Internal combustion engine cooling systems have been divided into two branches during their development: air cooling and liquid cooling. It is more correct to call a liquid cooling system hybrid, since the fan is used in both types of systems. The medium for dissipating excess heat in the process of removing it from a heated power plant is air. A cooling fan is a device that ensures stable and uniform heat transfer to the environment.
The hybrid cooling system has almost completely replaced the air cooling system in the design of production cars, so further we will talk exclusively about it. It is also worth noting that the function of the fan in both systems is similar. The cooling fan allows for forced and efficient airflow of the engine and radiator of the hybrid liquid cooling system.
We also recommend reading the article about the design of the thermostat for a liquid cooling system. From this article you will learn about the principles of operation of the device, its functions in the system, common faults of the element and methods for eliminating them.
The fan serves to better cool the engine and the fluid in the radiator. This effect is achieved by blowing the internal combustion engine and increasing the flow rate and total mass of air that passes through the cells and fins of the radiator. In most cases, the fan installation location is the space between the radiator and the power unit. The radiator fan itself is enclosed in a special casing.
Radiator fan device
A car fan for an internal combustion engine cooling system has at least four blades, which are mounted on a single common pulley. The blades are located at a certain angle relative to the plane of rotation. This is done for the most efficient intake and subsequent supply of air. There are no strictly established patterns in the design of the fan, although the most common design has become one that includes an impeller with 8 blades.
Drive types
The radiator fan may differ in drive design. Existing types are divided into:
- mechanical;
- hydromechanical;
- electric;
Mechanical drive
Such a drive is a design that is essentially a permanent drive from the crankshaft of the power plant. This drive is the simplest and is implemented using a belt drive. The main disadvantage of a mechanical drive is the power taken from the unit, which is spent to ensure constant rotation of the fan. Today, mechanical drives are practically not used in cooling systems on civilian cars.
Hydromechanical drive
This type of drive is a solution that is implemented by installing a viscous coupling (viscous coupling) or a hydraulic coupling. These couplings are constantly driven by the engine crankshaft. In order to keep the fan blades intact when the internal combustion engine is operating at maximum speed and high crankshaft rotation speed, the fan impeller is connected to the pulley via a hydraulic or viscous coupling. There is also a definition of a thermal coupling, which depends on the design features.
The clutch may become partially or completely blocked due to the increasing temperature of the fluid with which it is filled. Silicone is such a filling fluid. The increase in temperature occurs as a result of increased crankshaft speed and increased load on the engine. The clutch is blocked and the cooling fan begins to rotate. A hydraulic coupling differs in design from a viscous coupling and is blocked depending on the amount of oil in the coupling.
It turns out that the viscous coupling is often filled with silicone gel, which has the ability to change its properties under the influence of temperature. Silicone oil is poured into the coupling in an amount of about 30 or 50 ml. Clutch blocking affects the fan rotation speed regardless of the engine crankshaft speed. If the power unit reaches high speed mode, then the clutch slows down the rotation of the impeller, thereby protecting the fan from destruction at high rotation speeds. The main task of all types of couplings, which differ in operating principles and design features, is to maintain the fan rotation speed within strictly limited limits. The viscous coupling provides the speed range that the impeller needs for the most efficient cooling.
As already mentioned, mechanically driven fans have become rare, but have not completely disappeared. Such a device can still be found on some car models that have a longitudinally located power unit. Another segment of cars in which the installation of a fan with a similar type of drive is widespread and justified is powerful SUVs. Such machines are able to overcome water obstacles and are prepared for operation in conditions of extremely high humidity. The fact is that any electronics fails after contact with water, and viscous couplings are completely sealed devices and are not afraid of moisture.
Electric drive
The active development and implementation of electronic control and monitoring devices for various systems during engine operation has led to the emergence of an electrically driven radiator fan. This drive has a separate electric motor and its own control system. The controller allows you to set the intensity of the impeller operation and flexibly change the speed and duration of fan rotation based on the readings of the temperature sensor. The sensor measures the temperature of the coolant in the internal combustion engine. This solution not only increased efficiency, but also made it possible to achieve improved uniformity of engine cooling compared to systems that are based on the use of a viscous coupling.
The role of the fan in the cooling system
The process of evolution of the cooling system initially followed two main paths, so two main types of systems were used in production cars: air cooling and liquid (or rather, hybrid). The fan is used in both types of cooling systems, since the final carrier that dissipates the heat removed from the engine is air. The fan performs the function of a device that ensures constant and uniform heat removal into the atmosphere.
