The clutch, like any other element of the car, can fail over time. Most often this is manifested by clutch slipping, which directly affects the dynamic characteristics of the car. If the clutch slips, the dynamics of the car will decrease and traction will deteriorate, and over time, problems with the gearbox may arise. To prevent this, you should know why the clutch slips and what to do in such a situation.
How to check the clutch?
There are several verification methods. The main one is based on the use of measuring equipment, which you most likely do not have. We are talking about a special measuring gauge. The advantage of this method is that the clutch discs do not require dismantling - you just need to lift the car on a lift.
Such a check will take a lot of time, but the method will allow you to get an accurate result. This method of verification is used at service stations. How else can you check the clutch on a car? There are other alternative methods that do not require equipment.
What is the life of the clutch disc?
As a rule, vehicle manufacturers do not specify specific clutch disc service life. This is due to the fact that clutch wear depends on many different reasons, among which the operating conditions of the vehicle play an important role. The same part under different operating conditions can last from 5 thousand to 100 thousand km. mileage Participation in racing, slipping and frequent sharp starts at high speeds - all this reduces the service life of the part.
It is customary among car owners to replace the disc every 80-90 thousand kilometers, however, it is better to first diagnose the condition of the part.
Slip check
This check is carried out if there are prerequisites for improper clutch operation. But depending on the nature of the breakdown, the method may differ. The most common situation is clutch slipping. In this case, its correct operation is checked as follows:
- We put the car on the handbrake.
- Let's start the engine.
- We activate third gear (fourth is possible).
- Depress the clutch and press the gas pedal.
If the engine stalls, then most likely the clutch disc is worn out and requires replacement. However, such a result is not always accurate.
Basket installation
To repair or replace the clutch basket, you need to unscrew the bolts holding it. If you can see that the basket petals are very worn, it is best to replace the entire part.
To install a new basket, it is necessary to straighten or center the gearbox input shaft, since otherwise the displacement of the disk will not allow the box to be put on. Therefore, the operation of inserting the disk with the mandrel into the flywheel must be performed very carefully.
After putting the basket in place, you need to tighten the clutch bolts. In this case, the bolts are tightened gradually, over 3 or 4 turns of the flywheel.
The final step in replacing the basket is to install the release bearing on a well-lubricated shaft.
The specific technology for removing the clutch basket and replacing it depends on the type of engine and type of clutch mechanism, but for most cars it is similar to that described above.
Checking slippage
How else can I check the clutch disc? The second method does not involve the use of any special techniques. When driving in city mode, the driver simply needs to carefully monitor the behavior of the car. For example, if the car goes up very hard, there is a burning smell or a drop in speed for no apparent reason, then slipping occurs. In this case, you can try to replace the clutch disc, however, in this case, other elements of the system may be the culprits for this behavior of the vehicle, and the clutch may turn out to be serviceable. So additional diagnostics will be required.
Clutch service life and factors affecting service life
Unfortunately, there are no specific figures, for the simple reason that everything depends on a lot of factors. Among them are the following:
- Driving style (racing, sudden starts, frequent slipping, etc.);
- Product quality and operating conditions;
- Foreign liquids and objects caught on the clutch;
- Incorrect installation and adjustment of the clutch.
- Signs of a bad clutch
- The dynamics are disrupted (especially when driving downhill);
- Difficulty shifting gears;
- Jerks when changing gears;
- Burnt smell, extraneous sounds (grinding, crunching, etc.).
When the clutch "leads"
When the clutch “leads”, unpleasant sounds appear from the gearbox, and it becomes more difficult to engage gears. In this case, there is a way to check the clutch:
- Turn on the engine and set the gear to neutral.
- Depress the clutch pedal.
- Turn on first speed.
If you have to exert force when activating the gear and there are strange sounds coming from the box, then this primarily indicates that the flywheel disc is not disengaging. Most often, this problem is solved by bleeding the hydraulics and adjusting the pedal.
Is it possible to drive like this?
It is highly undesirable to continue operation with a slipping clutch. It is not always possible to accurately control the moment when sliding begins, and this will release significant power.
