On older internal combustion engines, the problem of increasing changes in thermal clearances, increasing due to wear in the valve mechanism, was solved with the help of adjustments. This work was performed by a specially trained person. Valve adjustments were required every 10,000 km or due to wear. The specialists disassembled the engine and manually adjusted the valves - it must be said that this was a rather labor-intensive procedure that required special skills and qualifications from the master. Also, for this task, a specialized tool was needed - a set of probes.
Device
The operating principle of this unit is that the mechanism can automatically change its length by an amount equal to the clearance in the valves. The movement of the component elements in the assembly is carried out due to springs and oil, which comes from the car’s lubrication system. Let's see how the hydraulic compensator works. We already know what it is. So, a compensator is a housing in which a plunger pair is installed. She can move. In turn, this part consists of several elements:
Cylindrical pushers, parts in the cylinder head, and levers in the drive can be used as a housing for the hydraulic pusher.
There is a hole at the bottom of the plunger that is closed by a ball valve. The operation of the hydraulic compensator is possible due to the spring located between the plunger and the bushing. Almost all elements are arranged this way. VAZ hydraulic compensators are no exception (Priora 2172 is also equipped with them).
Flushing
Using new oil will not always help eliminate knocking. This is due to how severe the fault was. In this case, it is necessary to identify the faulty element and dismantle it for subsequent washing in gasoline. Often, due to the use of bad oil, gradual contamination of the compensator occurs. The removed compensators are mounted back into place in the order in which they were dismantled. It is worth noting that washing the elements is a rather complex process that will require special skills from the car owner.
Operating principle
When the camshaft cams are positioned with their back side towards the pusher, a gap is formed between the valve and the shaft. Oil enters the compensator housing through a special channel. Due to the force of the spring, the plunger will begin to rise. This is how the gap is compensated. In addition, the oil enters a special cavity in the compensator through the valve. As the camshaft rotates, the cam will begin to exert downward pressure on the tappet. At this moment the ball valve will already be closed. The plunger pair works like a rigid unit. She presses on the valve. A small amount of lubricant gets into the gap that forms between the plunger and the hydraulic compensator bushing. Oil supplied from the system helps compensate for this leak.
How to find out a faulty element
Having dealt with the causes of a possible malfunction in the engine, you need to consider a method for identifying the faulty part. In specialized workshops, a knocking hydraulic compensator is determined using acoustic diagnostics.
In addition, a knocking hydraulic compensator can be detected on a disassembled engine. To do this, you need to remove the valve cover and push each of the elements. Elements that easily sink will be faulty, since the lowest pressure prevails in them. The most important thing when diagnosing a malfunction is that the camshaft cam does not affect the units. It is impossible to determine the faulty element using other methods.
About the design of gas distribution mechanisms
In a simple case, the compensator is an extension of the valve heel. More precisely, the hydraulic compensator is mounted on the valve and transmits the force received from the cam. This diagram is clearly shown in the figure:
Here the compensator comes into contact with the cam
What is considered is one of the options. But there is another one, when the cam presses on the rocker arm. The rocker itself is pushed up by two different elements. On one side it will be a valve, on the other - a hydraulic compensator. The first of them moves, the second remains at the same level:
The compensator presses on the rocker from below
If the compensator is faulty, a gap will appear between the cam and the rocker arm.
Note that the lever rocker arm of the valve was not discussed above. The diagram with a lever rocker is shown below. The compensator looks different there than in cases “1” and “2”.
Previously, the timing design used a single camshaft (SOHC), and the force to the valve heels was transmitted through a lever. In order to eliminate the gap, the lever was equipped with an adjusting screw 5. It was fixed with a lock nut 6:
Timing diagram with lever rocker arms
The mechanism discussed above can be equipped with hydraulic compensators. Their device is shown in Figure “b”:
Schemes “a” and “c” correspond to the first and second cases. There shouldn't be any questions here.
Externally, the design of compensators may vary, but the principle of operation will always be the same. The main design elements are the following parts: check valve (ball), plunger spring 5 and valve spring 6. Number 3 indicates the plunger sleeve, and part 2 is the plunger.
Note that hydraulic compensators are not used in the design of the 4A-FE and 5A-FE (Toyota) engines. They are available in motors of the following series: 2S, 1NR, ZR, TR, 5M.
