What it is
Hydraulic compensators are parts for tuning a car engine.
The device automatically adjusts the valve clearance. The GKK was never installed by the factory on the old sevens. Some cars of that time had mechanical type regulators. But the efficiency of their work left much to be desired.
Owners of the VAZ 2107 must manually adjust the valve clearance every ten thousand kilometers. To do this, you have to dismantle the cover and use a feeler gauge to set the gaps.
Built-in mechanical elements are subject to wear. An incorrectly adjusted gap leads to increased engine noise. As a result, the car's dynamics decrease and fuel consumption increases. After 50 thousand mileage it is necessary to install new valves.
Hydraulic compensators on the VAZ 2107 are free of these disadvantages. The part lasts a long time: it works properly for up to 150 thousand kilometers. The gap is set automatically and is constantly maintained at the desired level.
The engine responds positively to such care, which is reflected in an increase in engine life, its power and in a decrease in gasoline consumption.
Hydraulic compensator 21214, specifics
In 2013, I ordered a batch of hydraulic compensators in Germany from the trendsetter in this area, the German brand INA. I won’t talk for a long time about their quality; they are a supplier of “German troika” conveyors. The first thing I did, like a true young man, was to take the hydraulic valve out of the “factory engine,” put it next to the “German” and pick up a micrometer. The first difference was purely visual. This is clearly visible in the photo. This is the ball shape and the height of the compression skirt. But that was only the beginning. Everything is like in a Russian fairy tale. The further you go, the worse it gets. The diameter of the factory miracle is 0.03 mm less. That is, there is simply no need to talk about maintaining the working pressure in the cup-hydric pair. Any hydraulic engineer, or just a mechanical engineer, will tell you that this is an unacceptable gap for hot oil. Result: inability to compress the valve spring and incomplete opening of the valve.
The need to use additives
Replacing the VAZ 2112 hydraulic compensators, a video about which is presented in the article, should be done only after the car owner knows what changes occur when using additives. They promise that they can reduce noise and clean channels and holes in hydraulic compensators. Be careful when purchasing generic additives. Read the instructions carefully. What type of engine is the additive intended for, what oil is it used with. Inattention can damage the engine.
After the VAZ 2112 hydraulic compensators (16 valves) have been replaced, a video about which you can watch in the article, you should inquire about the quality of the additives that are designed to change the properties of the oil. That is, improve the quality in order to achieve the effect we need at the moment. There are additives that improve the sliding effect. Rubbing parts with additives have a lower coefficient of adhesion. Due to this assistance, the engine increases power.
Hydraulic compensators on the VAZ 2109 should be used with additives that can increase the coefficient of adhesion. In automatic transmissions, it is necessary that the two wheels of the turbine transmit torque better. The hydraulic compensator must receive oil constantly and in the required quantity. If these conditions are violated, the operation of the hydraulic compensator is disrupted. This means that the gaps in the gas distribution mechanism will also be compromised. Not only knocks appear, but the normal operation of the engine is also disrupted.
The installation of hydraulic compensators on a VAZ 2107, a video about which you can watch in the article, must be accompanied by the use of the correct additives that will eliminate the consequences described above. If they are really high quality, then the desired effect will be achieved. The channels will be cleaned, the knocking will disappear.
But this effect will happen if the additive is original and not a fake. There are a great many low-quality additives on the market. Buy with caution, it is better to double check. Liqui moly Hydro, for example, is one of the most popular. If you also use oil from this company, you really get the effect. What the manufacturer promised, he delivered.
Now Hado has appeared on the additive market. It can be purchased at an affordable price. This is a product of the Ukrainian chemical industry. According to consumer reviews, there are no particular complaints. Additives really eliminate noise. Whether or not to use these compounds to eliminate noise and flush hydraulic compensators is up to everyone to decide for themselves. The main thing is to first make sure you need it, and then purchase it. When purchasing, pay special attention to the manufacturer. You can't allow counterfeits to come in. A fake can lead to complex and expensive repairs. But the price should not be too low, since in this case you risk purchasing a fake. The acceptable cost is 900 rubles.
One of the options for improving the VAZ 2107 engine is the installation of hydraulic compensators. This part not only reduces noise from the operation of the power unit, but also completely eliminates the need for periodic adjustment of valve clearances. Installation of hydraulic compensators is possible in a garage, for which you will need to prepare the system elements and the necessary tools.
