The Electronic Engine Control Unit (ECU, “brains”) is the brain center of any engine, which contains a set of microprograms and algorithms necessary for the proper operation of the engine and all its systems.
A large number of sensors located throughout the car take readings from certain devices and transmit them to the ECU, after which the “brains” correct the operation of a particular system.
In this article I will talk about the VAZ 2114-2115 ECU; you will learn about the main functions, features, as well as common malfunctions of this unit.
Physical location
The ECU of the “fourteenth” is located in the cabin directly under the instrument panel. If necessary, you can gain access to the “brains” from the passenger side; to do this, you will have to dismantle the decorative trim. If during the diagnostics a malfunction of the control unit was discovered, it will need to be dismantled for a more detailed study or repair. Before this, it is necessary to de-energize the car by disconnecting the terminals from the battery. Violation of the dismantling rules, as well as any experiments with voltage, can irreversibly damage the ECU.
ECUs of the following models were installed on the VAZ 2114-15:
- January("4", "5.1.X", "7.2");
- BOSCH("M1.5.4", "M7.9.7");
- ITELMA 5.1;
- GM-09.
Is it possible to install another control module on a car?
Various ECU models are installed on VAZ 2108 - 2115 cars, which belong to the following families:
- January 4, installed on the very first models of injection engines. They supported only a small number of sensors and provided fuel injection into a common air manifold;
- January 5 – 6 were installed on more modern cars. These ECUs provided injection into each cylinder individually, but did not support oxygen sensors;
- January 7 began to be installed in 2007. These ECUs are not inferior to foreign analogues and support all known sensors, thanks to which they control the engine more efficiently;
- Various GM models. Depending on the class, type and cost, these ECUs are similar to devices January 4 – 7;
- Various Bosch models. Depending on the class, type and cost, these ECUs are similar to devices January 4 – 7;
- Various Itelm models. These ECUs, depending on the class, type and cost, are similar to the January 4 – 7 devices.
Each model, even within a family or class, is only suitable for a specific combination of engine, sensors, wiring and firmware. Therefore, even different models within the same family should be installed only after consultation with a specialist in injection systems. Even if different ECU models are equipped with the same electrical connectors, a simple replacement will, at best, lead to poor engine performance.
How it works?
The main executive element of the control unit is a microprocessor; it processes the received information, makes calculations and issues commands, adjusting the operation of all systems. The processor is guided by an embedded microprogram, which clearly defines all scenarios for the operation of the motor and all its systems “for all occasions.”
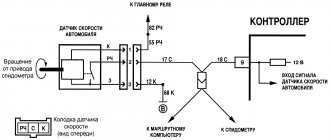
The ECU receives information from the following sensors:
- Oxygen sensor (lambda probe);
- MAF (mass air flow sensor);
- DPKV (crankshaft position sensor);
- TPS (throttle position sensor);
- DTOZH (coolant temperature sensor);
- Fan switch sensor;
- Knock sensor;
- Speed sensor;
- Exhaust valve.
The received data is processed, after which the operation of the motor or its individual systems is adjusted. So, based on certain needs, the following can be adjusted:
- Idle speed;
- Ignition;
- The amount of fuel in the air-fuel mixture (FA - “poor” or “rich”).
- Exhaust toxicity control;
- Operation of fans, etc.
In addition, the ECU is related to and also receives information from systems such as ABS, ESP, airbags and passive safety systems, as well as the anti-theft system.
In addition to the microprocessor, the ECU has other modules
RAM – Random Access Memory or, more simply, random access memory. Any changes in the operation of the motor and each malfunction will be recorded and stored in RAM memory. Errors are stored until you turn off the ignition. After this, the RAM is reset until you start the engine again. After starting the engine, self-diagnosis of all systems occurs, sensors send information about the state of things in certain nodes, the ECU analyzes the received data and, based on its own algorithms, makes a decision whether everything is good or not. If some data does not correspond to the concept of “norm”, an error is generated and recorded in memory, and the driver receives a warning on the instrument panel. Typically, this is either a “Check Engine” or another indicator that lights up on the dashboard.
PROM - Programmable Read Only Memory - is an analogue of RAM, the only difference is that this memory stores the ECU microprogram (firmware) and a set of necessary engine control algorithms. This type of memory is not reset, it is a kind of “hard drive” if translated into a computer. terminology Correcting this microprogram will allow you to change or reconfigure the operation of some systems and engine performance as a whole; this is popularly called “brain rewiring”.
EPROM is an electrically reprogrammable read-only memory device. This module contains secret access codes and various passwords that ensure the security of the car. Each time the engine is started, a set of passwords and codes are compared with the passwords in the immobilizer, if everything is “ok” the engine starts.
