Every year the share of cars with diesel engines is increasing. And if previously such engines were associated with commercial vehicles, now tractor engines can often be seen on small cars. Such a high popularity of diesel cars is due to low fuel consumption and high torque. Due to the turbine, the power of such cars is no less than that of gasoline cars, and the consumption is one and a half to two times lower. But you need to understand that diesel is a completely different philosophy. These internal combustion engines have their own differences and repair features. In today's article we will look at a fairly common problem - air leaks in the diesel fuel system.
Symptoms
Usually, in this situation, the engine starts well when cold, but further operation at idle raises questions. Among the characteristic symptoms are:
- Shaking and tripping of the power unit.
- Slow response to the gas pedal.
If the problem continues to be ignored, a long and difficult start-up of the internal combustion engine may occur. Sometimes the situation reaches the point where starting the car becomes completely impossible. There is too much oxygen in the system for the mixture to ignite properly.
Where does the air leak come from?
In the system of gasoline and diesel engines, there are many places where air can be sucked in:
- the intake manifold gasket does not provide a tight seal;
- throttle flanges are not sealed;
- the pipe leading from the air filter to the throttle body is damaged;
- the sealing rings on the injectors do not provide a tight seal;
- vacuum brake booster;
- vacuum hoses (vacuum hoses);
- adsorber valve;
- idle speed sensor (if equipped).
Causes of suction
There are many reasons for this problem. This:
- Rotten clamps and dried out fuel hoses. This is the most popular reason why air appears in the return line of the diesel fuel system. This problem is especially relevant for car owners with plastic hoses. Unlike brass ones, they have quick releases. Of course, replacing such a hose is much easier. However, it is the quick releases that turn out to be the most fragile in this element. As a result of vibrations, the plastic wears out and the rubber sealing rings wear out. Often a similar problem can be found on cars with a mileage of 200 thousand kilometers.
- Rusty tubes, especially at the entrance to the gas tank. The problem is relevant for cars with high mileage or for cars that have not been used for a long time (more than six months).
- Poor filter or booster pump seal.
- Violation of the tightness of the return line and the fuel injection pump drive shaft.
- Damage to the pump cover and the axis of the diesel supply control lever.
It is possible that air in the fuel system of a diesel engine (Volkswagen or another brand of car) enters through the fuel injection pump itself. However, it is better to entrust all diagnostic operations and repairs of this pump to professionals, otherwise there is a risk of incorrectly assembling the mechanism. Among the common causes of air leaks into the fuel system of a diesel engine is a poor-quality filter or its loose fit to the surface. This is the most banal option.
Note that air leaks into the fuel system of a diesel engine appear when both the direct and return branches are damaged. Due to the design features of the injection pump or engine, some of the fuel may remain in the pump, which ensures good starting. However, with further work, characteristic problems appear. The engine does not have enough fuel, and it begins to “suffocate” without it.
Testing on injection pump and hoses
Diesel fuel return
The following is done.
- All tubes supplying diesel fuel and pumping it out of the pump are removed. New hoses are installed, the return ends of which are placed in any container with diesel fuel located above the injection pump (high pressure pump).
- You need to unscrew the bolt from the drain fitting.
- Using a syringe inserted into this very fitting, pump out the air.
- Tighten the bolt and start the engine for literally 1-2 minutes.
Leave the car for 6-7 hours, do not touch it. After this, start the engine and draw the following conclusions:
- If there is a problem-free start and stable operation of the internal combustion engine, conclude that the fuel line is damaged, because after pumping out the air, fuel flows normally from the new hoses and container, there is no suction;
- If the difficulties are repeated, the engine is tripping and is unstable or does not start at all, then the problem is something else.
Pump out the air again. Lower the container with diesel fuel below the injection pump. Leave the car untouched for several hours. Start the engine and draw the following conclusions:
- with normal operation of the internal combustion engine, conclude that the pump does not suck in air, and the difficulty is apparently related to the filter;
- if the difficulty repeats, nothing has changed, it means that the fuel injection pump is clearly faulty, it is intensively sucking in air.
Pump out the air again. Now you need to clamp the hose that connects the return channel to the pump. Wait a few hours and draw the following conclusions:
- if no more problems are observed, the engine starts normally, which means the problem is in the return channel (it is clamped, as soon as you open it, air will begin to suck in);
- if the problem recurs, doubts again fall on the pump.
In a word, air can enter the diesel fuel system in different ways, from several points. And the total number of potentially dangerous “windows” will depend on the age of the car, operating conditions and much more.
