Author: Evgeny Zhivoglyadov. Date of publication: June 22, 2022. Category: Automotive equipment.
Tire pressure sensors have long ceased to be a fashionable device. For a modern driver, this is a de facto must-have (necessity), especially when operating a car in winter. This is confirmed by the trend of standard installation of such control systems on all imported medium and premium class vehicles.
In a new expensive car, an air pressure check sensor is already present or installed as an option. Owners of domestic “horses” or budget models can take care of having a useful gadget on their own. The modern automotive electronics market offers a lot of universal solutions, including the radio frequency electronic intelligent autonomous system (Tire Pressure Monitoring System, or TPMS for short). Wheel pressure controllers are in the highest demand.
What does TPMS give to the driver?
- The ability to quickly respond to a puncture.
- Save fuel by maintaining an effective pressure level.
- Peace of mind for not checking the wheels before driving (when starting the engine, the controllers will automatically detect qualitatively significant minimal losses in air pressure in the tires).
Classes, types and types of sensors
The catalog of available universal tire pressure checking systems is presented quite widely. They are divided according to two main characteristics. The first is the installation method.
- External TPMS, also known as Direct System. The controllers resemble ordinary “caps” that are screwed onto the nipple in 10 seconds. Their big advantage is ease of installation and low weight (9.6–10 g). The first makes it possible to use the system without beading/beading tires. Secondly, there is no need to balance the wheels.
- Embedded devices (Indirect). Such a device can only be mounted with flange and flange, since the controller is attached to the slope of the wheel rim using special clamps. They weigh more than external controllers, so after installation they will require an additional action - balancing.
Based on the completeness of the information displayed, systems are divided into high and low classes. In the second case, only an alarm signal is displayed on the monitor (or smartphone/tablet display), and the source of the problem is not indicated. High-end models, in addition to danger signals, can also show the level of air pressure and the damaged wheel, which greatly simplifies the driver’s actions.
Developers of these technologies separately offer TPMS for trucks, motorcycles, and cars. There are also universal options (which are suitable for all cars) and individual ones for a given car model.
Principle of operation
There are several control systems that differ in measurement principles.
- Indirect determination of pressure loss by the change in the number of revolutions per unit time of one of the wheels. It is measured through the signal of the anti-lock braking system (ABS). If three wheels rotate equally, and the fourth one rotates faster, then its rolling radius has decreased due to a change in shape when punctured. Based on the deviation from the norm, it is even possible to calculate the absolute value of pressure with a certain error, although it is unreliable and conditional.
- Also indirectly, but using an indicator that directly depends on pressure. The ABS controller identifies the natural frequency of the tire system and the air in it. This value depends on the pressure, which can be calculated using a microcontroller. It's difficult, but it works.
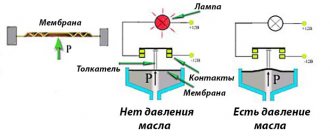
- Direct pressure measurement by a sensor located on the wheel rim. It can be mounted from the inside in the valve area or even designed as a cover that presses down on the spool. The device holds air and experiences a load, which is converted into an electrical signal.
The last option is the most common; sensors are installed on the wheels of expensive cars, as well as tuning in the budget segment.
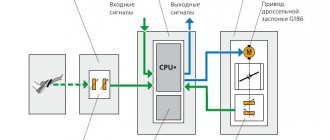
Each transmits telemetry information via a radio signal to a common unit. There it is deciphered, the device number and pressure value are highlighted. The computer knows where each source is located, since during their initialization they were registered in the general structure of the car controllers.
All that remains is to display information, light and sound warnings on the driver’s dashboard or a separate monitor specifically dedicated to monitoring pressure.
How does a tire pressure sensor work?
The operating principle of an electronic tire pressure sensor is the same for all electronic devices. Its essence:
- a controller attached to the wheel collects information about its condition (temperature, pressure);
- transmission of collected data from sensors to the transceiver is carried out via a radio channel (bluetooth), with a diagnostic frequency of no more than 2–3 seconds;
- when indicators exceed the upper limit of standard values or fall below a set level, the program gives a signal. The latter can be light or sound. Pressure limits can be set independently in the range specified by the device manufacturer (usually 1.7–3.2 bar).
Some TPMS also output information to a smartphone via Bluetooth.
Possible faults
Despite the fact that the TPMS is located inside the wheel and is well protected from mechanical damage, its failure can be caused by centrifugal forces, temperature changes and other negative influences. The exact cause of the sensor's malfunction can only be determined through special research, so if you do your own repairs, it is enough to simply replace this part.