So much so that the linings can burn completely in a matter of seconds. After which the car will be completely immobilized, possibly in a dangerous place on the road, and during repairs it will also be necessary to replace the flywheel, which is covered with cracks from overheating.
After the first signs of slipping, you must, without sudden acceleration and at low speed, proceed to the repair site, where you can replace the complete clutch. Attempts to save money on individual parts usually lead to unnecessary work on removing and installing the gearbox.
Checking disc wear
Let us remind you that the clutch disc necessarily has its own resource. Many car owners forget about it and change it only when driving the car becomes uncomfortable. In urban driving mode, this resource decreases quickly, and if the car has “ran” about 70-80 thousand kilometers in the city, then the clutch disc is simply bound to “fail”. However, when driving on highways, the car can travel more than 300 thousand kilometers without replacing the clutch disc.
The easiest way to determine the degree of wear on the clutch disc is by using the pedal stroke. To do this you need:
- Place the machine on a level surface.
- Start the engine and warm up to operating temperature.
- Engage first gear and slowly release the clutch. In this case, the engine must not be allowed to stall. Please note at what point the transmission of torque to the wheels begins. If vibration appears on the car body, stop checking.
If the clutch begins to engage at the very beginning of the pedal stroke, then this indicates that everything is in order with the disc and its degree of wear is either low or absent at all (the disc is new). If the clutch occurs in the middle of the pedal stroke, this may indicate disc wear, but not always. Some machines may have a similar pedal adjustment, in which the disc engages in the middle of the pedal stroke.
avtoexperts.ru
The clutch is an important and integral part of cars with manual and robotic transmissions; without it, it would not be possible to operate the car in different modes and change speeds. The clutches of modern cars are structurally verified, reliable and have a long service life (which we will, of course, talk about later), but still do not last forever. Sooner or later the question of checking and diagnosing the clutch arises. And here comes the problem.
Pictured is the clutch disc
If the clutch elements were in plain sight, then there would be no question at all - even a person far from car repair can determine the condition by eye, but the clutch is structurally located somewhere in the depths, so it will not be possible to look at it without effort. Of course, you can remove the gearbox, transfer case and other units that block access, but usually this is such a labor-intensive process that you don’t want to go through it just for the sake of diagnostics. So, it is most often necessary to draw conclusions about the need for repairs based on indirect signs. Fortunately, they also have a lot to say.
Symptoms
Usually the desire to check the clutch does not arise out of nowhere and is accompanied by the appearance of some problems that “come out” even during normal operation of the car. Difficulties when changing gears, jerks when starting and accelerating, a burning smell even in normal driving modes, strange noises and loss of dynamics. Very rarely does everything appear at the same time, but if at least one of the above is observed on the car, then it’s worth thinking about the health of the clutch. For each of the symptoms, the clutch may have nothing to do with it, so their presence is not an automatic indication for repair or replacement, but a reason to pay more attention to the issue.
Two ways to determine wear
The easiest way to determine clutch disc wear is that there are no problems with diagnosing this. There are two ways.
The first is to check in motion. On a free road, accelerate to the highest gear (fifth or sixth depending on the manual transmission), try to accelerate sharply and watch the tachometer and speedometer. If the revolutions and speed grow synchronously, then everything is fine, but if the so-called variator effect is observed, when the revolutions first jump sharply, then the speed gradually begins to increase, then the clutch slips, which means it is worn out. This is most pronounced in top gear, so it is recommended to use it to check.
Clutch disc worn 40%
The second method is even simpler: while standing still, engage fourth gear and try to get going. If the engine stalled or the car, although it moved, but with very great effort, then everything is fine with the clutch, but if the start of movement happened relatively smoothly and easily, then, probably, the clutch is already working as a torque converter and “erodes” the torque, which means it's time to change it.
The above is most likely not even a breakdown, but simply an exhausted resource. Many people ask what is the service life of the clutch, but the answer to this question greatly depends on both the driver’s experience and operating conditions. A beginner who spends all his time in traffic jams, constantly driving with a trailer and slipping, can burn out the clutch in 30-50 thousand kilometers. For an experienced driver who only drives on the highway in an empty car, the clutch can last almost forever. If we put aside the extremes, then under “normal” operating conditions, the clutch lives for 100-200 thousand kilometers .
