Brake fluid and problems associated with it
Post by Lexa032 » Nov 11, 2014 11:36 am
Re: The brake fluid has turned black! What is the reason?
Post by Sash » 11 Nov 2014, 11:52
Re: The brake fluid has turned black! What is the reason?
Post by Lexa032 » 11 Nov 2014, 12:01
Re: The brake fluid has turned black! What is the reason?
Post by Sash » Nov 11, 2014, 12:30 pm
Re: The brake fluid has turned black! What is the reason?
Post by Valkin » 11 Nov 2014, 13:53
Re: The brake fluid has turned black! What is the reason?
Post by Warlock » 11 Nov 2014, 16:49
Re: The brake fluid has turned black! What is the reason?
Post by Lexa032 » 11 Nov 2014, 18:11
Re: The brake fluid has turned black! What is the reason?
Post by Sash » 11 Nov 2014, 18:44
If you follow this logic, then right now people will write something like this)) So you can connect anything with anything and create a flood. Since I want to talk about brakes, I’ll rename the topic a little.
Lexa032, on the clutch pedal - does your main fluid flow flow down the rod into the passenger compartment? Maybe this is more of a problem than a dirty brake? Even on new Nivki cars, the GCS was often replaced under warranty due to its leakage. On my previous 213 Nivka, no one apparently changed the brake system at all for 11 years, the consistency was almost like jelly and the pedal did not sink at the same time
Re: Brake fluid and problems associated with it
Post by Lexa032 » Nov 12, 2014 10:46 am
Re: The brake fluid has turned black! What is the reason?
Post by Lexa032 » Nov 12, 2014 11:12 am
If you follow this logic, then right now people will write something like this)) So you can connect anything with anything and create a flood. Since I want to talk about brakes, I’ll rename the topic a little.
Lexa032, on the clutch pedal - does your main fluid flow flow down the rod into the passenger compartment? Maybe this is more of a problem than a dirty brake? Even on new Nivki cars, the GCS was often replaced under warranty due to its leakage. On my previous 213 Nivka, no one apparently changed the brake system at all for 11 years, the consistency was almost like jelly and the pedal did not sink at the same time
The renaming is a good idea.
No, Sash, we are not talking about any leaks. Everywhere is dry, like the Sahara. This evening, if my neighbor in the garage has time, I will change the fluid in the clutch. By the way, the pedal gets stuck if you hold the clutch depressed for more than 5-6 seconds.
Reasons for urgent brake fluid replacement
The replacement schedule established by the manufacturer provides for a mileage of 30,000 to 60,000 km, that is, on average it has to be changed once every 2 years. The presence of an ABS system does not change this frequency in any way. When it comes to sports cars, it is necessary to change the brake fluid after 15,000 km, since the speed limits of such cars are increased. However, these figures are only indicative, since if the color of the liquid changes (the appearance of sediment or cloudiness), it is necessary to replace the liquid earlier than agreed. Driving a car with such fluid leads to damage to the brake system.
For this reason, in addition to mileage, the color of this substance is an important indicator of the need to replace brake fluid. Visual control is not the only method of monitoring status. For example, at a service station, the fluid is checked using special testers that determine the moisture content, displaying information on the display about the need for replacement.
Glycol-based brake fluid must be replaced every 40,000 km. If you use a silicone-based fluid, the frequency of its replacement may be completely different, sometimes reaching 5 years.
An additional reason for the unscheduled replacement of this substance is the depressurization of the brake system, since, in addition to the leakage of part of the liquid, the remaining part is quite quickly filled with oxygen, which leads to a decrease in its boiling threshold.
The driver should always remember the importance of timely replacement of brake fluid, since brake failure is unacceptable. %rtb-4%
%rtb-4%
What kind of oil should I use and how much?
The manufacturer fills the 1.7-liter Chevrolet Niva engine with traditional motor oil with a viscosity grade of 5W-30 (API SL/CF TU 0253-069-48120848-2012) or 5W-40. Niva owners fill in different oils with a viscosity of 5W-30. For example, some of the popular ones:
- PC SUPREME 10W40;
- WINDIGO 5W40;
- Lukoil 10W40;
- Shell Helix 10W40 or 5W30;
- Mobil Super 3000 5w-40;
Manufacturer recommended scheduled maintenance every 15,000 km.
When purchasing, be aware that 3.7 liters of oil will immediately be poured into the engine. Therefore, you will have to buy at least 4 liters. Also, do not forget about daily monitoring of the level and, if necessary, adding fluid.
Suitable cleaning filter MANN W914/2 VAZ.
Interchangeability of different brands
Recommendation one: topping up brake fluid made on a different base is unacceptable and dangerous to the lives of vehicle passengers. That is, silicone or BSA cannot be added to the glycol composition and vice versa.
What is the danger: the consequences do not appear immediately, but after some time, until the material is mixed and heated as a result of the brakes being applied. A precipitate forms in the mixture and dense clots form, blocking the normal operation of the system - the brakes fail. In the best case, you will have to empty all the cylinders and pipes for thorough washing.
Now about whether it is possible to add liquid made on the same basis. It is quite permissible to dilute the glycol composition with a similar material, but with reservations:
- It is allowed to mix glycol fluids DOT 3, 4 and 5.1 with each other, DOT 5 is a silicone material, it cannot be added.
- If you added a glycol composition with a lower boiling point, for example, DOT 3, to the fourth series fluid, the brake system is not in danger, but upon arrival at the garage it is recommended to change the working environment. The reason is the deterioration of the properties of the mixture due to the addition of low-grade material.
- After adding a higher class fluid, for example, the 5.1 series to the DOT 3 composition, the temperature characteristics of the mixture will improve. It is not necessary to completely change the fluid in the brake system, unless you notice suspicious deviations - pedal failures or a weak response to its pressing.
