Stabilizers are responsible for the vehicle's stability on the road. To eliminate noise and vibration from the operation of stabilizer components, special bushings are used - elastic elements that make operation smooth.
What is a sleeve? The flexible part is made of rubber or polyurethane. Its shape is almost the same for different car models, but sometimes it has some features depending on the design of the stabilizer. To improve performance, bushings are sometimes equipped with wedges and grooves. They strengthen the structure and allow parts to last longer, and also protect them from mechanical influences that can damage them.
When is the transverse stabilizer bushing replaced?
The degree of bushing wear can be determined through a routine inspection. Cracks, changes in rubber properties, abrasions - all this indicates the need to replace parts. The bushing is usually changed every 30,000 km. Experienced owners advise replacing all silent blocks at once, regardless of their condition.
Unplanned replacement of the bushing is necessary when the following symptoms appear:
- steering play when cornering;
- noticeable swaying of the steering wheel;
- tilt of the body, accompanied by characteristic sounds (clicking, creaking)
- vibrations in the car suspension along with other noises;
- When driving straight forward, the car leans to the side;
- general instability.
Detection of such problems requires urgent diagnosis. It is the bushings that require priority attention. After replacing them, you can check the operation of the car, and if signs of malfunction persist, conduct an additional inspection.
Diagnostics
Knocking of the stabilizers is a guaranteed sign of the need to immediately replace the bushings. In addition, squeaks may appear, especially when it gets colder, when the rubber loses its elasticity.
To determine the need for replacement, it may be necessary to remove the crankcase protection. To check the source of vibration, place your hands on the stabilizer link and directly on the mounting bracket. The partner must press firmly on the hood of the car several times. If vibrations are felt on the brackets, which are transmitted to the rack, it is necessary to install a new set, even if no play was noticed when inspecting the seats on the stabilizer.
If the hole inside the bushing has taken the shape of an ellipse, cracks are visible on the surface, and the material has hardened, immediate replacement is necessary. Continued operation of the vehicle will significantly reduce the service life of the stabilizer struts.
Replacing front stabilizer bushings
Regardless of the car model, the general procedure for replacing bushings remains the same. Only the instruments and some parts of the procedure change. Even novice drivers will be able to guess what exactly needs to be done in the additional stages.
To replace the bushings, proceed as follows:
- Place the car on a pit or lift.
- Use tools to loosen the front wheel bolts.
- Remove the wheels completely from the vehicle.
- Remove the nuts securing the strut to the stabilizer.
- Disconnect the struts and stabilizer.
- Loosen the rear hub bracket mounting bolts and unscrew the front ones.
- Use improvised means to get rid of dirt where the new bushings will be installed.
- Lubricate the inside of the hose using silicone spray or soapy water.
- Install the bushings and follow the reverse procedure listed above to return the vehicle to service.
The rear stabilizer bushing is replaced in the same way. The only thing is that removing the front silent blocks is sometimes more difficult due to the complexity of the design of the front part of the car. If a driver can replace the front bushings, they can probably replace the rear bushings.
Often the reason for replacing bushings is the appearance of squeaking. Although this factor is not critical, it causes inconvenience to many drivers and passengers.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of stabilizer bushings consists of two steps:
- visual assessment;
- providing mechanical impact.
It is necessary to park the car on an overpass or pit to check the rubber bands. Some people use a lift for this purpose, but this can be dangerous. The fact is that diagnosing bushings involves strong tugging of the stabilizer, as a result of which the car sways and may fall. The same applies to jacks, from which the car will come off much faster than from a lift. This can lead to the most dire consequences, since the weight of the car is very large, and this entire metal structure can crush the mechanic.
Diagnostics of stabilizer bushings
The purpose of a visual assessment is to inspect the rubber bands for tears and cracks. If even one crack is found on one part, then the entire set needs to be replaced. Mechanical action requires brute force - grab the stabilizer next to the bushing that connects the part to the body, and pull it hard in all directions. During the process, knocking or squeaking noises may occur. This means the bushings need to be replaced. During the mechanical impact, do not be afraid to damage the stabilizer or the bushings themselves - they are designed for heavy loads, so your attempts to check the serviceability of the parts will not cause them any harm.