As for the two methods of checking, the first seems clearer and simpler to us, in the second a lot depends on the driver’s feeling of the car, on the elasticity of the engine, on the gear ratios in the gearbox, but, in general, both may well make it clear that the clutch is worn out and its it's time to change. Usually, at the first signs of slipping, you can still drive the car for some time without accelerating to the floor, but we would recommend not delaying the replacement - a slipping clutch is both uncomfortable and unsafe, because at the right moment there may not be enough traction.
Clutch basket arrangement
Failure detection
In addition to the fact that the clutch can wear out its life, some elements can also simply break. If the resource is associated with more or less decent mileage, then a breakdown can happen at any time. If the resource problem arises with a worn-out disk, then in case of breakdowns most often problems arise with the release bearing.
Release bearing
Releaser problems usually do not need to be diagnosed; they are more than obvious. They often manifest themselves in gear shifting. Of course, the problem could be something else, but if no more obvious reasons were found, then there is a high probability that it is the release mechanism - it either does not completely open the discs, or, on the contrary, prevents them from closing tightly. Most often, this is precisely the incomplete opening of the discs; in this case, it is customary to say that the clutch is “driving.” If such signs are detected, it is not necessary to immediately change the clutch; you can try to bleed the drive (if it is hydraulic, of course) or adjust the clutch pedal. Sometimes this helps solve the problem, but rarely.
It is also often recommended to draw conclusions about the operation of the release valve based on the sounds from the box - if there are problems with the bearing, there will be foreign inclusions. Indeed, this often happens, but we would not call it a very accurate indicator. Especially if it is not a strong grinding or impact, but something quiet. Like the banana joke, sometimes an extra sound is just an extra sound. An example is the first generation Renault Logan, many of whose owners paid attention to a quiet chomping sound when the car was idling. When the clutch was depressed the sound disappeared. It turned out that the source of the sound was the Valeo release valve installed at the factory; this is its design feature. Replacing with a new one from the same company did not give anything - they all “slurped.” With this sound, the bearing was completely serviceable, easily traveled hundreds of thousands of kilometers and did not annoy anything else. The only way to get rid of the sound was by installing a bearing from a different brand.
Checking the clutches of “robots”
As we have already noted, the clutch is used not only in mechanical, but also in robotic gearboxes. Despite the fact that the operating principle is similar, everything is controlled by an electronic control unit, so the checks that were used for mechanics are either completely impossible or may have dampened results due to the peculiarities of the electronic part of the “robot”. There are no special checks for such boxes, but you can additionally pay attention to a few points.
Robot DSG
Firstly, switching gearbox modes at idle. “D”, “R” and “N” should replace each other without twitching or extraneous sounds. Secondly, the smoothness of gear changes on the go; if there are strong jerks and delays, then something is wrong with the clutch.
Despite the development of electronics and very smart and complex systems, in terms of the quality and delicacy of work with the clutch, “robots” are still far behind “live” drivers, so they almost always wear out much faster. Moreover, this applies to both simple single-disk “robots” and more complex double-disk ones. But the presence of electronics allows you to count on computer diagnostics. What, how and with what equipment specifically can be diagnosed depends on the model of the box, but usually there are some possibilities. For example, on a very popular and widespread DSG, using a scanner you can not only read mechatronics errors, but also determine the wear of the disks, not only with proprietary software, but also with popular third-party programs such as VCDS. The fact is that with a DSG, unlike a manual transmission, the clutch is open by default, and the closure occurs only while moving, and its strength is varied by the control unit. Based on how tightly the electronics close the discs, you can draw fairly accurate conclusions about the thickness of the linings and the operation of the disc. If for manual transmissions all the checking methods we described are of an approximate and approximate nature, then for “robots” the scanner can display the residual thickness of the disks in millimeters, and the clutch replacement time can be determined with mathematical accuracy.