Like glycol, silicone compounds are also interchangeable because they are made on the same basis. The boiling point of DOT 5 and DOT 5.1/ABS is identical - 260 °C (wet material - 180 °C). There is a limitation here: it is highly undesirable to add Series 5 fluid to cars equipped with an ABS anti-lock braking system; only the “native” material is DOT 5.1/ABS.
If you find yourself in a hopeless situation and still fill the expansion tank of a car with ABS with Series 5 compound, empty the system as soon as possible when you get to a garage or car service center. The additive will not lead to an emergency and will not cause significant harm to the parts, but will shorten the service life of the rubber elements.
Replacing brake hoses Niva 2121
The front hoses on Niva 2121 and 21213 are distinguished by their length, the outer hose is longer than the inner one. There are a total of four hoses on the front of the car; on the rear of the car there is one hose from a VAZ 2101, from a tee.
To replace hoses on Niva 2121 you will need:
- Split wrench 8 - 10
- Open-end wrench 17
- Copper washers from the brake system of a VAZ
- Pliers
Replacing the front hose 2121:
- We hang and remove the front wheel.
- Next, you need to unscrew the end of the brake hose from the tube. To do this, use a 17 wrench to hold the end of the hose, and use a 10 wrench to unscrew the tube connector.
Then use pliers to pull out the hose clamp. We remove the hose from the hole in the body bracket, having previously twisted the flat of the tip so that it passes through the hole.
- Next, bend the stopper securing the hose and remove it. Niva front brakes
- The second hose is removed in the same way.
- Assembly is carried out in reverse order.
Which clutch is better to put on the Niva to “set it and forget it”
In this article we will tell you how to choose the right clutch for any Niva modification and where you can purchase everything you need with home delivery.
Content:
- What kind of clutch is there?
- We find possible problems and fix them
- Incomplete engagement or slipping
- Insufficient shutdown
- Sudden jerks
- The pedal “fails”
- We choose what to install on your SUV Chevrolet Niva, Niva 2121, etc. Modifications
- VAZ 2121 and other modifications of Niva
- Chevrolet Niva
- Why install a clutch from a Chevrolet Niva on a VAZ 2121?
- Features of Niva clutch maintenance and recommendations on how to extend its life.
What kind of clutch is there?
As always, the search for optimal solutions and answers to questions will begin with terminology. What is clutch? This is an intermediate link between the power unit and transmission.
The principle of operation of the mechanism, in general terms, is that it briefly disconnects the power unit from the gearbox. This ensures smooth mating of transmission elements when shifting gears and dampening of vibrations. The manual transmission is thus protected from unnecessary overloads and, accordingly, increased wear.
Why change brake fluid?
Let's start with the basics. Brake fluid acts as a pressure transmitter from the master cylinder (GTE) to the brake cylinders. The driver presses the pedal, the gas turbine engine (the simplest piston in a housing with a valve system) sends liquid pressure along the lines. The fluid transmits pressure to the working cylinders (calipers), the pistons extend and spread the pads. The pads are pressed with force against the working surface of the discs or drums. And due to the friction force that arises between these elements, the car stops.
The main properties of brake fluid include:
- incompressibility;
- resistance to low and high temperatures;
- neutral attitude towards plastic, rubber and metal parts of the system;
- good lubricating properties.
Please note: the property of incompressibility is stated first. That is, the fluid must clearly, without delay and fully transmit pressure to the working cylinders or calipers
Brake fluid has one unpleasant property: hygroscopicity. Hygroscopicity is the ability to accumulate moisture from the environment.
Water in the brake fluid volume reduces its resistance to boiling. For example, DOT-4 liquid, the most common liquid today, will not boil until it reaches a temperature of 230°C. And this is the minimum requirement of the American Department of Transportation standard. The actual boiling point of good brake fluids reaches 290°C. When adding only 3.5% of the total volume of water to the brake fluid, the boiling point will drop to +155 °C. That is approximately 30%!
The braking system generates a large amount of thermal energy during operation. This is logical, because the stopping force occurs when there is friction with a large clamping force between the pads and the disc (drum). These elements sometimes heat up to 600°C in the contact patch. The temperature from the discs and pads is transferred to the calipers and cylinders, which heats up the fluid.
And if the boiling point is reached, the liquid will boil. A gas plug will form in the system, the liquid will lose its incompressibility, the pedal will fail and the brakes will fail.
Characteristics
Basic requirements for brake fluid:
- Should not destroy rubber seals in the system. Maybe someone remembers red BSK brake fluid. Only the factory rubber bands remained alive. She ate all the “co-op and China” like a crocodile.
- Brake fluid must have lubricating properties. This applies to the surfaces of the brake pistons in the cylinders.
- Must have stable characteristics at low and high temperatures. This issue will be discussed in a separate paragraph below.
Classification of brake fluids
Let's decipher the mysterious abbreviation - DOT. It's simple - Department of Transportation, US Department of Transportation. In the USSR and Russia there have never been GOSTs for these products, so everything is produced in accordance with the specifications. And this is translated for the average user, “some to the forest, some to get firewood.” Maybe something has changed in 2022, but I doubt it. Further after the abbreviation DOT, there are also some mysterious “numbers”. Their translation into Russian is as follows:
- DOT3 – mineral base. 50% - alcohol, 50% - castor or camphor oil. Accumulates moisture relatively quickly. My personal opinion: can be applied and used in dry climates.
- DOT4 is the most common option today. The base is glycol. To bind the condensate, boric acid is added. The most versatile option.
- DOT1 is an improved version of DOT4. The boiling point is slightly increased and the viscosity at low temperatures is reduced. Relevant for the north and other “resort places” of our homeland.
- DOT5 – silicone base. Does not absorb moisture from the air. But as always, if there are pros, there are also cons. Accumulated water can collect in the lower parts of the brakes and freeze there. Applicability: sports cars and motorcycles.
