Modern car owners independently diagnose certain errors in the car's ECU. The scanner allows you to quickly and accurately identify any problems in systems and indicate further actions to eliminate them.
IMPORTANT! When checking independently with an auto scanner, a driver who encounters error p0130 does not have to contact the service center, but can fix the problem with his own hands. In the overwhelming majority of cases, the causes of this error do not require professional instruments and specialized equipment for repair.
Causes of error P0130
The most common causes of this error are:
- Disconnecting the oxygen sensor connector
- Corroded oxygen sensor connector
- Damage to the electrical wires coming from the oxygen sensor to the ECM
- Fuel supply limitation (fuel pump malfunction or fuel filter clogged)
- Air intake system leakage
- Air or fuel system leakage
- Malfunction of the mass air flow sensor
- Malfunction of the absolute pressure sensor in the intake manifold
- Malfunction in the fuel vapor recovery system
- Oxygen sensor malfunction
- Fuel pressure regulator malfunction
- Engine control module (ECM) malfunction
Possible causes of error P0130
Error P0130 is not necessarily directly related to the performance of the lambda probe. On the contrary, the most common cause of malfunction is electrical wiring.
The O2 sensor is located in one of the hottest areas of the engine compartment, namely, immediately behind the exhaust manifold. The temperature in this place reaches 300 degrees Celsius or more. The nearby sensor connector gets quite hot. Its contacts can collapse, oxidize, and lose mechanical properties. In this case, the electrical contact may be broken, resulting in error P0130.
In second place in the likelihood of error P0130 occurring is a failure of the oxygen sensor. The working element of the lambda probe is a ceramic porous base coated with a thin film of an oxygen-sensitive element. Exhaust gases pass through micropores, heated to a high temperature during the ignition process. After 50,000 kilometers, the working coating begins to rapidly decrease in thickness, and the O2 sensor loses its sensitivity. When the signal amplitude decreases below 0.45 Volts, the sensor does not meet the necessary parameters, and the engine control unit generates error P0130.
Some sources contain information that error P0130 can be eliminated for a while by washing the O2 sensor in a special composition or solvent, removing traces of carbon deposits from the working element. In isolated cases this has an effect, but only for a short time.
Error P0130 from the sensor located in Bank 1 can be detected by the engine control unit based on an incorrect comparison of its readings with the signal from the lambda probe located behind the catalyst. This situation may occur if the catalyst was removed abnormally. In this case, the readings of the first and second oxygen sensors are approximately the same, and the engine control unit mistakenly thinks that something has happened to one of the lambda probes. In practice, this problem is artificially eliminated by installing an additional fitting on the 2nd oxygen sensor, a special electronic filter, an emulator, or by performing chip tuning. At first, such “hiding” the removal of the catalyst can work successfully, but then sooner or later error P0130 “treacherously appears.”
Finally, one of the least likely causes of the P0130 error is a failure of the engine control unit. Such malfunctions do occur, but are extremely rare. As a rule, the engine control unit has reliable protection for input circuits against overloads. If a firmware failure occurs, then along with error P0130 many other engine errors will be diagnosed.
How does a mechanic diagnose a P0130 code?
To properly diagnose the P0130 code, you will need an advanced diagnostic scanner that can not only read stored trouble codes, but also view readings from various sensors in real time.
First, the mechanic reads all the stored data and error codes using an OBD-II scanner to find out when and under what circumstances the P0130 code appeared. He will then clear the error codes from the computer's memory and test drive the vehicle to see if the P0130 code appears again.
If the error code appears again, the mechanic will continue diagnosing to determine the cause of the error. To do this he will need:
- Advanced diagnostic scanner
- Digital voltmeter
- Smoke installation for detecting leaks in the intake system
How does a car behave with error P0130?
Error P0130, indicating problems with the voltage in the oxygen sensor circuit, directly affects engine performance. The most noticeable consequences of its occurrence are at high speeds of a car engine. The driver can expect the following troubles:
- Increased fuel consumption;
- Unstable engine operation at high speeds;
- Loss in dynamics - the car will begin to accelerate more slowly, and even with increased pressure on the gas pedal, the situation will not change.
Most often, the consequences of the P0130 error do not appear immediately.
It is important to note that driving a vehicle diagnosed with P0130 is extremely dangerous in terms of increasing the likelihood of failure of expensive engine components.
