Initially, the VAZ 21126 engine became the second version of the base engine 2112. In the first modification, 21124, the volume was increased and Euro 4 standards were met, but the torque/power was reduced. The manufacturer AvtoVAZ needed a powerful engine with a minimum service life of 200,000 km, so version 21126 has 145 Nm of torque and 98 hp. With. power, specified operational life.
ICE 21126
Engine characteristics 21126
Motor 21126 is the second version of the basic ICE 2112 out of five existing ones (21124, 21127, 21128 and 21129). The main tasks of the developers in this case were:
- increase power;
- increase resource;
- maintain the Euro 4 protocol;
- keep production costs within reasonable limits.
Block marking
Lada Priora cars, the production of which began in the same year, needed an engine with such characteristics. An important feature of the internal combustion engine marked 21126 was the inclusion of imported spare parts - a lightweight connecting rod and piston group from Federal Mogul, a timing belt and rollers from Gates.
The engine diagram remains the same:
- in-line transverse for front-wheel drive;
- 16 valves and 2 camshafts according to the DOCH scheme;
- hydraulic compensators and phased injection;
- intake manifold combined with the receiver;
- exhaust catalyst with integrated catalytic converter.
Engine assembly
The initial boost of the engines from version 21124 was carried out by the manufacturer, providing a potential of at least 50 hp. With. power for self-tuning.
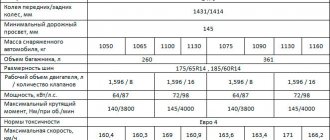
Taking into account the above, the technical characteristics of the AvtoVAZ 21126 power drive version are as follows:
| Manufacturer | AvtoVAZ |
| Engine brand | 21126 |
| Years of production | 2007 – … |
| Volume | 1597 cm3 (1.6 l) |
| Power | 72 kW (98 hp) |
| Torque moment | 145 Nm (at 4000 rpm) |
| Weight | 115 kg |
| Compression ratio | 11 |
| Nutrition | injector |
| Motor type | in-line |
| Injection | distributed electronically controlled |
| Ignition | coil for each spark plug |
| Number of cylinders | 4 |
| Location of the first cylinder | TVE |
| Number of valves on each cylinder | 4 |
| Cylinder head material | aluminum alloy |
| Intake manifold | combined with receiver, polymer |
| An exhaust manifold | catalyst |
| Camshaft | 2 pcs., marks on pulleys are offset by 2 degrees |
| Cylinder block material | cast iron |
| Cylinder diameter | 82 mm |
| Pistons | lightweight, manufacturer Federal Mogul |
| Crankshaft | from 11183 |
| Piston stroke | 75.6 mm |
| Fuel | AI-95 |
| Environmental standards | Euro 4 |
| Fuel consumption | highway – 6 l/100 km combined cycle 7.2 l/100 km city – 9.8 l/100 km |
| Oil consumption | maximum 0.1 l/1000 km |
| What kind of oil to pour into the engine by viscosity | 5W-30 and 10W-40 |
| Which engine oil is best by manufacturer | Liqui Moly, LukOil, Rosneft, Mannol, Mobil, Castrol |
| Oil for 21126 according to composition | synthetics, semi-synthetics |
| Engine oil volume | 3.5 l |
| Operating temperature | 95° |
| Motor life | declared 200,000 km actual 300,000 km |
| Adjustment of valves | hydraulic compensators |
| Cooling system | forced, antifreeze |
| Coolant quantity | 7.8 l |
| water pump | TZA |
| Candles for 21126 | BCPR6ES from NGK or domestic AU17DVRM |
| Gap between spark plug electrodes | 1.1 mm |
| Timing belt | Dyco, width 22 mm, service life 40,000 km |
| Cylinder operating order | 1-3-4-2 |
| Air filter | Nitto, Knecht, Fram, WIX, Hengst |
| Oil filter | catalog number 90915-10001 replacement 90915-10003, with check valve |
| Flywheel | from 2110 |
| Flywheel mounting bolts | box MT – M10x1.25 mm, length 26 mm, groove 11 mm box AT – M10x1.25 mm, length 26 mm without groove |
| Valve stem seals | code 90913-02090 inlet light code 90913-02088 exhaust dark |
| Compression | from 13 bar, difference in adjacent cylinders maximum 1 bar |
| XX speed | 800 – 850 min-1 |
| Tightening force of threaded connections | spark plug – 31 – 39 Nm flywheel – 62 – 87 Nm clutch bolt – 19 – 30 Nm bearing cap – 68 – 84 Nm (main) and 43 – 53 (rod) cylinder head – three stages 20 Nm, 69 – 85 Nm + 90° + 90° |
The manufacturer has a manual with step-by-step maintenance and repair operations, which describes the parameters and maintenance regulations. Since the service life is declared taking into account the assembly line with parts from foreign manufacturers, it is recommended to carry out major repairs using original spare parts. The quality of domestic companies does not reach the level of international brands Gates and Federal Mogul.