Application of brake fluid of different classes
DOT 3 class is perfect for passenger cars with drum brakes or with disc brakes on the front axle and drums on the rear axle. It contains glycol, making the price of a liquid of this class affordable. But the downside of this composition is the high absorption of moisture. A liquid of this class quickly accumulates moisture to a critical ratio.
DOT 4 class is one of the most popular among motorists. This fluid is suitable for all cars, in particular, with disc brakes on all axles. Its chemical composition includes ester compounds in combination with boric acid. Thanks to this composition, moisture in a liquid of this class is almost completely neutralized. This brake fluid will serve the car enthusiast for a long time.
The DOT 5.1 class is well suited for a sports car whose braking system is subject to heavy loads. Liquid class DOT 5.1 has the same composition as DOT 4, but due to the improved formula it can withstand a higher boiling point and provides more effective moisture absorption.
DOT 5 brake fluid is not often used on regular cars. It contains silicone, which makes it hygroscopic. But there is still one fundamental disadvantage to this. This brake fluid allows water to accumulate in the brake hoses of the system. This can lead to oxidation of system elements or freezing of water at temperatures below 0 C.
Liquids of the same class, but from different manufacturers, can be mixed with each other. It is not advisable to mix liquids of different classes. But if necessary, you can combine DOT 3 and DOT 4, DOT 4 and DOT 5.1. In this case, you must remember the rule that only liquids of the same or higher class can be added to liquids of a lower class. But under no circumstances should you add fluids of other classes to DOT 5 fluid, as this can lead to serious problems in the braking system.
Required Tools
In order to change the brake fluid on a Chevrolet Niva, you need the tools from the table below.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytdevru
Table - List of tools required to change brake fluid
| Tools | Note |
| Spanner | "at 8" |
| Transparent hose | Up to a meter long |
| Rags | To clean dirt |
| Syringe | Can be replaced with a rubber bulb |
| Tara | Can be replaced with a rubber bulb |
To carry out work, access from the bottom is required. Therefore, an inspection hole or overpass will be required. It is more convenient to replace the vehicle with a partner, but there are ways to carry out the task alone.
Also interesting: How to bleed the brakes of a Niva Chevrolet
Replacement frequency
According to the official technical regulations, brake fluid replacement on a Chevrolet Niva is required every 45 thousand km
In this case, it is important to change the entire volume of liquid, and not how much can be pumped out of the tank. In severe operating conditions, it is recommended to reduce the interval relative to the official one to 30-35 thousand
km. However, there are reasons why the brake fluid may need to be replaced sooner. Extraordinary filling of brake fluid is performed in the following cases:
- during operation, boiling of the liquid in the circuit periodically occurs;
- there is no exact information about the mileage at which the TJ was replaced;
- the brake circuit was airy for a long time;
- there is plaque on the walls of the tank;
- the fuel has a burnt smell;
- the tank has mechanical damage;
- a significant amount of liquid leaves the circuit, which is accompanied by airing;
- water or other technical liquid has entered the fuel fluid;
- significant change in color of brake fluid.
Failure to follow recommendations for brake fluid change intervals can lead to the following negative consequences:
- brake failure as a result of boiling of the fuel fluid due to an emergency or intensive stop of the Chevrolet Niva;
- noticeable dependence of the brakes on the ambient temperature;
- the occurrence of corrosion centers on metal elements with which the fuel fluid is in contact;
- jamming of the brake pistons, leading to uneven stopping of the vehicle.
Types of brake fluid
All automotive raw materials, including brake fluid, are manufactured according to existing international and domestic standards. Currently, the production of formulations is based on two standards:
- FMVSS Specification No. 116. This document was defined by the United States Department of Transportation (USDOT). According to this specification, brake fluid is divided into classes (from DOT-1 to DOT-5).
- SAE J1703 and SAE J1704 specifications. These documents were published by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE).
In most cases, American standards are used in the production of brake fluid; the second specification is in less demand. In this article we will describe the types of brake fluids according to the DOT classification. In addition to the listed groups, there are also compositions based on mineral oil. Such raw materials have different production standards; in practice, they are used much less frequently.
Next, we will consider the main features of the types of brake fluid according to DOT, including how often to change each brake fluid.
- DOT-1, DOT-2 – used by manufacturers extremely rarely;
- DOT-3, DOT-4 - the most popular types of brake fluid, the composition is based on polyethylene glycol;
- DOT-5 – the composition is dominated by silicones;
- DOT-5.1 is an improved version of the DOT-4 composition and has more advanced properties.
It is important to consider that the two classes DOT-5 and DOT-5.1 are completely different in their properties. They are not interchangeable. Each class is divided into two categories:
Each class is divided into two categories:
- For vehicles without ABS.
- For vehicles with ABS.
The category must be marked on the packaging with the composition or indicated in the labeling itself (DOT-4/ABS).
In our country, an additional classification of brake fluids can be used; it includes the names DOT-4.5, DOT-4+, DOT-4*, etc. However, such subclasses do not exist in the original standard, so these markings can be considered a marketing ploy.
In addition to how often to change brake fluid, it is important to know which classes of fluids can and cannot be combined. The general rules on this issue are:
- It is permissible to mix the following compositions: DOT-3, DOT-4 and DOT-5.1.
- The DOT-5 composition is incompatible with other brake fluids.
The composition of the first three types of DOT is based on glycol compounds. They also contain the same additives. Since the compositions are almost identical, brake fluids of these classes can be mixed. Products labeled DOT-5 are manufactured using other substances. The main difference is the large amount of silicones. When in contact with glycol compounds, silicones form completely new substances, and the properties of the entire liquid are lost.
Despite the similarity of compositions, liquids of classes DOT-3, DOT-4 and DOT-5.1 are also best not mixed. Modern manufacturers use different types of additives, and when these substances are combined, harmful chemical reactions can begin. It is recommended to combine only formulations from the same manufacturer.
