No matter how reliable the unit is, it is still necessary to carry out routine maintenance work in a timely manner to extend its service life. This applies to all components and assemblies of the car, including the transmission. In this article we will look at the issue of maintenance and oil change in the gearbox (both in automatic and manual transmissions of a car).
We will also try to determine what time intervals should be between routine transmission maintenance work, or at what mileage this work should be carried out. At the same time, we will consider which transmission oils are best to use, and we will also pay attention to the nuances and features that need to be known and taken into account when performing transmission maintenance work.
Transmission, oils and fluids
The word “transmission” comes from the Latin transmissio - “forwarding”, “transfer”. The vehicle's transmission serves to transmit torque from the engine to the wheels, allowing you to change the magnitude of the torque and the direction of rotation.
Historically, lubricants for transmissions and drive axles were called oils. But with the advent of automatic transmissions in English-speaking countries, the concept of ATF (Automatic Transmission Fluid) appeared - fluid for automatic transmissions.
Oil change intervals
The manual transmission oil change schedule can be found in the technical documentation for the car. Unfortunately, manufacturers often do not consider it necessary to write about this in the instructions. In this case, you should listen to the advice of professionals. Experts recommend changing transmission oil every 100,000 km or after 7 years of standard vehicle use, whichever comes first. If your car is subjected to frequent loads and operating conditions leave much to be desired, you need to change the oil every 60,000 -70,000 km. The time interval also depends on the type of oil and vehicle class.
Stages of work
1. Drain waste:
- set the selector to neutral mode, raise the handbrake, put the car in a pit or lift it on a lift;
- Place a container directly under the drain plug to catch the old oil;
- dismantle the pan and remove the sealant and remaining oil;
- remove the filter, first placing a waste container under it.
2. Treat the surface of the pallet:
- Wash the tray together with the magnets with gasoline using a brush;
- wipe with a lint-free cloth;
- if it is necessary to replace the filter, it can be done at this stage;
- if the part remains, it must be treated with gasoline.
3. Place the pallet:
- degrease the area where the tray will be installed;
- change the gasket, apply a sealing compound to the joint areas;
- install the pan and tighten the bolts.
4. Pour in oil (using a funnel, pour in the same amount of liquid that was drained).
5. Push in and add lubricant (help will be needed at this stage):
- disconnect the hose, which is located on the left (in the direction of travel) and serves to cool the oil;
- place one end in the prepared container;
- put the gear in neutral, raise the handbrake, start the engine;
- the new oil will displace the old one (when fresh transmission fluid appears, you need to measure the drained volume for subsequent refilling into the system).
6. Check the oil level (this should be done, focusing on the hot and cold marks; it would be better to underfill a little rather than overfill).
How to change transmission oil
It is best to change the oil on a lift or inspection pit. If there is neither one nor the other, you can get by with jacks. Among the tools, be sure to prepare a syringe and several containers for the used liquid in advance.
You need to start changing the oil with a short drive of 10–15 km. This will allow the oil to warm up and flow through the entire hydraulic system to achieve the required fluidity. After checking in, it is better to leave the car for 15 minutes. In order not to waste time, you can immediately install the car on a lift or jacks.
Unscrew the oil filler cap. It would be more advisable to immediately check all seals and gaskets, and if they are unsuitable for further use, immediately replace them. After checking, you must carefully open the drain plug and allow the liquid to drain completely.
After removing the used lubricant, the hole is closed. Since the filler hole is quite small, new transmission oil is poured using a syringe to the level of the lower edge.
Brilliance
Probably the most honest answer is from a Chinese company that is not in the EU. He recommends for his manual transmissions the first shift is 10,000 km, and the next 40,000 km or 3-4 years.
An early first shift makes a lot of sense: new units have rough and uneven surfaces that quickly turn into chips. Their timely removal significantly extends the life of the transmission. This applies to both mechanical transmissions and so-called “robotic” transmissions. For automatic transmissions, it is recommended once every 60,000 km or once every six years.
Hyundai
Koreans recommend changing the oil in manual transmissions every 120,000 km, and in automatic transmissions - every 90,000. For models with a full transmission, the oil in the transfer case and differential must be changed every 120,000 km.