Common mistakes when diagnosing code P0130
The most common mistake when diagnosing a P0130 code is to rush to replace the oxygen sensor without first checking it.
Before replacing the sensor, it is necessary to perform a thorough diagnosis using special equipment and consider all possible causes of the error.
Since there can be multiple causes for the P0130 code, replacing the sensor may not solve the problem and may cause the code to reappear.
On which cars is this problem most common?
The problem with code P0130 can occur on different machines, but there are always statistics on which brands this error occurs more often. Here is a list of some of them:
- Alfa Romeo
- Audi (Audi a4, Audi a6, Audi TT)
- BMW (BMW E46)
- Chery (Chery Amulet, Tiggo, Fora)
- Chevrolet (Chevrolet Aveo, Cruz)
- Citroen (Citroen C4, Berlingo)
- Daewoo (Daewoo Matiz, Nexia)
- Fiat (Fiat Ducato)
- Ford (Ford Focus, Fusion)
- Geely (Geely SK)
- Hyundai (Hyundai Accent, Santa Fe, Solaris, Sonata, Tucson, Elantra, ix35)
- Infiniti (Infiniti i30)
- Iveco (Iveco Daily)
- Jeep (Jeep Wrangler, Grand Cherokee)
- Kia (Kia Rio, Sid, Sorento, Spectra, Sportage, Cerato)
- Mazda (Mazda 3)
- Mercedes (Mercedes Vito, w203, w210)
- Mitsubishi (Mitsubishi Lancer)
- Nissan (Nissan Almera, Maxima, Primera, Terrano, X-Trail)
- Opel (Opel Agila, Astra, Vectra, Zafira, Corsa, Meriva, Omega)
- Peugeot (Peugeot 206, 207, 307, 308, 406, Partner)
- Pontiac (Pontiac Sunfire)
- Renault (Renault Duster, Logan, Megan, Sandero, Fluence)
- Skoda (Skoda Octavia, Rapid, Fabia)
- Subaru (Subaru Outback, Impreza, Legacy, Forester)
- Suzuki
- Toyota
- Volkswagen (Volkswagen Golf, Jetta, Passat, Polo Sedan)
- Volvo
- VAZ 2107, 2110, 2114
- Gazelle
- Lada Vesta, Granta, Kalina, Largus, Niva, Priora
- UAZ Patriot
You can sometimes encounter other errors with fault code P0130. The most common are: P0053, P0100, P0105, P0125, P0131, P0132, P0133, P0134, P0135, P0136, P0141, P0150, P0151, P0152, P0153, P0158, P0170, P0171, P0300, P030 1, P0302, P0303, P0304 , P0314, P0325, P0400, P0443, P0500, P0507, P0560, P0600, P0740, P2251, P2297.
What repairs can fix the P0130 code?
To resolve P0130, you may need to:
- Connecting the OBD-II scanner to the vehicle diagnostic connector
- Checking for an Error Code
- Analysis of data stored in the vehicle's ECM memory
- Clearing error codes from computer memory
- Test drive your vehicle to see if P0130 appears again
- Check and, if necessary, repair or replace electrical wires or oxygen sensor connector
- Checking and, if necessary, replacing the oxygen sensor
- Check and, if necessary, replace the engine control module (ECM)
Technical description and interpretation of error P0130
This diagnostic trouble code (DTC) is a generic powertrain code. The P0130 code is considered a common code because it applies to all makes and models of vehicles. Although the specific repair steps may vary slightly depending on the model.
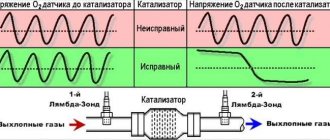
DTC P0130 refers to the first oxygen (O₂) sensor located on Bank 1, upstream of the catalytic converter. It measures the amount of oxygen entering the exhaust gases.
There are four wires to the O₂ sensor. Two wires are for the heating element and two wires are for sensor data. The heating element should have battery voltage on one wire when the engine is off. And grounding on the other.
The PCM supplies a voltage of 0.5 volts to the O₂ sensor, which it varies depending on the oxygen content of the exhaust gases. The PCM also provides grounding for the sensor.
Changes in oxygen content cause changes in the resistance of the O₂ sensor. This change in resistance affects the 0.5 volt voltage supplied by the PCM. It can vary from 0.1 to 0.9 volts. A value of 0.1 indicates complete leanness and 0.9 indicates complete enrichment.