Air and liquid cooling systems
There are two types of engine cooling systems: air and liquid. In modern vehicles, as a rule, a liquid cooling system is used, while an air cooling system is used in motor vehicles and small generator sets.
Air cooling system
As the name suggests, this system uses air flow to remove excess heat from the engine. This design solution was widely used in the 60-70s of the twentieth century by such manufacturers as Fiat, Volkswagen and others, including the domestic Zaporozhets.
With an air cooling system, the thermal regime of the engine is determined by the temperature of the oil in the lubrication system, which should be in the range of 70-110 °C.
The main disadvantages of the air cooling system:
- significant power consumption for fan drive;
- increased noise level during operation;
- deterioration in filling the cylinders with the fuel-air mixture;
- air flows are directed unevenly - this can lead to local overheating;
- High thermal stress of individual parts can lead to overheating of the engine.
That is why modern manufacturers prefer a liquid cooling system.
Liquid cooling system
This cooling system is installed on modern cars with an internal combustion engine. Engine parts that are exposed to heat are cooled using liquid. In some cases, this may be water or antifreeze, but the most common solution is antifreeze.
Why change brake fluid?
It is not for nothing that motorists are concerned about the question of how often they need to change the brake fluid. The quality of the brakes depends on it. For example, if the fluid is used longer than expected and has lost its properties, the brakes work worse, and the car slows down more slowly.
It is known that when driving in urban areas, problems with the brake system are not immediately identified. This is due to the fact that the city road does not have sharp slopes and rises, and the deterioration of the brakes is almost not noticeable. But if such a car starts to slow down on a slope, the main brakes may not cope with the task, then drivers use the parking brake.
It is important to know how often to change brake fluid and what type of compound is best to use. First, let's look at what role TJ plays in a car, as well as the main features of its compositions
Newly purchased brake fluid has all the necessary properties. Its physical characteristics are as follows: boiling point - approximately +260 ° C, the liquid is incompressible.
During operation, the water content of the product increases, causing its compressibility to increase. This leads to a decrease in the boiling point (sometimes this figure decreases by two or more times).
During braking (with pressure on the brake pedal), the caliper pistons are squeezed out and the discs (drums) are compressed. In this case, heat is released, the temperature of the liquid becomes +250...+300 °C (an even greater increase in temperature is possible). Normally its boiling point is higher and it does not boil.
If boiling begins, gas bubbles form in the liquid. Gradually their number grows, they increase in size. Bubbles are compressible, and the fuel fluid as a whole also becomes compressible, thereby losing its properties. The effect of the brakes deteriorates, in some cases braking becomes impossible. As you can see, it is necessary to change the brake fluid frequently in order to prevent boiling.
A large amount of water in brake fluid is detrimental to the braking system. Many of you immediately have a question about how water penetrates into its composition if the entire system is completely sealed. While the vehicle is in use, the brake fluid heats up. When heated, it expands, and the pressure increases accordingly. The liquid is usually contained in a small tank with a special valve. To equalize the pressure, it opens.
In cold weather, on the contrary, the liquid cools, and the pressure drops to a negative value. To re-equalize the pressure inside and outside the tank, the valve opens and lets air in. This air subsequently condenses and turns into water.
Water is formed not only during the direct operation of the car. Even if the car is not used or you don't drive it often, you still need to change the brake fluid, just like if you drive it regularly.
When is clutch bleeding required?
The operation of the clutch system is based on the laws of physics - the properties of hydraulic/brake fluid to compress/decompress under load. If air gets into the system, its properties change. As a result: the hydraulics stop responding to pressure or react late, which leads to jerks and jolts when pressing the pedal.
Signs of “airing” of the system
If the following symptoms appear, it's time to change the hydraulic fluid:
- the pedal is depressed too easily, but the gear does not change;
- the pedal moves normally, but the gear engages with vibration or delay;
- the clutch pedal “sticks” to the floor, slowly returning to the top position.
Even one of these signs is enough to check the system.
“Sinking” can also be caused by a broken return spring.
Before bleeding the clutch, find out that the spring mechanism is not the cause of the malfunction.
In what cases is the clutch hydraulic drive pumped?
Bleeding of the clutch and braking systems is mandatory if:
- The liquid used has already served its purpose
. Changes in physical and mechanical properties over time are the norm. The recommended period of use for hydraulics is 1-2 years (as a rule, the period is indicated on the container).
The liquid loses its properties, even if stored in an airtight container.
the clutch or brake system is being repaired
. When cuffs, seals, seals are changed, leaks are eliminated, depressurization occurs. Result: leakage of working fluid and airing. Needs replacement.
It is easy to speed up new bleeding if you loosely tighten the fastenings of the clutch mechanism units. Air leaks freely through the micro-holes.
Clutch/braking system components are severely worn
.
In case of wear of parts, only bleeding is not enough, because the cause of airing does not disappear. To fix the problem, you must first repair or change the functional elements, and then change the working fluid.
Brake fluid Niva Chevrolet, gourmet
brake fluid DOT-4+, Brembo In 2022, I began to work very closely with the trendsetter in brakes, the Italian concern Brembo. I was sent a dealer catalog and in the service section I found brake fluid. The jar contains the company logo, the inscription “made in Italy”, and product characteristics. A technician confirmed that this product is made in-house. The price is a little more expensive than competitors, but it's worth it. Kinematic viscosity (pumpability) at minus 40 is 1400 cCt (DOT-4 – 1800), which allows it to be classified as DOT-4+ and used in cold climates.
53
Features of using brake fluid
Without a special chemical solution, no hydraulic drive will work. It will not work well even if the quality of this substance is inadequate. Therefore, it is necessary for the driver to know what kind of hydraulic fluid is poured into the brake system on his car.
Vehicle fluid is divided into classes, and depending on the basis on which it is made, the frequency of changing the brake fluid is determined. It's quite easy to check. You need to look into the GTZ reservoir and look at the color of the filled liquid.