Stabilizer bushings creaking
Causes of squeaks
Car owners often complain about the creaking of the stabilizer bushing. Often appears with the onset of frost or dry weather. However, the conditions of occurrence manifest themselves individually. The main reasons for this problem are:
- Poor quality of the material from which the stabilizer bushings are made;
- Rubber hardens in the cold, which makes it inelastic and creaks;
- significant bushing wear or bushing damage;
- car design (for example, Lada Vesta).
Methods for solving the problem
Some car owners try to lubricate silent blocks with various lubricants (including silicone grease). However, in practice this has only a temporary effect (and in some cases does not help at all). Each lubricant attracts dirt and debris, creating an abrasive material. This leads to a reduction in the service life of the bushing and the stabilizer itself. Therefore, we do not recommend the use of any lubricants.
In addition, it is not recommended to lubricate the bushings, as this will disrupt their operating principle. After all, they are designed to hold the stabilizer securely. Essentially it is a cornering action, it acts on a corner to create rolling resistance to the car as it turns. Therefore, it must be firmly attached to the hub. This is not possible in the presence of grease, as it can now also curl, causing the squeaking noise again.
Most car manufacturers recommend bushings for this problem. So, the general advice to car owners dealing with stabilizer squealing is to drive with such squealing for a certain period of time (a week or two is enough). If the bushings do not "rub" (especially with new bushings), they will need to be replaced.
In some cases, replacing rubber bushings with polyurethane ones helps. However, this depends on the machine and the bushing manufacturer. Therefore, the decision to install polyurethane bushings remains solely with the car owner.
To solve the problem, some car owners wrap the part of the stabilizer that goes into the sleeve with electrical tape, thin rubber (for example, a piece of a bicycle tube) or fabric. Original hubs (for example, Mitsubishi) have a fabric insert inside. This solution will allow the stabilizer to fit more tightly into the hub and relieve the car owner from unpleasant sounds.
Description of the problem for specific vehicles
According to statistics, the most common problem with creaking stabilizer bushings was experienced by owners of the following cars: Lada Vesta, Volkswagen Polo, Skoda Rapid, Renault Megan. Let us describe their features and the replacement process:
- Lada Vesta. The reason for the creaking of the stabilizer bushing in this car is the specific design of the suspension. The fact is that in Vesta the stroke of the stabilizer rods has become greater than in previous VAZ models. In them, the struts were attached to the levers, and in Vesta - to the shock absorbers. Therefore, before the stabilizer rotated less and did not make unpleasant sounds. In addition, the Vest has more suspension travel, which allows the stabilizer to turn more. There are two ways out of this situation - reduce the suspension stroke (lower the descent vehicle) or use a special lubricant (manufacturer's recommendation). To do this, it is better to use a silicone-based lubricant that is resistant to washout. Do not use lubricants that are aggressive to rubber (also do not use WD-40).
Replacing the stabilizer bushing on a VW Polo
- VW Polo. Replacing the stabilizer bushing is not difficult. To do this, remove the wheel and place the car on a support (for example, a wooden structure or a jack) to relieve stress on the stabilizer. To remove the bushing, remove the two screws 13 holding the mounting bracket bushing, then remove it and remove the bushing. Assembly is carried out in reverse order.
Another popular way to get rid of squeaks in Volkswagen Polo bushings is to place a piece of an old timing belt between the housing and the bushing. In this case, the belt teeth should face the sleeve. To do this, you need to make a small allowance on the surface on all sides. This procedure is performed for all sleeves. An original solution to the problem is to install Toyota Camry silent blocks.
