Gasoline is a product of petroleum distillation and is a liquid mixture of hydrocarbons. Because it is a class of compounds and not a specific mixture, its composition can vary widely. Therefore, the same volume can have different masses.
The density of gasoline is the ratio of mass to volume measured at a certain temperature. According to the existing GOST R 32513-2013, the temperature for measuring density is set at 15 o C. The previous standard GOST 305-82 considered the measurement temperature to be 20 o C.
The most important characteristic of gasoline for users is the octane number (a characteristic indicating the degree of detonation resistance).
In Russia, several types of gasoline are used with different octane numbers:
AI-80 – fuel for older brands of trucks, motorcycles and chainsaws, municipal and agricultural equipment. Now the production of these cars has been discontinued and it is difficult to find gasoline of this brand at gas stations.
AI-92 is a fuel for passenger car engines. It looks transparent and clean, density at 15o C is 725-780 kg/m3.
AI-95 is a fuel for foreign cars. During its production, manufacturers used technologies that increased its octane number and, accordingly, its performance properties. Its density is 750 +/- 5 kg/m3 at a temperature of 15o C.
AI-100 is a new type of fuel that is sold at some gas stations. This is a product with special EcTo additives (Environmentally friendly fuel). The presence of additives increases the performance properties of gasoline. Due to this, the price is also high. Its density ranges from 725 to 750 kg/m3 at a temperature of 15o C.
Gasoline density: what is it?
The density of gasoline quantifies the mass of a flammable substance with a hydrocarbon composition in the total volume of fuel liquid. The nominal unit of fuel volume is taken to be 1 kg/l. The density of gasoline is expressed in kg/m3. In simple terms, the characteristic expresses the specific gravity of gasoline in a liquid substance.
Since gasoline, unlike kerosene, changes its properties with decreasing temperature, to correctly determine the density it is necessary to record the temperature at which the study takes place. Russian GOSTs set this temperature at +15 degrees Celsius; previously, regulatory documents were oriented at +20 degrees. At the moment, measurements taking place at a temperature of +15 degrees are considered valid.
The same volume of gasoline can have different specific gravity of fuel. The lower the density of gasoline, the smaller the mass of the substance, while the volume remains the same.
The density of gasoline depends on what kind of oil was used in production and how it was processed.
The higher the density of the fuel, the higher its efficiency and the better its interaction with the vehicle engine. Any car enthusiast has noticed that when driving on flat terrain, the engine runs without interruption, gasoline burns quickly, ensuring maximum energy efficiency. However, when driving into mountainous areas, uphill, the engine quickly heats up and begins to “spoil.” And it's not just a matter of gravity. During the rise, the pressure inside the working chamber changes, and the gasoline mixture begins to lose its density, igniting more slowly.
How much does 1 liter of diesel fuel weigh?
But these are facts, and what can you learn about gasoline if you look at the numbers. For example, how much does a liter of gasoline weigh? And can it be measured? Of course, knowing these numbers can open up a completely different way of looking at this liquid.
As you know, gasoline is divided into several categories, namely: A-76, A-80, A-92, A-95 and A-98. It should be noted that the weight of one liter of gasoline may differ in each case. So, we know some data on the weight of liquid in a volume of one liter, each brand of gasoline.
- On average, the weight of one liter of A-76 gasoline is 0.730 kg. But this is at a temperature of +20°C.
- On average, the weight of one liter of A-80 gasoline is 0.730 kg.
- On average, the weight of one liter of A-92 gasoline is 0.760 kg.
- On average, the weight of one liter of A-95 gasoline is 0.750 kg.
- On average, the weight of one liter of A-98 gasoline is 0.780 kg.