All these recommendations relate to “normal” vehicle operation, the manufacturers warn. In more severe cases, the intervals should be shortened.
But what does “heavy” operation mean? Here are the factors that shorten the life of the transmission:
- Frequent trips over short distances;
- Frequent trips on uneven, dusty roads without asphalt;
- Frequent use at low temperatures;
- Regular trips in traffic jams with frequent turning off and starting of the engine;
- Frequent steep ascents and descents;
- Use of a trailer, caravan or roof rack;
- Using a car as a truck or taxi;
- High-speed traffic - more than 140 km/h.
When to change the oil in a manual transmission
In the vehicle's operating instructions, the manufacturer provides detailed information on the recommended maintenance schedule for this vehicle. Here is also a list of suitable brands of ATF gear oils. If the driver ignores the recommendations of the developers, the car’s behavior will show signs of unstable operation of the manual transmission: unfamiliar sounds, jolts when changing gears, a burning smell in the car’s interior, etc.
How to check the level and change the oil in the transfer case?
Since it is impossible to determine whether the oil level in this part is sufficient “by eye”, you will have to measure its level with your finger through the filler hole. This should be done by placing the car on a very flat surface, letting the fluid settle and only then unscrewing the control bolt. The oil needs to be changed, not topped up, even if the level is just below the transfer port. To do this, you first need to check whether there are any impurities in it, what shade of color the oil is - whether it is cloudy.
The whole difficulty of replacement lies in the difficulty of accessing the fill hole, so an inspection hole or lift may be required. Lifts also sometimes require repairs, which can be done by these guys https://pro-podemnik.ru/uslugi/remont-avtopodemnikov/ First, you will have to pump out the old oil with a special syringe. Medical is also suitable, but there is quite a lot of oil, a lot of visits will be required, a syringe for pumping out liquids will cost 600-800 rubles. It is better to change the oil immediately after a trip, when it is warm and more fluid. Before opening the drain hole, it is better to rinse it thoroughly and even degrease it. After pumping out the oil and filling the transfer case with fresh lubricant, be sure to degrease the drain hole and plug so that a sufficient layer of sealant “sits” on them. Thanks to it, the plug will “sit back” as tightly as possible and dust will not get inside even during very extreme driving.
Types of oils and features of their use
All gear oils differ in the type of base. Inexpensive mineral oils are almost never produced today and are mostly used in rear-wheel drive vehicles. A significant “disadvantage” of such compositions is their short service life and the absence of substances that promote self-cleaning.
Semi-synthetic oils can be found in gearboxes of front-wheel drive economy class cars. Under normal operating conditions, oils of this type can protect parts from wear until the car travels 50,000 - 60,000 km. Special additives included in the composition of “semi-synthetics” protect the metal well from destruction as a result of friction and corrosion, and the reasonable price makes these oils the most popular on the market.
The most expensive and high-quality oils are rightfully considered to be synthetic oils that can withstand strong temperature changes. “Synthetics” are most popular in areas with frosty winters and hot summers. High-tech additives make synthetic oils truly durable.
Paying attention to the types of oils, the car owner should know that the characteristics of the composition intended for manual transmissions differ significantly from those for automatic transmissions. You cannot replace one with the other.
How to change the oil in a manual transmission
It is recommended to change the oil in the gearbox in autumn or winter. It is during this period that the unit bears the heaviest load and the probability of its failure is high. An urgent oil change is also required for newly purchased used cars with a mileage of over 60,000 km. The independent procedure for replacing the working fluid in the gearbox consists of several stages.
- We warm up the oil by driving for ten minutes. Placing the car on a specially equipped pit with the wheels secured using “shoes”;
- Unscrew the oil filler plug;
- Remove the drain plug and drain the oil into a container;
- We fill the unit with new oil using a syringe to the lower limit of the “oil filler” neck (be careful not to overfill), tighten the cap (most often you need a new set of cap and o-ring).
If you are not confident in your own abilities, seek help from professional mechanics.
