P0135 is an oxygen sensor (bank 1, sensor 1) heated circuit fault. This error code tells the driver that there is a malfunction in the heating mechanism of the first lambda probe, the one installed before the converter. Error p0135 can be determined using a car scanner or self-diagnosis (using a paper clip and counting the blinks of the check icon on the instrument panel). Since there may not be other symptoms indicating a problem with heating the oxygen sensor.
Technical description and interpretation of error P0135
This diagnostic trouble code (DTC) is a generic powertrain code. The P0135 code is considered a common code because it applies to all makes and models of vehicles. Although the specific repair steps may vary slightly depending on the model.
The malfunction means that the heated circuit in the oxygen sensor on bank 1 reduces the time required to enter the closed circuit. Sensor #1 will be the front sensor after the engine.
When the air heats up and reaches operating temperature. The oxygen sensor reacts by switching according to the oxygen content in the exhaust surrounding it. The ECM monitors how long it takes for the oxygen sensor to begin shifting.
It determines, based on the coolant temperature, how much time has passed since the sensor responded. If a lot of time has passed before the oxygen sensor starts working properly, a P0135 code will appear.
You can also look for a similar problem with code P0141 (Bank 1 Sensor 2).
Replacing the lambda probe
In most cases, a part such as a lambda probe cannot be repaired, as evidenced by statements about the impossibility of repair from many automobile manufacturers. However, the inflated cost of such a unit from official dealers discourages anyone from purchasing it. The optimal way out of this situation could be a universal sensor, which costs much less than its native analogue and is suitable for almost all car brands. Also, as an alternative, you can purchase a used sensor, but with a warranty period, or a completely exhaust manifold with a lambda probe installed in it.
However, there are cases when the lambda probe operates with a certain error due to severe contamination as a result of combustion products deposited on it. In order to make sure that this is really the case, the sensor must be checked by specialists. After the lambda probe has been checked and its full functionality has been confirmed, it must be removed, cleaned and reinstalled.
In order to dismantle the oxygen level sensor, it is necessary to warm its surface to 50 degrees. After removal, the protective cap is removed from it and only after that you can start cleaning. It is recommended to use phosphoric acid as a highly effective cleaning agent, which can easily cope with even the most stubborn flammable deposits. At the end of the soaking procedure, the lambda probe is rinsed in clean water, thoroughly dried and installed in place. At the same time, do not forget about lubricating the threads with a special sealant, which will ensure complete tightness.
The structure of a car is very complex, so it needs constant maintenance and timely preventative maintenance. Therefore, if there is a suspicion that the lambda probe is faulty, it is necessary to immediately diagnose its performance and, if the fact of failure is confirmed, replace the lambda probe. Thus, all the most important functions of the vehicle will be maintained at the same level, which will guarantee the absence of further problems with the engine and other important elements of the car.
Reasons for the error
Code P0135 may mean that one or more of the following problems have occurred:
- Damaged oxygen sensor (lambda probe), bank 1, sensor 1.
- The second lambda probe heater fuse is blown or short circuit to ground.
- Poor electrical connection at the second oxygen sensor connector.
- Open or short to ground in the wiring harness.
- The engine control module (ECM) is faulty.
- There may be a short circuit in the O₂ heater circuit wiring system (oxygen sensor).
- The resistance of the oxygen sensor heating element (O₂) may be high.
- The oxygen sensor heating element may have an internal short circuit.
How is error P0130 diagnosed?
For P0130 to be stored in the vehicle's ECU, the oxygen sensor must be faulty for 1 minute or more. If no data is received from the sensor (or it is erroneous, for example, the lambda probe slowly changes values) for a minute, then error information P0130 is stored in memory.
It is worth noting that if the oxygen sensor fails and no signal is received from it, error P0134 can be diagnosed along with error P0130.
How to Troubleshoot or Reset Trouble Code P0135
Some suggested steps to troubleshoot and fix error code P0135:
- Visually inspect the electrical wires and oxygen sensor 1 (bank 1) connector.
- Read all stored data and error codes using an OBD-II scanner. Clear your memory of error codes and take the car for a test drive. This will help determine if the P0135 code appears again.
- Review the oxygen sensor data to see if it is working.
- Measure the voltage at the oxygen sensor 1 heater circuit (bank 1).
- Measure the resistance in the oxygen sensor 1 (bank 1) heater circuit and compare the value to the manufacturer's specification.
- Find the fuse diagram and check the integrity of the corresponding fuse element.
