History of the creation of ZMZ 406
The Zavolzhsky plant engine number 406 begins its history from the very end of the eighties. At the engine design stage, it was clear that the power unit would become a promising invention. This conclusion could be safely made taking into account the advanced trends in engine building that were embedded in its creation.
The latest achievements in engine building at that time were considered:
- electronic control of processes occurring in the power unit;
- sixteen valve cylinder head;
- installation of an injection system to power the internal combustion engine;
- the use of a cast iron block implied a long service life of the internal combustion engine, taking into account two repair borings for cylinders and a crankshaft of three sizes.
The first prototype was assembled in 1989, then the Zavolzhsky Motor-Building Plant and the Gorky Automobile Plant were in close cooperation. GAZ intended to get a new engine for the promising new Volga model - Gas 3105.
On the eve of 1991, the engine underwent every conceivable and unimaginable test. It was completely ready for mass production. But it was 1991, the collapse of the country and the collapse of the economy could no longer be prevented. With great difficulties, in difficult economic conditions in 1992, the Gorky Plant sent an experimental batch of engines to the OPP.
A year later, the assembly of motors in small batches began. And already in 1994, the 406 engine received registration for the Gas 3102 Volga. And a year later this engine was installed on GAZELLES. It should be noted that the engines of those years had carburetor and not injection power. Also in 1995, the Zavolzhsky plant produced several prototypes of the ZMZ 406 with an injection type of power supply.
By the end of 1996, the assembly of ZMZ 406 was transferred to the main conveyor. In 1997, full-scale serial production of the new internal combustion engine began. In parallel with the work of the main conveyor, engineers and designers work. They are looking at various engine upgrades. As a result of their work, modernized power units ZMZ 409 AND ZMZ 405 will soon appear.
Use in cars
Now this engine can be installed on any Gazelle and Volga model. Moreover, it is officially installed on some cars and trucks. However, due to the fact that many people tend to use it on other models, small problems may arise. As a rule, this leads to rapid breakdown of the pump, or the injectors simply stop working, the engine begins to struggle or oil leaks. There may be problems meeting specifications. In this case, you need to contact a service station. If the problem is even more serious, then contact the specialized centers of the plant. They are scattered throughout Russia and some CIS countries. The 406 engine (GAZ also helps fix problems, no worse than ZMZ) is so popular that high-quality repairs will not cause big problems. These manipulations will not take much time, and most importantly, they will not require global financial costs.
Source
Main features of the ZMZ 406 internal combustion engine
The power unit of the 406 model, produced by the Zavolzhsky plant, which produces automobile engines, can safely be called a pioneer of the domestic engine industry. It was on the ZMZ 406 engine that some of the advanced technologies of world engineering leaders were used for the first time. But let's talk about all this in order.
Cylinder block
The internal combustion engine cylinder block is cast from highly durable cast iron. Because of this, the total mass of the product has increased, but there is no need to use replaceable liners (cylinders). Also in favor of cast iron as a product material is the special rigidity and strength of the structure.
DOHC system
For the first time in the domestic engine industry, the DOHC system is used in the engine gas distribution system. Where there are two overhead shafts. One shaft has eight valves and is responsible for the intake of the combustible mixture. The second shaft with eight valves is responsible for the exhaust gases.
Cylinder head
As a result, each individual cylinder has two valves for exhaust and two for intake. ZMZ 406 was the first domestic power unit on which a sixteen-valve cylinder head was installed. The number of valves doubled compared to previous engines increases the possibility of purging the combustion chamber during the release of exhaust gases. And while filling the cylinders with the combustible mixture, the filling coefficient is multiplied.
The cylinder head valves on this engine are equipped with hydraulic pushers. This mechanism is used for the first time in the domestic engine industry. Hydraulic pushers automatically adjust the thermal clearances in the valves, thereby eliminating periodic, manual adjustment of the valves.
