First of all, I express my deep gratitude for the help, providing a garage with the necessary equipment to my friend Demich (Demid91), thank you bro)
Now it’s a matter of pressing in the seats, for this we used the “electric stove-fire extinguisher” method already tested and patented by Demich, and if anyone has problems with this, we’ll see you in court... The process itself: we heat the head (not ours, but the cylinder block) degrees to 90, and We cool the seats with a carbon dioxide fire extinguisher (-70 degrees Celsius) and press them with mandrels made from modified old valves.
But as in our business, it’s expected without any jambs: the 7th saddle chipped 2 times, 1st saddle went out of alignment and burst, the next day everything was fixed and all the saddles were in their places.
The need to replace the valve seat may arise in the following cases.
1. The saddle is worn. While countersinking the valve seat for lapping, you discover that there is no seat material for further refinement. The valve sits so deep that the gap cannot be adjusted. The only solution may be to replace the saddle. 2. The seat and valve are burnt out. And what's the reason? You never know the reasons! The seat and valve were poorly ground or the clearance in the valve drive was insufficient. It doesn't matter anymore. It is important that when you remove the blackness on the valve seat with a countersink, you discover that there is not enough material. And then point 1. 3. The fit of the saddle in the head has weakened. Corrosion is noticeable on the outer diameter. 4. A crack was found in the valve seat. 5. When tuning the head, you change the valves to larger ones. Accordingly, larger saddles are needed. Check first to see if you can use the saddles you have. Replacing seats is not a very difficult job, but in case of an error you will have to go to a car dealer or for recycling.
How to Remove an Old Valve Seat
The easiest and most convenient way on the machine. When the seat is bored, its thickness and strength decrease, and then at one point the cutting force exceeds the friction force in the joint. The remainder of the seat is rotated and can then be removed with pliers. If you are going to install larger diameter saddles, then you will need to bore the seat next.
Replacing the VAZ valve seat
In the design of the head, the main element is the valve seat; this can be understood by studying in detail the mechanism of operation of the valve.
The main task of the seat is to compress the valve, thus preventing the possibility of gas leakage, because contact of the valve with the seat is a necessary condition for the operation of the entire system.
The contact between the parts allows you to regulate and remove heat from the plate itself with greater efficiency; the heat leaving the valve is transferred through the seat itself to the cylinder head, after which cooling with liquid occurs. As a result of engine activity, certain parts wear out, including those that lead to valve seat defects. The resulting depressurization disrupts the complete heat transfer of the plate with the seat, after which the parts completely break down.
Therefore, the tightness of connections is a very important component in such matters; this effect can only be achieved by forming an appropriate profile for the seat, which controls the balance of wear of parts.
How to understand that a VAZ valve seat needs to be replaced
The first step is to clean the seat and engine chamber, because invisible cracks may appear under the deposits that have formed. You can also determine if cameras are broken by color; they will differ from others. Therefore, based on these signs, it is possible to determine the wear of the seats and the need for repair work. Factors for change may be:
- Part wear is the main reason for replacement. This can be checked using countersinking; if it is found that it is impossible to fine-tune the seat and adjust it, it is necessary to take measures to change it.
- Fume of saddles.
- The formation of corrosion, most often it occurs along the outer diameter.
- Formation of cracks at the base of the seat.
- If it is necessary to modernize the cylinder head, which includes replacing the valve or increasing its diameter.
Instructions for changing the valve on a VAZ car
First, we must be sure that replacement is necessary; the whole process is quite complex, so there is no point in undertaking it without special tools and knowledge.
You will make the shift at your own responsibility, so if something doesn’t work out for you, you will have to contact the auto buyout service.
The first step is to check the tightness of the cylinder head to determine if there are any cracks; if you do find them, you should first seal them by welding, and only then bore the seats.
To remove the seats, you will need machine tools, and then bore the seat until it takes the shape of a thin ring that can rotate in the socket. We achieve similar results using a cutter mounted on a drill. All work is carried out carefully to prevent damage to the seat.