What to do if error P0130 occurs
As you can understand from the description of the problem, there are not many factors that lead to error P0130. Accordingly, the driver or technician can get rid of the malfunction by performing the following algorithm of actions to determine the cause of the problem and eliminate it:
- The first step is to check the wires that supply the first lambda probe (installed before the catalyst);
- If power is supplied through the wires, carefully inspect the oxygen sensor connector for corrosion, damage, carbon deposits, contamination and other defects;
- Next, it is recommended to check the voltage between the lambda probe signal wire and ground. To do this, you need to connect the voltmeter probes to them. If the oxygen sensor is working properly, its voltage will be around 0.45 Volts (if the voltmeter shows a different number, it is recommended to check the voltage value for your specific car model, as it may differ);
- It is also recommended to use an ohmmeter to check the resistance of the oxygen sensor heater (two white wires). The resistance value will vary from 2 to 10 ohms, depending on the car model. The exact value can be found in the documentation for the sensor;
- If the problem is not related to the wiring and oxygen sensor, you need to check the mass air flow sensor and the tightness of the exhaust manifold; the gaskets may need to be replaced. Be sure to diagnose the presence of suction in the circuit after the flow meter.
After completing the necessary steps to eliminate the P0130 error, you should let the engine run for some time in various modes (especially those in which the Check Engine light came on) and reset the error.
Most often, error P0130 is diagnosed on Opel, Kia, Hyundai, Subaru and Ford vehicles.
Diagnosis and problem solving
Trouble code P0135 means that there is a problem with the heated oxygen sensor (lambda probe) heating element circuit. The control module monitors the time required to warm up the sensor. And it begins to send the corresponding signal.
The code is triggered when the sensor takes too long to heat up. Water entering the oxygen sensor connector may cause the lambda probe heater fuse to blow.
Before replacing the sensor, check the condition of the heated oxygen sensor fuse and connectors. If the fuses and connector are good, replacing the sensor (O₂ bank 1) usually solves the problem.
The main symptoms of a malfunctioning lambda probe
The main sign of a faulty lambda probe is a change in engine operation, since after its breakdown the quality of the fuel mixture supplied to the combustion chamber significantly deteriorates. The fuel mixture essentially remains uncontrolled, which is unacceptable.
The reason for the lambda probe to fail to operate may be the following:
- depressurization of the housing;
- penetration of external air and exhaust gases;
- overheating of the sensor due to poor-quality engine painting or improper operation of the ignition system;
- obsolescence;
- incorrect or interrupted power supply that leads to the main control unit;
- mechanical damage due to incorrect operation of the vehicle.
In all of the above cases, except the last one, failure occurs gradually. Therefore, those car owners who do not know how to check the lambda probe and where it is located will most likely not immediately notice the malfunction. However, for experienced drivers it will not be difficult to determine the reason for changes in engine performance.
The gradual failure of the lambda probe can be divided into several stages. At the initial stage, the sensor stops functioning normally, that is, at certain operating moments of the motor, the device stops generating a signal, subsequently destabilizing the idle speed.
In other words, they begin to fluctuate over a fairly wide range, which ultimately leads to a loss of quality of the fuel mixture. At the same time, the car begins to jerk for no reason, you can also hear popping noises that are uncharacteristic of the engine, and a warning light always lights up on the instrument panel. All these anomalous phenomena signal to the car owner that the lambda probe is not working properly.
At the second stage, the sensor stops working completely when the engine is not warmed up, while the car will signal the driver about the problem in every possible way. In particular, there will be a noticeable loss of power, a slow response when pressing the accelerator pedal and the same popping noises from under the hood, as well as unjustified jerking of the car. However, the most significant and extremely dangerous signal of a lambda probe failure is engine overheating.
If you completely ignore all previous signals indicating a deterioration in the condition of the lambda probe, its breakdown is inevitable, which will cause a large number of problems. First of all, the possibility of natural movement will suffer, fuel consumption will also increase significantly and an unpleasant, pungent odor with a pronounced hint of toxicity will appear from the exhaust pipe. In modern automated cars, in the event of a breakdown of the oxygen sensor, an emergency lock can simply be activated, as a result of which subsequent movement of the car becomes impossible. In such cases, only an emergency call to a tow truck can help.
However, the worst case scenario is depressurization of the sensor, since in this case the movement of the car becomes impossible due to the high probability of engine failure and subsequent expensive repairs. During depressurization, exhaust gases, instead of exiting through the exhaust pipe, enter the atmospheric reference air intake channel. During engine braking, the lambda probe begins to detect an excess of oxygen molecules and urgently sends a large number of negative signals, which completely disables the injection control system.
The main sign of sensor depressurization is a loss of power, this is especially felt during high-speed driving, a characteristic knocking sound from under the hood while driving, which is accompanied by unpleasant jerking, and an unpleasant odor that is emitted from the exhaust. Depressurization is also indicated by visible deposits of soot formations on the exhaust valve body and in the area of the spark plugs.
How to determine a faulty lambda probe is described in the video:
On which cars is this problem most common?