Timing drive
The timing drive here is chain driven. The chain resource according to manufacturers' requests is 200 thousand km. There are known cases of chain service over a period of 500 thousand km. But there have been cases when the timing chain broke in less than 100 thousand km. Therefore, it is necessary to inspect the timing chain for mechanical wear and damage after a mileage of 70 thousand km. However, if the chain breaks there will be no major damage, the 406 valve motor will not bend. The timing drive is two-stage; the first fuel mixture distribution shaft is driven from the crankshaft sprocket, and from it the shaft responsible for the exhaust gases is driven.
Also, it was on the ZMZ 406 that a hydraulic chain tensioner was used for the first time in the Russian engine industry. Its functions include maintaining optimal voltage for the timing drive. Subsequently, this innovation was adopted on many power units.
Other Features
A special feature of this engine is its short piston stroke of 86 mm, compared to a cylinder diameter of 92 mm. This design contributed to an increase in the compression ratio. The compression ratio of ZMZ 406 is 9.3:1. This approach helps to increase the efficiency of the power unit.
Also, an innovation on the ZAZ 406 engine is the use of an injection power system and the use of an electronic system that controls fuel injection and a contactless ignition system
Driver mistakes
Because of the eternal desire to improve their unit, many try too hard and end up simply killing the engine. What mistakes should you not make when working with the 406 series power apparatus? It is better not to optimize an engine, the price of which varies within 100 thousand rubles.
You should not listen to the advice of inexperienced drivers who suggest reducing the flywheel weight. This will only lead to unnecessary problems and not increase power. Air swirlers are superfluous. There is no need to listen to specialists who offer to install them. If you use them, the power will be proportionally reduced. The vehicle speed does not increase when the intake air heats up. Engine reliability will decrease if droplets of water are added to the intake tract. Designers, on the contrary, try to separate the liquid from the fuel as much as possible, because when it gets into it, it contributes to the onset of corrosion. Some recommend installing an electric tensioner to change the technical characteristics of the engine. However, it not only costs a lot of money, but also completely kills the power unit. And these are not all (but the most common) mistakes made by drivers.
Modifications of the ZMZ 406 engine
In general, there is no power unit under the exact marking ZMZ 406. This is a generalized name for several engines that are very similar to each other.
Here are their main differences:
- ZMZ 4061 10 is a 16-valve 2.3-liter engine with a compression ratio of 8:1. The power system has a carburetor. Such a low compression ratio allows the use of gasoline with an octane number of AI 76 as fuel.
- ZMZ 4062 10 is the same 16-valve engine with the same volume. Only the compression ratio of this engine is 9.3:1. The power supply system of this internal combustion engine is an injector and electronic fuel injection control.
- ZMZ 4063 10 this engine differs from the previous one in that it has a carburetor in the power system. The compression ratio of 9.3:1 guarantees smooth operation of the internal combustion engine on AI 93 gasoline.
Carburetor ICE models differ significantly in power from injection foreign analogues. For example, internal combustion engines produced in Europe with a volume of 2.3 liters develop power of up to 150 hp, power and torque of more than 200 Nm. The power of domestic carburetor ZMZ 406 with the same volume is only 100 liters. It was possible to achieve the best technical indicators by creating the injection model ZMZ 406. Its technical characteristics are close to European indicators.
Technical data ZMZ 406
- Manufacturer ZMZ 406 Zavolzhsky plant for the production of automobile engines. Release period from 1997 to 2008.
- A four-stroke gasoline engine with an in-line arrangement of four cylinders.
- The material used to make the BC is a particularly durable cast iron alloy.
- DOHC gas distribution system with two timing shafts and 16 valves. The timing chain drive has two stages, equipped with a hydraulic tensioner.
- The ZMZ 4062 model has an injection power system. The ZMZ 4061 and ZMZ 4063 are equipped with a carburetor system.
- The piston stroke of this internal combustion engine is 86 mm, the diameter of its cylinders is 92 mm.
- The 4061 model has a compression ratio of 8:1, while the 4062 and 4063 models have a compression ratio of 9.3:1.
- The exact volume of the internal combustion engine is 2286 cubic centimeters.
- The fuel used is AI 76, AI 92 depending on the compression ratio.
- European compliance standards for toxic emissions for the injection version of ZMZ 4062 Euro 2 and Euro 3.
- The weight of the power unit is 185 and 187 kilograms.