Skoda Rapid. According to numerous reviews from the owners of this car, original VAG silent blocks are best suited. According to statistics, most owners of this car do not have problems with them. Many owners of Skoda Rapid, as well as Volkswagen Polo, simply tolerate a slight creaking of the bushing, considering this a “childhood disease” of the VAG concern. A good solution to this problem would be to use so-called repair hoses, the diameter of which is 1 mm less. Case components: 6Q0 411 314 R - internal diameter 18 mm (PR-0AS), 6Q0 411 314 Q - internal diameter 17 mm (PR-0AR). Sometimes car owners use silent blocks from similar Skoda models, for example from Fabia.
Renault Megane. In this case, the procedure for replacing the bushing is similar to that described above.
Some car manufacturers, such as Mercedes, produce stabilizer bushings equipped with dust collectors. They protect the inner surface of the sleeve from water and dust. Therefore, if you have the opportunity to purchase such sleeves, we recommend that you do so.
It is recommended to lubricate the inner surface of the bushing with lubricants that do not damage the rubber. Especially silicone based ones. For example, Litol-24, Molykote PTFE-N UV, MOLYKOTE CU-7439, MOLYKOTE PG-54 and others. These lubricants are multi-purpose and can also be used to lubricate brake calipers and brake guides.
The purpose of the front and rear suspension stabilizers is to increase the vehicle's stability when cornering.
What will you need for replacement?
You won't need many tools to do this job, but you will still need to prepare them ahead of time.
To replace stabilizer bushings you need:
- jack;
- ruler or caliper;
- special extension for the key;
- ratchet wrench;
- ring wrenches, one for 13, and the other for 10;
- extended socket heads or regular ones (14,13).
It is worth noting that this is only a basic set of tools; in fact, others may be needed. This is due to the need to unscrew the fastening nuts when removing the stabilizer. This is the whole problem, because with a regular wrench you will not be able to unscrew the fastening nuts (during operation they become stuck to the part). In this case, many resort to emergency measures - using a hacksaw or grinder. In the process of loosening the nuts, the stabilizer links may be damaged, so replacing the rubber bands alone will not do.
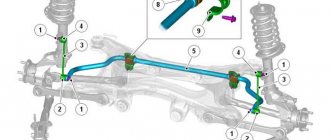
Rear and front anti-roll bar - design
The centrifugal force caused by the rotation of the vehicle causes the body to roll and feel tilted, which can cause the vehicle to roll over. To avoid such situations on the road, a stabilizer bar (STR) was invented, which is now installed on various types of independent vehicle suspension (both front and rear). This is an important element of the suspension; it works on the torsion principle, connecting opposite wheels with torsion flexible parts.
Do not install this element on the rear wheels of vehicles that use their own torsion beam as suspension.
The rear and front anti-roll bars are made of round spring steel. The rod is made in the shape of the letter “P”. It is attached using clamps and rubber bushings to the car body (across). The configuration of the stabilizer can be very complex, since it is located under the body, where many different components and mechanisms of the vehicle are located. Let us immediately add that rubber bushings allow the SPU to rotate.
The stabilizer is connected to the suspension elements using shock absorbers (the so-called bones) and double wishbones. Moreover, such a connection is most often made using struts (in fact, the transverse stabilizer bar is an ordinary braid), although assembly is possible without the use of additional bars.
Let's sum it up
As you can see, the rear stabilizer bushing or the front stabilizer bushing is a simple element both in terms of design and replacement. At the same time, the bushing of the stabilizer link and the bushing of the stabilizer itself are different, so it is important not to confuse these elements when selecting the necessary spare parts.
The vehicle suspension is one of the most important parts, subject to heavy loads and taking on all the impacts of a rough road. Thanks to its operation, the driver can feel comfortable and not be afraid that while driving the situation may get out of control. However, due to heavy loads, especially when driving on bad roads, which is not uncommon in the Russian Federation, its parts often fail. The most common problem is broken stabilizer bushings. Let's take a closer look at why this happens and how the stabilizer bushings are replaced.
How do front and rear anti-roll bars work?