The meaning of this code is that the O₂ (oxygen sensor) voltage has been low for more than 2 minutes, or the sensor is not active at all. This is perceived by the Engine Control Module (ECM) as a malfunction and therefore sets the P0130 OBD2 error code.
Oxygen sensor malfunctions and error codes
Among the possible breakdowns of the lambda probe, the following can be distinguished: loss of sensitivity, non-functional heating. As a rule, the on-board computer will not show you a breakdown if the problem is loss of sensitivity. It’s another matter if the heating circuit breaks, then the malfunction will be recorded.
- Error P1115 - a breakdown has occurred in the heating circuit
- Error P1102 - low resistance on the oxygen heater
- Error P0141 - the heater has broken down on the second sensor
- Error P0140 - sensor number two has broken
- Error P0138 - the second sensor indicates an excessive signal level
- Error P0137 - the second sensor indicates a low signal level
- Error P0136 - there is a short circuit to ground of the second sensor
- Error P0135 - the heater on the first sensor has failed
- Error P0134 - the first sensor has no signal
- Error P0133 - the first sensor responds slowly to the request
- Error P0132 - there is little oxygen in the system, the signal is high at the first sensor
- Error P0131 - too much oxygen in the system, low signal at the first sensor
- Error P0130 - the first sensor sends incorrect signals
Lambda probe error is on: causes and diagnosis
If the oxygen sensor becomes unusable, the following symptoms appear:
- When the engine is idling, a “triple” sensation is felt, as if one cylinder is not functioning. But before you sin on the lambda probe, make sure that the ignition system is operating normally.
- A noticeable increase in gasoline consumption - up to 12 l/100 km and more.
- There are dips during acceleration, unstable dynamics, and a drop in engine power.
- There is an engine error light on the dashboard.
If valve lapping paste was not used when repairing the cylinder head, then such symptoms may also appear. Repairs must be carried out to the highest possible quality.
If the sensor fails, “CHECK ENGINE” may not be displayed. All oxygen sensor errors are presented in the table:
| Error code | Detailed description |
| P0130 | The oxygen sensor receives an incorrect signal or does not have one at all |
| P0131 | Low signal level |
| P0133 | The response from the oxygen sensor is too long |
| P0134 | No response |
| P0135 | Damage to the DC heating element |
| P0136 | Short circuit in the ground circuit of the second oxygen sensor |
| P0137 | Low signal level of the second DC |
| P0138 | High signal level of the second DC |
| P0140 | Break of the second sensor |
| P0141 | Overheating of the heating coil on the second DC |
| P1102 | Low or no signal readout resistance |
| P1115 | Sensor heating circuit malfunction |
When the last error (P1115) appears, all of the above symptoms begin to appear. This lambda probe error is considered the most common on most cars.
Error code p0130, detected by the auto scanner, indicates low voltage in the lambda probe circuit (or oxygen sensor mounted upstream of the catalyst). Almost all modern car models are equipped with oxygen sensors in the exhaust system, which can significantly reduce toxic emissions and make the engine more productive.
Error p0130 can be detected both when the sensor itself breaks down and when there is a short circuit in its wiring.
How does this malfunction manifest itself?
Oxygen sensor 1, bank 1 is installed in front of the catalyst (after the 1st exhaust manifold in a V-engine). It is designed to control the oxygen concentration in the combustion gases immediately after the exhaust manifold. Combustion quality is controlled by the residual amount of oxygen.
An electrical signal is generated in proportion to it, which is supplied to the engine control unit. The control unit, in turn, based on these data, adjusts the parameters of ignition, fuel injection, and the composition of the working mixture to reduce the amount of oxygen in the exhaust gases. This ensures minimal fuel consumption and high environmental performance of the engine.
This is interesting: Error P0170 on Mitsubishi cars - step-by-step diagnostic and repair guide
If there is no signal in the oxygen sensor circuit (O2), the following malfunctions are possible:
- a significant increase in fuel consumption per unit of travel (up to 50%);
- uneven engine speed;
- problems when starting the engine, especially when hot;
- loss of engine power, throttle response;
- increase in the concentration of harmful substances in exhaust gases;
- the appearance of a characteristic smell of fuel from the exhaust pipe;
- sudden engine stop.
If these symptoms appear, the “CHECK ENGINE” indicator lamp may not work, so it is imperative to perform computer diagnostics of the engine. This error belongs to standard OBD II codes, and can be diagnosed by the simplest ELM327 device.