Power
ZMZ 4061 at 4500 rpm, equal to 100 l., forces, ZMZ 4063 at 4500 rpm, equal to 110 l., forces, ZMZ 4062 at 5200 rpm, equal to 145 l., forces. Torque 177, 186, 201 Nm at 3500 and 4000 rpm, for the corresponding ZMZ models.
Fuel consumption
Fuel consumption when driving in city mode is 13.5 liters per 100 km, mileage, on the highway 8.8 liters, total fuel consumption is 11 liters per 100 km, mileage. The data corresponds to the consumption of Gas 31105 with manual transmission.
How many liters of oil and what kind to fill?
The permissible consumption of motor lubricant is 0.1 liter per 1000 km, mileage. Types of oil used: 15W40, 10W40, 20W40, 10W30, 5W40, 5W30. Engine oil volume is 6 liters. To replace, take 5.4 liters. Replace engine lubricant every 7 thousand km.
Engine life
According to manufacturers, the operating life of the engine is 150 thousand km. In reality, with careful driving and proper timely maintenance, this figure can be twice as high.
Tips for changing oil
It is most convenient to change the oil in an inspection pit or overpass.
It is not allowed to operate the engine with the oil filler neck open, as this causes untreated air to enter the engine and, as a result, increases wear on engine parts.
After stopping the engine, the oil level must be checked after 10-15 minutes to allow the oil to drain into the engine sump. Along with this, checking the lubricant level in the engine is carried out with the machine standing on a horizontal plane.
The tools you will need to change the oil are: a wrench or a ratchet with a 24mm head; device for removing the oil filter; containers for waste; gloves; bedding on the ground; rags; new filter and new oil.
Suitable components: synthetic motor oil Shell “Helix Ultra 5W-40” 550021556 volume 4 l. The price of such a canister is about 2300 rubles. Original oil filter for engine 2101S-1012005-NK-2 “KOLAN” art. 2101С1012005НК2 costs 300 rubles. Analogs: BIG Filter GB1173 – 285 rubles, Finwhale LF110 – 250 rubles.
Prices are current for the summer of 2017 for Moscow and the region.
We recommend that you read additional information about flushing oils that are advisable to use when changing the main engine oil in the engine.
Popular questions when changing oil on Gazelle 406:
We change the oil for Gazelle 406. We warm up the engine to operating temperature and drive the car into the inspection pit. Unscrew the filler neck plug.
We find the drain plug, here it is, unscrew it, to get it off the ground, you need a key, it often gets stuck.
When it starts to spin well, remove the key, substitute the testing container and tighten it manually.
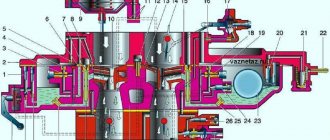
BC design
The cylinder head is cast from a particularly strong cast iron alloy. Jacket channels pass between the cylinders to circulate coolant. The cylinders are drilled into the BC. In the lower, inner part of the BC there are five supports necessary for installing the crankshaft plain bearings. The bearing caps are made by forging cast iron. They are bored together with the supports. Therefore, the covers cannot be swapped.
Numbers are stamped on the first, second, fourth and fifth covers for correct installation. The third cover is additionally processed at the ends. End machining is needed to install the thrust bearing half washer.
The oil seal holder and crankshaft cuffs, as well as the timing chain cover, are bolted to the ends of the BC. The oil sump is bolted to the bottom of the cylinder block.
Description of cylinder head design
On the BC, from above, through the gasket, the BC head is bolted. The head is made of aluminum alloy. It houses the exhaust and intake valves. Each individual cylinder has four valves, two exhaust valves and two intake valves. The intake valves are on the right side of the engine, and the exhaust valves are on the left. The valves are driven from two camshafts by hydraulic pushers.
The presence of hydraulic pushers simplifies the maintenance of the car engine. Since the need for periodic adjustment of thermal clearances in the valves disappears. On the surface of the hydraulic pusher there are holes and grooves necessary for the passage of motor lubricant into the pusher.