When installing a new saddle, a tension of 0.1-0.15 mm is used. By outer diameter. In this case, the difference in temperature conditions is 180-200 degrees; liquid nitrogen is used to cool the seats.
If there is no nitrogen, you can use a regular refrigerator to cool the part to 30 degrees. Then they press it in very quickly so that the temperature does not equalize. To change the valve you must have with you:
- stove
- cutters
- refrigerator
- caliper
- hammer
- pressing
- replacement saddles
We remove the cylinder head, wash it and clean it of carbon and dirt. We prepare all the necessary tools.
We clean the saddle.
We remove the old saddle.
...as well as a seat.
Before installing new saddles, they must be placed in the refrigerator compartment.
After which it is worth heating part of the cylinder head to about 200 degrees to perform pressing.
We take out the saddles placed in the freezer.
We place the saddle for crimping.
We wait until the parts cool down and then, armed with saddle cutters, we cut out a chamfer.
We do the same on other cylinders.
Nuances of machining
The procedure ends with machining of the new element. Here you should cut the appropriate chamfer. It is best to use a special machine for such purposes. This way it is possible to achieve maximum accuracy.
The cutter is firmly centered and the processing process begins. It is important to understand that it is impossible to achieve the same accuracy using hand cutters.
But in the absence of other options, we have to act with cutters. You will need to cut 3 edges. These are external, internal, and also upper central. The last one is the narrowest. It is with this that the valve comes into contact.
If you are in doubt about the accuracy, as well as the quality of your own workmanship, find a metalworking shop nearby. Even a regular milling machine will do. And the result will probably be better than using a roller cutter. But here the decision is yours.
Boring is an objectively complex task that requires maximum precision and accuracy. Therefore, such work is carried out independently solely at your own peril and risk. The best solution is to seek qualified help.
Has anyone had to change valve seats? What was the most difficult thing? Did you manage to achieve the desired result? Which way to solve the problem do you think is optimal? With your own hands or through a workshop?
Replacing valve seats.
The need to replace the valve seat may arise in the following cases.
1. The saddle is worn. While countersinking the valve seat for lapping, you discover that there is no seat material for further refinement. The valve sits so deep that the gap cannot be adjusted. The only solution may be to replace the saddle. 2. The seat and valve are burnt out. And what's the reason? You never know the reasons! The seat and valve were poorly ground or the clearance in the valve drive was insufficient. It doesn't matter anymore. It is important that when you remove the blackness on the valve seat with a countersink, you discover that there is not enough material. And then point 1. 3. The fit of the saddle in the head has weakened. Corrosion is noticeable on the outer diameter. 4. A crack was found in the valve seat. 5. When tuning the head, you change the valves to larger ones. Accordingly, larger saddles are needed. Check first to see if you can use the saddles you have. Replacing seats is not a very difficult job, but in case of an error you will have to go to a car dealer or for recycling.
How to Remove an Old Valve Seat
The easiest and most convenient way on the machine. When the seat is bored, its thickness and strength decrease, and then at one point the cutting force exceeds the friction force in the joint. The remainder of the seat is rotated and can then be removed with pliers. If you are going to install larger diameter saddles, then you will need to bore the seat next.
If you just need to replace the stock saddle, use another method. Clamp a small abrasive wheel into the chuck of an electric drill. Turn on the drill and cut into the saddle material. At some point the tension on the seat will loosen and it will be possible to remove it. It is advisable for this to happen before the wheel cuts into the head material.
Another way. The old valve is inserted into the head. The one who was here. And they weld it to the saddle at 3...4 points. And then the seat is knocked out with a hammer on the valve.
New saddle
The material of valve seats is quite varied. Bronze, steel, stainless steel, metal ceramics, cast iron. Cast iron is used for valve seats manufactured at AVTOVAZ. Such saddles can be easily processed with hand tools. But valve seats made of hardened steel can only be ground. For this you need a specialized machine.