Reasons for failure of VAZ 2112 hydraulic compensators
- Using inappropriate or poor quality oil
- Oil filter malfunction
- Failure to comply with oil change schedules
- Increasing the landing gap in the plunger pair
- Worn high pressure chamber check valve
- Incorrect operation of the engine lubrication system
- “Airiness” or partial filling of the hydraulic compensator with oil
- Microparticles of worn parts entering the hydraulic compensator in the oil
In this article we will tell you how to correctly replace hydraulic compensators on a VAZ 2112. What you need to consider when purchasing this part, and what alternative options are available when replacing this device.
Hydraulic compensators. What is it and why do they knock
Modern cars are becoming more advanced and smart. This also applies to the gas distribution mechanism. It is very important that the valve always opens and closes at the right time, so that ideally there are no gaps between the camshaft and the valve itself. This offers many benefits, such as increased power and reduced fuel consumption. Previously, valves were adjusted manually, then mechanical “wide” pushers appeared (which, by the way, are still used today on many cars), but the pinnacle of evolution was hydraulic compensators or simply “hydraulic compensators”. They have many positive aspects, but they also have a lot of negative ones, in particular they can knock. Today I will try to talk about the device in a simple and understandable language, as well as some breakdowns, there will be a video version at the end...
Design of hydraulic compensators and types of devices
The design of the hydraulic compensator in its modern form involves two schemes. However, structurally they differ little, and in any case, the entire mechanism is hidden in a non-separable metal case. The only difference is where the device is mounted: in one case these are the sockets of the gas distribution mechanism, in the other - the sockets of the valve rocker arms. The set of parts in both cases is the same: plunger with bushings, valve and plunger spring, ball valve.
At the moment, there are 4 types of compensators - some are gradually becoming a thing of the past, but are still found in power units, while others are confidently becoming more widespread.
Hydraulic support, the principle of which is based on interaction with levers and rocker arms. Nowadays such mechanisms are practically not found, but in previous generations of power units they were used very actively.
Roller hydraulic pusher - it is used quite often.
Hydro support.
A hydraulic pusher (hydraulic compensator) that regulates the clearances between the valves and the camshaft. Widely used on new car models.
Accordingly, the future lies in various modifications of hydraulic pushers, while hydraulic mounts are quickly becoming obsolete among car designers.
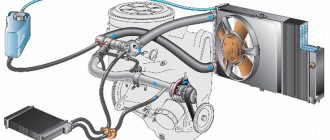
Installation of hydraulic compensators on a VAZ (classic engine)
After installing hydraulic compensators
there is no need to adjust the valves, the engine becomes much quieter (the valves stop knocking). But there are also disadvantages: the hydraulic compensator mechanism is very sensitive to the quality of engine oil (dirty oil can clog the mechanism).
Description of the installation process of hydraulic compensators. So, we have an engine:
The pan with the air filter, gas draft and block cover are removed. As you can see, everything inside is dirty with oil residues :(.
The sprocket counter washer is flared
The asterisk is installed so that the marks are opposite each other.
The sprocket mounting bolt is unscrewed; for reliability, the sprocket is suspended with wire.
We unscrew the nuts securing the bed and remove it together with the camshaft.
This is what the engine looks like after removing it :). Everything here is also clogged with fuel oil :(.
This is what the camshaft looks like - there is wear and risks.
And this is one of the levers.
We remove the levers and lay them out, remembering the position.
We unscrew the cams and carefully, so as not to tear off the low edges, tear off the bushing of the adjusting bolt and unscrew them.
We wipe off all the dirt, cut down the area opposite the 2nd valve so that it is in the same plane as the sockets.
We carefully clean everything with kerosene.
The planes of adjacent nests are ground in for greater tightness with a sharpening stone.
Now you can screw in the bushings. Here lies ambush number 1
. Not every bushing fits perfectly into the socket. Sometimes it is enough to screw the bushing designed for the first socket into the second socket, and the second will ideally screw into the first. In this case, it is clear that the bushing did not go into the first socket, and it was screwed into the second, and the first was left for a snack. In our case, we still had to take one bushing from another set. The one we rejected can easily enter another car without any problems.
This is what screwed-in bushings with pushers look like.
Now we unscrew the bushings, remembering their position.
We throw support washers into the head and press them using a special mandrel.
You can admire the installed washers.
Press the O-rings into the distribution plate. Here lies ambush number 2
. Again, the rings do not always fit perfectly into the plate. You can try others from the kit, sometimes it helps. In our case, we had to take one more ring from another set. If everything worked out, we assemble the assembly with the bushings.