DSG robot - checking the remaining clutch
In general, checking the clutch is not a big problem. Evaluate the feeling of using the gearbox and conduct a couple of simple tests - that’s the whole recipe. The clutch on the “mechanics” is a long-lasting unit, it does not break and wear out its life very often. But if the clutch is still worn out, then it is better not to delay replacing it - such a ride is uncomfortable and unsafe. And taking into account the fact that the cost of replacement work is considerable, it is better to replace it as a set without particularly understanding which element has suffered the most - it will be cheaper in the end than going into the unit a second time.
Checking the release bearing
It's not enough to just know how to test your clutch. You also need to be able to check the release bearing, since this element plays an important role in the transmission system. Often its failure is confused with the failure of the entire clutch system.
The check is carried out with the clutch pedal depressed, since it is in this position that torque is transmitted to the bearing. It moves away and pulls the clutch disc behind it. Therefore, it is not recommended to hold the clutch pedal down for too long, as this puts unstable loads on this part and leads to its rapid wear.
A clear sign of bearing wear is sounds when the clutch pedal is pressed (knocking, rustling). However, if such sounds appear in cold weather, then there is no need to worry. This part has a low expansion coefficient at low temperatures due to the high strength of the steel. And the glass itself, where the entire assembly is located, has a high expansion coefficient. Therefore, when heated, the sound should disappear.
In addition, there are other signs that indicate a clutch malfunction: incorrect gear shifting, the inability to engage some gears at all. It is also worth paying attention to the jerking of the car when driving at speeds.
What contributes to accelerated clutch wear?
The first and main reason for accelerated wear of the clutch is careless handling by the driver, namely sudden starting, slipping, and holding the clutch pedal for a long time. It is important to understand that there are two parts in the clutch that fail most quickly and, accordingly, do not tolerate harsh operating conditions - the clutch friction disc and the release bearing. The clutch disc begins to wear out faster, and its increased wear is characterized by a specific smell, which is called a “scorched clutch,” and the release bearing, due to prolonged idling, crunches and buzzes.
The second point lies in the quality of components. If you purchase the clutch separately, then the difference in the quality of the components has a detrimental effect on the entire assembly. A poor-quality clutch works less and sometimes slips. And finally, the third reason is incorrect clutch installation. It could be one of the following:
- the friction disc is installed on the reverse side;
- the release bearing does not “sit” enough in its place;
- The clutch disc was not centered during installation.
How to check clutch cylinders?
If the cylinders are faulty, the car may either not respond to the clutch pedal at all or respond incorrectly. Often, car owners whose main or auxiliary cylinder does not work complain that the car starts moving even when the clutch pedal is pressed. This primarily indicates a faulty cylinder. Checking them is quite simple: considering that there is nothing special to break there, you only need to check if there are any fluid leaks in the cabin (immediately above the clutch pedal and under the hood). If there are no leaks, then most likely everything is fine with the cylinders.
Characteristic
The clutch system is a separate design that allows the drive shaft of the motor to be disconnected from the mechanical drive to the drive wheels for a short period of time. This is done to switch to a higher or lower transmission gear. Also, with the help of the clutch, they achieve smoothness when turning on and off the load on the internal combustion engine. This helps prevent damage to the crankshaft of the power unit.
For all vehicles with a manual transmission, the clutch device is standard. So, it consists of a flywheel, a driven disk, a “basket” and a release bearing.
Design features
Clutch basket is the popular name for the pressure plate, which is an integral part of the car transmission. It is a structure with a convex round base, into which pressure springs are built-in.
These elements are connected to a special round platform called a clamping platform. It has a smooth, sanded surface on one side to ensure a tight surface fit. From the center of the basket there are special pressure springs attached to the flywheel.
The purpose of a car's clutch assembly is to smoothly connect the flywheel of the car's power unit and the gearbox shaft. This is done by connecting a disk (in other words, a basket) to the driven element.
There are single-disk mechanisms with one driven disk and multi-disk ones. Most cars have a single-disc design. There are also dry and wet mechanisms. Wet works in an oil environment. Most of the components installed in the machines are dry.
According to the method of actuation, clutch mechanisms are divided into mechanical, electrical, hydraulic and combined. Nowadays, most cars are equipped with manual varieties.