Maintainability
Thanks to the cast-iron cylinder block, the engine is very resistant to overheating and often forgives minor temperature violations. Provided that high-quality motor oil is used, cylinder wear reaches one tenth of a millimeter even over runs of several hundred thousand km. Compression decreases mainly due to wear and coking of the piston rings. And then the oil consumption due to worn oil scraper rings exceeds reasonable limits, as, in principle, on any heavily worn engine.
During a major overhaul, you can install non-tuning pistons to match the repair size to which the block was bored. The estimated cost of a complete and high-quality overhaul of K4M/K7M engines is about 100,000 rubles. At the same time, a contract engine can be purchased for no more than 50,000 rubles. But the price of the new engine is an astronomical 300,000–400,000 rubles, depending on its modification. Most cars are worth less by the time an engine replacement may be needed.
Disadvantages and advantages
The indicated characteristics of the engine and real experience in its operation since 2007 allow us to judge the shortcomings:
- a broken timing belt is fraught with major repairs;
- due to the need for high-quality lubrication, the vehicle operating budget increases;
- The cost of overhaul is affected by the high price of the timing belt and rollers, ShPG of foreign manufacturers, even if it is made by hand.
On the other hand, the motor has much more advantages; they outweigh the indicated disadvantages:
- lack of constant valve clearance adjustments;
- increase in service life, power and torque;
- reduction of noise and vibrations;
- economical fuel and oil consumption;
- compliance with Euro-4 standard.
Metal gaskets last longer, and the timing belt does not need to be constantly tightened and monitored for accidental slippage when oil gets in.
Why is adjustment necessary?
The correct procedure depends on:
- uninterrupted operation of the LADA Kalina engine (operation with a reduced noise level in the timing belt, no errors in the camshaft sensor);
- reduction of fuel consumption to a level close to that regulated by the manufacturer;
- less wear on the camshaft cams and the pushers interacting with them.
- cleanliness of combustion chambers and valve plates due to the absence of carbon deposits.
Valve adjustment in a Lada Kalina car should be carried out with a periodic mileage of 20 thousand km or a little more.
It is not recommended to neglect this procedure, since the regulatory value of the gaps at the valves of the intake and exhaust circuits changes. This circumstance provokes a loose fit of the valve discs to the seat seats, which inevitably leads to the formation of carbon deposits, incomplete combustion of fuel, damage to the discs with subsequent burnout and other troubles in the timing belt in the LADA Kalina model. As you can see, in the absence of the required clearances, there is a violation of the correct functioning of the engine as a whole, and the only harmless point here is the owner’s acoustic discomfort due to the increased noise of the timing belt.
Note that adjustment of the valve mechanism requires 8 valve engines of Lada Kalina cars.
What cars was it in?
Immediately after its release, AvtoVAZ management began using the 21126 engine to power the following Lada models:
- Priora - from 2007 to 2016, all trim levels;
- Kalina - from 2007 to 2013, Luxury equipment;
- Kalina-2 - since 2013, on cars with automatic transmission;
- Granta - since 2011, Norma and Luxury equipment.
Lada Granta
Currently, Priora engines are equipped with 21127 engines, which have become the next version of the development of the 21126 internal combustion engine. On the other two models - Kalina-2 and Granta, this engine is used mainly with the JF414 automatic transmission from the Japanese manufacturer Jatco.
Operating principle of hydraulic compensators
The main purpose of using HA in the Priora engine is to simplify the engine maintenance procedure. If previously it was necessary to adjust each valve separately, now this procedure is carried out automatically.
Structurally, the hydraulic compensator is a cylindrical part, which consists of a plunger pair located inside its body, as well as a check valve.