We install what we got into the head.
Now the crucial moment - you need to check that the plunger does not jam. Loosen the bushing until the plungers move freely in the bushings.
Now we throw the springs inside.
This is what the block head looks like now.
And install the plungers in their places.
Now you need to adjust the stroke of the plungers. To do this, we install valve drive levers 4,6,7 and 8 and install a bed with a camshaft turned in accordance with the instructions :).
We install a special device to accurately calculate the stroke of the plungers.
With the help of such a thing, the stroke is measured.
To access levers 1 and 8 you have to use the bent tip.
Having removed the bed, we throw washers to bring the plunger stroke to normal. We used not only the rings from the kit, but also others of different thicknesses to more accurately set the stroke.
Then we align them with a mandrel.
We do the same with the remaining plungers.
Now we drill the oil drain in the bed, removing the camshaft from it.
And cut the thread.
This is what happened.
In order for the tube to be straight down, you need to cut the thread on it to a certain level.
And then bend it on the spot to the desired angle so that it fits exactly into the hole of the cross.
After blowing and cleaning the bed and camshaft, we put them back together.
We install the lubrication system pipes. Fill the system with oil. We plug with our fingers those bushings in which the oil has reached the top.
Installing the ball valve
And a plunger. Here lies ambush number 3
. It is necessary to check the tightness of the valve. To do this, a ball is thrown into the plunger and blown. It should not allow air to pass through. If unsuccessful, you can try replacing the ball. We had to take one ball from another set. The valve is re-checked in place; the plunger must resist being pressed into the valve body.
We install the levers in their places.
And we install the bed with the camshaft in place. You must remember to set it to its original position.
We tighten the nuts and tighten them with the required force.
This is what the installed system looks like.
We screw the sprocket into place and lock the lock washer.
This is what the result looks like. All that remains is to install the cover and air filter.
First start of the engine with installed hydraulic compensators:
All this disgrace was done to the car _and_ VAZ-21063 1990, mileage 283 thousand km at the time of installation..
installed and tuned and started... guys, you know I want to strangle my whistling carb with a cut pan and forward flow, which disturbs the quiet monotony of the engine... it rumbles so much, it’s already pleasant (almost starts to rev)... I recommend... It’s enough to eat, but the result is worth it...
To begin with, I would like to inform you that our spark plug wrench-tube is suitable for unscrewing a pair of nut-bolts from a well... then I recommend running the threads of each ring... and when tightening, estimate the number of turns and tighten carefully... it’s better to undertighten than to look for a new plate... I also say this I have to say that I doubted the tightness of the connection of the oil supply tube (with the thread that) from the distributor bed to the “tee”... so I installed the thread on a threaded anaerobic sealant (blue)... and the end of the tube entering the “tee” was coated with sealant (high-temperature and carefully without excess)... that’s all the washers fell into the wells without shrinkage and were previously brought to their normal “flat” state through a hammer-anvil pair... I checked the tightness when pumping oil with the plunger pairs inserted (see the instructions, when pumping oil the plunger begins to rise, etc.) without any checking the tightness of the ball and plunger head...
The engine runs really quieter and does not affect the service life of the shaft and bed. The service life of the compensators themselves has not yet been studied.
When installing a non-original shaft, you need to pay attention to whether it is designed to work with hydraulic compensators. Hydraulic compensator shafts differ in the height of the cams and the contact with the plunger occurs slightly differently. If at the original lift it is almost not noticeable, then if you add another 2mm of valve travel, the angles become much larger and the contact with the plunger will not be where expected.
z.y. However, to remove the original valve supports, I recommend having a 21mm socket. The spark plug has a size of 20.6 mm, sometimes you have to persuade it to fit with a hammer, and the stamped steel head may not withstand the force. but with all the advantages, there is one disadvantage, the system does not tolerate old and dirty oil, I had just this and it turned out that they poured me something at the station that is unclear... the result is that one valve rattled very quickly, one of the plungers stopped working, but after complete cleaning and filling clean oil on your own, and not something unknown that was poured at the stations, everything fell into place, although I had to spend the entire day off cleaning...
