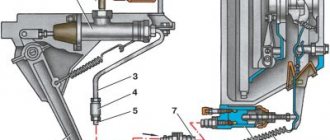
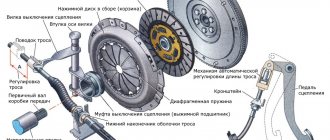
The clutch is a mechanism designed to transmit engine torque to the gearbox, as well as smoothly connect and disconnect the engine with the transmission mechanisms. With its help, you can start driving a car, change gears, stop with the engine running, and maneuver during sudden changes in speed.
The clutch mechanism protects the vehicle's engine and transmission parts from damage and overload during rapid gear changes and sudden braking.
At the end of this article, watch the video tutorial , which very clearly demonstrates how the clutch mechanism in a car works.
And below we will talk about the principle of operation of the car clutch, the design and types of drives for engaging and disengaging the clutch, and how to properly use the clutch mechanism on cars with a manual transmission.
How the car clutch works
The principle of operation of a car clutch is to smoothly connect and disconnect two metal discs: one is rigidly attached to the engine shaft, and the second to the gearbox.
The clutch mechanism is activated by a cable leading from the pedal into the engine compartment of the car directly to the clutch mechanism itself. When the pedal is pressed, the engine and transmission are disconnected.
The main parts of the clutch mechanism are:
- Crankshaft flywheel;
- Drive disk (pressure);
- Driven disk.
The disk that transmits the engine force is called the drive disk (also known as the clutch disk or “basket”). It is hinged to a stamped steel casing, which in turn is rigidly bolted to the crankshaft flywheel. This type of fastening allows the clutch drive disc to change the distance to the housing.
When moving longitudinally, the clutch “basket” presses a disk called the driven . It is connected to the input shaft of the gearbox. In the working position, the driven disk is fixed between the flywheel and the pressure plate, and when the clutch pedal is pressed, it is released.
Smooth engagement of the clutch is ensured by the discs sliding until they are completely pressed against each other. To do this, the driven disk is made of several parts separated by elastic plates. It also has special linings made of material that is resistant to heat and wear. The clutch pressure plate is also spring-loaded and has heat-insulating gaskets.
When the clutch pedal is released, the driving and driven discs are pressed against the flywheel by strong springs, forming a rigid structure. In this case, the gearbox shaft begins to rotate at the same speed as the crankshaft, transmitting force to the transmission units and then through the drive shafts to the wheels. The car starts moving.
But the speeds of the two shafts cannot instantly become the same; in this case, the car will “jump” and stall. Therefore, the clutch control pedal is released smoothly in order to equalize the rotation of the drive and driven discs using friction forces. Then you can press the accelerator pedal to change the speed of rotation of the crankshaft and, accordingly, control the speed of the car.
This type of clutch is called dry, disc and permanently closed. This means that for it to work, the disc surfaces need to be dry and connected to each other when the pedal is released.
Tips for beginners
To avoid burning out the clutch when starting and changing gears, use the basic recommendations from the Akademika driving school.
Algorithm for moving away with a manual transmission:
- start the engine;
- press the brake and clutch pedals all the way;
- move the handbrake to the down position;
- put the lever in first gear;
- smoothly release the clutch pedal while keeping your right foot on the brake;
- press on the gas little by little, releasing the brake.
To change gear correctly, first depress the clutch all the way. Shift to the desired speed by moving the lever and slowly release the pedal until the engine changes RPM. Add some gas and release the clutch completely.
The main thing is, don’t be afraid, do everything smoothly and consistently. If that doesn't work and the car stalls, turn on the hazard lights. Calm down and start over. It is important to learn how to start and change gears correctly, so that you can reinforce this habit later. Only daily practice and self-confidence will help with this!
Operating principle of clutch actuators
The principle of operation of the car's clutch drive, with which the force from the pedal is transmitted to the shift mechanism, can be mechanical, hydraulic or electric.
The mechanical clutch drive is structurally the simplest: it consists of a steel cable connecting the pedal rod and the clutch lever. There is usually a threaded connection on it, which can be used to adjust the length of the cable. The disadvantage of this drive is that it requires more force when pressing the pedal.
The hydraulic drive is more comfortable to use, especially if you have to use the clutch frequently. Its operating principle is similar to the operation of the brake system: when you press the pedal, the piston presses on the fluid, which, moving in the cylinder, sets the clutch lever pusher in motion. In this case, the pedal stroke is softer, but you need to monitor the condition of the hydraulic hoses and control the level and quality of the hydraulic fluid poured into the system.