Official service centers of FAVORIT MOTORS Group offer a wide range of services for maintenance, diagnostics and repair of cars of any make and configuration. Do not neglect problems with the gearbox, other components and assemblies of the machine, your safety depends on their condition! Transmission oil catalog Ask a question
MTF classification
The American Petroleum Institute (API) classified gear lubricants into groups - GL 4 and GL 5. The main additive packages for these groups differ in the amount of extreme pressure additives. In MTF GL5 their content is much higher, approximately one and a half times. On the one hand, this is good. But such additives in large quantities have a bad effect on non-ferrous metals of synchronizers. Therefore, most domestic gearboxes require GF4 class oils.
Information about this can be seen in the service books. If there is no such documentation, it is better not to take risks and, when changing the oil, still use GF-4. Especially if the model is Russian. Both GF5 and GF4/GF5 are applicable to foreign-made boxes. Gear oils are characterized by viscosity values of 75W90 and 80W90. The technical documentation for the car will tell you which viscosity is best to use.
The most popular semi-synthetic Lukoil oils on the Russian market are TM4 and TM5 with viscosities 75W-90 and 80W-90. They are not only used in gearboxes, but are also applicable to transfer cases, differentials and rear axles. These products stand out for their relatively low prices. ZIC GF Top 75W-90 synthetic lubricant is also good. It was recognized as the best in the rating for manual transmission. MTF Castrol and Liqui Moly are popular.
Types of gear oils
There are three main types of hydraulic fluid:
- Mineral;
- Synthetics;
- Semi-synthetic.
In general, regarding gears and gearboxes, there is no significant difference between mineral and synthetic bases. Mineral oil served as the basis for the creation of synthetics, due to the need to use additives and additives. As a result, synthetic oil lasts longer than mineral oil. Anti-scuff additives contain sulfur molecules, which, under conditions of increased load, react and form modifications of the metal.
Semi-synthetics are used for reinforced transmission mechanisms and in structures where EP characteristics are required.
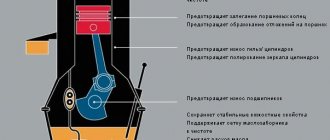
Why you need to service your transmission
Motor oil most often operates at the optimal temperatures for which it is designed - simply because the engine is heated by internal combustion and has more efficient cooling. In a gearbox, heating occurs only from friction forces, and it overheats much more often. In hot weather and during intensive use, the temperature in the transmission can exceed the engine temperature by 15-20 degrees Celsius. And overheating accelerates oil degradation.
The individual components of the transmission wear due to friction against each other. The chips get into the oil and the only way to remove them before they start clogging the fine grooves is to change the oil. In gearboxes, these shavings are mainly steel; in manual gearboxes, particles of worn synchronizers - brass, bronze and various composites - are added to this. In the case of automatic transmissions and CVTs, there is also waste from friction discs. Let's not forget about the dust that gets into the valves during the overheating/cooling cycle. When digging deep puddles, water can also get inside.
Today's "downsized" turbocharged engines make things worse because they produce more torque and put more stress on the transmission. It seems obvious that a little attention is needed to cope. But how much attention? Here manufacturers cannot give clear answers.
The Russian magazine "Behind the Wheel" recently asked several large manufacturers for recommendations and received different answers even for brands of the same concern (and with the same units in them). There are probably many reasons, including the fact that each brand has its own after-sales service policy. Anyway, here are the recommendations for different brands.
Types of oils or fluids (types of gearbox lubricants)
- Mineral is the most popular lubricant for low-speed gearboxes. A cheap type of liquid that quickly loses its properties. It is recommended to change this fluid every 30-40 thousand km. mileage
- Semi-synthetic type - suitable for high-speed gearboxes. The lubricating fluid from this group is saturated with additives to improve chemical properties and anti-corrosion properties. The recommended replacement interval is 40-50 thousand km. mileage
- Synthetic type is the most expensive type of lubricant with a large number of high-quality additives. Mainly used in automatic transmissions. The recommended replacement interval for “synthetics” for manual transmission is 60-80 thousand km. mileage, for automatic transmission up to 50-60 thousand km.