I drove about 1.5 thousand on them, the feeling at the moment is twofold, if everything is good, then the engine is really quieter, pulls very well, runs smoothly, my glitch with cylinders 1 and 4 has disappeared, for some reason there are always spark plugs They were black, but everything was fine. It’s very pleasant to drive, especially at speed on the highway, you can hear not the engine but all the other bearings...
but there is one thing, they are very picky about cleanliness, it so happened that out of ignorance I poured the sewing oil, which was lying in layers in the engine, fuel oil, so to speak, and with this fuel oil the oil channels were clogged and the hydraulics were stopped working, the engine seemed to be cleaned with more, but this fuel oil will still float up from somewhere and clog the channel
Debugg
Since there are several hydraulic compensators in a car, it is worth using acoustic diagnostics to determine the faulty one. An experienced technician knows how to check hydraulic compensators for functionality using acoustic diagnostics, that is, sound.
For an experienced master, such manipulations are not difficult. After identifying the problematic hydraulic compensator, to eliminate the knocking, it is necessary to wash it, return it to its place and restart the engine. If this measure does not help, you will have to replace it. Let's consider step-by-step actions in the case of both procedures.
How to wash the hydraulic compensator?
The mechanism in question must be washed in a room protected from dust and drafts. It won’t be possible to not disassemble the engine at all, but there is also no need to rid it of every screw.
At the preparatory stage, prepare three deep containers the size of the compensator, as well as a flushing liquid, which can be kerosene or good 92-grade gasoline.
Also, before washing, leave the car in the garage for a day to allow as much oil as possible to drain into the pan. Further actions are as follows:
- Disconnect the battery to de-energize the car.
- Get rid of the air filter.
- Remove the bolts to remove the cylinder head cover.
- Remove the hydraulic compensator from its sockets after removing the rocker arm axles.
- Use a synthetic bristle brush to clean the outside of parts.
- Wash the hydraulic compensators in the first container. To do this, immerse each of them in the liquid and press the ball valve through the hole in the plunger using a wire. Be careful not to break the spring. Next, press the plunger itself. As soon as you notice that the movement has become easier, carefully squeeze out the valve ball and drain the fluid from the compensator. Use a syringe to additionally rinse the channels in the body and proceed to a similar rinse in the second container.
- At the final stage, you will be tested; for this you will need a third container with flushing liquid. How to check hydraulic compensators before installing them in place? It is enough to dip them into the third container, draw liquid into the HA and lower the valve, then remove the part with the plunger up. If you press the plunger with your finger, it should not move.
- If there is no movement, return the parts to their place by installing the rocker arms, cylinder head cover and other elements. Remember to tighten the bolts from the middle to the edges.
After the assembly is completed, start the engine and wait a couple of minutes until it idles, at which there should be no knocking after flushing. Cleaning also helps get rid of knocking after the engine warms up and reaches operating temperature.
Why are hydraulic “adjusters” needed?
As the engine gradually reaches operating temperature, its other components also heat up. The associated expansion of parts causes a decrease in a variety of gaps in the power unit. And adjusting the gaps in the gas distribution mechanism is a very important operation, since the stability of the engine largely depends on it. It is clear that manual adjustment is a tedious and ineffective task; special mechanisms cope with it much more successfully. Moreover, during active vehicle operation, the valves are constantly under both mechanical and thermal load. And we must not forget that all timing components heat up unevenly, which, combined with natural abrasion, leads to increased wear of the valve mechanism.
The operating principle of hydraulic valve compensators is based on ensuring optimal thermal clearance. But it should be different, since the intake valves, compared to the exhaust valves in contact with hot gases, heat up an order of magnitude less. In addition, “regulators” are able to take into account the wear of the valve mechanism, although this does not solve the problem of increased fuel consumption and a decrease in engine power.
Returning to the issue of manually adjusting the timing belt, one cannot help but notice that such an adjustment should be carried out after 15 thousand km. However, it is highly not recommended to carry out such a procedure without very specific skills, since it is necessary to take into account a wide variety of temperature fluctuations. This is the same as in the case of the average temperature in the ward, which does not provide objective data on the condition of the patients. And a completely different matter are hydraulic compensators that regulate the gap automatically, taking into account current parameters.
