We are used to the fact that to charge a car battery, you need to remove it, take it home, connect it to a charger (charger) and charge it in accordance with the recommendations for this type of battery. In principle, everything is correct when we are talking about simple and inexpensive cars of imported and domestic production. But now there are more and more foreign cars that have a lot of sophisticated electronics. There are complex on-board computers, sensors, multimedia and anti-theft systems, all kinds of assistants, a bunch of settings, diagnostic information, etc. And it is contraindicated to turn them off. What to do in such a situation?
Why is this necessary?
20–30 years ago, the dilemma associated with removing the battery did not even arise. Our fathers and grandfathers calmly charged the battery, having first removed it from the car. They even handed over the battery if they needed help starting a neighbor’s car in the yard. But then, among the complex electronic devices in the car, only electromechanical watches were found. Yes, they stopped after removing the battery, but after reinstalling the battery and securing the terminals, everything was easy to bring to the required values - the inconvenience ended there.
Today the situation is completely different. This is primarily due to the advanced equipment of a modern car, which is full of electronic devices. Many control devices are connected to the on-board computer.
And the consequences of removing the battery from its regular place leads to various troubles:
- ECU settings are lost;
- The car radio is blocked;
- maps in the navigator are deleted;
- climate control settings go off, etc.
Of course, these are small risks and not a threat to performance as a whole - you can always re-enter the code, and the computer parameters will be restored after 10-20 km, but still...
Thus, today recharging the battery without removing the terminals is an opportunity to avoid various inconveniences associated with reinstalling the car’s electronic systems. Moreover, not everyone knows how to reinstall some operating programs on some cars - you need the skills of a technician. In addition, drivers do not want to fiddle with keys and disassemble the battery mounts. On premium foreign cars such as Mercedes-Benz, dismantling is too inconvenient, since the manufacturer has provided for removing the battery only during replacement, and this happens once every 5-7 years.
Vehicle electrical and electronic wiring
All these are reasons why car owners do not want to remove the terminals. Therefore, we often find ourselves witnessing this situation: a person in the yard cannot start his car, he asks a friend to lend him a battery, but he is categorically against it - he will not allow him to remove the battery, because the device is built into electronic systems. Find the “crocodiles” and light a cigarette - that’s the only way.
When do you need to charge your car battery?
If the car is equipped with volatile components, when the battery is removed, the settings are reset and a safety lock is activated, which creates inconvenience. If you remove the battery and charge it at home, you will need to reconfigure the electronics and enter the security code. Moreover, it is necessary to configure not only the radio, but also the on-board computer (daily mileage, information on fuel consumption, other statistics will be erased). In some cases, a prolonged lack of power will make independent adjustment of electronic devices impossible; the driver will have to contact a service center for help.
If the autonomous power supply is disconnected/connected incorrectly, a sudden voltage drop may occur that is sufficient to damage the controller software; you will have to re-flash it.
What to use for charging
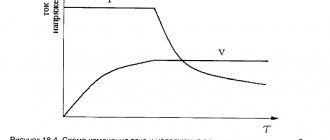
So what is the danger of directly applying current to the terminals? One of the safety rules involves using the correct charger (charger). The greatest risk when recharging is a sharp increase in voltage, which can burn out all the electrics. Therefore, you need to choose a charger that would produce a stable 15.3-15.7 V - this voltage is tolerated “painlessly” by car electronics.
However, many different memory devices are sold on the modern market. As practice has shown, many of them produce up to 17–18 V impulsively and even constantly. Such devices can easily burn car electronics if you charge the battery without removing it from the car.
Battery charger
You can find out whether the charger is suitable or not using the data sheet supplied with the device. Study it carefully - the technical parameters of the memory should be indicated here. This way, you will be able to understand whether it is safe to charge with the terminals not removed or not.
Important point! Still, a lot depends on the circuit diagram of the charger. If force majeure occurs, the current at the terminals may still exceed critical values, even if this is not indicated in the parameters. Therefore, disconnecting the terminals and then applying voltage is theoretically a more correct solution.