Air leaks can occur both from the supply hose line and from the return channel system. The airing point may include not only the connection points, but also the surface of the hose itself. The metal part rusts, a hole is formed, from where air is sucked in.
How to check?
To make sure that the cause of unstable engine operation is air leaks, you need to visually analyze the flow of fuel into the cylinders. To do this, turn the engine with the starter for about 20-30 seconds. So we will fill the exhaust tract with gases, after which we will analyze them. If there is something wrong with the fuel system, a small amount of smoke (usually gray in color) will come out of the pipe. If the exhaust has a bluish-gray tint, it means that a large volume of oil is entering the combustion chamber.
Where can air get in?
To check for leaks in your engine, you need to understand where to look. On engines equipped with an injector, air can be sucked in in the following places:
- gasket on the cylinder head flange where the intake manifold fits;
- brake system vacuum booster housing;
- vacuum take-off hose for amplifier;
- throttle gasket;
- through nozzles with weak sealing rings;
- on the idle air control flange;
- through a jammed valve of the adsorber tank.
Worn carburetors, whose seat flange has bent due to high temperature, often allow air flow at the junction with the manifold. The second “sore” spot is the throttle valves of both chambers, which become oval as a result of wear. The suction occurs through the side gaps and causes spontaneous outflow of gasoline from the main diffuser, causing the engine to spin up to 2000 rpm at idle.
The weak link of a diesel engine is the fuel line running from the tank to the high-pressure pump. Plastic tubes and clamps lose their tightness over time and the pump, which creates a vacuum in the area, draws air through invisible cracks. It passes through the main line and is fed through the nozzles into the combustion chambers. The main problem is identifying the problem: leaky connections do not leak because the external pressure is higher than the internal pressure.
Professional diagnostic methods
The classic way to check the tightness of this system is with compressed air. To do this you will need a small amount of fuel and chalk. The last thing you need to do is rub the tubes and hoses through which the fuel moves. Next, remove the fuel intake from the tank and remove the coarse filter. Compressed air is supplied to the fuel intake at a pressure of no more than 0.5 kgf/cm2. At home, this pressure can be taken from a regular tire tube or wheel. Next, all tubes and hoses are inspected. Particular attention is paid to connection points. As practice shows, in 80 percent of cases the reason lies here. In such areas, the chalk will darken as the fuel flows out.
Please note that damage may also be of a “valve” nature. That is, air can only enter the system in one direction.
Let's consider another method. To accurately diagnose the air in the diesel fuel system, it is necessary to disconnect the injection pump from the lines and power it from another container with fuel. Usually a three-liter bottle and two meter-long durite hoses are taken. To prevent them from coming off, you also need clamps of appropriate sizes.
Prevention
In general, in 99% of cases, air enters the system due to poor quality maintenance. And, as you know, it is easier and cheaper to prevent a problem than to fix it. Therefore, a responsible driver must:
- regularly check the condition of the fuel system, change consumables and filters;
- choose high-quality filters and consumables;
- refuel with good fuel;
- change worn out elements in a timely manner - tubes, clamps;
- maintain injectors in a timely manner;
- If you suspect that the engine is not working correctly, immediately go for diagnostics.
Diagnostics and repair of fuel equipment
Sign up for a service station
What's next?
So, we disconnect the hoses from the pump and install recently purchased ones in their place. We lower their ends into a container with fuel (it is important that it is as clean as possible and without traces of water). We secure the hoses so that they do not move, and start the engine. This way we will find out which of the highways was damaged. It is advisable to replace the deformed element immediately.
At the end of the procedure, remove air from the fuel chamber of the pump. It is not recommended to simply rotate the starter for this.
Repair and maintenance of intake manifolds
A modern intake manifold is a complex part. Breakdowns also happen to it. Let's look at typical ones.
Leakage problems
This is the first problem with intake systems, as well as many other components of the car. Vibrations, changes in humidity, pressure and temperature affect rubber (paranitic, etc.) seals, of which there are quite a few in complex intake systems. Additional air may enter the mixture, the so-called “suction”.
Additional portions of oxygen deplete the mixture, the engine loses traction, and problems with idle speed appear. There may be engine ECU errors. All these symptoms indicate problems with the tightness of the intake tract.
Air leaks in the intake manifold can significantly affect the dynamic performance of the engine as a whole. After the seal is restored, engine operation returns to normal.
Gaskets for intake and exhaust manifolds of VAZ 2106
Intake manifold contamination
The intake tract must be checked from time to time for deposits on the walls. A problem like this can have a significant impact on the dynamics of the car. The manifold becomes clogged especially often on engines with an exhaust gas recirculation system. In such cases, it is necessary to disassemble and clean the device with a special compound.