So, we found out how much a liter of gasoline for each of the above brands will weigh. But another characteristic of gasoline is also known. Thus, the weight of one liter of gasoline will directly depend on the ambient temperature. Moreover, the higher the temperature on the thermometer, the lighter the weight of a liter of gasoline. Some laboratories carry out special measurements of gasoline. For example, at a temperature of +16°C, the density of A-92 gasoline is 0.765 g/l. If we start from the measurements given above, we get the weight of one liter of gasoline heavier. Why? The whole thing depends on the ambient temperature. For this reason, the weight may vary in each individual measurement. It is a completely different matter if such measurements are carried out, therefore, as the temperature increases or decreases. Then we will be able to know the exact density of gasoline.
But today no one buys gasoline one liter at a time. For example, some people immediately fill up the full tank of their car. At the same time, the appetite of a particular car varies. Others buy gasoline in cans. For example, if you have a canister with a capacity of 19 liters, then you can accurately calculate the weight of an empty canister and a full one. A canister filled with gasoline weighs 16.325 kilograms. Accordingly, an empty canister without contents has a mass of 2,550 kilograms. Moreover, if we assume that one liter weighs 0.725 kg, then a simple calculation should be performed. From the sum of the weight of the gasoline canister (16.325 kg), subtract the sum of the empty canister (2.550 kg). As a result, we get the amount of 13.775 kg of gasoline in a nineteen-liter canister. You can easily check this amount by making the following calculation:
13.775 kg / - 0.725 kg = 19 liters.
So, using such mathematical operations, you can accurately calculate the mass of gasoline in a particular canister.
But someone might object, why convert the unit of measurement liter into kilograms or even tons? In fact, this is not done easily for fun. For a large number of consumers of fuels and lubricants, this is one of the important tasks, and especially for accountants of a particular enterprise. In the process of accounting for the storage of either bulk or liquid substances, in our case gasoline, there is often a need for conversion. So, converting volume into mass is extremely important and even necessary in order to make it easier to fill out reporting documentation, financial calculations, and also make payments for wholesale fuel sales. This is mainly due to the fact that the generally accepted form of supply of fuel and lubricants is a tank, which has a fixed capacity. But, accounting is always carried out in units of mass! Moreover, if gasoline is sold wholesale, it is much easier to count in tons. This is how arithmetic works out when calculating the weight of gasoline!
To begin with, I would like to clarify what is meant by specific gravity (hereinafter referred to as SG) in physics and chemistry, and only then move on to the specific gravity of diesel fuel or, as it is also called, the specific gravity of diesel fuel.
Let's go over the theory.
Density of AI-92 gasoline
AI-92 is a fairly high quality gasoline with an octane number of 92, determined by a research method. This is the most popular gasoline labeling at Russian gas stations. Has strong anti-knock properties.
The initial temperature is taken to be +15 degrees. Under such conditions, the density of AI-92 gasoline is 740-770 kg/m3.
Please note that the specific gravity of gasoline is not related to the octane number. The octane number directly depends on the chemical composition of the liquid; the density depends on external conditions and changes at different temperatures and pressure. Fuel with a low number, such as AI-80, can have a high density, and vice versa. The best way to determine fuel density is an independent measurement.
AI 76 technical specifications
AI 76 gasoline was produced in accordance with GOST 2084 and had an octane number of at least 76. This grade of gasoline was widely used, since car engines of that time had a fairly simple design and did not have increased requirements for fuel quality. This brand of gasoline was widely used for both passenger cars and trucks and agricultural machinery. At the end of the 90s, with the development of automotive technology, AI 80 gasoline replaced AI 76 gasoline.
Density of AI-95 gasoline
The second most common brand of gasoline with increased resistance to chemical spontaneous combustion. Gasoline is of excellent quality. The engines of most modern vehicles can only be fueled with gasoline with excellent physical properties, such as AI-95 and higher.
The addition of aromatic additives to AI-95 improves the technical characteristics of the liquid, making it safe for the engine and internal fuel lines. At a temperature of +15 degrees, the composition demonstrates a density in the range from 745 to 755 kg/m3.