In the cylinder head, guide bushings and valve seats are inserted into the valve holes. At the bottom of the cylinder head there are combustion chambers, at the top there are supports for the shafts of the gas distribution mechanism. The supports have covers made of aluminum. The first cover along the vehicle, common to the first two supports of both shafts. It contains persistent plastic flanges. They are inserted into the grooves on the shaft journals. Other support covers are processed together with the cylinder head supports. Therefore, they cannot be swapped. All covers, with the exception of the first double, are numbered. The top of the cylinder head is covered with an aluminum alloy cover.
Description of the design of ShPG ZMZ 406
The pistons of the 406 engine of the Zavolzhsky plant are made of a special aluminum alloy. All pistons have indentations at the bottom. These recesses prevent the pistons from colliding with the valves if the timing chain breaks. When assembling the engine after repair, for the correct installation of the pistons, there is an inscription “Front” on their wall. This inscription is located above the boss of each piston. The piston must be positioned so that this inscription is in front of the movement of the car.
Each piston is equipped with two compression rings and one oil scraper ring. Compression rings are made of cast iron. The surface of the upper ring, the one that interacts with the cylinder walls, is coated with a thin layer of chromium. This speeds up the ring grinding. The surface of the compression ring located below is covered with a thin layer of tin. The inner surface of this ring has a groove. This ring must be installed on the piston, with the flow upward, towards the bottom of the piston.
The oil scraper ring has three elements: two thin steel disks and an expander. The piston is connected to the connecting rod using a piston pin. Floating connection design. In other words, the finger moves freely both in the piston and in the connecting rod head. The pin is held against lateral displacement by two spring retaining rings installed in the piston bosses.
The connecting rods are made of forged steel and have an I-section rod. In the upper head of the connecting rod there is a pressed bronze bushing. The lower head on the connecting rod has a cover screwed to the connecting rod with two bolts. The covers are processed together with the connecting rods, so they cannot be swapped. The caps and connecting rods are numbered so that they are not confused during assembly. The bolt nuts securing the connecting rod cover are equipped with self-locking threads and do not require additional locking.
The piston bottoms have forced cooling. To do this, holes are drilled in the connecting rod rod and its upper head. Through them, under pressure, motor lubricant reaches the bottom of the piston, thereby cooling it. The weight of the piston and connecting rod assembly must be the same in all cylinders. The permissible difference is 10 grams. The lower head of the connecting rod holds the connecting rod thin-walled plain bearings.
Carburetor K151D Specially for the 406th engine
I’ve been struggling with the gazelle for a long time now and I’ve heard enough, Mom, don’t worry... “Don’t go into the bridge! They need a specialist there.” “Don’t go into the box! At our repair base they go through it several times and it doesn’t always work.” “Don’t even think about messing with the carburetor, everything there works on the highest magic and you need a carburetor technician - a master of black and white magic.” I have a head and hands! I climbed into the carburetor and did not regret it, I went through everything according to the manual and according to Svetlov. If anyone is interested, search for “Svetlov’s improvements” on YouTube; he’s generally a smart guy and explains everything clearly. It all started with the fact that one fine morning I came to start the car, which had already been warmed up by Binar, and it was a bummer. I started it, although I started it with a choke just to be sure, it warmed up a little and I started, and I felt there was no tension in the pedal, although I started and drove out. I think I’ll go back, otherwise I’m blocking the exit for the next car. Somehow I crawled 2 meters back. The cable fell off. I have to go to work, time is pressing. I think now I’ll pull out the choke and slowly drive 3 km to work. And the choke also broke off, I couldn’t find it in its place =) In short, it was decided to look for a carber under the bulkhead. For 1500 I found a guy with 3 carburetors, one ideally for a bulkhead, another incomplete, the third a complete piece of iron. I bought 2 different repair kits and in different stores, because the set of gaskets and jets is different for everyone. Well, I started picking =)
relatively clean, albeit used
The difference between K151 D and others is that one tube faces the head. If there is a second one, then it goes to 402 and to UAZ, to the distributor
I removed the screw, otherwise it was useless anyway, they once told me that they didn’t care. needs to be adjusted =)
By the way, I took the needle on the recommendation of someone from here =) If the author is found, I’ll add a link =) An ordinary Solex, only the needle is installed, so you don’t have to unscrew the landing
Apart from the smell of gasoline, I didn’t do anything bad =) my wife put up with it, for which I thank her =) she put up with my stove last time, I was lucky with her =)
It’s not a bad idea to take photos of the process; you can always see what happened and how it stood.