The operating principle of this mechanism is simple. During operation of the power unit, the camshaft cam presses the bottom of the cylinder. In this case, the hydraulic compensator moves, as a result of which the plunger presses on the valve and, accordingly, it opens.
The clearance mentioned above is regulated by the oil pressure entering the cavity under the plunger. The greater the oil pressure, the stronger it acts on the plunger and, accordingly, the valve opens with a larger gap.
Maintenance
To ensure the declared resource, engine 21126 must be maintained in accordance with the regulations below:
- after 10,000 km, change the engine oil with the appropriate filter;
- The battery, attachment belts and crankcase ventilation can withstand 20,000 km;
- The tank cap, antifreeze and cooling system hoses, fuel and air filters cannot overcome the 40,000 mileage mark;
- It is recommended to replace the oxygen sensor after 100,000 km, and the timing belt after 180,000 km.
Complex design solutions have been added to the internal combustion engine, so it is necessary to meet the deadlines for replacing consumables.
2.11. Adjusting the clearances in the valve drive
Rotate the crankshaft only by the bolt securing the pulley to it (do not turn the crankshaft by the camshaft pulley).
It is inconvenient to turn the crankshaft by the bolt securing the pulley to it, so to set the camshaft cams to the upper position, engage any gear (preferably fourth) and slowly roll the car until the cams take the desired position. If it is not possible to roll the car, hang up any front wheel and, having engaged any gear, align the cams by turning the hung wheel.
The order in which the gaps are adjusted does not matter.
To compensate for the thermal expansion of the valve, a gap is structurally specified between the end of the valve stem and the camshaft cam. With an increased gap, the valve will not open completely, and with a decreased gap, it will not close completely.
The gap is measured with a feeler gauge on a cold engine (at a temperature of +20 ° C) between the camshaft cam (the cam should be directed upward from the pusher) and the valve pusher adjusting washer. The nominal clearance for the intake valve is (0.2±0.05) mm, for the exhaust valve - (0.35±0.05) mm. The gaps are adjusted by selecting the thickness of the shims. Spare parts are supplied with washers with a thickness of 3 to 4.5 mm every 0.05 mm.
Counting from the camshaft drive belt: valves 1, 4, 5 and 8 are exhaust, valves 2, 3, 6 and 7 are intake.
Malfunctions, causes, elimination
Since the 21126 engine is a 16-valve front-wheel drive design with an overhead camshaft position, it is prone to characteristic breakdowns:
| No startup when crankshaft rotates | 1) ignition coils are faulty 2) failure of electronic control 3) DPKV breakdown 4)fuel system malfunction | 1) Repair or replacement 2) flashing or replacing controllers 3) replacing the crankshaft position sensor 4) replacing the pressure regulator, cleaning the fuel module, injectors and ramp |
| The engine won't start | 1) cold 2) warmed up | 1) recharging the battery, cleaning the power system, replacing the coolant temperature sensor, replacing injectors, repairing the fuel management system 2) in addition to the above, replacing the air filter |
| The speed is floating XX | 1) vacuum hose connections 2) cylinder head gasket 3) clogged air filter | 1) replacing or tightening clamps 2)use a new gasket 3) cleaning or replacing the cartridge |
| Misfire in XX mode | 1)low compression 2) injector failure 3) failure of the ignition coils 4) faulty spark plugs | 1) replacing rings; valve stem seals2) installation of new injectors 3)repair or replacement 4) gap adjustment or replacement |
If you follow the requirements of the operating instructions and maintenance regulations, these troubles can be avoided.
Detailed diagnostics of hydraulic compensators on Lada Priora
Sometimes, to determine the causes of knocking hydraulic compensators on a 16-valve Lada Priora engine, the thermal state of the engine alone is not enough. A set of tests makes it possible to more accurately determine the factor that causes extraneous noise.
Diagnosing the condition
One of the common complaints is knocking noise both cold and hot. However, as the speed increases, the symptom disappears. One of the following options is relevant:
- Worn or damaged ball valve. You can't do without replacing the hydraulic compensator.
- Contamination of the internals of the hydraulic fluid with wear products due to the choice of incorrect lubricant or untimely replacement. Washing the internals and changing the oil composition to a standard one eliminates the problem.