Formulas for calculating density, weight and volume of diesel fuel
To calculate the density, mass and volumetric amount of diesel fuel, an online calculator or calculation formulas are used. To calculate the parameters, it is necessary to take into account the ambient temperature and specify the type of fuel poured into the tank. When calculating, the correction factor and the difference in temperature (between measured and reference) are taken into account. The result obtained is approximate, since the measuring equipment has an error. Accurate data can only be determined through laboratory analysis.
Formula for determining the weight of diesel engines
To determine the weight, an equation of the form m=p*V is used, where:
- m—calculated mass (in kg or t);
- p—density reduced to temperature;
- V is the volume of the tank in which fuel is stored.
To determine capacity, you need to measure the dimensions of the container and then calculate the volume using formulas. At oil depots, tanks are used that have marks on them indicating that the tank is completely filled. On the outside of the tank there is a factory marking plate on which the volume and measurement error are indicated.
Formula for determining the volume of diesel fuel
To determine the volume, an equation of the form V=m/p is used, where:
- m - declared mass of cargo (in kg or t);
- p—density reduced to temperature;
- V is the volume of the tank in which fuel is stored.
The weight is indicated in the accompanying documents for the cargo. The attached documentation must contain a section indicating the type of fuel delivered. If the paragraph is missing, then the density is calculated using a hydrometer and correction factors (to determine the weight at a standard temperature of 20°C).
Formula for determining density of diesel fuel
To determine the density, an equation of the form p=m/V is used, where:
- m - declared mass of cargo (in kg or t);
- p—density reduced to temperature;
- V is the volume of the fuel tank.
The weight is determined from the accompanying documents or by weighing the tank truck or other container (you need to know the weight of the empty container or empty vehicle). To calculate the volume, a mark placed inside the container is used. The capacity can be checked by draining the liquid into a verified reservoir. Then the density is determined, which is reduced to reference values by summing or subtracting a correction factor multiplied by the temperature difference.
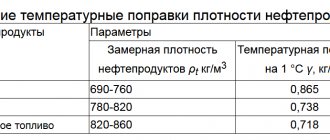
Density of gasoline: table of densities according to GOST
The density of a flammable substance is determined by regulatory documents, the main one of which is GOST 32513-2013 dated November 22, 2013. This standard describes the key properties of gasoline that affect its performance, including density, octane number, the presence of sulfur and lead in the composition, and a description of acceptable additives.
In addition, the volume of fuel produced for purchase by foreign enterprises must comply with the requirements of the international Euro-5 standard. This format involves assessing the density of gasoline at a temperature of +20 degrees, and also includes an assessment of the safety and environmental friendliness of the composition.
Adjustment of the ratio of individual components of the gasoline mixture is also carried out according to GOST standards. For example, the hydrocarbon composition is regulated by GOST-31872. Exceeding the permissible values for olefins, paraffins and saturated alicyclic hydrocarbons automatically leads to the release of hydrocarbons during the combustion of gasoline in the engine.
It has been determined through research that hydrocarbons having a branched network with up to 4 C atoms have a higher density than compounds of cyclic hydrocarbons with benzene rings. All together determines the limits within which the density of gasoline lies.
We present a simplified version of the reference table, which numerically expresses the density for mass brands of gasoline in Russia.
Table 1
Density of gasoline according to GOST
| Name | Density in kg/m3 at a temperature of +15 C |
| AI-92 | 760 |
| AI-95 | 750 |
| AI-98 | 780 |
| AI-95 Premium | 725-780 |
| AI-98 Super | 725-780 |
The most expensive of the existing classes of gasoline, AI-100, has a maximum octane number and improved characteristics due to the presence of ECTO additives. The brand has its own density, the values are between 725 and 750 kg/m3.
Features of converting gasoline of different brands from liters to tons
To correctly carry out the calculation, you need to know the density values of the required brand of petroleum product based on the table. It is best, of course, to take a fuel sample and measure the density of the fuel at a set temperature according to current standards.
On average, the density of fuel at 20 ºС is 0.75 g/l. Using the directory data and performing a simple calculation, we find that the volume of one ton of gasoline ranges from 1282 to 1429 liters.