Beryllium bronze valve seats have the advantage of dissipating heat away from the valves. This material is often used for racing cars. But for daily city driving you don’t need to rev the engine to 8,000 rpm. Therefore, beryllium bronze seats are not needed.
What to use?
Such work involves the use of rough tools that are characterized by almost jeweler precision - countersinks and cutters. Such tools with narrow specifications are used exclusively for engine repairs.
A selection of cutters for valve seats is used for recessing the required diameter sizes. Such actions make it possible to give the plate maximum closing density.
Countersinks are used in the same way when repairing valve seats. But there is one difference - the countersink is used not only on mechanical, but also on power tools.
Tool
If we are replacing valves with our own hands, be it a VAZ or another car, we must not miss such a nuance as the presence of a special tool. Here's what you'll need:
Sets: wrenches, sockets, screwdrivers for dismantling and installing machine elements.
Valve desiccant. It is needed to compress the springs in order to eliminate the cracks (locking elements).
This is interesting: About the Chevrolet Niva throttle body: problems and solutions
Lapping tool. The valves require lapping to ensure compression. Purchasing a special device is not advisable; you can use a drill and a piece of hose.
The hose tightly connects the valve stem and the drill attachment and grinds in with translational movements. Then pour diesel fuel at the junction of the valve and the seat; if it does not leak, then the job is done efficiently.
Tool for removing oil seals. When replacing valves, you need to change the caps on the bushings, which will be quite difficult to do with your own hands. It is better to use a special puller.
Using improvised tools can cause damage to the integrity of the part, which will lead to the need to purchase new seals.
There is another device - a micrometer. It will give an accurate measurement of the rod parameter and identify valve wear defects.
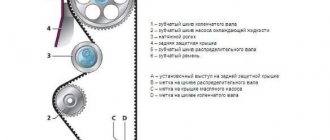
A key for fixing the crankshaft in order to adjust the correct operation of the timing belt.
It is advisable to have a torque wrench to tighten the bolts.
Consumables
In addition to valves, you will need:
- suitable sealing caps;
- cylinder head gasket;
- valve cover gasket;
- if necessary, sealant;
- cylinder head mounting bolts, sometimes it is possible to use old bolts;
- lapping paste or powder.
Countersinks and cutters for repairing valve seats – what to choose?
Replacing valve seats with your own hands requires the presence of not only a rough tool, but also an almost jewelry one - a roller cutter or a countersink. These highly specialized tools are used only for repairing internal combustion engines. A set of cutters for valve seats is used to grind out the desired shape of their internal diameter . This operation allows you to achieve a tight seal from the plate. In order to accurately process the valve seat, it is advisable to have a drawing of the mechanism at hand.
The cutter is made in the form of a metal cylinder, in which there is a hole and two or one conical surface; its angle can vary from 15 to 60 degrees. There are incisors on the surface of the cone. A set of countersinks for repairing valve seats is used in the same way as cutters, but there is one difference. The countersink can be used on mechanical and electrical tools.
Valve seat blank
For all popular engines, valve seat blanks are offered, both standard sizes and repair ones, with an increased outer diameter. For rare engines, blanks must be ordered or made to order.
Such blanks are quite cheap; if you don’t find one for a certain motor, you can choose the size from the available items. But don’t forget that companies that produce engine parts (Kolbenschmidt), in particular valves, also produce seats of the same sizes, so ask in stores in your city. After installation, the seat will need to be processed - chamfered for the valve.
How to properly replace, trim and process valve seats
Valve seat - a small ring with a bevel on the inner surface.
It is installed in the holes of the cylinder head intended for installing valves and distilling the air-fuel mixture and exhaust gases through them. The part is pressed into the cylinder head at the factory.
Performs the following functions:
- hole tightness;
- transfers excess heat to the cylinder head;
- provides the necessary air flow when the mechanism is open.