Malfunction of the electronic engine control unit (ECU, ECM, controller)
An electronic engine control unit, abbreviated as ECU, ECM, controller, is an electronic device that, using various signals from engine sensors, controls the composition and amount of fuel supplied to the engine.
Having a built-in diagnostic system, it can recognize problems in the system, warning the driver about them through a warning lamp (Check engine). It also stores diagnostic codes that indicate areas of trouble to help technicians make repairs. Symptoms of a malfunction of the electronic engine control unit:
— Lack of control signals for injectors, ignition, fuel pump, valve or idle mechanism, and other actuators. - No response to Lambda - regulation, temperature sensor, throttle position sensor, etc. - No communication with the diagnostic tool. — Physical damage (burnt radio elements, conductors).
You can purchase an electronic engine control unit (ECU, ECM, controller) from us!
DON'T STROKE - BUY CHEAPER! ! !
Causes of malfunction of the electronic engine control unit:
1. Unqualified intervention in the car’s electrical system when installing alarms and carrying out repairs. 2. “Lighting up” from a car with the engine running. 3. “Reversal of polarity” when connecting the battery. 4. Removing the battery terminal with the engine running. 5. Turning on the starter with the power bus disconnected; 6. Contact of the electrode during welding work with the sensors or wiring of the vehicle. 7. Water entering the ECM. 8. Broken or shorted wiring. 9. Malfunction of the high-voltage part of the ignition system: coils, wires, distributor
ECU diagnostics involves reading errors recorded in the controller’s memory. Reading is performed using special equipment: PC, cable, etc. via diagnostic K-line. You can also get by with an on-board computer that has the function of reading ECM errors.
The ECU stores diagnostic codes that indicate areas of trouble to assist technicians in making repairs.
If the ECM fails due to a problem in the wiring or actuator, a simple replacement may not give anything other than two, three, etc. burnt blocks.
To find out which controller is on your car, you will have to remove the side frame of the car's instrument panel console. Remember the number of your ECU and find it among the tables presented.
You can purchase an electronic engine control unit (ECU, ECM, controller) from us!
DON'T STROKE - BUY CHEAPER! ! !
The information will also be useful to you: Varieties of electronic engine control systems (ECM, controllers), which are installed on different models of the VAZ family car.
If you haven't found the answer you are looking for, then ask your question! We will respond shortly.
Don’t forget to share the information you find with your friends and acquaintances, as they may also need it - just click one of the social networking buttons.
Source
Troubleshooting
To read errors in the ECU, you need a special diagnostic scanner; without it, it is impossible to find out why, for example, the “Check” is on. After errors are found, they are deciphered, followed by diagnostics or repair of a specific unit. Simply “clearing” errors is not correct, this is an error, since this will only clear the ECU memory, but will in no way solve the problem.
ECU malfunctions and causes of failure
It is not immediately possible to understand that the control unit is not working correctly; it manifests itself in different ways, these could be malfunctions in the operation of some engine systems, or problems with diagnosing the ECU itself. There may be illogical, chaotic appearances, as well as disappearances of errors and problems with the engine and the car as a whole. Simply put, “glitches”, they can be noticed by an experienced specialist.
Algorithm of actions to restore ECU operation
To repair the engine ECU, the following operations are needed:
- Find the location of the breakdown.
- Re-measure the resistance.
- Find the conductor attachment points.
- Attach a wire with the required resistance in parallel using a soldering iron; it is recommended to leave the old wire in place.
After the measures taken, the system should work stably. If ECU errors recur, you must contact a service center.
The service life, safety and reliability of the vehicle depend on the timely repair of the engine control unit.
Among the reasons are:
- Mechanical damage (cracks, impacts, etc.);
- Exposure to moisture (“drowned people”, as well as cases where the car was stored improperly);
- Outside interference (reprogramming, incorrect firmware, etc.);
- Overheating or hypothermia;
- Voltage drops in the on-board network, as well as a short circuit (due to incorrect connection of the battery terminals, as well as attempts to “light” and other violations of the rules for operating the on-board network);
- Corrosion or oxidation of some areas of the board or other important elements of the ECU.
Where is the ECU located on the VAZ 2114
In a VAZ 2114 car, the control module is installed under the center console of the car, in particular, in the middle, behind the panel with the radio. To get to the controller, you need to unscrew the latches on the side frame of the console. As for the connection, in Samar modifications with a one and a half liter engine, the mass of the ECU is taken from the power unit housing, from the fastening of the plugs located to the right of the cylinder head.
Location of the VAZ 2114 ECU
In cars equipped with 1.6- and 1.5-liter engines with a new type of ECU, the mass is taken from the welded stud. The pin itself is fixed on the metal body of the control panel near the floor tunnel, not far from the ashtray. During production, VAZ engineers, as a rule, do not securely fix this pin, so over time it can become loose, which will lead to the inoperability of some devices.