How does it work
The operation of any motor provides torque on the flywheel. By controlling the gas pedal, the driver only increases the number of revolutions on the flywheel or reduces them. In order for a heavy vehicle to start moving smoothly, this torque must be transferred from the flywheel to the gearbox and drive wheels. This torque must be transmitted as smoothly as possible. Otherwise, the engine will stop and stall. It is also necessary to smoothly disconnect the transmission from the engine when stopping. The clutch system is responsible for the smooth transmission of torque.
The principle of operation of the clutch is simple and clear. It is enough to imagine two disks - both of them rotate. One of them is the drive disk (flywheel), the second is the clutch system disk. If, while the flywheel is rotating, the driven element of the clutch is pressed against it, the torque will begin to be transmitted to the transmission. And from there the energy will go to the drive wheels. This will allow the car to start moving smoothly.
As you can see, everything is very simple. The principle of operation of the clutch is to press and disengage the friction driven disk of the clutch to the flywheel through a mechanical or hydraulic mechanism. In the first case, a cable mechanism is used. The second contains the clutch slave cylinder. It contains brake fluid inside.
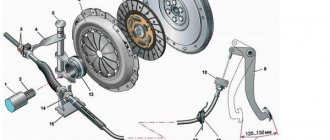
ABOUT THE CLUTCH DEVICE
Its design on this car is similar to mechanisms 2113 and 2115. It is made of a dry, single-disc mechanism. It is produced with a device that dampens torsional vibrations, and also has a pressure spring. The VAZ 2114 clutch device is shown in the figure.
Clutch components
The VAZ 2114 clutch consists of (see picture):
- Cable with a casing;
- Cable tip (lower);
- Adjusting nut;
- Housing for attaching the shell to the gearbox;
- Separating washers;
- Nut for adjustments;
- Rubber protective shell;
- Cable lead;
- Shutdown plug;
- Basket;
- Bolts securing the basket to the flywheel;
- Pressure disk;
- Flywheel;
- Driven disk;
- Gearbox input shaft;
- Shield;
- casing;
- Spring (pressure);
- "Squeeze";
- Pad;
- Release housing;
- Cable end;
- Cable thrust washer;
- Cable fastening unit;
- Pedal axle;
- Release spring;
- Off pedal.
As can be seen from the mechanism diagram, there are two working units, one of them will be the master, and the second will be the slave. The second includes a disk with linings riveted on both sides and damper springs installed. It is installed and moves along the splines that are present on all gearbox input shafts. When the pedal is pressed, the driven disk is pressed against the flywheel by the pressure disk.
The drive unit includes a pressure disc with a clutch housing, which is attached to the flywheel with six bolts. To center it, there are pins on the flywheel and guide holes in the housing. The clutch has a backlash-free design and is operated by a cable.
To turn it off, a clutch drive is installed, which operates by pressing the pedal. The cable is hingedly attached to it with its upper tip. The lower end of the cable also has a hinged connection with the shutdown fork. With its movement, the “cable” turns it, and it moves the “releaser”.
Signs of slipping
It was described above how to find out that the clutch is faulty. When the car is moving, the interior will smell like burning. The car will accelerate worse. A decrease in speed is noticeable when overcoming a steep climb. These are all symptoms of a slipping clutch.
There is a simple way to diagnose this malfunction. So, with the engine running and the handbrake on, engage the gear. Then, after smoothly pressing the accelerator pedal, release the clutch. If the engine stalls, then everything is in order and the clutch is fully operational. If the car is running (while standing still and not moving), then the clutch slips.
Let's sum it up
As you can see, the Gazelle clutch (Business, Classic, etc.) must be of high quality and reliable, while providing a sufficient level of comfort when operating the vehicle.
Finally, we note that it is also important to purchase only original products from well-known manufacturers, since cheap kits or counterfeits of the original are characterized by poor quality of work and a short service life, especially on loaded machines like the Gazelle.
To reduce the risk of purchasing counterfeits, you need to pay attention not to the packaging, but to the presence of holograms and markings on the parts themselves, and also purchase clutch kits only from trusted suppliers.