Hydraulic compensator 21214, specifics
In 2013, I ordered a batch of hydraulic compensators in Germany from the trendsetter in this area, the German brand INA. I won’t talk for a long time about their quality; they are a supplier of “German troika” conveyors. The first thing I did, like a true young man, was to take the hydraulic valve out of the “factory engine,” put it next to the “German” and pick up a micrometer. The first difference was purely visual. This is clearly visible in the photo. This is the ball shape and the height of the compression skirt. But that was only the beginning. Everything is like in a Russian fairy tale. The further you go, the worse it gets. The diameter of the factory miracle is 0.03 mm less. That is, there is simply no need to talk about maintaining the working pressure in the cup-hydric pair. Any hydraulic engineer, or just a mechanical engineer, will tell you that this is an unacceptable gap for hot oil. Result: inability to compress the valve spring and incomplete opening of the valve.
Operating principle of hydraulic compensator
A ball-shaped valve supplies engine oil to the hydraulic element cavity. Under the influence of lubricant, the piston of the device extends, which leads to an increase in the height of the hydraulic valve. This leads to a reduction in the valve clearance in the gas distribution mechanism to a minimum level.
The oil stops flowing when it reaches the maximum compression level. When production occurs, the valve again releases the required amount of oil. Thanks to this, pressure is constantly maintained in the GKK, which reduces the valve clearance.
If you decide to install a compensator, be prepared to use only high-quality oil.
Disadvantages of using hydraulic compensators
There are practically no disadvantages when installing hydraulic compensators on the VAZ-2107. But one point should be taken into account - you need to use only high-quality oil and filters. When small particles get inside the hydraulic pushers, complete or partial failure occurs.
The size of the gap changes, which leads to the appearance of shock-type loads. And they are the reason for the reduction in the resource of the mechanism. Similar consequences will occur if the oil pressure in the system decreases. Therefore, if you decide to install hydraulic compensators on a VAZ-2107, you will have to purchase only high-quality oil and filters, and also monitor the level.
Advantages and disadvantages of hydraulic compensators
After installing hydraulic compensators on the VAZ 2107, it reduces noise when the engine is running. The high-frequency component caused by the operation of the standard timing belt disappears from the sound spectrum. When driving in 4th gear at speeds up to 80 km/h, the sound of the engine is completely inaudible in the cabin.
Timing parts with hydraulic compensators wear out more slowly, since they do not experience constant shock loads caused by the presence of gaps. The camshaft and rocker lobes maintain a smooth surface even with high mileage. When installing hydraulic compensators on a mechanism with already worn cams, the latter gradually level out during operation.
Engine characteristics (power, throttle response, efficiency) remain unchanged. But due to the absence of differences in valve clearances, engine operation becomes uniform.
The conditions of abundant lubrication in which the hydraulic compensator parts operate ensure a complete absence of wear on the latter. During the first 20-30 thousand mileage, the plungers and bushings grind in, their mating surfaces become mirror-like. With further operation, no traces of wear appear on the parts, their linear dimensions do not change.
The only drawback of hydraulic compensators is their increased sensitivity to the quality of engine oil and the presence of contaminants in it. Otherwise, the plunger may get stuck, causing a change in the gap and the appearance of shock loads that can damage the mechanism. The same consequences are caused by “oil starvation” of the engine.
How do hydraulic compensators work?
Hydraulic compensators on the VAZ-2107 allow you to eliminate thermal gaps in the valves when the engine is running. Operation occurs in a fully automatic mode; adjustments and any other settings are not required.
When repairing the gas distribution mechanism, it is enough to just change the valves and grind them in. There are no washers or adjusting nuts in the design. Engine oil moves to the hydraulic compensators, and due to pressure, the dimensions of these elements change. The valve is displaced under the influence of a hydraulic pusher on one side and a spring on the other.
Pros and cons of a hydraulic compensator
There are many positive aspects to this mechanism:
- It is completely maintenance-free and works automatically
- Increased timing system resource
- Maximum pressure, which gives good traction
- Minimum fuel consumption
- The engine always runs quietly
Well, despite all the advanced design, there are also a fairly large number of disadvantages.
- Since all work is based on oil pressure, you need to fill in only high-quality lubricants. Synthetic is desirable
- Need to change oil more often
- The design is more complex
- Expensive repairs
- Over time, they can become clogged, which impairs engine performance (consumption and traction), and the timing belt begins to make noise.
The biggest disadvantages are that the design is expensive and complex, and is VERY demanding on the quality of the oil. If you pour “don’t understand what” they will very quickly fail and require replacement. For example, conventional mechanical pushers are much simpler and less demanding on the quality of lubrication.
