Technical description and interpretation of error P0030
This diagnostic trouble code (DTC) is a generic code. The P0030 code is considered a common code because it applies to all makes and models of vehicles. Although the specific repair steps may vary slightly depending on the model.
In cars, heated oxygen sensors are used to determine the oxygen content in the exhaust system before and after the catalytic converters. They use feedback to adjust the fuel system. To maintain an optimal air-fuel mixture ratio of 14.7:1.
Oxygen sensors use a heated circuit to heat the sensor for faster feedback. The oxygen sensor may use three or four wires depending on the vehicle.
Two are typically used for feedback to the powertrain control module (PCM). And the other wires are intended for the heater and powering the heated circuit. Three-wire sensors are usually grounded through the exhaust system. And four-wire ones have a separate ground wire.
Code P0030 refers to the sensor upstream of the Bank 1 catalytic converter, which is located on the #1 cylinder side of the engine. The error means that the problem with the HO₂S sensor heating element has not been resolved. This code is triggered when the sensor takes too long to heat up.
Spark plugs, BB wires, coil
If a VAZ-2114 car stalls, the “check” is on, or the engine “troubles” at idle, you need to pay attention to the ignition system. The main elements are spark plugs and high-voltage wires. Often on domestic cars there is a breakdown of spark plugs or wires. It is necessary to check these elements for serviceability and replace if necessary. The best way to check is to install a pre-made set of spark plugs or wires.
This way we can narrow down our search. If even one spark plug is faulty, it is better to replace the entire set. Otherwise, there is a high probability that the breakdown will happen again, only on a different cylinder. It is also recommended to check the spark plug gap between the central and side electrodes. Over time, this gap increases. The normal value should not exceed 1.3 millimeters. If the gap is larger, it can be corrected by bending the side electrode closer to the central one. If the distance between the electrodes is too large, a spark is difficult to form. Part of the fuel mixture will simply go into the air. Typically, the service life of spark plugs is 20 thousand kilometers. Some people install iridium ones because they last longer. But as motorists say, there is no point in overpaying. The characteristics of the internal combustion engine will remain the same, and the cost of such spark plugs is equivalent to three or four sets of regular ones, which are no worse.
Less often on a VAZ, the ignition coil itself fails. At the same time, the “check engine” lamp lights up on the instrument panel. The engine may stall, start poorly, or stall. The coil cannot be repaired and must be replaced completely with a new one. As for the wires, you can check them by measuring the resistance.
Symptoms of malfunction
The main driver symptom of P0030 is the MIL (Malfunction Indicator Light) illumination. It is also called Check engine or simply “check light”.
They can also appear as:
- The “Check engine” warning light on the control panel will light up (the code will be stored in the ECM memory as a malfunction).
- In some cases, the engine control module (ECM) may put the vehicle into limp mode.
- Sometimes there may be no symptoms despite a stored DTC.
If trouble code P0030 appears, the vehicle may continue to drive, but the problem must be corrected as soon as possible. To prevent potential problems such as sensor circuit failure and increased fuel consumption. If the problem is ignored for a long time, unstable operation of the engine is possible, as well as damage to other components.
The “check” light is on for the VAZ-2114: possible causes and solutions to the problem
After self-diagnosis of errors and elimination of their causes on a carburetor or injection engine, a malfunction message may remain on the standard panel. If the problem has been deleted, this means that the code combination remains in memory. We'll look at the description of the faults below, and now we'll tell you how to remove the code from memory. To remove it after testing the device, when VAZ 2114 errors appear, the codes themselves must be written down. After this, the daily mileage reset button is pressed again, this will clear the fault from the control unit’s memory.
Resetting the "Check Engine" error
It often happens that the instrument panel 2114 8 or 16 valves displays a check error - engine malfunction, the orange icon is on. Self-diagnosis does not always allow you to accurately check and determine how to fix such a problem. To fix the problem and find a solution, you should perform more detailed diagnostics of the car using a computer and additional equipment. Perhaps, during diagnostics, an unknown error indicates a malfunction in the microprocessor, on-board network or sensors. After the problem is fixed, the receipt may remain.
The "Check Engine" indicator indicates a problem with the engine.
How to reset the fault code:
How to Troubleshoot or Reset Trouble Code P0030
Some suggested steps to troubleshoot and fix error code P0030:
- Clear error codes from the car's computer memory.