GAZelle gearbox oil: when to change, choosing gear oil in a GAZelle gearbox, changing the oil in a GAZelle gearbox. Useful tips and tricks.
Manual transmission on a GAZelle car: device, main faults and signs of problems. Gazelle gearbox repair, tips and recommendations.
Installing a Japanese engine and automatic transmission on a GAZelle: what to look for when replacing units. Engine power, automatic or manual transmission, tips.
GAZelle Next with a diesel engine: characteristics, strengths and weaknesses of the Cummins diesel engine. Upgraded 150-horsepower diesel engine for GAZelle Next.
Automatic transmission on the domestic GAZelle Next car: features of automatic transmission, advantages and disadvantages of automatic transmission.
Advantages of installing a diesel power unit instead of gasoline or LPG. Choosing a suitable diesel engine for GAZelle and UAZ (UAZ) to replace a gasoline engine.
Removing, checking the condition and installing clutch components
Dust generated during the operation of the clutch and accumulating on the surface of its components may contain asbestos that is harmful to health. NEVER blow dust off clutch components with compressed air or inhale it. DO NOT use petroleum-based solvents or gasoline to remove dust. To wash off the dust into a prepared container, you should use compounds designed for cleaning brake mechanisms. After cleaning and wiping the clutch components, drain off the used cleaner and place the dirty rags in a properly marked container.
Causes of malfunction
Several reasons can be identified. This usually happens if the manufacturer's recommended free play of the pedal is violated. Also, this situation occurs due to wear or oil getting on the surface of the friction lining of the clutch disc, due to wear of the leaf spring on the clutch basket.
In hydraulic systems, the clutch slips due to a malfunction of the cylinder drive. Often this malfunction occurs due to deformation of the drive disk, as well as due to failure of the release bearing. If the reason is insufficient free play, then to eliminate the problem, dismantle the system and pedal assembly. Next, rinse well and change the pads if necessary. If the leaf springs are weakened, then the basket is replaced. The clutch is a consumable item, just like filters and belts.
The main signs of a clutch failure.
On any car, the clutch wears out as it is used, and its operation begins to be worn out. Clutch diagnostics should be performed when the following signs are detected:
- On cars that have a manual transmission, the clutch “grabs” even if the pedal is in the top position. The higher it is, the more worn out the clutch is. This can be easily checked when driving the car.
- Decrease in dynamics. If the clutch discs slip, the power generated by the engine will not be fully transmitted to the gearbox and wheels. This problem is often accompanied by the smell of burnt rubber.
- Reduced dynamics when driving with a trailer. The problem here is the same as in the previous paragraph.
- When starting from a standstill, the car jerks. This may occur due to a damaged surface of the driven disk due to overheating. Overheating, in turn, can occur as a result of excessive force on the clutch part.
- The clutch "drives". This problem is the opposite of slippage, where the drive and driven discs do not fully disengage when the clutch is depressed. As a result, the driver has difficulty changing gears, and sometimes some, or even all, of them simply do not engage. Also, when switching, unpleasant sounds may be heard.
Not only do natural processes wear out the clutch, but improper operation of the vehicle also contributes to this. It should not be overloaded, tow trailers that are too heavy, especially when moving downhill, and you should not start with slipping. Such use leads to a critical operating mode of the clutch, due to which it may partially or completely fail. If at least one of the described symptoms is detected, the clutch must be checked. Driving a car with a faulty clutch not only causes discomfort, but also further worsens its technical condition, which leads to expensive repairs.
How to troubleshoot
Every car enthusiast must know what to do if the clutch slips. After all, this problem should be solved as soon as possible, so that during the movement the breakdown does not lead to failure of the motor.
Before removing the gearbox and checking how worn the clutch system components are, it is recommended to make sure that the pedal has sufficient free play. Each manufacturer has a different parameter.
For domestic cars, the free play size is from 20 to 30 millimeters. But it is better to find out exactly the parameter in the operating instructions. When the free play is abnormal, it should be adjusted by tightening or releasing the clutch cable.
If the free play is normal, but the clutch slips, the reason may be disc wear. This is the most common problem. In this case, it is necessary to dismantle the gearbox, unscrew the fastenings of the clutch basket, then remove it. Next you can see the driven friction disc. It must be removed and replaced with a new one suitable for the specific car model.