The electric drive differs from the mechanical one in that the clutch release cable is driven by an electric motor, which is activated when the pedal is pressed. Otherwise, its design is not much different from a mechanical drive.
Clutch operation
When operating the vehicle, it is necessary to periodically check the level in the reservoir that supplies fluid to the hydraulic clutch drive. If the level is less than normal, it must be restored by adding brake fluid. Otherwise, when its level drops to zero, the force of your foot on the clutch pedal will be transferred to nowhere.
Low fluid levels or improper clutch adjustment can cause your vehicle's gears to engage with extreme effort or not engage at all. And if, with the clutch pedal fully pressed, you still manage to “shove” into first gear, then the car will spontaneously begin to move slowly, although at the moment the engine must still be separated from the drive wheels.
How to use the clutch on a car correctly
In practice, working with a car’s clutch is mainly expressed in developing the skill of properly starting off, especially on an uphill slope. In busy city traffic, skillful use of the pedal will allow the car to move smoothly and not stall during sudden braking.
When starting to move, you need to release the clutch pedal, catch the moment of contact of the discs, balance the speed of their rotation, and then smoothly release the pedal. The reference point is the engine speed. If the engine runs smoothly, the clutch engages correctly.
The clutch should only be used when starting, changing gears and when stopping the vehicle. Compliance with this requirement will extend its service life.
- A sharp or, conversely, slow release of the clutch pedal at start leads to accelerated wear of the working surface of the discs.
- Stopping at a traffic light with the pedal pressed and the gear engaged will not have the best effect on the operation of the pressure springs, bearing and release fork.
The two main malfunctions of the clutch mechanism are insufficiently tight contact of the discs and insufficiently complete separation of them.
- In the first case, the clutch slips, and the car will experience poor acceleration dynamics. This is usually the result of wear on the driven disk and its friction linings.
- In the second case, as a result of incomplete separation of the disks when the gear is engaged and the pedal is pressed, the car tries to move.
If these malfunctions cannot be eliminated by adjusting the drive, then repair of the mechanism itself is necessary under stationary conditions.
What happens when you press the pedal
It is physically impossible to change speed with constant engine pressure on the gearbox. The clutch was invented in order to smooth out vibrations. It absorbs impacts during the transition from gear to gear, protecting the car from overloads.
The switching process is as follows:
- the driver from inside the car presses the clutch pedal with his left foot;
- the fork moves the release bearing;
- the release bearing secures the blades of the diaphragm spring;
- the compressed spring stops pressing on the pressure plate;
- the engine is disconnected from the transmission;
- the driver releases the clutch pedal;
- the fork does not affect the release bearing and spring;
- the pressure plate presses the driven disk against the flywheel;
- The transmission is reconnected to the engine.
Proper clutch operation
Commands to move the clutch disc and flywheel in and out are given by the driver by pressing the corresponding pedal, which is located under the left foot. The principle of operation of the clutch pedal is that it moves the disc away from the flywheel through a mechanical drive system. When it is released, the disk again comes into contact with the flywheel, transmitting torque to the transmission.
A complex mechanical unit, the gearbox, is attached to the input shaft of the transmission. It also cannot work without a clutch, since making shifts without temporarily disconnecting it from the engine is very difficult, and for beginners this task is generally impossible to solve.
Torque is transmitted to the gears of the input shaft, which stops when the clutch pedal is pressed. In the neutral position of the transmission, this does not matter, since even with the input shaft moving, it does not engage the output shaft.
To transfer torque to the output shaft, the driver depresses the clutch to stop the input shaft. Then he uses a lever to select the desired gear, connecting the gears of the shafts; after releasing the pedal, the torque is transferred from the primary shaft to the secondary one.
When driving a car, you need to know some points that will allow you to avoid common mistakes:
- The design and operation of the clutch, when you press the pedal, leads to the fact that the torque is no longer transmitted to the drive wheels and the car, after driving for some time, will stop by inertia, but the engine will run and never stall.
- If the gearbox is in neutral, the car will not move and the engine will not stall.
The clutch pedal has three conditional positions in which the main phases of the system’s operation occur:
- top position when the pedal is not pressed;
- middle or working position. On different cars this position may be higher or lower from the floor, so when transferring to a new car you need to find it;
- bottom position with the pedal fully depressed.
It is in the middle position that the disk comes into contact with the flywheel; in order to avoid excessive wear of the parts, they must be connected very smoothly. The main mistake of beginners who know that the clutch needs to be released gradually: after reaching the engagement of the disc and the flywheel, they suddenly drop the pedal, the car jerks several times and stalls.