- Test drive the vehicle to see if the P0030 code appears again.
- Perform a visual inspection and, if necessary, repair or replace damaged electrical wires.
- Check the grounding and correct the problem if necessary.
- If there is a problem with the PCM, reprogram or replace the engine control module.
Additional comments for troubleshooting P0304
To properly diagnose a P0304 trouble code, a mechanic will need an advanced scanner that will not only read stored trouble codes, but also view sensor readings in real time. This data can help determine the root cause of the error.
The recommended service interval for replacing spark plugs is usually indicated in the vehicle's service book. Worn or damaged spark plugs are one of the most common causes of cylinder misfire, especially in high-mileage vehicles. If the vehicle is equipped with an ignition distributor with a cap and slider, these must also be replaced according to the vehicle manufacturer's recommendations. These components are mechanical and wear out over time. Spark plug wires are usually replaced when the spark plugs themselves are replaced.
Newer vehicles may be equipped with ignition coils, which typically last longer than the above components. To quickly determine whether the problem is a faulty ignition wire or coil, you must move the wire and/or ignition coil to a different cylinder. If the error code appears again, it is a sign that a worn or damaged ignition wire and/or coil is causing the cylinder to misfire.
Diagnosis and problem solving
Trouble P0030 can only be caused by the oxygen sensor heater circuit or the oxygen sensor itself. Diagnostics usually begins with checking the sensor wiring. Typically the heated oxygen sensor comes with four wires.
Two wires go directly to the heater circuit, and the other two are for powering and grounding the sensor. You may need a wiring diagram for your car. To be sure you are testing the correct set of wires.
Wiring check
Test the heater circuit using a digital multimeter or volt-ohmmeter. Consult your vehicle's wiring diagram to determine the exact pinout of the ground connector.
The reading should be close to the battery voltage. If this is not the case, then there is most likely a problem with the sensor's power supply.
It is also necessary to check the grounding. To do this, you need to connect the positive terminal of the battery to the red wire of the multimeter. And the black wire to ground to check the grounding of the circuit. The result should be 12V, if not then this indicates a grounding problem at the sensor.
Sensor check
If the power and ground are ok, then the next option is to check the sensor heating element. To determine if it has an open circuit or high resistance.
Set the volt-ohm meter to Ohm scale, check the resistance of the heater circuit using the electrical diagram as a reference.
Make sure you have disconnected the O₂ sensor. The heater circuit inside the sensor should have little resistance. Exceeding the limit value indicates a break in the heating part. Therefore, the oxygen sensor will have to be replaced.
Oxygen sensor
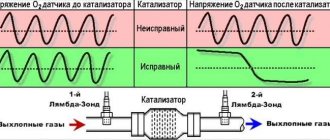
This is one of the most common reasons why the “check” light is on on the VAZ-2114. All Ladas of this model leave the factory with a catalyst. As a result, an oxygen sensor is needed for its proper operation. The ECU uses it to determine which ignition timing to set next, as well as the composition of the mixture.
If the sensor stops providing information or sends incorrect data, the ECU will take average values as a basis, and a “check” will light up on the instrument panel. What is the solution to this problem? Many people simply place a fake one. The best option is to install a mechanical blende. It screws into the standard hole and simulates the operation of a lambda probe. The ECU constantly receives the same, normal lambda value. Such a sensor will no longer be able to break, since it has a special coating.
On which cars is this problem most common?