Camshaft theory
Some people asked if possible to make some kind of comparison. What can we compare camshafts for a field with if an engine is an analogue of a human heart? Probably with the training of certain muscle groups. For those who have ever played sports, or at least watched them on the couch on TV, there is no need to explain that athletes have different figures. A weightlifter, a marathon runner, a swimmer, and an all-around athlete are completely different physical activities and muscle groups. Camshafts are divided approximately the same. There are lower shafts, which make it convenient for the engine to knead dirt and drag something heavy, but the speed on the highway will be no more than 90 km/h. There are “high” shafts, the engine “sings” when the revolutions rise above 4000 and the car flies towards the horizon. There are “universals”, this is a slight increase in the elasticity of the engine over the entire range of its operation. There are narrow-range specialists, this is when the shaft “turns” in a certain speed range (usually these are sports variants).
In fact, in this area, like in many others, there are a very large number of secrets. I’ll reveal one of them))) On many Niv forums, the issues are discussed that the radios of three manufacturers are very similar in their characteristics, only the names are different. Behind all these radios there is one designer, who moved from the company and is still riding on his “legacy”))).
Basic faults
Hydraulic compensators, like any car part, tend to wear out and break. They are constantly under load. But they work for a long time: from 120 to 150 thousand mileage. Sometimes they fail ahead of time.
Two circumstances indicate a malfunction:
- a characteristic knocking sound appears, reminiscent of a clattering sound;
- motor power decreases.
Engine knock
The main sign of wear of a spare part is the appearance of a clattering sound. Since extraneous knocking noises can occur on the VAZ 2107 for various reasons, you need to check what is its source. To do this, you will have to open the hood and start the engine.
A characteristic clattering sound comes from under the valve covers and does not disappear while the engine is running. At the same time, the sound may have interesting features.
- The knocking noise appears on both a warm and cold engine. If you increase the speed, it may stop. This indicates possible valve ball wear. The hydraulic compensator will have to be completely replaced. But before doing this, make sure that the device is not dirty. A good cleaning may easily fix the problem.
- The engine starts knocking only after warming up. This indicates that the elements of the part have worn out. It's time to buy a new one.
- The characteristic clattering sound appears only at elevated speeds. Most likely there is too much or too little oil coming in. You need to check its level. And if necessary, repair the oil receiver.
- The knocking is constantly present and does not subside under any conditions. This usually occurs when there is a gap between the rocker and the camshaft lobe. Try cleaning the hydraulic compensator or replacing it with a new one.
Reduced power of the power unit
If the hydraulic compensator malfunctions, this inevitably leads to a decrease in engine power. You will feel that the dynamic characteristics of the VAZ 2107 have decreased. And this is not surprising!
Indeed, as a result of an incorrectly set valve clearance, the wrong amount of fuel enters the engine. As a result, the fuel mixture is formed in incorrect proportions, which reduces the power of the power unit.
How to get rid of the knocking of hydraulic compensators with your own hands
Increased engine noise may indicate the presence of serious malfunctions, which can lead to complete inoperability of the unit.
The knocking of hydraulic compensators when cold does not belong to this category, but if this part is not adjusted, the engine will consume more fuel, develop less power and the comfort of driving the car will sharply decrease. The wear of the piston group will also increase due to incorrectly selected gaps in the gas distribution system.
This article will tell you in detail how to eliminate the knocking of hydraulic compensators, as well as how to do this work efficiently and with minimal time and financial costs.
Knocking of hydraulic compensators: reasons
To understand how to get rid of the knocking of hydraulic compensators, you need to have a good understanding of the operating principle of these parts. The thermal expansion of the metal as a result of heating was the reason for the invention of this type of mechanism.
In old-style cars, instead of hydraulic compensators, adjusting bolts were installed, with the help of which the thermal gap was manually adjusted. This method of eliminating increased gaps in the gas distribution system required the car owner to spend a significant amount of time and money, because the need for manual adjustment arose every time the car traveled 10 - 15 thousand km.
In modern cars this function is fully automated using small inserts between the rocker arms and the valve stem. The operating principle of this part is quite simple:
- Oil from the lubrication system enters the cylindrical cone of the compensator under pressure when the camshaft cam does not apply pressure. Inside the part there is a plunger pair, with the help of which the filling of the internal cavity with oil is regulated until the moment when the pressure part of the mechanism extends to a distance that completely compensates for the existing gap between the part and the valve stem.
- At the moment when the camshaft rotates to the angle required to start applying pressure to the valve, the oil supply is shut off and, taking into account the fact that oil is a practically incompressible liquid, the compensator maintains the required length and transmits the force from the camshaft to the valve stem without delay.