It is advisable to select chargers with a buffer storage mode. This means that excess voltage will not harm either the battery or the charger - therefore, you can keep the battery connected to the network for an unlimited amount of time. For example, these include the stationary Dnepr-6 and its analogues. Good chargers should be additionally equipped with a voltage scale to make it more convenient to control the current parameters. In this case, you will not need to connect a separate tester.
In what case is charging with terminals allowed?
In all cases where the potential danger from disconnecting the terminals from the battery is greater than the likelihood of damage to the equipment from connecting the charger without performing this procedure, it is recommended to connect the DC source without removing the connecting elements from the battery.
If, after disconnecting the terminals from the battery, their further use is impossible, then it is also more advisable to connect charging without disconnecting the wires from the battery.
For example, if there are cracks in the connecting element, such an operation can lead to destruction of the metal. In the absence of spare parts, such a breakdown may lead to the fact that it will no longer be possible to start the engine and, accordingly, operation of the machine will be impossible.
How to properly charge the battery without removing it from the car
If you still decide to charge the battery directly on the car, without removing the terminals, follow the sequential instructions.
- Preparation. Open the hood of the car. We take a tester and take readings. If it shows less than 12.7-12.8 V, then the battery needs to be recharged. For example, it is charged at 70-80%, and additional recharge is needed from an external source.
- Compound. We install the wires of the disconnected charger. The ends of the wires should have crocodile-shaped clothespins. We connect the “plus” first, then the “minus” - although, in principle, if the current circuit 220 is broken, the sequence of connecting the poles does not matter much.
- Connection to a 220 V network. Plug the charger into a socket. We activate the “on” button on the current supply device. We monitor the amperes on the charger. At the same time we look at the voltage scale.
- Standby mode. The battery will take the required amount of energy, and the charger can be turned off.
- Shutdown. Press the “off” button and remove the plug from the socket. Remove the wires from the terminals. We measure the battery voltage - it should show 12.7–12.8 V.
Checking the battery with a multimeter
One of the alternative solutions that makes it possible to reduce the risk of shorting the on-board network when supplying current from an external source is to connect the charger to the cigarette lighter. In this case, the load will be taken over by the spare power supply, which will prevent the risk of a short circuit.
Precautionary measures
When working with electric current, safety comes first. For this reason, it is prohibited to perform this operation in a damp room. Failure to comply with this requirement may result in electric shock or damage to the charger.
Modern battery charging devices are well protected from polarity reversal. If the terminals are connected incorrectly, the fuse will blow, but the main circuit should remain unaffected.
It is not recommended to check the functionality of the safety elements, so you should be careful when connecting the wires coming from the charger to the battery.
All electrical contacts must be in perfect working order. The presence of sparks in the immediate vicinity of flammable substances can result in a fire.
Still have questions or have something to add? Then write to us about it in the comments, this will make the material more useful, complete and accurate.
Charging the battery in the cold
The ideal service life of a battery manufactured by a reputable manufacturer is 5-7 years. Most often, batteries “die” earlier if the owner does not know how or does not know how to maintain them in winter or with the onset of cold weather. We are, of course, talking about serviceable batteries with screw-out caps.
Popular brands:
Mercedes-Benz E-Class, Mitsubishi Pajero Sport, Skoda Rapid
Below are instructions on how to carry out maintenance of such batteries in winter with recharging:
- unscrew the plugs;
- we measure the electrolyte density and level with a hydrometer, especially carefully in the outermost jars, since this is where the amount of liquid often decreases;
- add distilled water according to the level if the amount of electrolyte in the jars is low;
- put the battery on charge - connect the charger wires and plug it into the 220 network, as described above;
- wait 8–10 hours - this time is enough for the liquid in the jars to begin to boil and for the electrolyte to mix with the added water;
- disconnect the charger and screw the plug into place.
Checking battery electrolyte density
You can also focus on the “eye” of the battery. It usually lights up green when everything is normal with the electrolyte, and the voltage is also normal. However, our experts consider this approach to be incorrect, since the “eye” is usually located on the middle jar, where the electrolyte level rarely decreases. It does not show how things are in the plus and minus banks, where the most loads occur due to the terminals.
The most common mistakes when charging a battery
Sometimes even experienced motorists make “classic” mistakes when charging a battery, forgetting about basic safety rules. The main ones are:
- Charging the battery at home or in an apartment. It is strictly forbidden to charge the battery in a residential area due to poor ventilation of the room and the possibility of the battery exploding.