Engine tuning
By default, engine 21126 is already boosted by AvtoVAZ designers. However, the power of the internal combustion engine can be further increased by tuning. It is enough to take into account the following nuances:
- The ShPG is already as lightweight as possible, but you can bore the cylinders and use a piston group of a larger diameter;
- tuning of the gas distribution mechanism is most often used - split gear and lightweight Nuzhdin camshaft;
- tuning of the intake and exhaust systems is used - 4 throttles for each cylinder, a “spider” exhaust tract diagram, respectively.
Tuning 21126
To turbocharge the engine, a high modernization budget will be required, the engine life will noticeably decrease and scheduled maintenance will become more frequent.
Thus, ICE 21126 has become an improved version of the previous modification 21124. The power characteristics and service life have increased, the design of the timing drive has been simplified, and the replacement of the belt and rollers has been made easier.
If you have any questions, leave them in the comments below the article. We or our visitors will be happy to answer them
Location of valves in a VAZ 2110, 2111, 2112 car
Using the above diagram, we will look at the structure of engines and the arrangement of valves in the VAZ 2110, 2111 and 2112 (with an injector and carburetor) for 8 valves.
3 – pusher; 4 – surface of the bearing housing;
5 – shaft for distribution; 6 – washer for regulating fuel supply;
7 – oil reflecting cap; A - gap between the mechanism cam and the adjusting washer.
In this diagram we will look at the structure of VAZ 2110, 2111 and 2112 engines with 16 valves. The 16-valve engine version uses a DOHC-type twin-shaft timing belt as shown in the picture below.
Next you can see a side section of the engine. As you can see, the 16-valve engine uses two camshafts, but otherwise the system is not much different from the 8-valve version.
And now a little about the innovation in the VAZ 2112, where an injector is used instead of a carburetor. Gasoline engines have either a fuel injector or are equipped with a carburetor. These two units perform the same function - they form a combustible mixture for supply to the engine. But how are they different? Differences between a carburetor and an injector:
- In the carburetor, the combustible mixture is sucked into the engine, and in the injector it enters the engine cylinders through injection.
- The carburetor is unstable, while the injector ensures efficient engine operation.
- The operation of the injector does not depend on weather conditions. The carburetor freezes in severe frosts.
- An injection engine picks up speed easier than a carburetor engine.
- The injector is more picky about fuel quality.
Features of the ignition switch on Priora
The Priora ignition switch is a unit equipped with an anti-theft device and a restart blocker for the starter mechanism. As can be seen from the diagram, the voltage from the battery is supplied to output 30 of the VAZ ignition device. To ensure protection of the unit circuit, relay K4 is installed in the fuse block. When the ignition key on a Priora is set to position 0, the locking rod of the anti-theft mechanism extends. The key can only be removed in this position.
Different circuits are activated in different key positions:
- I. In accordance with the connection diagram of the connection wires, in this position the operation of the motor control system, the excitation circuit of the generator unit, optics, and alarm are activated. The instrument panel, windshield cleaning system, and power windows are also included, if included in the package.
- II. In this position, all components activated in position I work, as well as the starter device (video author: Alexey Wolf).
Pinout of the lighting control unit on Priora
This switching and control combined module has several functions and is used to turn on/off parking lights, headlights, select the desired light switching mode, turn on/off fog lights, adjust the brightness of the backlight combination, control the headlight range control, on/off and control light inside the cabin and instrument lighting. The module is connected to the vehicle’s on-board network via chip No. 1118-3724500.
The standard terminal pinout on a VAZ 2170 is as follows:
| G, 56b | To the gear motor for adjusting headlights |
| 58b | Output to backlight sources |
| 31 | Weight |
| Xz | +12 volts (from terminal 15 of the ignition switch) |
| 56 | To the relay for switching high and low headlights |
| 1,3 | From rear and front fog lights |
| 2,4 | To the rear and front fog lamp relays |
| 58 | To the size lamps |
| 30 | +12 V from terminal No. 30 of the ignition switch |
Self-repair of the Priora comfort unit, is this possible?
If you have never encountered soldering, diagnostics of printed circuit boards of varying complexity and configurations, or do not have the necessary diagnostic or soldering equipment, then it is better to address the repair question to qualified specialists. If you have the above skills and understand the causes of malfunctions, independent repairs are carried out quite often. This is due to the fact that various microcircuits or chips constantly fail. For example, having established that the reason for the turn signal failure is a failed control driver, it is always possible to purchase a new part and simply re-solder it to replace the faulty one.