Electrically driven cooling fan
The fan electric motor is powered from the vehicle's on-board power supply. Existing solutions can be divided into:
- fan with thermal switch;
- fan with electronic unit;
Cars at an early stage did not have electronic control units. The electric motor of the cooling system fan was activated and turned off by a thermal switch, which some car enthusiasts confuse with a temperature sensor. The temperature sensor is often built into the engine block housing. The signal to the dashboard in the cabin comes from it, since temperature control near the combustion chamber is much more important than the coolant temperature.
The thermal switch is similarly activated when the temperature rises, but relies on the readings of the coolant temperature sensor in the radiator. The device operates in a narrow temperature range. For example, the fan is activated at a coolant temperature of 85 degrees Celsius, and it will turn off at 70 degrees. The principle of operation of the device is quite simple. If the temperature rises above a predetermined threshold, then the contacts in the thermal switch close, which will lead to the closure of the cooling fan power supply circuit. Current is supplied to the electric motor and the impeller begins to rotate. Reducing the temperature to the minimum threshold will cause the contacts to open and the fan will stop working.
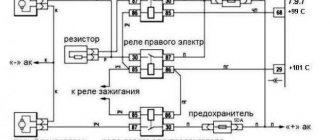
It is noteworthy that the design of the electric fan drive with a thermal switch can be installed on almost any motor. The fan control circuit is noticeably more complex in modern models with an ECU and includes a number of elements and actuators, including the main ones:
- coolant temperature sensor;
- ECU;
- fan relay;
- electric motor;
The temperature sensor measures the temperature of the coolant in the power unit. Modern cars can have two sensors at once, which are installed in different places. One temperature sensor is placed at the outlet of the engine or in the thermostat housing, the other is placed in the pipe at the outlet of the radiator. The fan is controlled taking into account the readings of both elements and subsequent assessment of the difference in the data received from the sensors. For more efficient control, additional devices are also used, among which it is worth noting the crankshaft speed sensor and air flow meter. The readings of these sensors are necessary to accurately determine the mode in which the engine is operating at a certain moment.
A set of signals from the sensors is transmitted to the engine ECU, which analyzes them and activates the fan relay at the right time. The fan works exactly as much as is necessary to achieve the optimal temperature indicator in relation to a specific speed mode and load on the internal combustion engine.
Car models that have an air conditioning system often receive two fans at once. Each of these fans has a separate switching circuit. Fans can operate synchronously or separately, which will directly depend on the temperature and operating conditions of the internal combustion engine. The fan switching relay is gradually replacing the dedicated fan control unit for maximum effective control of its operation.
There is also a function where the fan is automatically turned on after the engine is turned off. This is necessary to prevent the temperature in the cylinder head from rising too sharply immediately after stopping the heated engine, since as a result, the circulation of coolant in the system immediately stops.
How to repair an engine cooling fan yourself?
Before removing the fan, you need to disconnect the ground wire from the battery, as well as all wires going to the fan. After this, you can unscrew the fan mounting bolts and remove it.
To prevent breakdowns and improve the quality of cooling, you need to periodically clean the fan from various contaminants using a brush.
Sometimes it happens that the culprit of a fan malfunction is ordinary dirt. To check this, you only need to bend the engine casing and assess the condition of all equipment. In most cases, brushes will need to be replaced, as they often fail due to excessive contamination and subsequent rapid wear.
Quite often, the breakdown consists only of poor contact of the wires. This occurs due to severe oxidation of the contacts (in the connecting plugs), which have never been cleaned during the entire period of operation of the car. That is why, before changing anything, you need to carefully check the condition of the wires, and if necessary, replace or clean them.
At the next stage, the performance of the rotor, or rather its windings, is checked. If she's okay, then you can breathe a sigh of relief. If a break or short circuit occurs, you will have to inspect each turn to identify the malfunction. But before this, you need to thoroughly clean everything from dirt using a metal brush and a rag with a solvent, which in no case should contain chemically aggressive components.
When the engine overheats and the fan does not turn on, this indicates a breakdown of the electric motor. This part cannot be disassembled and subsequently repaired, so the electric motor only needs to be replaced.
The process of purging the radiator and replacing the fan, in relation to a Ford Focus car, is shown in the video.
Common faults and diagnostics
Remember that diagnosing a malfunction of a cooling system fan should be done with extreme caution, as the rotating impeller can seriously injure your fingers or other parts of the body! It is not uncommon for a faulty fan to suddenly start moving!
Cooling system fans are installed both in front of the radiator and behind it, on the engine side. There is no established uniform standard regarding the installation location among designers. Many car owners also often wonder in which direction the fan blows. There is an opinion that it blows the radiator for better cooling of the coolant. It is worth remembering that the fan blows exclusively on the engine, regardless of its location. Installation in front of the radiator does not mean that only the radiator itself is blown. Changing the blowing direction is unacceptable.