To perform more accurate calculations, it is necessary to correct for temperature, because The density according to the standard in the reference books is indicated taking into account the temperature from plus 15 to plus 20 ºС. If the temperature is outside this range, a temperature correction must be taken into account.
Hydrocarbon Density
| Fuel | Density at 20 ºС, g/cm3 |
| Oil | from 0.74 to 0.97 |
| Jet fuel | from 0.76 to 0.84 |
| Automotive fuel | from 0.71 to 0.76 |
| Engine oil | from 0.88 to 0.94 |
| Aviation fuel | from 0.73 to 0.75 |
| Diesel fuel | from 0.80 to 0.85 |
| Fuel oil | from 0.92 to 0.99 |
To accurately calculate the hydrocarbon density using these data at a given temperature, you will need average temperature correction data:
| Density at 20oC | Correction for temperature by 1oC | Density at 20oC | Correction for temperature by 1oC |
| from 0.650 to 0.659 | 0,962 * 10-3 | from 0.830 to 0.839 | 0,725 * 10-3 |
| from 0.660 to 0.669 | 0,949 * 10-3 | from 0.840 to 0.849 | 0,712 * 10-3 |
| from 0.670 to 0.679 | 0,936 * 10-3 | from 0.850 to 0.859 | 0,699 * 10-3 |
| from 0.680 to 0.689 | 0,925 * 10-3 | from 0.860 to 0.869 | 0,686 * 10-3 |
| from 0.690 to 0.699 | 0,910 * 10-3 | from 0.870 to 0.879 | 0,673 * 10-3 |
| from 0.700 to 0.709 | 0,897 * 10-3 | from 0.880 to 0.889 | 0,660 * 10-3 |
| from 0.710 to 0.719 | 0,884 * 10-3 | from 0.890 to 0.899 | 0,647 * 10-3 |
| from 0.720 to 0.729 | 0,870 * 10-3 | from 0.900 to 0.909 | 0,633 * 10-3 |
| from 0.730 to 0.739 | 0,857 * 10-3 | from 0.910 to 0.919 | 0,620 * 10-3 |
| from 0.740 to 0.749 | 0,844 * 10-3 | from 0.920 to 0.929 | 0,607 * 10-3 |
| from 0.750 to 0.759 | 0,831 * 10-3 | from 0.930 to 0.939 | 0,594 * 10-3 |
| from 0.760 to 0.769 | 0,818 * 10-3 | from 0.940 to 0.949 | 0,581 * 10-3 |
| from 0.770 to 0.779 | 0,805 * 10-3 | from 0.950 to 0.959 | 0,567 * 10-3 |
| from 0.780 to 0.789 | 0,792 * 10-3 | from 0.960 to 0.969 | 0,554 * 10-3 |
| from 0.790 to 0.799 | 0,778 * 10-3 | from 0.970 to 0.979 | 0,541 * 10-3 |
| from 0.800 to 0.809 | 0,765 * 10-3 | from 0.980 to 0.989 | 0,528 * 10-3 |
| from 0.810 to 0.819 | 0,752 * 10-3 | from 0.990 to 1.000 | 0,515 * 10-3 |
| from 0.820 to 0.829 | 0,738 * 10-3 |
How to count:
- From the gasoline passport we take the density of the fuel at a temperature of plus 20 oC.
- Determine the average temperature of the fuel in the gas tank.
- We calculate the difference between plus 20 oC and the average fuel temperature.
- Using the temperature correction column, we find a correction of 1oC, which corresponds to the density of the selected fuel at plus 20oC.
- We multiply the temperature correction by the temperature difference.
- We subtract the number obtained in point 5 from the density value at plus 20 oC, if the average temperature of the fuel in the gas tank is higher than plus 20 oC. Or we add this number if the fuel temperature is below plus 20 oC.
For example, the density of gasoline at plus 20 oC from the gasoline passport is 0.801 g/cm3. The temperature of the fuel in the gas tank is plus 25 oC. From the table we take the density of the fuel at a given temperature. We get:
- Temperature difference: 25 oC – 20 oC = 5 oC.