How does a car behave with error P0130?
Error P0130, indicating problems with the voltage in the oxygen sensor circuit, directly affects engine performance. The most noticeable consequences of its occurrence are at high speeds of a car engine. The driver can expect the following troubles:
- Increased fuel consumption;
- Unstable engine operation at high speeds;
- Loss in dynamics - the car will begin to accelerate more slowly, and even with increased pressure on the gas pedal, the situation will not change.
Most often, the consequences of the P0130 error do not appear immediately.
It is important to note that driving a vehicle diagnosed with P0130 is extremely dangerous in terms of increasing the likelihood of failure of expensive engine components.
Possible causes of error P0130
Error P0130 is not necessarily directly related to the performance of the lambda probe. On the contrary, the most common cause of malfunction is electrical wiring.
The O2 sensor is located in one of the hottest areas of the engine compartment, namely, immediately behind the exhaust manifold. The temperature in this place reaches 300 degrees Celsius or more. The nearby sensor connector gets quite hot. Its contacts can collapse, oxidize, and lose mechanical properties. In this case, the electrical contact may be broken, resulting in error P0130.
In second place in the likelihood of error P0130 occurring is a failure of the oxygen sensor. The working element of the lambda probe is a ceramic porous base coated with a thin film of an oxygen-sensitive element. Exhaust gases pass through micropores, heated to a high temperature during the ignition process. After 50,000 kilometers, the working coating begins to rapidly decrease in thickness, and the O2 sensor loses its sensitivity. When the signal amplitude decreases below 0.45 Volts, the sensor does not meet the necessary parameters, and the engine control unit generates error P0130.
Some sources contain information that error P0130 can be eliminated for a while by washing the O2 sensor in a special composition or solvent, removing traces of carbon deposits from the working element. In isolated cases this has an effect, but only for a short time.
This is interesting: Repair of the driver's door lock of Nissan Tiida and Qashqai - restoration of the cable
Error P0130 from the sensor located in Bank 1 can be detected by the engine control unit based on an incorrect comparison of its readings with the signal from the lambda probe located behind the catalyst. This situation may occur if the catalyst was removed abnormally. In this case, the readings of the first and second oxygen sensors are approximately the same, and the engine control unit mistakenly thinks that something has happened to one of the lambda probes. In practice, this problem is artificially eliminated by installing an additional fitting on the 2nd oxygen sensor, a special electronic filter, an emulator, or by performing chip tuning. At first, such “hiding” the removal of the catalyst can work successfully, but then sooner or later error P0130 “treacherously appears.”
Finally, one of the least likely causes of the P0130 error is a failure of the engine control unit. Such malfunctions do occur, but are extremely rare. As a rule, the engine control unit has reliable protection for input circuits against overloads. If a firmware failure occurs, then along with error P0130 many other engine errors will be diagnosed.
How is error P0130 diagnosed?
For P0130 to be stored in the vehicle's ECU, the oxygen sensor must be faulty for 1 minute or more.
If no data is received from the sensor (or it is erroneous, for example, the lambda probe slowly changes values) for a minute, then error information P0130 is stored in memory. 10 seconds after this, the driver will be notified of existing problems in the operation of the engine by the Check Engine light on the dashboard. It is worth noting that if the oxygen sensor fails and no signal is received from it, error P0134 can be diagnosed along with error P0130.
Debugg
In any case, troubleshooting begins with the wiring of the DC and its connector, then the voltage value of the sensor signal is checked. And depending on the technical characteristics of the lambda, changes in parameters should occur within appropriate limits. And if it is possible to see the operation using a diagnostic tool, then we warm up the engine to operating temperature, watch for voltage changes, no, we take a multimeter in our hands and, connecting the probes to the corresponding contacts of the sensor, check the serviceability of the input signal circuit (measure between the positive contact of the sensor and mass). Then, having disconnected the power supply, we check the voltage for a minute; jumps should occur in a certain range depending on the operation of the engine. If this does not happen or the value is outside the limits, the oxygen sensor is faulty and must be replaced.
After replacing the sensor (by the way, you should remember that not all cars can replace the original DC with a universal one), clear the error programmatically or by removing the battery terminal for 10 minutes and let the car run for several minutes at full and partial load to make sure the error is eliminated, so It’s quite rare, but it still happens that P0134 is not associated with a failure of the lambda probe or a break. Then an analysis of the operation of other electronic circuit systems is required.