Any electric motor or viscous coupling of different power and production technology, as well as the electronic unit or regulator designed for control, cannot provide a 100% guarantee of protection against malfunctions. The problem is further aggravated by the fact that a failed fan of the cooling system of the power unit will immediately entail serious consequences in the form of engine overheating. Even control devices designed to promptly inform the driver at a critical moment fail. It is necessary to monitor the condition of the fan and its serviceability with enviable regularity. While driving, it is also worth taking another look at the temperature indicator on the instrument panel at the first opportunity.
Simpler systems with a thermal switch are easy to diagnose faults. As for modern cars, then it is very important to correctly determine not only the breakdown of the fan itself, but also to identify the failed element in a chain of several devices. At the very beginning of the diagnosis, you need to find the problem that caused the fan to stop working. Any of the sensors, the control unit or the electric motor itself can fail. You can easily diagnose the problem yourself by following the recommendations below.
Mechanical drive systems are diagnosed quickly. Just watch the fan, which should rotate constantly. If you see rotation and the impeller blades are intact, then look for the problem elsewhere. Engines with a viscous coupling overheat due to a faulty fan only if the clutch does not provide sufficient blocking of the impeller at high crankshaft speeds. The result is a low fan speed and airflow that does not correspond to the load on the motor. Clutch malfunction can be determined by analyzing the fan rotation speed at low and high speeds.
If your car has an electric cooling fan, then start by monitoring its operation. When the fan does not turn on due to obvious overheating, you can use the following method for diagnosing systems with a thermal switch:
- you need to disconnect the thermal switch connector, which is often screwed into the bottom of the radiator tank;
- Next you will need some wire. Using caution, we use the specified wire as a jumper, which must be used to close 2 sockets of the disconnected connector;
If the fan is forced to start after such an operation, then the malfunction of the thermal switch is quite obvious. A non-working fan will mean a malfunction in it or in other parts of the circuit. The design may also consist of a double temperature sensor. The check should be done in two stages, although the principle remains the same. At the very beginning, the first two contacts are closed, after which the fan should rotate at low speeds. Next, the second pair closes, after which the rotation speed should increase noticeably.
It also happens that the radiator cooling fan blows constantly, without visible pauses. Such symptoms are quite common. This may indicate a failure of the power sensor. The check should be carried out with the ignition on by further removing the corresponding connector from the sensor. If the fan does not turn off after this, then the shutdown regulator should be replaced. Additionally, you can check the fuse if problems with the performance of the cooling fan have not disappeared.
The main thing to remember is that, as in any other electrical circuit, it is worth diagnosing the malfunction of individual components using the method of elimination. The condition of the wiring, connectors and plugs will require no less attention. In some cases, the breakdown can be quickly eliminated by simply repairing the cable, which requires insulation, and by cleaning the contacts. Replacing the plug may be no less productive. If after all the diagnostic procedures the fan still does not work, then it needs to be dismantled and replaced.
The above methods cannot be recommended for those car owners who have a car with an electronic device for controlling the rotation speed of the cooling fan. An inexperienced driver can independently check only the serviceability of the fuse that is responsible for this section. Next, you need to contact a car service center for help.
How to find the cause of a fan failure?
A faulty engine cooling fan can cause the power unit to overheat, so you need to constantly monitor the fan's performance. If it breaks, it is necessary to find the cause of this problem as quickly as possible and eliminate it.
First of all, remove the plug connector from the temperature sensor. If it is single, then you can check its serviceability by manually shorting the terminals in the plug with a piece of wire. If the temperature sensor is double, then the red-white and red wires are closed first - the fan should rotate slowly. Then connect the black and red wires - the fan should rotate quickly. The fan should work in all cases, but if it doesn’t, it should be replaced.
When the fan is running, but only at high speed, the additional resistance needs to be replaced.
If all these checks are unsuccessful, then you should check the fuse. The fan connector on the red-white or red-black wire is supplied with power from the battery terminal with a positive charge, and the brown wire is supplied with a negative wire from the battery. If the fan does not work, it means it is faulty; otherwise, you need to carefully inspect all the plugs and connectors on the wires going from the temperature sensor to the fan.
When the engine cooling fan does not turn off but runs constantly, this may indicate a failure of the fan switch sensor. Its serviceability can be checked as follows: turn on the ignition and remove the wire tip from the sensor. The fan still does not turn off - the sensor is being replaced.
The video below shows how to check and replace the temperature sensor on VAZ cars.
In some cases, there is no need to completely change the device, since the damage may be minor and it will be much cheaper to repair it yourself.