Main types of faults
We answer the question of how to check hydraulic compensators for functionality. It can be noted that there are four reasons for the occurrence of malfunctions:
- Increasing the size of the gaps in the areas indicated by the arrows in the photo below. Gaps are formed between the plunger and the plunger bushing. The result will be increased oil leakage. The compensator simply will not have time to “select” the thermal gap;
- In rare cases, the check valve does not close tightly. Which, at a minimum, makes it impossible to create sufficient pressure generated between the sleeve and the plunger;
- The bushing should move freely relative to the plunger. In the areas indicated in photo 3, a blockage may appear, and then the plunger pair jams;
- Clogged engine oil passages are another reason why compensators stop working.
Points 1-3 are illustrated in the photo:
The first failure always occurs as a result of abrasive wear. If you use low-quality oil, you will get the appropriate result. The second malfunction is the result of wear or clogging. The latter, by the way, is more common. Well, jamming can occur due to gradual coking or due to the appearance of deposits.
Each of the reasons received a number from 1 to 4. Next, links are made that say which reason causes this or that effect. Read carefully.
Testing process from start to finish
Let's consider the answer to the question of how to check the serviceability of hydraulic compensators in practice. You need to open the hood, start the engine and listen:
- Let's say that immediately after starting the engine increased noise appears, and after 5-6 seconds it disappears. Conclusion: the compensators are working properly, oil just leaked out of their cavity;
- At idle there is an intermittent noise. As the speed increases, the noise disappears completely. Conclusion: there is a malfunction, but it is due to the second or third reason (see above);
- When a warm engine is idling, a continuous noise may occur. As the rotation speed increases, the noise goes away. Conclusion: the cause of the malfunction that occurs is indicated under number 1;
- Similar symptoms were mentioned above. But the engine may behave differently: noise appears at high speeds and disappears at low speeds. This means that the cause of the malfunction is oil foaming;
- Let's say there is a characteristic noise from one or more valves. The effect does not depend on the rotation speed. Be aware that this malfunction can be caused by any of the reasons listed in “Chapter 2”;
- Sometimes you can hear noise in idle mode, which increases with increasing frequency up to 1500-2000 rpm, but no more. This effect is not related to the operation of hydraulic compensators.
Now we just have to figure out what causes the oil to foam. In fact, both a lack and an excess of engine oil leads to the effect. Advice: you need to add consumable fluid to the MIN mark or get rid of its excess.
Increased noise levels do not always indicate a malfunction. From some of the hydraulic compensators, if the car is left on a slope, oil may leak out completely, but the deficiency will quickly be replenished with the engine running. You can get rid of the unpleasant effect in a few seconds. Why is the engine started?
From all that has been said, a simple conclusion is drawn: you should park your car on a slope only when necessary. All experienced car owners know about this.
ORDER CHIP TUNING OF YOUR CAR RIGHT NOW!
Leave an online request for the service and we will contact you to clarify details
On older internal combustion engines, the problem of increasing changes in thermal clearances, increasing due to wear in the valve mechanism, was solved with the help of adjustments. This work was performed by a specially trained person. Valve adjustments were required every 10,000 km or due to wear. The specialists disassembled the engine and manually adjusted the valves - it must be said that this was a rather labor-intensive procedure that required special skills and qualifications from the master. Also, for this task, a specialized tool was needed - a set of probes.
Sample recommendations for repairs
Let the malfunction be caused by the reason indicated under number 1 or 2. Then the compensator must be replaced, and there can be no other options. If we talk about “reason 3”, it is usually recommended to clean the compensator, but this will require dismantling.
Four types of hydraulic compensator modules
It’s better to immediately replace the faulty module without disassembling it. The diameter of the module body does not exceed 10-15 mm, and repairs will be difficult.
If the noise of the compensators appears at high speeds, a conclusion is drawn about foaming of the oil (see above). The cause of the malfunction is then looked for like this:
- Check the oil level on a cold engine;
- If necessary, add oil or drain excess. The last step is simple to perform: instead of the dipstick, a tube from a dropper is installed, and the liquid itself is drawn out with a “pear”;
- Start the engine, gradually increase the speed;
- If the noise effect appears again, it is concluded that air enters the lubrication system through damaged parts.
In the latter case, the owner has a direct route to service. We wish you success.