These are donors, I also looked at what and where they were, and the details were not only left over, but also missing =)
I sanded one and the other a little and chose whichever was smoother
Pay attention to the order in which the gasket and membrane are installed; the membrane is always on the side where the edge is, in this case near the lid, which was sanded with sandpaper on the table.
This is an important point. If the accelerator pump foot does not reach the cam, it needs to be bent a little. I clamped it with locking pliers and unscrewed it with a screwdriver. There is no pin in the photo, I applied it and looked at how much more it needed to be bent, it is better to carefully bend it several times. In general, Svetlov’s video shows everything.
I looked at connecting the tubes here
and here too
Next we connect the numbers with tubes: 1-1, 2-2, etc.
I set it up with the carburetor guy =) I didn’t have time to do that myself, he turned it by ear and that’s it, he tore off 500 rubles, now I’ll set it up myself.
Description of the crankshaft design
The crankshaft material is high-strength cast iron. There are eight counterweights on the crankshaft. It is kept from moving along the axis by thrust washers installed on the journal, which is located among the crankshaft. A flywheel is attached to the rear end of the latter. It is needed to accumulate and release energy when the need arises. A bearing and bushing for the gearbox input shaft are inserted into the hole located in the middle of the flywheel. There are oil lines inside the crankshaft to supply lubricant to the plain bearings, then to the connecting rod and through the connecting rod line to its upper head.
Features of the ZMZ 406 cooling system
The cooling system of the engine in question is made in a traditional style. The cooling liquid is pumped by a water pump through the BC, BC head, and radiator. The system uses a flat poly V-belt. Such a belt eliminated the possibility of unexpected breakage.
The system includes a thermostat. It directs the flow of coolant in a large or small circle, depending on the engine warm-up temperature. Also, if necessary, pump 406 supplies cooling liquid to the heater, thereby providing warmth and comfort in the car interior. The system includes a temperature sensor that constantly indicates the temperature of the coolant. It allows the driver to constantly monitor the temperature of the internal combustion engine.
Lubrication system ZMZ 406
The motor lubricant, located in the oil pan, is taken through the oil receiving strainer by a gear pump and moved under pressure into the oil filter, where even the smallest impurities are removed. After cleaning, the oil enters the crankshaft channels. Next, it is pumped inside the crankshaft journals, where it ensures reliable lubrication of the rubbing parts. Further, under pressure, through a channel in the connecting rod, oil lubricates the piston pin and part of the oil falls on the piston bottom, thereby cooling it. Having completed its task, the engine lubricant flows into the oil pan and the lubrication process is repeated again.
Features of the ZMZ 406 electronic ignition system
The electronic ignition on the ZMZ 406 engine is a purely Russian invention. The electronic filling is completely unified. There are several versions of the software electronic unit. The software is installed depending on specific technical characteristics.
For example, the 4061 10 engine has a compression ratio of 8:1, it is designed to run on AI 76. This engine requires software that will facilitate the operation of the engine on this fuel. If an electronic unit with software for a 4061 engine is installed on a 4063 model, the engine will not work normally. This suggests that the ignition units with software are not interchangeable, for example, an engine cannot be installed from 4061 to 4062.
What are the differences between carburetor and injection power systems?
Initially, an internal combustion engine with a carburetor power system was invented. The carburetor was responsible for preparing the composition of the combustible mixture. Later, the injector was invented. The use of an injection system made it easier to start the engine, reduced fuel consumption, and improved engine dynamics. Why did this happen, what is the difference?
This question can be answered by understanding the processes occurring in carburetor and injection power units. The performance of an engine with a carburetor directly depends on the crankshaft speed.