- After the valve returns to the closed position, the entire cycle of operation of the hydraulic compensator is repeated again.
Click on the picture to enlarge
Considering the fact that the internal volume filled with oil can vary depending on the size of the gap, it is possible to completely avoid delays in valve opening and, as a result, increased noise of the gas distribution mechanism.
Unfortunately, hydraulic compensators, like any car part, can fail. A malfunction of this part will inevitably lead to the formation of a characteristic knocking sound during engine operation. Most often, hydraulic compensator noise is caused by the following reasons:
- Wear.
- Manufacturing defects.
- Internal valve jammed.
- Air in the internal cavity of the part.
- Valve mechanism clogged.
What is required to install on the seven
To install the elements on the “seven” yourself, you need to have the following tools and accessories on hand:
- Torque wrench.
- A set of wrenches (socket wrenches, socket heads, open-end wrenches).
- Drills and electric drill.
- Copper and steel wire.
- New gasket for the timing cover.
- Angle grinder or some files.
- Rags.
- Fine abrasive grinding disc.
- Set of hydraulic compensators.
- Frame for block head washers.
- Mechanism for replacing plungers.
Even before checking the hydraulic compensators, you need to prepare a special tool - without it it is quite difficult to carry out all the work.
Installation of hydraulic compensators
It will be much easier to purchase an assembled cylinder head with hydraulic compensators for a VAZ-2107. But if you still decide to redo it yourself, then follow these steps:
- All channels through which oil flows must be closed during the work.
- Install hydraulic pusher bushings.
- Press the block head washers.
- Press the O-rings into the hydraulic tappet plate.
- Mount the entire mechanism on the head.
- Install the springs and plungers, then install the valve drive levers 4, 6, 7, 8.
- Check the stroke of the plungers and make adjustments if necessary.
- You need to make a hole in the camshaft pastel and place a tube in it.
- When installing the hydraulic system, ensure that all pipes are directed correctly.
Typically, hydraulic pushers come with detailed instructions that indicate the pipe routing diagram for each engine type.
Replacing rocker arms on a VAZ 2107
Rockers (rocker arms) are one of the elements of the valve timing mechanism of the VAZ 2107 engine. The purpose of the part is to transmit energy from the camshaft cam to the valve stem. Since the rocker is constantly exposed to mechanical and thermal stress, it wears out over time.
Rocker arms are designed to transfer energy from the camshaft lobe to the valve stem
Determining the suitability of rocker arms
If during operation of the “Seven” there is a decrease in engine power or a characteristic knocking sound is heard in the cylinder head, then the likely cause is a broken rocker arm. During repair work, it is necessary to clean the rockers from dirt and carbon deposits and check them for wear and damage. If any defects in parts are found, they are replaced with new ones. If the rocker arms are in normal condition, install the products on the cylinder head.
If the rocker arm is heavily worn or there is visible damage, the part needs to be replaced
Is it possible to level the rocker arm?
When adjusting valves or repairing the cylinder head, you may notice that the rocker arms are slightly at odds with respect to the camshaft, i.e., the distance between the rocker plane and the camshaft journal is not the same. To eliminate this nuance, some owners of “classics” align or change the springs that press the rocker arms, or replace the rocker itself, but the problem may still remain. In fact, on all classic Zhiguli models, including the VAZ 2107, misalignment is not as bad as incorrect valve clearance. Therefore, it is the gap that deserves attention. The main thing is that the parameter is adjusted properly and is 0.15 mm when cold.
When the rocker arm is skewed, some motorists change the part itself, the springs, and sometimes the camshaft, but they do not achieve the desired effect
How to replace a rocker arm
If there is a need to replace the rocker arms on the “seven”, for example, 1 part in case of its breakdown, then it is not necessary to dismantle the camshaft. To do this, it will be enough to pry the spring with a screwdriver, remove it, and then remove the rocker itself. The new part is installed in the reverse order. If all the rocker arms are being replaced, then it is wiser to dismantle the camshaft.
Is such a replacement legal?
Recently, there has been a law according to which a car engine does not require mandatory registration. In fact, the engine of a “classic” becomes an ordinary spare part, like a bumper or thermostat. But you need to adhere to the recommendations that come from experts. When purchasing a motor, enter into a sales contract. If possible, check the traffic police database for the car from which the power unit was removed. The seller must provide you with documents that confirm his absolute right to own the car or engine.