The design of the UAS system is such that it cannot withstand angular, longitudinal and vertical vibrations of the vehicle suspension. When it comes to leveling a passenger car with the road surface, front and rear anti-roll bars do a great job. Their operating principle is based on the precise redistribution of the incoming axial load between the suspension elements.
During transverse angular vibrations (lateral roll) of the vehicle, the anti-roll bars move in opposite directions. In this case, one bar is lowered and the other is raised. At the same time, the sleeves allow the central part of the SPU to be twisted. The resistance of the described element increases with increasing body roll, making the car lined up on the road. Tie rods (bones) also provide better traction when cornering.
The rear (or front) anti-roll bar performs its function better the stiffer its design. This hardness depends on:
- jack geometry;
- the shape of the mechanism and its correspondence to the lower “bends”
- properties of the metal used in the production of GP.
A car with rigid front and rear stabilizers easily overcomes the sharpest turns (and the driver does not even feel the roll when cornering). New possibilities open up for car designers as they can install different degrees of IS system stiffness on the rear and front axles. Installing a stabilizer of one or another rigidity allows you to achieve a certain balance in vehicle control.
What are bushings and why are they needed?
The main task of bushings is to reduce the noise of the suspension when driving and attach the stabilizer to the car body. As a rule, they are made from two materials: polyurethane and rubber. The parts have high elasticity and strength, which is why there are no squeaks or knocks when the height of any of the wheels changes. In addition, it is impossible to rigidly attach the stabilizer to the body, since the distance from the attachment point to the edge of the stabilizer changes when bending.
Bushings can be made from different materials
Often, a faulty bushing can be indicated by various sounds that occur when driving and making sharp turns - squeaks, knocks, and so on. This phenomenon is associated with the loss of elasticity of the bushing, as a result of which it becomes very rigid. Dust or sand may also accumulate under this part.
Advantages and disadvantages of SPU
Despite the apparent simplicity of the design of the mechanism we are interested in (for its fastening you only need a strong support, a high-quality rubber bushing, rods, bones), it easily copes with the tasks assigned to it. It is worth mentioning here, however, that LSS reduces the travel of the independent suspension and “takes away” several other important properties from it. For this reason, a stabilizer bar is not installed on SUVs.
When driving such all-terrain vehicles equipped with all-terrain tires on bad roads, there is a noticeable loss of contact between the wheel and the road and its suspension. This negative phenomenon is caused precisely by the use of SPU. It is obvious that car designers do not intend to abandon the use of a stabilizer in these cases either. Currently, several options for modernizing SPU designed for SUVs have been developed.
For example, TRW has developed a modern system consisting of hydraulic cylinders that act as struts, a lateral acceleration sensor, a hydraulic pump and a special control unit. This system, which does not require rubber bushings, has proven to be an effective replacement for traditional LSS.
Western automakers have begun installing adaptive suspensions on their cars. These mechanisms eliminate the need for SPU, guaranteeing ideal vehicle behavior (no roll) in all driving conditions (acceleration, cornering, hard braking, etc.).
Mitsubishi ASX Club
Since the internal size of the bushing was reduced from the outside, the bushing when put on the amplifier became larger, but the covers are tensioned without any problems. We tighten the cover bolts with our hands and tighten them a little. A little. Then we screw the eggs back on, put on the wheels and remove the car from the trestles (stands). Then we tighten the cover bolts and wheel nuts. New bushings on the car, left and right. View from above.
As you can see, when the covers were tightened, the new bushings opened up more than the original ones, apparently due to a change in size. The stops on the stabilizer seem to be rubber, so they should not knock even with broken bushings. I screwed up and forgot to take photos of the new bushings on the car, side view. A test drive showed that there seemed to be less knocking, but we couldn’t get strong knocking noises. However, I have nothing done to the front struts. I unscrewed the rack, looked at the mating plane - I couldn’t find any “filled” places on the metal. And I couldn’t find any places where it could knock. True, I didn’t unscrew the strut from the steering knuckle for fear that there might be a camber adjustment in this place. I put this question aside for later. I'll go with new bushings and listen