedometer)
- fuel consumption (for BC)
- coolant sensor
- emergency oil pressure
- check lamp
- oil level sensor
- tachometer signal
History of application
Electric starters were not used immediately, although at the beginning of the 20th century there were even electric cars. At first, engines were started simply by turning the crankshaft manually. The first starting devices for automobiles were pneumatic and operated on compressed air. For example, the Rolls-Royce of Russian Emperor Nicholas II was equipped with such a device. However, the pneumatic starter circuit was cumbersome and capricious. And, as soon as electric motors began to be suitable in size and power for the needs of the automotive industry, designers switched to designing electric starters. They are still used today.
Electrical circuit of ECM VAZ-21104
1 — block of the ignition coil wiring harness to the ignition system harness; 2 — block of the ignition system harness to the ignition coil wiring harness; 3 — ignition coils VAZ-21104; 4 — immobilizer warning sensor; 5 — immobilizer control unit; 6 — spark plugs; 7 — nozzles; 8 — diagnostic block; 9 — block of the ignition system harness to the ABS cabin group harness; 10 - controller; 11 — electric fuel pump; 12 — block of the ignition system harness to the fuel level sensor harness; 13 — block of the fuel level sensor harness to the ignition system harness; 14 — block of the ignition system harness to the injector harness; 15 — injector harness block to the ignition system harness; 16 — block of the ignition system harness to the side door harness; 17 — speed sensor; 18 — idle speed regulator; 19 — throttle position sensor; 20 — coolant temperature sensor; 21 — mass air flow sensor; 22 — oil pressure warning lamp sensor; 23 - phase sensor; 24 — oxygen sensor; 25 — crankshaft position sensor; 26 — knock sensor; 27 — solenoid valve for purge of the adsorber; 28 — oil level sensor; 29 — coolant temperature indicator sensor; 30 — block of the ignition system harness to the instrument panel harness; 31 — block of the instrument panel harness to the ignition system harness; 32 — ignition relay; 33 - ignition relay fuse; 34 — fuse for the electric fuel pump power supply circuit; 35 — electric fuel pump relay; 36 — electric fan relay; 37 — controller power supply fuse; 38 — ignition system harness block to the air conditioner connector; 39 — instrument cluster; 40 — ignition switch; 41 — electric fan of the cooling system; 42 — on-board control system unit; 43 — starter relay; 44 — contacts of the 8-terminal blocks of the instrument panel harness and the front harness; 45 — contacts of the 21-terminal blocks of the instrument panel harness and the rear harness; 46 — trip computer; 47 - diagnostic connector.
- A - to the “plus” terminal of the battery;
- B1 — grounding point of the ignition coil wiring harness;
- B2 — grounding point of the fuel level sensor harness;
- B3, B4 - grounding points of the ignition system harness;
- C - to the starter;
- D - to the driver's door interior lamp switch.
According to the scheme described above, fuel regulation in a car is carried out. Moreover, it depends not only on the load of the valves in the engine, but also on the corresponding position relative to the throttle valve. With the help of a diagram of electrical wiring and valves, it is possible to understand which of the relays or fuses is malfunctioning and replace it in time. In this case, one of the main roles when supplying fuel is played by electrical equipment (controllers) that regulates the operation of the injector.
Source
VAZ ignition switch pinout
The ignition switch in cars of the VAZ family fails from time to time due to weakening of the contact posts or burning of the contacts inside it. It also happens that the cams of a plastic roller are produced. You can disassemble the lock and clean it, but it’s better to just replace it with a new one, considering that it costs pennies compared to imported locks.
But if connecting the wires together did not result in the starter operating (or it did not turn on the first time), check the solenoid relay on the starter. The contact spots on it may also burn out, which will prevent the circuit from closing normally. Alternatively, you can use a screwdriver to short-circuit the two large terminals on the solenoid relay (before doing this, put the car in neutral and use the handbrake). When closed, the starter should begin to spin vigorously. If this happens, remove and change the solenoid relay. If the starter rotates “sluggishly” when it closes, you will have to remove it and check the condition of the brushes.
All operations are performed with your own hands, without the help of car service specialists. Moreover, the price of an ignition switch on a VAZ2106 is up to 100 rubles. To replace it, you will need to know the pinout of the wires coming from it, for which the editors of the site 2 Schemes.ru have prepared a large reference material.
The ignition switch is designed not only to start the engine - it performs several functions at once:
- supplies voltage to the vehicle’s on-board network, closing the circuits of the ignition system, lighting, sound alarm, additional devices and instruments;
- at the driver’s command, turns on the starter to start the power plant and turns it off;
- turns off the power to the on-board circuit, preserving the battery charge;
- protects the car from theft by fixing the steering shaft.