Procedure for removing the mechanism
It is easiest to repair or replace the clutch basket when the entire engine is overhauled. If the power unit is removed, then you can inspect, repair or replace worn parts of this part of the car without much effort. In this case, dismantling the unit does not present any difficulties.
Let's take a closer look at how to disassemble the clutch and how to remove the failed part. The operation scheme is simple. The main thing is to comply with the technological regulations given below:
- First you need to remove the gearbox (gearbox). If the gearbox does not need to be repaired, then there is no need to disconnect the drives before removing the battery and mass flow sensor and draining the oil.
- Unscrew the drive (cable) that activates the mechanism and remove it.
- Unscrew and remove the starter.
- Unscrew the top bolts securing the box.
- Unscrew all electrical wiring harnesses and the speed sensor chip.
- Loosen the drive nut on the right side and completely unscrew the nut on the left side.
- Unscrew the suspension arm.
- Unscrew the ball joint.
- Remove engine protection.
- Remove the reverse signal switch chip.
- Unscrew the torque rod from the gearbox and remove the lower cover of the clutch housing.
- Loosen the nut of the gearbox control drive clamp and remove the rocker.
- Unscrew the lower bolts and gearbox mounting nut.
- Jack up the engine.
- Unscrew the gearbox from the pillow.
- Remove the box and gain access to the necessary component of the car.
Recommendations from experts
Do not forget about certain features of the car. The engine crankshaft is always in a balanced state. Therefore, at the time of dismantling, the clutch system casing tilts. The mounting screws are unscrewed according to their diameter - each bolt should be removed sequentially.
After dismantling, you can see a disk with worn friction linings. They can be updated if the rivet head is less than 0.2 millimeters away.
Clutch Specifications
Technical requirements for brakes
- The clutch lining must be firmly glued with VS-YUT glue. Peeling of the overlays is not allowed.
- The thickness of the new clutch lining is (5±0.1) mm. The permissible thickness of a worn lining is 3 mm.
- Driven disk. 1. When replacing friction sectors, select them with a thickness variation of no more than 0.1 mm.
- The non-flatness of the friction surfaces of the driven disk is allowed no more than 0.3 mm under a uniformly distributed load of 150 N (15 kgf). Disc straightening is allowed.
- The thickness of the new driven disk with linings is (13.5±0.47) mm. The permissible thickness of a worn disc is 10 mm.
Technical requirements for pressure plate flange
- The difference in the weight of the levers is allowed no more than 0.01 kg.
- Fluctuations in the load of the coupling springs are allowed no more than 20 N (2 kgf).
- The width of the groove for the roller is 6±0.18 mm. The permissible gap between the roller and the wall of the support groove is no more than 0.7 mm. The permissible gap between the lever fork and the flange support is no more than 1 mm. The permissible gap between the pin and the hole for it in the flange support is no more than 0.3 mm.
- Non-flatness of the friction surface of the pressure plate is allowed no more than 0.15 mm.
Technical requirements for the drive disk
- Non-flatness of friction surfaces is allowed no more than 0.15 mm.
- The thickness of the new drive disk is (23±0.105) mm. The permissible disc thickness is 22.4 mm.
Technical requirements for the engagement clutch
- The internal diameter of the flange coupling slider is 72±0.074 mm. The diameter of the flange for the slider is 72±0.174 mm. The gap between the slide and the flange is 0.1...0.248 mm. The permissible gap between the slide and the flange is 0.61 mm. The maximum gap is 1 mm. The outer diameter of the slider for the bearing is 90±0.025 mm. The permissible gap in connection with the bearing is no more than 0.005 mm.
- The inner diameter of the bushing for the lever pin is 17±0.07 mm. Finger diameter 17±0.15mm. The permissible gap between the bushing and the lever pin is no more than 0.5 mm. The maximum gap is 0.7 mm.
- The thickness of the bearing housing cover flange is (9±0.1) mm. The permissible flange thickness is 6 mm.
- The gap at the joint of the sealing rings should be no more than 1.5 mm.