Replacing the valve seat is required when it is not possible to restore its tightness using mechanical processing (numerous treatments in the past, burnout, severe wear). You can do this yourself.
Part repairs are performed when:
- plate burnout;
- after replacing the guide bushings;
- with a moderate degree of natural wear;
- if the tightness of the connection between the ring and the plate is broken.
Correcting worn and damaged saddles at home is done using cutters. In addition, you may need a welding machine or a powerful gas torch, a standard set of wrenches necessary for dismantling and disassembling the cylinder head, lapping paste, and a drill.
- Replacing seats
- Removing old planting elements
- Installation of new saddles
- Saddle repair
Replacing seats
The replacement procedure consists of two important procedures: removing old parts and installing new ones.
Removing old planting elements
Replacement of valve seats is carried out on a dismantled cylinder head with a disassembled gas distribution mechanism. You can remove the old ring using a welding machine, if the material from which it is made allows this.
To perform the procedure, a valve seat remover is made - an old unnecessary valve is taken, the plate of which must be machined to the size of the inner diameter of the seat.
After this, the resulting tool is recessed into the seat, 2-3 mm short of the edge, and “grabbed” by welding in 2-3 places. Afterwards, the valve along with the metal ring is knocked out from the back side with a hammer.
Important! The welding procedure may cause some deformation of the seat. In this case, standard saddles will have weak fastening, which can lead to their spontaneous dismantling during engine operation. Rings of increased diameter are required, which are not sold in stores, but are made to order.
» alt=»»> Valve seats made from metals that cannot be welded can be removed by screwing a piece of pipe into it, used as a valve seat remover. To do this, a thread is cut on the inner surface of the ring. A similar thread is applied to the outer surface of a metal pipe of suitable diameter.
An old valve is taken and first welded to the end of the pipe in the reverse position. In this case, the valve stem is inserted into the hole intended for it, the pipe is screwed into the thread, after which the element is removed by tapping the stem.
Installation of new saddles
Before starting the installation procedure of new saddles, the seats under them are cleaned of dirt. After the cylinder head should be heated evenly to a temperature exceeding 100˚C. At the same time, the metal expands, allowing the ring to be pressed in.
The mounted part is cooled using liquid nitrogen. In its absence, you can use a combination of ice and acetone, which allows you to reduce the temperature of the metal to -70˚C. The dimensions of the parts are selected in such a way that the difference between the diameter of the seat and the ring is no more than 0.05-0.09 mm on cold parts. » alt=»»> The valve seat is pressed into place using a special mandrel or a piece of pipe of suitable diameter. The part should fit into the seat with little effort. It is important that the ring fits without distortion.
After pressing in and cooling the cylinder head, you should check whether the element is loose in the seat. If there is no gap and the replaced element is held tightly in place, the replacement procedure can be considered complete. Next, you need to trim the valve seats using cutters.
Important! During the standard replacement procedure, the valve plates of all valves are set quite high. However, some experts recommend processing the chamfers so that the exhaust valves sit slightly deeper than the normal position. The intake valve seat is left in its normal position.
Saddle repair
Repair of valve seats is carried out when they are naturally worn out and the disc does not fit tightly to its seat.
In order to restore the geometry of the rings, valve seat cutters are used - a set of milling heads that allow making the necessary angles.
Roller cutters can be used in combination with special equipment. However, it is expensive. Therefore, at home, a ratchet wrench with an extension is used. Properly treated areas have angles of 30˚, 60˚ and 45˚. The processing of valve seats to create each of them is carried out with the appropriate cutter.
Grinding valve seats does not require heating or other processing. Grooving is done “dry”. In the future, at the time of lapping, it is necessary to use a special lapping paste. To achieve the best result, it is recommended that lapping on new seats be done by hand rather than using a drill. » alt=»»> Another type of repair is the grooving of seats for repair inserts. To do this, according to the algorithm described above, the saddles are removed, after which the places for them are ground with a special cutting tool. The size of the repair area should be 0.01-0.02 cm smaller than the insert. Installation is carried out after heating the cylinder head and cooling the mounted elements.