To get going correctly, you need to depress the clutch pedal, engage first gear, quickly release the pedal to the middle position and the pedal is held there for about three seconds. After the car has driven about one meter, the pedal is completely released.
When changing to a higher gear, the clutch must be released quickly, and the higher the gear, the faster the pedal is released. All these skills are achieved gradually through repeated training.
Video: How does the clutch work?
Why do you need a clutch?
All types of internal combustion engines produce torque within a limited speed range. To change the speed of rotation of the drive wheels, the internal combustion engine must be additionally equipped with a transmission. It allows the engine to operate in the optimal speed range, while changing the rotation speed by changing gears.
But changing gear is a technically complex process, since it requires a temporary interruption in the supply of torque from the engine to the transmission. But then, in order to smoothly change speed, you will need to turn off the engine. The purpose of the clutch is to interrupt the communication between the gearbox and the engine when it is running. That is, this unit stops transmitting torque from the engine to the gearbox when the engine is continuously running.
Peugeot 308 lamp base
Published: 05/29/2018
Spread the love
Spread the love Headlight bulbs for Peugeot 308 The Peugeot 308 bulbs used since 2007 are H7 halogen lamps with a power of 55 watts. Cylindrical in shape, with two contacts. — H1 halogen lamp with a power of 55 watts. Small, elongated size with one electrical contact. — H8 halogen lamp with a power of 35 watts. L-shaped lamp with plastic...
Peugeot 308 lamp base Read more »
Types of clutches
According to the clutch actuator system, clutches can be divided into:
- friction (mechanical);
- electromagnetic;
- hydraulic.
The most common type of clutch is a friction clutch, which uses friction in its operation.
Electromagnetic, on the other hand, uses an electric motor with current to operate, which starts when the pedal is pressed. And the hydraulic clutch works by flowing oil fluid from a special reservoir into the master cylinder. Fluid fills the cylinder and, under pressure, the master cylinder piston pushes the slave cylinder rod, propelling the vehicle. Depending on the number of driven discs, the clutch can be single-disc or multi-disc. And according to the type of friction - dry and wet.
Automotive single-plate clutch device
Diagram of a double-disc clutch device
General design of a double-disc clutch
- Engine flywheel friction surface - blue color on the left
- Two driven discs - brown
- Intermediate drive disc - blue
- Pressure drive disk - green color
- Compression Springs - Gray
- Housing - blue color on the right
Not shown in the picture
- Forks
- Clutch release levers
- Release bearing
- Clutch release fork
- Release springs
Starting a car on a hill
Many novice drivers experience serious difficulties when starting a car on an incline. But, knowing the principle of operation of the manual transmission clutch and the sequence of actions, they will do it much more confidently. This sequence of actions can be used when the handbrake in the car does not work well:
- the clutch and brake pedals are initially depressed with the engine idling;
- the clutch pedal is slowly and smoothly released until the engagement of the clutch disc and transmission is felt, at which point the car begins to tremble;
- the foot is removed from the brake pedal, but the car will not roll backwards, since the clutch acts as a brake;
- the gas pedal is pressed and the car begins to roll forward.
Replacing brake hoses on Niva
Published: March 29, 2018
Spread the love
Spread the love Replacing brake hoses Niva 2121 - 2123Contents1 Replacing brake hoses Niva 2121 - 21231.1 Diagram of the brake system VAZ 2121 - 21213 Niva1.2 Diagram of the brake system VAZ 21232 Replacing brake hoses Niva 21213 Replacing brake hoses Niva 21233.0.1 We at VK Definitely the brake system Niva is the most important part of the car. Therefore it is necessary...
Replacing brake hoses on Niva Read more »
Length of wipers for Nissan Almera g15
Published: 12/30/2017
Spread the love
Spread the love Wipers for Nissan Almera g15 Production of Nissan Almera in our country began in 2012. The car immediately began to be in great demand. The joint production of the Renault Nissan concerns planned to make the car affordable. The price for the basic package was supposed to be 430 thousand rubles. An automatic transmission could also be installed on the car...
Length of wipers on Nissan Almera g15 Read more »
Do-it-yourself replacement of brake pads and brake discs
Published: 01/13/2019
Spread the love
Spread the love Replacing brake pads and brake discsContents1 Replacing brake pads and brake discs1.1 How to check if we are waiting for brake pads to be replaced?1.2 Replacing brake pads - what do we need?1.3 Replacing brake pads - watch out for it Sufficient basic tools, spray lubrication, several hours of time and replacing brake pads and discs yourself will not...
Self-replacement of brake pads and brake discs Read more »