If the color is brown or yellow, then the base is glycol. For the car owner, this means that the vehicle will have to be changed quite often. As a rule, it is changed after one or two years, depending on how many kilometers and on what road the driver drives the car during this time. In terms of mileage, experts recommend focusing on the figure of 60,000 kilometers.
When there is red hydraulic fluid in the reservoir, its base is silicone. In this case, you can change the brake fluid after five years.
You can often hear the question from inexperienced drivers: why change the brake fluid?
Brake fluid, like other chemicals, loses its properties over time, which impairs its performance and can lead to an accident. When the brakes are applied frequently enough, for example on a bad road or when driving at high speeds with obstacles, the temperature in the brake system rises to 150 degrees or higher. These frequently repeated temperature changes lead to the loss of the desired properties of the brake fluid. This can be visually determined by the loss of color of the poured liquid. It loses its brightness and becomes faded.
In addition, brake fluid absorbs moisture well. And when the brake system loses its tightness, the fluid becomes saturated with oxygen. All this also affects her working qualities.
You can check its condition using a tester designed for this purpose. This device determines the boiling point of brake fluid.
It is considered normal if it shows above 175 degrees. If the readings are 165-175 degrees, you need to look at how long this liquid “works.” If it is more than a year, then it needs to be replaced.
Where and how to order the service?
If the car owner does not have a device for foot or manual tire inflation, then you should contact a tire service station. There are many such organizations today. It is important to choose qualified and experienced professionals.
Overinflating wheels can result in the following:
- Reducing the smoothness of the car.
- Deterioration of adhesion to the road surface.
- Increasing the level of background noise from the highway.
- Increased load on the chassis.
- Quickly erase the cover protector.
Under-inflation of tires leads to the following consequences:
- An accident due to poor road grip and poor vehicle control.
- Increased fuel consumption.
- Quickly erase tires.
Types of brake fluid in DOT class
The main parameters of brake fluid are moisture absorption and boiling point. The higher the boiling point, the higher the quality of the liquid and its price.
DOT 3 fluids are based on glycol compounds. Their production is inexpensive, but at the same time, the hygroscopicity of DOT-3 is higher than other classes; they accumulate moisture faster, which causes a decrease in the boiling point.
DOT 4 fluids have higher performance and are used in cars with disc brakes. They are based on compounds of esters and boric acid. The latter completely neutralizes water condensate. This causes a reduction in moisture volume compared to DOT 3 fluids, helping to maintain the set boiling point and extending the life of DOT 4 fluids.
DOT 4 class combines high quality brake fluids.
DOT 5 brake fluids are made on a silicone basis, they are not hygroscopic, do not absorb water when it enters the brake system, do not form mixtures with it, which sometimes causes the accumulation of moisture in the lower part of the brake system, as well as the freezing of this water entering the system, in case of low temperatures.
Brake fluids classified as DOT 5.1 are similar in composition to DOT 4, but they use additives that increase the boiling point, which makes it possible to use DOT 5.1 for high-speed cars.
If the brake system already contains DOT 5 fluid (but not DOT 5.1), you cannot add DOT 3 or DOT 4 to the same system, otherwise the brake system will malfunction.
Brake fluids classified as DOT 4 can be mixed with DOT 3. Identical brake fluids can be mixed with each other.
The rule required is that a higher class liquid may be added to a lower class liquid, while back-mixing is not permitted. For example, when a car has been filled with DOT 3 fluid, it is allowed to add DOT 3, DOT 4 and DOT 5.1 fluids. As a result, the quality of the liquid will even be improved.
Which road should I take?
The modification of cars for operation on low-pressure tires is usually carried out by specialized enterprises: auto repair shops. They have special equipment and staff responsible for a specific process. But for most car owners, turning to specialized workshops is associated with material costs.
There is another way - this is a saving option when the vehicle owner does the work with his own hands. In this case, you must have the desire, be technically savvy and have the means.
You need to understand that a Niva on low-pressure tires is something different than a standard car. After the rework, a technical component may remain in it. In most cases, incomplete composition.
Important! The pressure in such rubber does not exceed 2–4.25 kg/cm², and the efficiency (efficiency factor) increases by 20% in comparison with standard tires!
Which brake fluid to choose
Glycol liquids have proven themselves best on the Russian market. Their properties make it possible to operate a car in our climatic conditions and at the same time have a high boiling point.
When choosing brake fluid, you should look at the brand and classification. Car manufacturers most often fill new cars with DOT 4. It is optimal in its qualities and is suitable for almost all cars.
Castrol DOT 4 brake fluid
When choosing a brand, you can start from your personal preferences in manufacturers of automotive chemicals. Traditionally, brake fluids of the Castrol, Total, and Mobil brands have shown the best properties. According to test results, liquids of these brands fully comply with the classification properties.
Mobil DOT 4 brake fluid
Bleeding the brake system Niva 2121, VAZ 2131, Lada 4x4
We carry out the work together with an assistant on an inspection ditch or lift.
Bleeding the brakes is necessary when replacing brake fluid, as well as to remove air that has entered the hydraulic drive during the repair or replacement of individual components of the VAZ 2121 brake system. We remove air first from one circuit of the system, then from the other. We start bleeding from the right rear wheel cylinder.
Remove the cap from the bleeder fitting of the rear brake cylinder of the VAZ 2131.
We put a transparent VAZ 2131 hose onto the fitting, lowering its free end into the vessel.
An assistant presses the brake pedal three to four times at intervals of one to two seconds and holds the pedal down. Using an “8” wrench, unscrew the bleeder fitting 1/2–3/4 turn. In this case, part of the brake fluid and air are forced into the vessel, and the pedal is lowered to the floor. Air bubbles are clearly visible in the transparent hose. We tighten the bleeder fitting Niva 2121 and repeat this operation until the release of air bubbles completely stops. When removing air from the system, monitor the fluid level in the master cylinder reservoir and add it if necessary. We pump the left rear wheel cylinder in the same way. Then we remove air from the upper fittings of the left and right cylinder blocks of the front wheels of the VAZ 2121.