It is not recommended to charge the battery in a residential area
- Smoking or open fire near a charging battery. During the charging process, electrolyte vapors are released, which, when interacting with an open flame, can cause an explosion.
- On batteries to be serviced, the plugs must be open when charging. They must be opened before charging. Failure to comply with these measures may cause an explosion of electrolyte vapors.
Twisted battery plugs
- Current too high. Selecting a current that is too high significantly reduces the life of the battery or can completely damage it.
Compliance with all these standards will increase the battery life and protect the person charging the battery and surrounding people.
Safety precautions
Above we talked about safety precautions when applying current to working battery terminals. Here are the steps it involves:
- first connect the positive wire of the charger, and then the negative one (in case you accidentally forget to disconnect the charger from the network) - disconnection is carried out in the reverse order;
- do not allow the wiring to come into contact with the surface of the battery, the car body and fuel hoses;
- plug the charger plug into a 220 V socket only after connecting the wires to the battery terminals - disconnect from the network too, only after discarding the wires;
- During charging, turn off all current consumers in the car - car radio, climate control, heater, headlights, etc.
Good ventilation in the room where the charger is installed is also important. Usually this is a garage where the car is driven. So, you need to make sure that the ventilation holes in the ceiling work properly. If the air in the room is stale, this can cause voltage drops in the network.
It is allowed to recharge the battery without removing it from the car. Although it is advisable, if you are far from safety precautions and cannot figure out the quality of the charger, entrust the procedure to specialists. You can also remove the terminals, apply voltage to the battery, and then deal with the “fly away” settings of the car’s electronic systems.
How is the procedure performed?
The procedure can be carried out in several ways depending on the current situation. This can be charging with a special charger or from another battery. Let's look at how to charge a car battery without removing it from the car, taking into account the nuances of each option.
Charging with a charger
This option is feasible if there is an outlet near the vehicle. Most often, this method can be used in a garage where there is a car with a discharged battery. The sequence of actions will be as follows:
- take the charger and connect the wires from it to the battery terminals: positive to positive, negative to negative;
- put all electronics into sleep mode;
- if the battery has opening covers to release gases, then they should be opened;
- after connecting the charger terminals, you can plug it into a power outlet and begin the charging process;
- after the charging device signals the end of the charging process, it must be turned off and disconnected from the network;
- disconnect the charger wires and close the battery covers.
After all the above manipulations, the car can be started.
Attention! Charging using a charger can hardly be used if the car is discharged somewhere along the way or cannot start in the cold. For field conditions there is another method.
Charging with another battery
As another battery, you can use either the device from the second car or a spare one with a full charge. The algorithm of actions will be similar to the previous one, we will discuss the nuances separately in each paragraph:
- If you plan to charge from another car, then there should be no points of contact between it and your car. If charging from another battery, then it should stand on the ground, without touching the car being charged.
- Connect the positive terminals of the batteries together using the red charging wire.
- Connect the black wire to the negative terminal of the “donor”. Its other end must be connected to any metal part of the engine being charged by the car. If you cannot find a suitable place, you can connect it to the negative terminal of the battery being charged. But this will increase the risk of damage to a dead battery.
- In order for charging to be more efficient and the donor battery not to run out, start the engine of the car that is acting as a charger.
- When the process is completed, before starting the engine of your car, you must turn off the donor engine.
- If the engine starts, you need to disconnect the wires: first the black negative, then the red positive.
Is there a GOST for chargers?
We consider this type of terminal sealing to be careless. The conductor is soldered, but the entire wire must be clamped!
We consider this type of terminal sealing to be careless. The conductor is soldered, but the entire wire must be clamped!
The battery charging algorithm is not specified by any standards: each manufacturer chooses it at its own discretion.
The current GOST R 53165–2020 (IEC 60095–1:2018) applies to batteries, not chargers. Interestingly, it mentions a charging voltage of 16.0 V for open-type batteries and 14.8 V for batteries with VRLA valves. None of the chargers we tested produce such a voltage. However, we will not consider this a disadvantage: GOST recommends the indicated voltages for subsequent battery tests, and not for operation.