Malfunctions and their possible causes
The cost of a new, original unit is quite high, so do not rush to buy a new product, figure out the causes of the malfunctions. Of course, there are always cases when the board cannot be repaired and it is more advisable to simply install a new product to replace the faulty one. Do not forget that the causes of malfunctions can be frayed or broken wires that are connected to energy consumers.
According to statistical data collected on technical support forums, car owners quite often complain about malfunctions in the operation of power windows, turn signals, and parking lights.
If we talk about the components of the printed circuit board itself, the most common breakdowns are associated with: - a break in the W-Line communication line; — burnout of control drivers; — burnout of controllers responsible for correct operation; - the output of their transponder; — significant oxidation of contacts.
"Important! Before carrying out any electrical work, disconnect the power supply by disconnecting the negative terminal of the battery."
Car alarm connection points for Lada Priora 2011
Author RA9UBD
Ignition switch: + 12V – brownStarter – redIGN – blue/black
Tidy: Tacho signal - brown/red Handbrake - brown/blue (For more details, see Diagram 1)
Connector X3 (See Fig. 1) BCM: Driver's door limit - blue/black Right front door end - brown Rear door end - gray/red Trunk end - yellow/red Trunk opening (low-current input, possible without a relay, additional channel directly to the alarm) - blue red
Connector X1 (See Figure 1) BCM: Turns – blue, blue/black
Ts.Z. - brown; The wire is located inside the driver's door, in the harness from the button block. (See Diagram 3 for details)
Hood end cap – white/black; Connector X2-17 (If an engine temperature sensor is used, then according to scheme 2)
The block is located behind the panel, near the gas pedal. To remove the block, remove the left and right panels, unscrew the two 10mm nuts, left and right, securing the block.
Connection to central locking
When connecting the central locking (see diagram 3), if you connect only to the brown wire in the driver's door, then all doors will close and only the driver's door will open. To open the remaining doors, you need to use a wire in the alarm for two-step opening of the central locking system, and connect according to the diagram below.
The remaining doors are opened by the second impulse, relay K1. Relays K2 and K3 are also activated; they are needed to block the right power windows. If this is not done, then when you open the remaining doors, the right windows will open slightly for 0.8 seconds, i.e. from the impulse to open the central locking, the second step. It is necessary to block the power windows due to the peculiarities of the electrical circuit of the Priora doors.
If the configuration does not include power windows on the rear doors, then relay K3 does not need to be installed, and accordingly, cell X1-11 in connector X1 is not used. (The color of wire X1-11 is not known.) If the configuration does not include power windows at all, then there is no need to use relay K2.
Air conditioning systems
One of the consumers is a heating device. It is part of the climate control system. A control controller works with this system. The work is automatic. The driver only sets certain parameters.
On cars, the electrical circuit of a VAZ Priora may contain air conditioning systems. After pressing the button, the relay is activated, the compressor is turned on, power is supplied to the electromagnetic clutch, and the pump is turned on. The air conditioning turbocharger begins to rotate, creating pressure, and begins to regulate refrigerant through the system.
Why are hydraulic compensators knocking?
The 21126 engine is a reliable design with a long service life, but even with such characteristics, difficulties may arise in the operation of the gas distribution mechanism. Over time, when driving a Priora, a characteristic knocking sound of the hydraulic compensators occurs when cold or hot. In this case, there is a drop in the power of the power unit and an increase in the noise level of the latter.
It is worth noting that the service life of this part for VAZ 2170-72 Priora cars is about 100 thousand kilometers. It may vary and depends on the quality of the oil used.
The main reason why knocking occurs is the characteristics and quality of the engine oil. The design of hydraulic compensators implies increased sensitivity to the characteristics of the lubricant and, accordingly, deviations from the manufacturer’s recommendations directly affect the service life of the hydraulic fluid.
Video on the topic:
» Quite often the knocking problem is solved by changing the engine oil. In this case, it is necessary to flush the engine with a special liquid.
Almost always, after an oil change, a characteristic noise from the compensators follows, because the new oil has not had time to rise to the plunger pair of the hydraulic valve. This is observed for about the first five minutes of engine operation, after which the knocking stops.
If after changing the oil the situation has not changed and the knocking continues, then there is the option of flushing the power unit, which is done in two ways:
- Use of special flushing fluid. It is poured into the engine and temporarily used in it. However, its effect is questionable, since there are often fakes on the market, and they do not help.
- Dismantling and manual washing of each hydraulic compensator.