Remove the cap of the upper fitting of the front wheel brake cylinder block (for clarity, the wheel has been removed).
We pump the front brake cylinders of one circuit.
To pump another circuit, remove air from the lower fittings of the front wheel cylinder blocks in random order.
Remove the cap from the lower fitting of the front wheel brake cylinder block.
Let's pump another circuit.
If there is no air in the system, the Niva 2131 brake pedal should be “hard”, i.e. when pressing, go no more than half the distance to the floor.
Chemical composition and properties of fuel fluid
The brake fluid used in Chevrolet Niva cars complies with the DOT4 standard and consists of almost 98% polyglycol. The remaining percentage consists of additives that improve the characteristics of the base and perform a number of valuable functions: protecting metal parts from corrosion, and reducing the oxidation of fuel fluid under the influence of high temperatures.
All types of liquids are characterized by two parameters - kinematic viscosity and boiling point.
The first is responsible for the ability of the liquid to circulate in the lines at operating temperatures from -40 to +100 degrees.
The second is for the prevention of vapor locks that occur when the fuel oil boils and inevitably lead to brake failure.
There are two thermal characteristics of TF: the boiling point without water impurities (“dry” TF) and the boiling point with a content of up to 3.5% water (“wetted” TF).
All polyglycol-based brake fluids are very hygroscopic, i.e. prone to absorbing moisture from the environment.
The need to replace the TJ
Regardless of whether the car is parked in a garage or driven around the clock, the “brake fluid” poured into its system constantly absorbs moisture (remember the “breathing” hole in the reservoir cap!).
Over some time, the water content in polyglycol will increase above the permissible level, and accordingly, the viscosity and temperature properties of the fluid will drop catastrophically.
The DOT4 fluid used in the Chevrolet Niva, compared to DOT 3, absorbs water more moderately and has improved temperature characteristics:
| Liquid class | Temperature boiling, O WITH | Viscosity, mm 2 /With | ||
| "Sukhoi" TJ | "Moisturized" TJ (water up to 3.5%) | "Moisturized" at +100 0 WITH | "Moisturized" at -40 0 WITH | |
| DOT3 | not less than 205 | not less than 140 | no more than 1.5 | not less than 1800 |
| DOT4 | not less than 230 | not less than 150 | no more than 1.5 | not less than 1500 |
According to the FMVSS 116 standard, 150 degrees indicated in the table is the maximum temperature to which the brake fluid can heat up, without boiling and the formation of vapor locks, during emergency braking of a car from a speed of 160 km/h to a complete stop.
Please remember. No matter what colleagues say that they have never driven at a speed of 160 in their lives and will never drive, they should not forget that every day there is more and more water in the “brake housing”, and one day the pedal may “get stuck” at minus 20, or in the summer, during a long descent from the mountain, “sink” to the floor. With all the sad consequences.
Fluid replacement interval
The Chevrolet Niva manufacturer recommends completely replacing the brake fluid every three years.
These recommendations are based on the rate of hydration of fuel fluid and the loss of its basic qualities in average climatic conditions.
What exactly needs to be filled when replacing
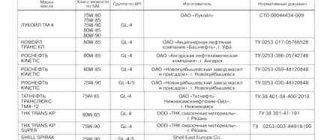
For the first filling, the plant uses brake fluid DOT4, SAEJ 1703, FMSS 116, brands ROSDOT (Tosol-Sintez, Dzerzhinsk) and KAPROS-DOT (Sibur-Neftekhim, Dzerzhinsk).
If desired, you can use products from other brands if their labeling matches the “original”.
It is strictly not recommended to use other brands of diesel fuel, for example DOT3 or DOT5.
- DOT3, apart from its low price, has no other advantages, although it corrodes seals and cuffs much more effectively.
- DOT5 is based on silicone, and mixing it with polyglycol means that the Shnivy’s braking system is guaranteed to fail.
Self-replacement of fluid in the brake system
Preparation for replacement work:
- Purchase 1.0 liters of TJ of the required brand. The capacity of the brake system of our car is 0.5 liters, but believe me, you will have very little left.
- Prepare a tool - an “8” wrench or, preferably, a special socket wrench with a slot and a bolt for fixing, a blunt flat-head screwdriver.
- Make a container for collecting waste from a colorless plastic bottle of 0.35-0.5 liters and a rubber hose about 0.5 m long and with an internal diameter of 6.5 mm.
- Place the car on an overpass or inspection hole. Unload the rear axle and wheels by jacking up the body on both sides.
- Find a smart assistant and instruct him. An assistant is definitely needed; no one has ever been able to twist the fittings under the car and press the pedal at the same time.
- Before starting work, press the pressure regulator rod with a screwdriver (this is why the rear wheels are unloaded).
Self replacement process
- Clean off dirt and remove the protective cap from the bleeder screw screwed into the brake cylinder (actually, its correct name is “air bleeder valve”).
- Place a plastic bottle hose over the valve.
- At your command, the assistant presses the brake pedal 3-5 times and holds it. Presses sharply, releases smoothly, holds pressed patiently and waits for the command “Release!”
- Unscrew the valve (fitting) 1/3…1/2 turn (you won’t be able to do more with one step, but you don’t need more).
- Dirty brake fluid will leak out of the hose. Tighten the fitting. Give the command “Release”.
- Leave the hose and wrench on the fitting. Look under the hood and add fresh fuel oil to the reservoir.
- Return under the car and repeat the cycle of pumping and topping up until clean, clear fuel fluid begins to flow out of the hose.
Be careful. Do not allow the fluid level in the tank to drop below “Min”. If the system sucks in air, everything will have to start all over again.