The problem with code P0030 can occur on different machines, but there are always statistics on which brands this error occurs more often. Here is a list of some of them:
- Acura
- Audi (Audi a4, Audi q5)
- BMW (BMW X5, E90)
- Chery (Chery Tiggo, Fora)
- Chevrolet (Chevrolet Aveo, Captiva, Cruz, Lacetti, Malibu, Trailblazer)
- Citroen (Citroen Berlingo)
- Daewoo (Daewoo Matiz)
- Dodge
- Ford (Ford Mondeo, Fiesta, Focus, Fusion)
- Geely
- Honda
- Hyundai (Hyundai Solaris, Elantra)
- Kia (Kia Picanto, Rio, Sid, Spectra, Sportage, Cerato)
- Mazda (Mazda 3, Mazda 6, Mazda cx7)
- Mercedes
- Nissan (Nissan Pathfinder)
- Opel (Opel Antara, Astra, Vectra, Corsa)
- Peugeot (Peugeot 308, Partner)
- Porsche (Porsche Cayenne)
- Saturn
- Skoda (Skoda Octavia, Superb, Fabia)
- Subaru (Subaru Outback, Impreza, Legacy, Forester)
- Suzuki (Suzuki Grand Vitara)
- Toyota
- Volkswagen (Volkswagen Golf, Jetta, Passat, Polo Sedan, Touareg, Tiguan)
- Volvo (Volvo s80, xc90)
- VAZ 2107, 2112, 2113, 2114, 2115
- Lada Granta, Kalina, Niva, Priora
- UAZ Bukhanka, Patriot, 409
With fault code P0030, you can sometimes encounter other errors. The most common ones are: P0031, P0036, P0037, P0050, P0057, P0102, P0130, P0134, P0135, P0141, P0341, P0343, P2101, P2118, P2251, P2626.
Algorithm for checking elements to eliminate error P0300
Since there are many possible causes for error P0300, it is necessary to adhere to a certain troubleshooting algorithm. Here is a sequence of actions to quickly detect the cause of misfires:
If the problem cannot be identified, the next step is to check the spark plugs. Twist them and inspect for oil deposits or damage to the electrode. Also make sure that the spark plug has the correct gap;
The above are the basic steps that most often help to find the cause of the P0300 error code. When checking the above elements, pay attention to their condition - the presence of soot, traces of mechanical damage, and so on.
Other possible causes of the P0300 error must be determined depending on what other errors the scanner indicates during diagnosis. That is, if the oxygen sensor fails, then in addition to P0300, error P0134 or P0130 may occur. Try eliminating other errors that are diagnosed together with P0300, perhaps this will immediately eliminate it too.
( 413 votes, average: 4.49 out of 5)
Related Posts
Error P0326 - knock sensor signal is out of range
Error P0100 - problems in the mass air flow sensor (MAF) circuit
Causes of misfires
Ignition coils
Bad ignition coils are a common problem on many vehicles, including BMW, Ford, Hyundai, Mazda, Nissan, Volkswagen and GM. A faulty ignition coil needs to be replaced.
Candles
If the spark plugs have not been changed for more than 15 thousand km, replacing them would be a good idea. Worn spark plugs require higher voltage to produce a spark, which puts more stress on the ignition coils.
Some car manufacturers update ignition coils during vehicle production. If one of the ignition coils has failed and the manufacturer has updated the part, then the auto mechanic may recommend replacing all ignition coils with updated ones as a precaution.
Carbon on valves
In many modern vehicles, especially those with direct fuel injection, carbon buildup on the intake valves and injectors can cause misfire.
Some mechanics may recommend cleaning the valves with a special spray or foam, as this is cheaper and sometimes helps. A more effective option is to clean the intake valves manually.
Watch the video on how to clean the valves:
Clogged fuel injectors also need to be cleaned or replaced. This repair is expensive because it requires more labor. It is necessary to remove the intake manifold and some other parts.
Air leak
Vacuum leaks, as well as a stuck EGR valve or purge valve, can cause misfires that mostly occur at idle but go away at higher rpms.
Read more here: How to find air leaks at home?
Adjustment of valves
In some older Honda vehicles, misfire can be caused by improperly adjusted valves. The misfire may be more noticeable when the engine is idling after a cold start.
As valve system parts wear, valve clearances change. To compensate for this, the valves in many Honda engines must be adjusted at recommended intervals.
Timing belt
Sometimes an engine may misfire if the timing belt or chain were not correctly aligned when replacing the timing belt. If the problem occurs after replacing the timing belt or chain, the first step is to check the timing marks.
Oil leak
In many high mileage vehicles, oil leaking into the combustion chamber due to worn valve seals and oil rings can foul the spark plugs and cause a misfire.
Often, misfires appear at idle, but disappear after increasing the speed. Blue smoke is another symptom of oil leakage into the combustion chambers.
In many older vehicles, cleaning the engine compartment or driving through deep puddles can cause the engine to misfire as water gets into the ignition parts and causes short circuits.
Replacing the spark plugs and ignition wires often solves the problem. Ignition coils that have cracks or signs of sparking should also be replaced. In older vehicles with an ignition distributor (distributor), the distributor cap and rotor are also replaced.