The problem with code P0135 can occur on different machines, but there are always statistics on which brands this error occurs more often. Here is a list of some of them:
- Acura (Acura MDX)
- Alfa Romeo
- Audi (Audi a4, Audi TT)
- BMW
- Chery (Chery Amulet, Tiggo)
- Chevrolet (Chevrolet Aveo, Ventura, Cruz, Lacetti, Tahoe)
- Chrysler (Chrysler Sebring)
- Citroen (Citroen C3, C4, Berlingo)
- Daewoo (Daewoo Matiz, Nexia)
- Daihatsu
- Dodge (Dodge Durango, Caravan, Neon, Stratus)
- Fiat (Fiat Doblo, Ducato, Stilo)
- Ford (Ford Galaxy, Mondeo, Taurus, Focus, Escape)
- Geely
- Honda (Honda Accord, Odyssey, SRV, Stream, Fit, Civic, HR-V)
- Hover
- Hyundai (Hyundai Accent, Santa Fe, Sonata)
- Iveco (Iveco Daily)
- Jeep (Jeep Grand Cherokee)
- Kia (Kia Rio, Sefiya, Sid, Spectra, Sportage, Shuma)
- Lexus (Lexus gs300, lx470, rx300)
- Mazda
- Mercedes
- Mitsubishi (Mitsubishi Airtrek, Outlander, Galant, Grandis, Karizma, Lancer, Pajero, Space Star)
- Nissan (Nissan Qashqai, Maxima, March, Note, Sunny, Tiida, X-Trail)
- Opel (Opel Astra, Vectra, Zafira, Corsa, Omega)
- Peugeot (Peugeot 206, 207, 307, 308, 406, 407, Partner)
- Renault (Renault Duster, Logan, Scenic)
- Skoda (Skoda Octavia)
- Ssangyong (Sanyeng Aktion, Kyron)
- Suzuki (Suzuki Grand Vitara, Liana, Swift)
- Toyota (Toyota Avensis, Ipsum, Kluger, Corolla, Crown, Land Cruiser, Mark 2, Prado, Premium, Harrier, Estima)
- Volkswagen (Volkswagen Golf, Passat)
- Volvo
- VAZ 2105, 2107, 2110, 2112, 2114, 2115
- Gazelle Business, Chrysler
- Zaz Chance
- Lada Kalina, Niva, Priora
- UAZ Patriot
With fault code P0135, you can sometimes encounter other errors. The most common are: P0030, P0107, P0130, P0132, P0134, P0138, P0155, P0161, P0170, P0171, P0174, P0300, P0301, P0302, P0303, P0304, P0314, P0400, P0443, P059 7, P1135, P1409, P2243 .
Types of sensors and operating principle
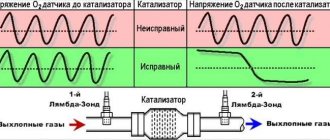
The lambda probe is installed in the exhaust system. Sensors are divided into two types: two-point and broadband.
The two-point sensor consists of ceramics, the elements of which are coated with zirconium dioxide on both sides. Installed in front of or behind the catalytic converter.
The principle of operation is to measure the level of oxygen concentration in the environment and exhaust gases. If the level changes and becomes different, a voltage is created at the ends of the sensor elements, from low to high. Low voltage is created if there is excess oxygen in the system.
Otherwise, if the system does not have the required level of oxygen, high voltage will be created. These signals are sent to the engine control unit, which distinguishes them by current strength.
The wideband sensor is a more modern design. It also has two ceramic elements. One of them can be called “pumping”. It is responsible for activating the process of pumping or removing air from the system.
The second element can be conventionally called “two-point”. The principle of operation is based on the fact that as long as there is the required amount of oxygen in the mixture, the current strength on the “pumping” element does not change and is transferred to the “two-point” element.
It, in turn, receiving a constant current from the “pumping” element, maintains a constant voltage between its elements and is inactive.
As soon as the oxygen level changes, the "pumping" element supplies the changed voltage to the "two-point". This, in turn, ensures either pumping air into the system or pumping it back.
Eliminating an error in the heating circuit
First, we make sure that the sensor wiring is intact, and then we check the condition of the contact chip (we clean the oxidation). After which it would be logical to check the resistance of the lambda heating. On a warm engine, at a normal temperature of 20 °C, we remove the chip from the sensor and measure the resistance between two wires of the same color (they are supplied with 12V power).
Having done all of the above, cleaned the contacts or replaced the sensor, error P0135 should disappear after a few minutes of engine operation. Having a computer at hand with a special program installed, you can check this and delete the event recorded in the archive. You can also reset the error by removing the terminal from the battery.
How can I fix error 0141
Methods to combat the problem are as follows:
- delete the stored fault codes from the control unit’s memory and carry out a road test to check (the error may have appeared only once);
- replace the oxygen sensor;
- repair or replace the sensor wiring or connector;
- Replace the fuse in the lambda probe heating circuit.
Additional recommendations
Error P0141 can only be caused by a malfunction in the heating circuit of the oxygen sensor 2 installed after the catalyst. This sensor and fault code are in no way related to the first lambda probe.
Oxygen sensors send information to the electronic engine control unit, which uses it to properly control the operation of the fuel injectors. If you disconnect one of these sensors or both lambda probes, the ECU will operate in emergency mode, which will lead to a significant increase in fuel consumption.
Note that errors related to oxygen sensors can sometimes be caused by malfunctions of other engine components. Therefore, do not rush to change the sensor immediately. Engine diagnostics must be carried out comprehensively. There are cases that the problem lies even in the failure of the control unit.