Warn your assistant: As the old brake fluid comes out, the pedal under his foot will move forward (fall through).
Don't forget to put the protective caps on the bleeder fittings back in place!
Caps. Photo: Yandex.Pictures
Sequence of bleeding the working brake cylinders
We work taking into account two circuits of the system according to the principle of “crosswise” and “first - the one farthest from the main cylinder”:
- Right rear wheel.
- Left front wheel, top valve.
- Left rear wheel.
- Right front wheel, top valve.
- Right front wheel, lower valve.
- Left front, bottom valve.
All. The brake system is filled with fresh fluid. But it’s too early to rejoice. Still left
Bleeding the hydraulic clutch system
The master and slave cylinders, the connecting pipeline and the system reservoir are filled with the same brake fluid, which performs the same functions - transmitting pedal force to the diaphragm spring, turning the clutch on and off.
On a Chevrolet Niva, the hydraulic clutch drive is structurally similar to the VAZ “classic”, and, in principle, DOT3 can be poured into it, but we will not deviate from the factory requirements.
Moreover, the system holds 0.153 liters, and we bought a whole liter.
The pumping procedure is the same:
- We remove the protective cap, set up the key and the hose of the “receiving vessel”.
- An assistant presses the pedal 2-3 times and holds it in the lower position.
- We unscrew the fitting, release the dirty liquid, and wrap the fitting.
- Add liquid to the reservoir.
Already mastered actions are complicated by the fact that access to the outlet valve (fitting) of the clutch slave cylinder is quite difficult.
When working with brake fluid, remember:
- If HF gets on the paintwork, plastic parts and wiring, it can cause damage. Remove it immediately with a clean cloth.
- Brake fluid is poisonous. Store it in a closed original container, out of reach of others.
In some highly respected sources you can find descriptions of other methods of replacing brake fluid, similar to the technology used at car factories for filling a new system under pressure.
Unfortunately, among colleagues and employees of existing car services, I have not yet had the opportunity to meet people who actually performed such work alone.
So, we will experience deep satisfaction from work done in the traditional way.
This is interesting: BMW e39 fuses: where they are, replacement
Opinion of car enthusiasts on replacing brake fluid
The service station offers to replace the TJ. To agree or not?
Over time, the fuel fluid becomes moistened, and this will lead to its boiling point being lower, and the brake system will begin to become covered with rust. The maximum period for replacing a fuel oil is 5 years, but I filled my cars with a fresh one every 3 years. If you come to a reliable car service center, the technician will use a special device to check whether replacement is necessary. I believe that after such testing you can trust the auto mechanic.
My own replacement technology.
First of all, you will need to make a cover with a spool from a tubeless wheel. A five-liter plastic bottle will be enough; you need to tighten it with a worm clamp on top. Then you need to pump out the fuel fluid from the main cylinder tank and pour a new compound into the tank. Now you need to tighten the cap, connect the compressor, using this cap you can adjust the pressure, it should be no more than 1 atm.
After this, you should put the hose from the dropper onto the bleeder fitting. After you open it, wait for the new fuel fluid to start flowing. Now you can close the fitting and start replacing it on the other wheel
At the same time, it is important to add the composition to the tank on time. Proceed as follows: rear right wheel, then front left; then the rear left and front right wheel
I usually use 700 ml of TJ. The work takes half an hour, and I also have time to make the lid. The spent composition after two years of use looks like a brown slurry.
Do you need to start the car when changing the vehicle?
The replacement procedure should only be carried out when the engine is stopped. You also need to bleed with the engine not running. Otherwise, the vacuum booster will have a negative impact, resulting in a poor-quality replacement. To replace the fuel fluid faster, first of all, I pump out the used compound from the tank with a syringe, then pour in a new fuel fluid, pumping according to the standard scheme until clean liquid flows out of the hose.
When to change brake fluid?
I know many motorists who replace them annually because the composition becomes wet. But I believe that if the car brakes normally, there is no need to go into the system again. Eliminating its airiness after such manipulations is not easy. And this affects brake performance worse than moisture. However, if your budget is not limited and there is a proven car service, then you can change the vehicle more often.
Do I need to dilute?
I don’t see any point in diluting the old composition of the new TJ. All this can lead to unpleasant consequences. You need to do this: drain the old composition, at this time let a friend add new liquid to the tank. You need to act in this way until, when you open the fitting, the fuel fluid flows without air bubbles.
Routine work
I won’t invent anything myself, but I’ll quote from the manual for servicing a German army SUV, that is, a Mercedes-Gelendvagen. Moreover, it is from the manual, for the army version. Quote. Complete replacement of the brake fluid in the system every two years. Fluid replacement by partial replacement is not permitted. Only by complete removal, through the opening of all fittings. It is allowed to use the NEW brake fluid released during bleeding, after it has settled and filtered. End of quote. There is nothing more to add.
Replacement of the rear brake wheel working cylinder of Chevrolet Niva
Tools:
- Brake bleeding wrench 8x10 mm
- Straight box spanner 10 mm (2 pcs.)
- Driver for socket attachment
- Extension for socket wrench
- Knob attachment 10 mm
- Rolling jack
- Support stand
- Brake fluid container
- Shoe
- Iron brush
Parts and consumables:
- Aerosol lubricant type WD-40
- Rear brake slave cylinder
- Brake fluid
Note:
If during operation there are traces of brake fluid leakage on the brake drum and the inside of the wheel, replace the working cylinder. Repairing the working cylinder often does not lead to positive results, and this requires special tools. Therefore, it is recommended to replace the cylinder assembly.
Helpful advice:
To loosen pipeline nuts, use special wrenches, since the nuts are overtightened and usually corroded, as a result of which the edges of the nuts are crushed when using regular wrenches.