Deposits on the walls of the intake manifold elements
Deformations and mechanical damage to the housing
Plastic and aluminum are widely used for the production of collectors, and these materials, as is known, can be deformed due to exposure to high temperatures. Plastic cracks and dries out over time. Aluminum manifolds may burst due to vibrations. Elements with severely damaged geometry must be replaced. Aluminum parts can be welded using argon arc welding.
Increased air temperature in the intake manifold
The causes of this problem may be:
- long-term idling in conditions of high air temperature (for example, in traffic jams);
- malfunctions of the cooling system and an increase in the overall engine temperature;
- poor ventilation of the engine compartment due to a clogged radiator;
- erroneous reading of the temperature sensor in the intake manifold;
- errors in the control unit firmware.
The solution is to check the cooling system components and diagnose electronic systems.
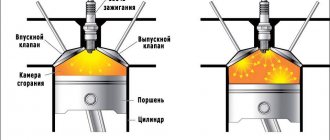
Popping sounds in the intake manifold
During ignition of the fuel in the engine cylinders, tightness conditions must be observed (both valves must be tightly closed). If the fuel is ignited with the intake valve open or slightly open, the fuel-air mixture may ignite in the manifold itself, resulting in a characteristic “popping” sound. Such breakdowns are quite dangerous - they can lead to significant damage.
We recommend: Do-it-yourself replacement of brake discs on a VAZ 2110
The causes of the malfunction may be:
- violation of the ignition system;
- incorrectly configured gas distribution mechanism;
- violations of the tightness of the intake valves;
- problems with the formation of the air-fuel mixture.
In such cases, it is necessary to conduct a comprehensive engine diagnostics to identify the causes of the popping noises.
Let's consider the procedure for replacing the intake manifold gasket using the example of a 2022 Chevrolet Aveo engine.
1. Before starting work, turn off the power to the vehicle by removing the negative terminal of the battery.
2. Remove the windshield wiper arms (only necessary in the case of a specific engine).
3. Remove the plastic latch clamps 1 and screws 2, and then remove the air intake grille 3.
4. Drain the cooling system by unscrewing the radiator drain plug 4.
5. Remove the air duct of the air filter 5 by unscrewing the screws of the clamps 6.
6. Remove the forced crankcase ventilation tube 7.
7. Disconnect throttle communications 8-11, remove throttle 12 itself by unscrewing screws 13.
8. Disconnect brake booster pipe 14.
9. Unscrew screws 16,17 of the manifold bracket, remove bracket 15.
10. Remove the fuel injector guide, disconnect the throttle cooling hose 19, unscrew the manifold bolts 18.
11. Move manifold 20 to the side, carefully remove gasket 21.
12. Clean and degrease the seats for the new gasket and install it.
13. Reassemble the intake system components in the reverse order of disassembly.
Pay attention to the order and tightening force of the units being repaired. Tighten the threaded connections gradually in order from the center to the edge of the part, or crosswise.
It is not recommended to independently repair complex mechanical components and elements of the fuel system.
Proper operation of the intake manifold guarantees long-term engine operation. With minimal knowledge and a set of necessary tools, it is possible to carry out routine maintenance or minor repairs yourself. With complex parts and electronics, it is better to contact a service center.
How to properly get rid of air in the system?
No matter how hard we try to carefully replace the old hose with a new one, there will still be air in the system. But how to remove it correctly? There are several ways to pump air in a diesel fuel system:
- A container with diesel fuel is being prepared. It should be located above the level where the pump is fixed. Then we find an area where there is a “return” fitting for draining fuel. This area should be washed thoroughly to prevent dirt from entering (the diesel fuel system is very sensitive to the slightest specks). Next, the fitting bolt is unscrewed and air is pumped out through the hole. You can pump it out with a vacuum pump (a syringe will also work). The operation is carried out until the fuel itself begins to flow. After this, the bolt is screwed into place and the engine starts.
- The fuel supply hose is removed from the injection pump and the airy diesel is sucked out until it begins to flow in a dense stream. Afterwards, the hose is put on the fuel injection pump fitting and crimped with a clamp. Next, unscrew the screw of the return line fitting. There is no need to pump out the air - it will go away on its own. Next, start the engine and let it run for several minutes to finally get rid of air particles.
- The filter mounting bolt is unscrewed. The last element is not removed. Next, you need to pour some fuel into the bolt hole. After this, the bolt is screwed into place. Loosen the fitting nut on the second or first injector. Then you need to start the engine. when diesel starts spraying out from under the injector nuts, they need to be screwed back in. This method is relevant if the cause of the leak is a loose fit of the filter itself.