You can attempt to bore correctly yourself at your own peril and risk. However, taking into account the complexity of the procedure and the required high precision of work, it is better to carry out such manipulations in a qualified auto repair shop or auto repair plant.
Valve mechanism design - operating principle and possible malfunctions
Valves are used to seal engine cylinders during gas exchange.
The principle of their operation is to ensure the intake of a mixture of fuel and air for its further compression. After ignition and exhaustion, the gases enter the exhaust system, and valves are also responsible for this. This mechanism operates in the aggressive conditions of an internal combustion engine and is constantly subjected to high dynamic loads, high speeds and heat. To reduce the rapid wear of the running parts of this part, the manufacturing materials most often have a high degree of alloying with nickel and chromium. The valve mechanism has two main components: the head and the stem. These car components come with a tulip-shaped, flat and convex head. At the end of the rod there are conical, shaped or cylindrical grooves for fixing springs on them. The main manifestation of a valve mechanism malfunction is a loss of engine power, as well as unstable operation of the engine as a whole. Failures of this type occur due to sticking and the appearance of a gap. Carbon deposits can also cause this problem; it accumulates near the valve itself and prevents it from closing.
Another sign of a malfunction is increased smoke emission during exhaust. A worn rod and guide of this mechanism will cause unnatural engine noise.
Need for replacement
On all cars, the repair principle is the same, just like replacing valves on a VAZ Priora can be done with your own hands.
The main sign of malfunctioning valves is a decrease in compression. This mainly happens for three reasons.
The first is burnout. This happens like this: the valve plates are destroyed or cracks appear in them, subsequently, at any position of the camshaft, the combustion chamber is depressurized.
Exhaust valves are mainly affected by this, because they are subject to a large thermal load.
In most of these situations, it is necessary to replace the valve seats, which is difficult to do with your own hands, since they will need to be pressed out and then pressed into place.
This problem may occur due to:
- incorrectly adjusted thermal gap, this applies to engines without a hydraulic compensator;
- a very lean mixture, this increases the temperature in the combustion chamber;
- The timing phases are not properly adjusted, which is why a fire is created during the period when the valve does not fit tightly to the seat. This can also contribute to the formation of carbon deposits in places where parts come into contact;
- a manufacturing defect;
- engine detonation for any reason.
The second is the bending of the valves as a result of a collision with the pistons. This is only possible if the timing belt breaks or jumps; the jump occurs due to a stretched belt or chain.
The third is rod wear. In the operating mode of the engine, the valves move along the guide bushings; during prolonged use, the rod wears out.
In this case, an excessive gap occurs between the inner walls of the bushings and the valve stems, which negatively affects the operation of the valve mechanism.
In this case, you will have to replace not only the valves, but also the guide bushings, which you can also do yourself.
Symptoms of a problem
The cause of unstable engine operation caused by loss of power, compression in any cylinder and vibration can be not only the valves.
If the timing belt breaks, it is not a fact that the valves will bend; the pushers more often break off. Even with the help of a compression gauge, you can only make sure that there is no compression in the cylinders, but you will not be able to find out the reason.
You can add a small amount of engine oil to the cylinder, but if the compression increases, the reason is the wear of the piston group.
To more accurately determine the diagnosis of the engine, it is better to conduct a test with a pneumatic tester.
Replacing valve seats for VAZs
- Registration
- Entrance
- To the beginning of the forum
- Forum Rules
- Old design
- FAQ
- Search
- Users
- List of forums AUTOLADA.RU
- Family "Samara"
The situation is as follows - compression 12-11.5-12-11. The culprit is that the valves do not hold pressure, although the head was done in the fall and everything was OK. A head with heavily sagging seats (the valves had to be filed). I found a service station where they replace seats, the price is 1600 rubles + new valves - 750 rubles. Is this work worth bothering with? How long will a repaired head last? The toad is strangling the head completely. I heard the opinion that it is useless to change saddles, a maximum of 15-20k is enough. Anyone who has changed saddles, please share your experience.
issue price - 1600 rubles + new valves - 750 rubles.