1. Engage first gear and install support blocks under the front wheels.
2. Remove the corresponding wheel.
3. Using a wire brush, clean the dirt from the brake pipe mounting area and the brake cylinder mounting bolts on the back side of the brake shield. To make it easier to remove the cylinder mounting bolts and the brake pipe mounting nut, apply WD-40 to the threaded connections.
4. Remove the brake drum as described here.
5. Raise the parking brake lever until the upper ends of the shoes come out of the piston grooves.
6. Unscrew the nut securing the brake pipe to the working cylinder.
7. Plug the hole in the tube, for example, with the cap of the air release valve.
8. Unscrew the two bolts securing the working cylinder, holding it on the other side.
9. Remove the slave cylinder.
Helpful advice:
After long-term use, the brake pipe nut “grows together” with the pipe into one piece, and when you try to unscrew the nut, the pipe twists and breaks. In this case, just move the tube nut a little, then unscrew the cylinder mounting bolts and disconnect it from the tube, unscrewing the cylinder from its nut. After disconnecting the cylinder from the tube, the mobility of the freed nut can be restored by moistening it with brake fluid and turning the nut with a wrench alternately in both directions.
10. Install the slave cylinder in the reverse order of removal.
11. Bleed the brake system (only the working cylinder on the wheel being replaced) as described here.
12. Be sure to install the protective cap on the air release valve.
The article is missing:
- Photo of the instrument
- Photos of parts and consumables
- High-quality photos of repairs
What you should know about brake fluid
Brake fluid is hygroscopic (absorbs moisture), which helps protect brake system components * Brake fluid is light yellow in color * Does not shrink in volume when compressed, which is ideal for use in automotive brake systems * Lubricates the pistons in the brake master cylinder and caliper pistons and wheel brake cylinders * Brake fluid lubricates the rubber seals in the main brake cylinder and in the brake cylinders installed on the wheels * Brake fluid has good resistance to temperature changes * DOT 3 brake fluid has a boiling point of 205 degrees * The boiling point of DOT 4 fluid is 230 degrees * After After two or three years of using brake fluid, the level of moisture content in it rises, which ultimately leads to the onset of corrosion of the brake elements and loss of properties of the fluid * When using brake fluid, it is recommended to use only the fluid that the automaker specified in the vehicle's operating manual.
The procedure for repairing or replacing components and mechanisms
In fact, according to the observations and assessments of specialists, repairing the master cylinder in a garage rarely leads to the desired result - increasing the efficiency of the brakes.
The recommendation is simple - it is easier to replace the master brake cylinder assembly, if we are not just talking about replacing the rubber seals.
When replacing the master cylinder reservoir, it is recommended to change the sealing gaskets, having first lightly lubricated them with brake fluid.
When completely replacing or dismantling the master cylinder for repair, first pump out the brake fluid from the reservoir and plug the pipelines.
It is strictly forbidden to repair the pressure regulator of the master cylinder. The characteristics of the regulator are set by the manufacturer during manufacture, so the pressure regulators are replaced as a set.
After repairing the brake cylinder, do not forget to bleed the brake system.
Good luck with your brake master cylinder repair.
Manufacturer's recommendations
If you do encounter any doubts or misunderstandings, it is never too late to consult an automobile expert. Always remember to undergo maintenance as your safety is entirely in your hands.
Most people know that routine car care includes checking
Squeaky brakes attract attention, as does a car that takes longer to stop than is usually necessary. But brake lube? Many car owners forget that it even exists
However, proper maintenance of your vehicle includes taking care of this essential fluid.
If you have questions about this oil, you are not alone. My workshop clients often ask whether the fluid needs to be changed, and if so, how often it should be done. Here are some tips and facts to answer the most frequently asked questions.
Question answer
Why is there not a word about a domestic manufacturer?
At the very beginning of this article, I already talked about the fact that there is no GOST for this product, this is the first and main reason. The second reason is the technological lag in the field of chemistry, oils, lubricants, rubber products and seals. Bad brake fluid is not the same as bad-smelling windshield washer. The consequences could be much worse. And I have no desire to put my reputation or the LIFE and HEALTH of people on the line.
Classification of brake fluid.
There are several systems for dividing brake fluids: according to viscosity, according to DOT standards, boiling point. In addition, there are generally accepted standards - SAE J 1703, ISO 4925, etc.
The most common of them is gradation according to DOT standards, it consists of:
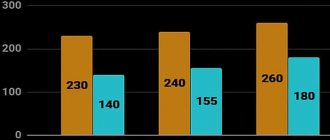
DOT3 (glycolic)
Recommended for classic cars with front brakes and rear drums.
Main characteristics:
- the boiling point in the “dry” state is not less than 205 degrees, in the “moistened” state (contains 3.5% water) - not less than 140 degrees;
- viscosity at negative temperatures (-40 degrees) – not less than 1500 mm2/s.
DOT4 (glycolic)
Used for modern vehicles with disc brakes on both axles.
Main characteristics:
- the boiling point in the “dry” state is not less than 230 degrees, in the “moistened” state (contains 3.5% water) - not less than 155 degrees;
- viscosity at negative temperatures (-40 degrees) – not less than 1800 mm2/s.
DOT5 (silicone) and DOT5.1 (glycolic)
It is used on sports cars with a fairly high temperature load.
Main characteristics:
- the boiling point in the “dry” state is not less than 260 degrees, in the “moistened” state (contains 3.5% water) - not less than 180 degrees;
- viscosity at negative temperatures (-40 degrees) – not less than 900 mm2/s.
Main elements of the system
The largest and most basic element is the fuel tank, but the total number reaches sixteen. Their volumes vary greatly.
- They are necessarily included in the engine cooling and lubrication systems.
- Axle housings and gearboxes are also extremely important for safety during travel.
- Chevrolet Niva filling tanks include power steering systems and hydraulic brake lines, front and rear shock absorbers.
- An integral part are tanks for windshield washer and air conditioning.