These are the main ways to remove air from the system. Please note that air may appear even if the fuel lines and other components are in good condition. It is enough to drive a certain distance on a “dry” tank. The air will be automatically sucked in by the pump and then supplied to the nozzles. You shouldn't let your car get into this state. It is advisable to refuel the car no later than the lamp on the instrument panel comes on.
How to bleed the fuel system: additional tips
Additional tips that will help keep the fuel system in working order include the following:
- Clean the threads of the drain plug in the vehicle's fuel tank. In the process, do not forget to substitute a basin or bucket. If you clean the thread properly, it will then unscrew well. Also, do not forget to change the gaskets regularly to prevent leaks.
- Try to keep the tank full. During the cold season, condensation forms in the vehicle; if there is free space in the fuel tank, over time it mixes with the fuel. There is another danger that is directly related to the quality of domestic roads. If you drive into a hole with a half-empty tank, the fuel may swing in one direction. Then the pump can supply air instead of diesel fuel.
- Try to fill with high-quality brands of diesel fuel. Otherwise, the diesel fuel composition will contain a large amount of foreign substances that certainly do not have a positive effect on the components of the fuel system.
These are the usual steps to bleed the fuel system in a diesel engine and significantly increase its service life in your vehicle.
Could there be leaks in other places?
It should not be ruled out that air can penetrate through other places into the engine. So, after diagnosing the fuel hoses, you should pay attention to the intake manifold.
Thus, oxygen that is not taken into account by sensors (mass air flow or absolute pressure) penetrates into the engine along with the fuel, which is the cause of unstable operation of the internal combustion engine. Among the reasons, experts highlight:
- Overheating, as a result of which the tightness of the gaskets is disrupted.
- Mechanical impact (for example, during careless repairs).
- Exposure to carburetor cleaners. This is a very caustic product that not only cleans dirt in the intake manifold, but also corrodes all rubber elements, including the sealant.
The most difficult thing to find is the leak between the intake manifold and the engine cylinder head. Oxygen can also enter due to loose injector seals or damaged air ducts. Let's consider what methods can be used to detect a problem if it does not arise in the fuel line:
- When oxygen enters the path after the flow meter, you should unscrew the air pipe with the sensor from the filter housing and start the engine. In this case, the part with the sensor is covered with your hand. If there is no suction, the engine should stall. If the engine continues to run, it means there is air in the diesel fuel system (Renault Kangu is no exception). In this case, the “sick” area will emit a characteristic hissing sound. The location of air leaks into the fuel system of a diesel engine must be found by ear.
- The problem can be diagnosed by spraying likely areas with mixtures such as VD-40. It is necessary to spray on the rubber pipe from the flow meter to the valve cover. Also spray the place where the block head connects to the intake manifold. Another area is the injector gaskets.
Emission testing
Exhaust check
A method invented a long time ago. It is used by most experienced diesel drivers. The essence of the method comes down to the following.
- The engine is cranked by the starter for one minute, but does not start.
- The muffler is checked at the same time.
If smoke comes out of it, then this indicates fuel is entering the cylinders, since there is no such thing as combustible smoke. If there is diesel fuel, it means there is no air in the system.
The smoke may have a grayish tint, there may be little or much of it, but this does not change the essence. On the other hand, it rarely happens that fuel does not enter the cylinders, but smoke continues to flow. In this case, you need to pay attention to the color of the smoke. If it is blue, this indicates that oil has entered the internal combustion engine cylinders.
Thus, exhaust testing boils down to the following: there is smoke, good, there is no air lock, there is no smoke - definitely, there is air in the system.
Troubleshooting
You can easily and clearly detect air leaks in the intake manifold using a smoke generator.
The most accessible way to find air leaks in the intake manifold is a visual inspection. Cracks and breaks in air hoses can be seen with the naked eye. You can also check how tightly the parts are connected to each other. It often happens that during repairs, for example, the nuts securing the carburetor or other components were not properly tightened. If there are no visible causes of malfunctions, then spraying “Quick Start” type compositions made on the basis of ether from a can along the joints of parts is very effective. The procedure must be carried out with the engine running. Ether that gets into the manifold through the cracks will cause changes in the operation of the motor - its speed should increase briefly. Finally, the question of how to detect air leaks in the intake manifold is easy to resolve if you have a smoke generator. With its help, finding places of leakage does not present any special problems. Having “pumped” the intake tract with smoke, you can visually observe where the integrity of the intake system is compromised - in this case, it is better to use a blue lamp (flashlight) - in its light it becomes more noticeable.