A bare head costs RUB 4,300. and it’s not a fact that I’ll get away with just grinding in the valves, because... very often you come across crappy guides.
Repair or not repair, that is the question.
The situation is as follows - compression 12-11.5-12-11. The culprit is that the valves do not hold pressure, although the head was done in the fall and everything was OK. A head with heavily sagging seats (the valves had to be filed). I found a service station where they replace seats, the price is 1600 rubles + new valves - 750 rubles. Is this work worth bothering with? How long will a repaired head last? The toad is strangling the head completely. I heard the opinion that it is useless to change saddles, a maximum of 15-20k is enough. Anyone who has changed saddles, please share your experience.
Causes of parts failure and their consequences
A characteristic feature of the guide elements is that they do not fail at once, but wear out gradually. The lifespan of parts on budget cars ranges from 180 to 300 thousand km, and on more expensive foreign cars it can reach 1 million km. The wear process is influenced by several factors that can accelerate it:
- the quality of the motor oil used and the timeliness of its replacement;
- temperature conditions of the power unit, the more often the engine overheats, the faster the rubbing surfaces wear out;
- the quality of the fuel and combustible mixture, whose vapors penetrate into any leaks and contribute to the process of slow destruction of parts.
Carbon deposits on the rod destroy the bushing quite quickly
A worn part is characterized by a “broken” internal hole, as a result of which the valve stem begins to move too freely in it, and then play appears. The rod warps during operation, and the plate does not fit well with the seat, the tightness of the interface is gradually lost. Gases escape from the combustion chamber into the mechanism, and oil enters from above, resulting in the formation of carbon deposits. It also accelerates wear, quickly rendering the part completely unusable.
How to change a valve seat: photo and video instructions
Valves, together with their seats, are subject to high thermal loads, as a result of which defects appear on them, such as cracks, burns, cavities due to overheating, or foreign objects enter the engine and damage the seat.
If the head has overheated, the valve seat and guide may become misaligned, resulting in a leak. The wear of the seat also occurs unevenly, along the axis of the cam, which is why the seat becomes oval. All these defects must be corrected using cutters, cutters or countersinks, and then the valves must be ground in; Using specialized equipment, you can adjust the seat in one go without subsequent grinding.
If the old seat cannot be corrected, then it must be replaced with a new one, and then processed and chamfered for the new valve. The replacement process can be divided into several parts: removing the valve seat, preparing a blank for the new seat, installing a new part and finishing with a chamfer fitting for the new valve. Let's look at everything in order.
Removing the seat
First, let's look at what not to do , although some automotive garage gurus recommend doing just that.
-valve welding + knocking out
First, the old unnecessary valve is adjusted to the dimensions of the seat, inserted onto the seat and the valve is welded to the seat. While it is still warm, knock out the valve and it comes out along with the seat. Due to the different expansion of metals - steel and aluminum - the tension decreases; when it cools down, it will not be so easy to come out.
Why shouldn't you do this? During welding, the entire head heats up and it will certainly move, it will become crooked and in addition to this, hidden cracks will open where there were internal stresses in the metal (and they exist in any case). Then you will wonder why my head suddenly turned out to be pierced.
The best way : Boring the valve seat on a machine until it becomes the size of foil and jumps out of the seat hole. But... this cannot be implemented in a garage due to the high cost of the equipment, and not every village will have such a machine. Therefore, let’s consider another method, easy and safe, and can be implemented in any garage.
Execution technology
The work is complex, but if you have the necessary skills, it can be done in a garage.