It is possible to make a diagnosis indicating that it is necessary to replace the Chevrolet Niva hydraulic compensators only after removing the camshaft. Usually the first signs are knocking in the valve mechanisms, which does not stop even after the engine warms up. There is a certain amount of truth in this statement, but it is recommended to use less time-consuming methods to begin with. First of all, you need to check the oil level and its cleanliness. If the level is insufficient, serviceable hydraulic compensators are not filled with liquid, as a result of which the plunger does not rise to the required level and the rocker knocks. Dirty oil can clog narrow passages. If changing the oil does not help, then you will have to take drastic measures.
We hear a bell, but we don’t know where it is.
The owner of a VAZ-21214 complained about constant knocking in the engine. Sometimes they last a very long time, sometimes not so long, but most often they happen on a cold engine. While we were standing and talking, the knocking appeared again and the engine began to feel feverish. It seems as if he is “trotting.” The knocking continued for no more than a minute and then disappeared. The client left the car and left. We agreed with him that I would call myself when I fixed the problem.
Based on the nature of the knock, it was obvious that one of the eight hydraulic compensators was faulty. But which one!? I didn’t want to change everything, or the first one that came to hand, so I used the “First Look” sensor.
It doesn't have such a name for nothing. If we translate it literally into Russian, we get – “First Look”. So it is, the name speaks for itself! Being in the diagnostician's arsenal, it can always be used first to quickly identify a malfunction. The sensor is installed on the section of the exhaust pipe of the muffler. Based on the pressure pulsation in the exhaust system, the quality and uniformity of operation of the engine cylinders is analyzed, an ineffective or faulty cylinder is localized, and the quality of the mixture is determined (lean or rich).
Tool for replacing hydraulic compensators
It is gratifying that replacing hydraulic compensators on a Chevrolet Niva does not require any special devices. You can get by with a standard set of keys, but it is better to prepare some available tools in advance. To work you will need:
- A set of keys;
- Screwdriver flat and Phillips;
- Metal brush;
- Medical syringe;
- Wire or nylon tie.
In addition, you need to prepare 1 liter of gasoline, a rag and a gasket under the valve cover.
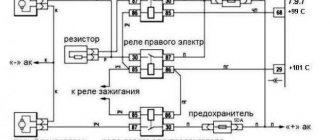
Installation of adjusting bolts on a Chevrolet Niva
New hydraulic compensators, as has already become clear, are expensive, and the guarantees that they will not knock again are minimal. It is for these reasons and because of the price dispute that adjusting bolts can be installed.
This is what the adjusting bolts look like.
The work is done the same, but you will have to adjust the valves separately and assemble the engine a little differently.
Video about replacing hydraulic compensators with bolts on a Chevrolet Niva engine
Assembly Features
- It is necessary to thoroughly clean all bolt wells.
- We mount the plates and tighten the new bushings.
- Next, tighten the bolts and install new springs with rockers.
- We install the camshaft in its place and tighten the chain. There is no need to install the oil ramp yet.
Now it is necessary to adjust the valves, and this is done in the same way as on any other car of the VAZ family.
- The valves are adjusted using a wide probe or indicator.
This is what the valve adjustment gauge looks like.
Such work is inconvenient due to the fact that adjustment is required every 10-15 thousand kilometers.
Algorithm for replacing hydraulic compensators
Although the work of replacing hydraulic compensators is classified as a service job, it is quite accessible for you to do it yourself. The most important thing is to adhere to the algorithm described below.
- The air pipe is dismantled. The valve cover is released. To do this, it is necessary to provide unobstructed access to it, as well as remove all fasteners and brackets from it.
- Remove the valve cover bolts (8 pieces).
- At this stage, it is possible to accurately determine the need to replace the HA. If, when you press the rocker, the pushers drop easily, then the hydraulic compensator is faulty. (you can use a flathead screwdriver to check by inserting it between the camshaft housing and the rocker)
- While turning the crankshaft as the engine rotates, it is necessary to align the mark of the camshaft gear with the casting on the bed body.
- By loosening the gear, the chain tensioner can be removed and recharged.
- The chain, in the same position as it was on the sprocket, is tied around it with wire or a clamp. Thus, it continues to remain in relative tension. The sprocket is removed from the shaft.
- The camshaft bed (housing) nuts are unscrewed.
- The rockers and hydraulic compensators can be dismantled without any hindrance; first, they are unscrewed with a 24mm socket,
and then removed from the occupied hole.
- New ones are installed with a tightening of 2 kgf. The assembly procedure is performed in reverse order.
Before replacing the HA, you can try rinsing the old ones by immersing them in gasoline. Sometimes this procedure significantly saves the budget.