The higher the speed, the greater the fuel consumption and the greater the emission of harmful substances. When you press the gas pedal of a carburetor car, the amount of gasoline vapor in the carburetor increases. It is so excessive that it does not have time to burn out; part of it burns out in the exhaust manifold. Thereby increasing gasoline consumption and the content of harmful substances in exhaust gases.
In an injection engine, everything happens differently. Any light pressure on the accelerator is controlled by the microprocessor. There is an instant correction of the required amount of fuel, which is injected directly into the combustion chamber. Precise correction of distributed injection improves the dynamics and acceleration of the car, reduces fuel consumption and reduces the amount of harmful substances in the exhaust gases.
Clutch gas 3221
The clutch on the car is single-plate, dry, friction, the drive is hydraulic.
Figure 4. Clutch
1 – master cylinder of the clutch release drive; 2 – clutch housing; 3 – flywheel; 4 – friction linings of the driven disk; 5 – pressure disk;
6 – support rings; 7 – pedal spring; 8 – diaphragm spring;
9 – clutch release bearing; 10 – master cylinder rod;
11 – pedal; 12 – gearbox input shaft; 13 – foam rings;
14 – release clutch; 15 – fork ball joint; 16 – casing; 17 – fork;
18 – working cylinder rod; 19 – connecting plate; 20 – working cylinder; 21 – bleeder fitting; 22 – damper spring; 23 – driven disk.
The clutch consists of an aluminum housing, a release clutch with a bearing and a fork, a drive disc assembly (basket), a driven disc, a master and slave cylinders, connected to each other by a hose and tube.
The drive disk (basket) consists of a casing in which a diaphragm spring, support rings and a pressure disk are installed. A spring attached to the casing presses on the pressure disk with its edges.
The driven disk consists of a hub with a splined hole and two disks, one of which has leaf springs riveted to it. Friction linings are attached to them on both sides.
Leaf springs with bends contribute to a better fit of the disc and additionally smooth out jerks in the transmission when the clutch is engaged.
For a smoother transmission of torque when starting the car or changing gears, damper springs are installed in the disk windows.
The driven disk is pressed against the engine flywheel by the pressure plate of the basket. Through friction linings that increase friction, torque is transmitted to the driven disk and then to the input shaft of the gearbox, to which the driven disk is connected by a splined connection.
The clutch release drive is used to temporarily disconnect the engine from the transmission. When you press the clutch pedal, the clutch master cylinder piston moves forward.
The displaced liquid enters the working cylinder through a tube and hose, pushing out a piston with a rod.
The rod acts on the shank of the fork, which rotates on a ball joint, with the other end moving the clutch release clutch along the gearbox bearing cover. The clutch bearing presses on the ends of the diaphragm spring petals. When deformed, the spring ceases to act on the pressure disk, which in turn “releases” the driven one, and the transmission of torque stops.
On the outside, the clutch mechanism is covered with an aluminum housing. The crankcase is attached to the engine cylinder block with six bolts and two reinforcements. On the other side, four studs are screwed into the crankcase to secure the gearbox.
The crankcase has a seat for the clutch slave cylinder and a window for installing the fork. To increase rigidity, a reinforcement is installed on the lower part of the clutch housing.
Typical malfunctions of ZMZ 406
Hydraulic tensioner
On the ZMZ 406, the hydraulic tensioner, which ensures normal tension of the timing chain, very often fails. It may jam. As a result, it stops performing its functions and the chain is not tensioned. The chain can stretch, jump and even break. The only good thing about this situation is that the 406 engine does not bend the valves.
Engine overheating
Overheating of the motor of this model is not uncommon. The problem is usually caused by a faulty thermostat or a clogged radiator. If everything is in order with them, then you need to find an air lock in the cooling system.
Loss of traction at idle
Idling failures, engine traction periodically disappears, all this is a sign of imminent failure of the ignition coil. If it is not replaced urgently, the car will finally break down.
High engine oil consumption
There could be several reasons:
- The problem may be caused by stuck oil scraper rings;
- valve seals that have become unusable;
- Also, the reason may be in the oil deflector; usually the oil goes into the gap between the labyrinth plate and the valve cover. To solve the problem, just remove the valve cover, apply sealant and install it in place.