There are several ways to remove the saddle. A quick, but not very correct method is to weld the valve onto the seat and then knock it out. The valve is ground to the size of the seat, inserted into it and scalded. Until the metal had time to cool. The saddle must be knocked out with a hammer. The entire structure should come out without any problems. But remember that welding heats up the metal, which can cause deformation of the head. By knocking it out, you can damage the seat under the saddle, which will entail additional work on processing the cylinder head. It is best to use a lathe. This way you can grind the saddle to such a size that it becomes like foil and can be easily taken out. If you don’t have a machine, you can use a drill and a cutter attachment. Stitching is carried out on one side until the tension weakens. The saddle can now be reached by hand.
The ideal option for installing a new seat is nitrogen, in which the seats should be pre-cooled. The fact is that their dimensions are slightly larger than the holes, and due to cooling the outer diameter decreases. Naturally, nitrogen in the garage is very rare. Then remember the properties of metal to expand and contract. The saddle is simply placed in the freezer for a couple of hours, and the hole is heated with a burner. If during installation it will be necessary to apply force, it is recommended to take a block suitable for the diameter of the seat and use it to press it.
Technical requirements
You can quickly and easily remove the valve seat insert using a soldering iron for soldering microwires in an inert gas environment - MIG (microware inert gas) welder. With the valve removed, apply a bead of solder along the edge of the insert seat adjacent to the wall of the seat. When the seam cools, it will shrink and the insert can be easily removed from the cylinder head.
In the case of cracked and severely burned inline seats, the cylinder head can often be repaired by replacing them with push-in seats. All cracks in the head must be repaired before the integral seat is bored. First, you must select a repair insert seat that has the required internal and external diameters, as well as the required thickness. Manufacturers of seat repair kits provide tables to help you select the appropriate seat repair insert. When replacing an insert seat, the new seat must be of the same or higher grade of material than the old one. The operating temperatures of inserted exhaust valve seats are 100°-150°F (56°-183°C) higher than the operating temperatures of integral seats, which reach up to 900°F (480°C). In order for the service life of repair seats and valves to be no less than that of the parts being replaced, some must be made of higher quality materials.
Manufactured valve seat repair inserts are made from a variety of materials, including:
- cast iron
- of stainless steel
- nickel-cobalt alloy
- powder metal
The cutting tool for making the seat is selected according to the outer diameter of the repair insert. The diameter of the bore of the seat must be less than the outer diameter of the insert seat. The tool holder is mounted on a guide rod selected to fit the hole in the valve guide. The tool holder feed drive is screwed in so that there are enough threads left to properly feed the cutter into the head being machined. The assembled assembly is installed in the valve guide so that the cutting tool rests on the seat being bored.
A seat repair insert is inserted between the support jig and the retaining ring. The locking ring is adjusted along the seat repair insert so that the cutter feed stops when the bore of the seat reaches a depth equal to the thickness of the new insert. The boring tool is rotated manually or using a gear motor. Boring continues until the retaining ring reaches the support jig. After this, the support jig and tool holder are removed. An appropriately sized mandrel and guide rod are secured to the impact head. It is best to cool the repair insert in solid carbon dioxide before installation so that it decreases in diameter.
With a strong blow of a heavy hammer, the repair insert is driven into the seat. First, the repair insert is pressed into the socket with strong blows of a hammer, and then with light blows it sinks until it fits into it all the way. Do not hit the impact head after the saddle is fully seated in the seat. The installed repair seat is caulked along the outer edge along the perimeter of the seat - in this case, the metal along the edge of the insert is slightly riveted, strengthening its adhesion to the seat. The seat in the repair insert is processed using the already described machining technology used to restore valve seats.
Repair inserts must remain in carbon dioxide until installed. This will significantly reduce the likelihood of metal being cut off from the walls of the mounting socket when installing a repair insert. Cut pieces of metal may get under the repair insert, preventing it from seating correctly. The cooled insert seat is placed on the seat.
When do you need to change guides?