- The temperature correction per 1 oC from the table for a density of 0.801 g/cm3 is equal to 0.765 * 10-3 g/cm3.
- We calculate the correction for temperature by 5 oC: 0.765 * 10-3 * 5 = 0.003825 g/cm3, or approximately 0.0038 g/cm3.
- We determine the required fuel density at a temperature of plus 25 oC (we subtract the correction, since the temperature of the fuel in the gas tank is higher than plus 20 oC): 0.801 - 0.0038 = 0.7972 g/cm3.
The question of how to correctly convert liters of gasoline into tons turned out to be not too difficult.
Gasoline density: how to measure
Measuring the density of gasoline must take place under standardized laboratory conditions and must be done at an exact temperature of +15 degrees. A change in the thermal value by 1 degree already gives a noticeable error in determining the specific gravity of the fuel.
There are special instruments that are used to measure various indicators of petroleum products, including temperature and density. These include an oil densimeter and a hydrometer. Researchers in physics often use the latter.
A hydrometer is an elongated narrow device with a scale printed on the outside. The meter is lowered into a vessel filled with gasoline. It is necessary to ensure that oxygen bubbles do not form at the surface of the device. If they have formed, the hydrometer is rotated until they completely disappear. The calculation is carried out based on the volume of fuel displaced by the tool. The graduation of the scale allows you to set the exact density value.
Calculating the density of gasoline at home is possible, but the results may have a significant error, depending on the temperature of the liquid at the time of the study. The process uses sterile containers made from chemically resistant components with a volume scale printed on the outside. First, the mass of the container is determined, which will then be subtracted from the total result.
Exactly 100 ml of fuel is poured into the vessel. The container containing the liquid is weighed and the mass of the container is subtracted. The resulting number is divided by the volume of fuel. This method of calculation is used by motorists who doubt the quality of the product supplied to the gas station. An unreasonably high fuel consumption may indirectly indicate a discrepancy between the quality of fuel and the documentation. Therefore, it is important to trust car refueling only to trusted points that value their reputation. The problem is especially relevant for transport and logistics companies, in whose budget the cost of fuel and lubricants is one of the main financial indicators.
#Petrol
A clear example of misunderstandings related to counting
On a warm day with an air temperature of 200C, a fuel truck poured 10 tons of diesel fuel into the underground tank of a gas station. The actual density of the product was 0.84 g/cm3 and the volume was 11950 liters.
After several hours of the fuel being in the indicated container, its temperature dropped to 40C. This led to a change in the density of the fuel: it increased by 0.0112 g/cm3. Therefore, the original volume from 11950 liters decreased to 11750 liters. That is, 200 liters.
Therefore, in practice, fuel shrinkage is calculated using the simplified formula “1 liter x 1 ton x 1 degree”. This will make it possible to roughly calculate how much the volume of fuel will change when its temperature, and therefore density, changes.
Information about the beginning of the transition to off-season and winter diesel fuel
Information about the beginning of the transition to off-season and winter diesel fuel.
Changes in the service network for liter and ruble program cards:
Changes in the ruble program card service network:
St. Petersburg, Leningrad, Novgorod, Pskov, Murmansk, Tver regions, Republic of Karelia.
PJSC NK "Rosneft" launched into industrial production a unique diesel fuel hydrotreating catalyst
The company announced the successful testing of the first batch of catalysts of its own production, intended for the hydrotreating of diesel fuel.
The crew of the ROSNEFT team won the title of Russian champion in road racing
At the Moscow Raceway autodrome, the 6th stage of the Russian Circuit Racing Series (RSCS) successfully ended for the LADA Sport ROSNEFT team.
Bashneft has started industrial production of the "hundredth"
ANK Bashneft, one of the divisions of PJSC NK Rosneft, announced the start of production of gasoline with an octane rating of 100 in industrial quantities.
2007-2019 © RusPetrol Company
Reproduction of site materials is permitted with the consent of the owner