The Kia Sportage 4 wheel pressure sensor transmits information to the receiving device via radio frequency, so its performance may be affected by other devices that use a similar principle of data transmission. If the TPMS is malfunctioning due to interference, the warning light on the instrument panel will illuminate yellow. If everything is in order with the wheels and the pressure is at a safe level, then you can turn off the malfunction warning system if the source of the interference is not found.
TPMS power supply
The device is powered by rechargeable batteries. Moreover, each sensor has an individual battery. The controller can operate either from batteries or from solar panels and the on-board network, it all depends on the model. A monitoring system powered by solar panels, unlike systems connected to the on-board network, is very convenient, since almost all devices operate from the cigarette lighter. This means there are no extra, dangling wires, and the cigarette lighter socket is always free.
Batteries for indoor sensors have a long service life. Typically it ranges from one to three years. After which the wheels are beaded again and the sensors are completely replaced.
All types of external controllers have a G sensor, which puts their power system into “sleep mode” when not in use. This allows you to increase battery life. Now almost all electronic sensors, whether internal or external, are equipped with limited energy consumption sensors.
How to connect sensors
A branded TPMS system kit usually consists of:
- From controllers with signatures for each wheel (the number depends on the class of car, usually the set includes four caps for passenger vehicles and six if it is a tire pressure monitoring system for trucks). A signature of two Latin letters, where the first determines the horizontal position, the second vertical. Example: LF – left (left) front (front).
- Instructions.
- Transceiver with 1-5 buttons on the sides to indicate pressure standards. There is double-sided tape on the back of the receiver mount for easy installation. This device is held securely, you can safely mount it on glass or panels.
- A set of keys for disassembling controllers or receiver.
- Connection adapter (provided for wired devices).
- Spare parts (stickers, gaskets).
The installation method depends on the type of device. External controllers can be installed independently by simply replacing the “original” air tube caps on the wheels. Here it is worth paying attention to the metal thread of the controller. It can be aluminum or brass. It is important that it coincides with the nipple’s own thread to avoid oxidation.
Internal TPMS is installed at tire service stations. The procedure is short and hassle-free, but it will protect the expensive tire pressure monitoring system from simple theft.
How to register sensors
After technical work on securing the elements, you can proceed to setting the parameters. The user can set tire pressure level limits for monitoring. For this purpose, special buttons are provided on the side of the receiver. Since they are needed solely for configuration, manufacturers try to minimize their number.
The modern market knows cases when the receiver gets by with just one button. To register data, you need to press it the required number of times. Example:
- press and hold for 1–3 seconds (long) – turn on/off;
- five short presses – start setting up the TPMS system;
- to set the lower limit, you can use the menu buttons (on the side, usually labeled with up/down arrows) or, again, click once on the main button;
- fix the standard - press and hold.
Along with the prescribed pressure standards, you can set the method of its measurement (bars, Kilopascals, psi), and the temperature units (Celsius or Fahrenheit). In the instructions, the manufacturer explains in detail the procedure for setting up its receiver; the driver should not have any problems with this.
Indirect pressure measurement system
This design is the most simply constructed. Therefore, its cost is relatively low. In fact, it is an extension of the ABS software block. In fact, the system does not register a lack of pressure, but a decrease in wheel dimensions.
If there is a puncture, air and tire escape, its diameter decreases. The relevant information is transmitted to the ECU, after which it is compared with the specified standard parameters. Detection of discrepancies allows you to determine which wheel has a puncture. Then the signal about insufficient pressure “lights up”.
Another variation is to measure the wheel speed. This solution is also a subroutine built into the ABS system. The length of the path for each bus is determined. Next, the information received is checked and compared with that recorded in the ABS. A discrepancy is indicated by an appropriate signal.
Since the determination of the proper pressure level is determined on the basis of the data obtained and their comparison, calibration is required after service work. The ECU receives new data for subsequent comparison with information received from the ABS subsystem. The main advantages of the indirect system:
- relatively low price;
- lack of additional structural elements.
There is also a significant drawback: low accuracy. The threshold for deviation from the specified pressure is 30%.
Sensor selection
The market for TPMS systems consists of dozens of models from no-name manufacturers (all overwhelmingly from China) and 3–5 reputable brands. Among the best options in terms of price/service life ratio, drivers noted the Japanese Carax tire pressure monitoring systems, better known among car enthusiasts as different versions of the CRX. Parkmaster devices performed well.
When choosing a specific device, you should pay attention to:
- on the range of action (signal transmission range; for Karax it starts from 8–10 meters);
- connection method;
- options (data transfer to smartphones/tablets, settings);
- warranty period;
- range of pressure limits that can be prescribed.
The way information is displayed/displayed is of great importance. More convenient than high-end systems (TPMS monitoring system screen constantly displays all wheels indicating pressure and temperature).