The main symptom indicating that the valve bushings have become unusable is increased engine oil consumption. When the rod has lateral free play (play), the valve stem seals are no longer able to prevent the penetration of lubricant into the cylinders from the upper engine compartment, where the camshaft is located. It flows into the increased gap between the valve stem and the inner diameter of the bushing and freely enters the combustion chamber.
Blue smoke coming out of the exhaust is a sign of oil combustion.
Signs of oil consumption due to problems with the guides are:
- bluish smoke from the exhaust pipe from escaping combustion products of lubricant that constantly enters the cylinders;
- the car practically does not lose in dynamics, but smokes a fair amount;
- light “fluffy” carbon deposits on the spark plug electrodes;
- liquid oil is observed on the skirts and threaded parts of the spark plugs.
This is oil deposits on the spark plug.
Since oil can also penetrate into the chambers due to the fault of the cylinder-piston group, it is necessary to carry out diagnostics to accurately determine the malfunction. As an example, it is proposed to take the popular VAZ 2106 car:
- Measure the compression in the cylinders. The goal is to ensure that the piston rings are in good technical condition.
- Remove the valve cover, loosen the chain and unscrew the camshaft gear, first aligning the marks.
- Dismantle the camshaft along with the bed and remove the rocker arms. Unlock the valve springs of the cylinder whose spark plug is more heavily covered with carbon deposits.
- Carefully remove the oil seal and try to rock the rod sideways with your hand, while moving it up and down.
Piston group
Valve seat
The valve seat is designed to improve the durability of the valve's contact area with the cylinder head. To make the seat, special alloy cast irons or heat-resistant alloys are used. A layer of refractory material is sometimes applied to the working surface of the exhaust valve seat. A cap or cuff made of oil-gasoline-resistant rubber prevents oil from entering the combustion chamber. To obtain a good seal, the seat collar, about 2 mm wide, is made with a variable angle. The outer surface of the seat may have a cylindrical or conical shape. The saddles are fastened by pressing with tension and caulking of the head, and steel saddles are additionally flared in the upper part. On the outer surface of the cylindrical and conical seats, annular grooves are machined into which the metal of the head flows when pressed. The conical seat is pressed into the seat with a small end gap, and the cylindrical seat is pressed until it stops. The heat flow from the working fluid in the combustion chamber is perceived by the valve head (especially the exhaust) and is transmitted through the chamfer to the seat, and through the valve stem to the guide sleeve, which necessitates intensive cooling of these parts. For this purpose, design solutions can be used: supply of coolant to the most heated zones; increasing the diameter of the valve stem and the length of its guide sleeve; transfer of heat from the head to the rod due to the agitation of liquid sodium in the valve rod as it moves (the cavity in the valve is filled 50...60% with sodium salts, the melting point of which is 97 ° C). To prevent the valve from jamming in the bushing at high temperatures and possible misalignment (in the valve drive directly by the shaft cam), the lower inner surface of the bushing is made conical or the diameter of the valve stem at the head is reduced. Typical defects of the valve assembly: deformation and breakage of the valves as a result of impacts of the piston on an unclosed valve due to a broken belt or camshaft drive chain, jamming of the shaft bearing due to insufficient lubrication or excessive rotation speed; deformation of the end surface of the valves (concave shape) when the engine overheats; uneven wear of the valve head and seat due to the formation of carbon deposits on the surface of the valve and seat chamfer; cracks and deep cavities on the valve seat and chamfer due to insufficient cooling, poor contact with the seat (carbon deposits, large valve clearance), impact at the time of landing, foreign objects entering the intake system, engine operation with late ignition and a lean mixture; valve burnout due to overheating when carbon deposits form on the working facets of the seat and valve (heat removal from the valve head sharply decreases), as well as when there is a small gap in the actuator (“stuck” of the valve); wear of the valve stem and bushing due to uneven expansion of the stem with uneven temperature distribution of the valve; accumulation of carbon deposits on the guide bushings due to low quality oil (presence of contaminants, low viscosity and poor lubricating properties). Return to list