Troubles the engine
To eliminate the problem, in order to eliminate the possibility of valve burnout, you need to notice the compression. If the compression is the same in all cylinders, then you should check the spark plugs. The last in the chain of faults may be the ignition coil.
Engine knock
The ZMZ 406 engine knocks due to failure of the hydraulic compensators. Their working life is about 50 thousand km, after which you don’t need to wait for them to knock, but simply install new ones. If the knocking of the engine is associated with wear or a defect in the ShPG, it is much more serious. A labor-intensive overhaul of the power unit awaits.
Gazelle
Model ZMZ 40524.10 is a gazelle carburetor known to everyone. The car brand “Gazelle” is one of the most popular and affordable trucks in Russia, which were originally intended for transporting not very large loads. Due to the huge number of such machines, we will consider several nuances of different gazelle systems. For example, a microprocessor ignition system, which is installed on the 406 model.
If the driver claims that his car makes some popping noises, jerking noises and loses its power. In this case, the power system, engine and ignition system should be checked. We checked the carburetor with a gas analyzer not during the operation of the 1st and 2nd chambers, cutoff, enrichment and during idling and did not find any violations. Next they check the engine. When checking the compression, no problems were identified, but the next time deviations from the norm were detected. It was concluded that the jerks and pops that the driver did not like were due to the jumping of the teeth of the upper chain.
Carburetor ZMZ 406 series
What to do if a gazelle loses power?
From the very beginning, you need to check how the diagnostic circuit and the on-board diagnostic system function, because when the travel image mode is activated, you should receive a malfunction code - 12. To read the code, the 10th and 12th contacts of the diagnostic block must be closed. Using a diagnostic toaster, engine sensor parameters are measured and then compared with typical values for average engines. The most common reason for a decrease in car power is contamination of the tube that connects the intake manifold and the pressure sensor.
Gazelle ignition system
The microprocessor ignition system ignites the working fluid in the cylinders and sets the required vehicle ignition timing for all engine modes. The ignition system performs the function of regulating the operation of the forced idle economizer. Thanks to the ignition system, engine operation becomes more economical, compliance with all exhaust gas toxicity standards is monitored, detonation is eliminated and the vehicle's power is increased. If we compare the classic system with this one, then this ignition system is much more reliable and durable. Here only the spark plugs can wear out.
How does diagnostic mode work?
When the ignition system is turned on, the indicator light begins to light. At that very moment, the diagnostic system begins to work. If the system is working properly, the light stops lighting, but otherwise it continues to light. That is, an extinguished warning light indicates that the ignition system is absolutely working.
Carburetor ZMZ 406 series
Why does the 406 engine sometimes not start during a freeze?
The most common reasons why the 406 engine does not start:
- Poor quality oil;
- The battery is not powerful enough, which prevents the engine from starting;
- Faulty starter;
- Misregulated ignition system;
- Poor quality gasoline;
- Failure to supply gasoline.
How to adjust the carburetor?
- Disconnect the choke actuator cord;
- Remove the air filter and carburetor cap;
- Check the level of the float chamber, it should be below 3 centimeters from the edges;
- Remove the plug from the float rod;
- Make sure the valve seal ring is tight;
- Install the carburetor top;
- Install the choke cable and air filter;
- Screw in the idle speed adjustment screw all the way, unscrewing it five turns. Carry out the same actions with the quality screw, but unscrew it three turns;
- Start the power unit;
- Let it heat up to 90⁰;
- By rotating the operational adjustment screw, select the crankshaft speed, about 700 rpm;
- Press the accelerator pedal and release quickly. If the engine stalls, increase the frequency;
- Stop by a car dealership and adjust the CO and CH of the engine.
Sources
- autodont.ru/dvigatel/carburettor/obzor-karbyuratora-zmz-406-serii
- zen.yandex.ru/media/carshistory/neubivaemyi-istoriia-uspeha-dvigatelia-zmz406-5cbb4663a56d7d00aec0825e
- drive2.ru/l/9285154/
- wikers.ru/engines/gaz/dvigatel-zmz-406.html
- avtodvigateli.com/marki/zmz-406-karbyurator.html