Provided the transaction is clean, there will be no claims against you. You can proceed to the next step after installing the 16-valve engine on the “classic”. This is registration with the traffic police. Many people have an ambivalent attitude towards the procedure, since some try to formalize the alteration so that everything is official, while others take advantage of the fact that no inspector has the right to inspect the engine, and cannot demand that the hood be opened either. Even during the state inspection, they don’t pay much attention to such alterations.
Installation of hydraulic compensators on classics.
Of course, you can adjust the valves yourself if you do everything according to the book, but here you will need skill. The valve is a delicate matter and requires the motorist to have experience in this matter. On the other hand, you can contact a service center, where they will adjust the valves for you for a symbolic 2200 rubles (+ cylinder head cover gasket). This is of course good, but I had to adjust the valves every 10tkm. I contacted one hundred, then I started doing the adjustment myself, but in the end I got fed up with all this and decided on an expensive timing belt modernization.
1. What is needed to install hydraulics on a classic head?
Let's look at cylinder heads 2101 and 21213 (21214 st.b. until 2008). So, the seats for the adjusting bolts are the same. The cylinder heads are identical, as a result, their timing parts are interchangeable (although AvtoVAZ does not recommend installing hydraulic compensators on Zhigulis during the WARRANTY period).
Therefore, to install hydraulics on a classic engine, we need to purchase: Hydraulic compensator 21214 of the old model (21214-1007160), Camshaft assembly 21214 (21214-1006008-00), Hydraulic compensator oil supply ramp 21214 assembled of the old model (21214-1007180SB).
It would also be a good idea to stock up on a torque wrench (0-100nm), a 21mm socket, a new valve cover gasket, and an aerosol carburetor or caliper cleaner.
2. Pitfalls when installing hydraulic compensators on a classic engine:
Mistake #1 Buying counterfeit products. Alas and ahh, but the problem of counterfeit spare parts for classics remains relevant. So buy original spare parts in stores such as Baltkam, Dvizhkom, Avtopiter, AutoAll.
Mistake No. 2 Dirt and old oil deposits when installing hydraulics. After dismantling the old clearance adjustment system, BE SURE to clean the installation areas of the hydraulics from old grease and oil deposits using a carburetor cleaner and compressed air. It is also necessary to blow out the oil rail of the hydraulics with compressed air to avoid clogging it with foreign small particles.
Error No. 3 Installing hydraulics without removing the retaining rings. Folks, these rings on the hydraulics are for transportation purposes; before installing the hydraulics on the engine, they MUST BE REMOVED!
Error No. 4 Violation of the tightening torque regulations for the threaded connections of the cylinder head and timing gear. So, if you tighten the cylinder head and timing belt by hand, at a discount, by eye, yes, I’ve done this 1000 times, everything will be ok, I promise, I answer with my mother... know, there is a special place in hell for you! Now live with it)
Based on the technical regulations: - the hydraulics are tightened in 2 broaches, the first with a force of 15 nm, the second with no more than 25 nm (from 20 nm to 25 nm); — the camshaft assembly with the pastel is tightened in 2 broaches: the first 20 nm, the second no more than 30-35 nm.
If you overtighten the hydraulics, they can wedge or become completely jammed, but if you don’t tighten the hydraulics, they will unscrew.
Error No. 5 Installing Niva rockers. So, the classic and Niva rockers differ in shape and size, the 2121 rocker is larger than the 2101. Therefore, after installing the 2121 rocker, many people start to jam their valve stem seals. The only correct choice would be to keep the old rockers.
3. Pitfalls when operating hydraulic compensators on a classic engine:
Stone No. 1 The quality of the engine oil and its replacement frequency. Hydronics like to work on synthetics and semi-synthetics. I leave the choice of oil manufacturer brand to your discretion. I use semi-synthetic 10w40 both in summer and winter. To make your choice easier, I’ll give you the following information: a 4L canister of the small one I use costs about 2000 rubles. I oil it approximately every 6-7tkm, along with filters and spark plugs.
Stone No. 2 Warming up the engine before starting to drive. Before you start driving, you must let the car idle (no more than 2000 rpm) for 5 minutes in summer and 15 minutes in winter. This is necessary to pump the hydraulic oil system.
Additional recommendations from the author of the article:
Recommendation No. 1 When installing hydraulics, be sure to install camshaft 21214.
Recommendation No. 2 If you want to get an increase in power, then it will also not hurt you to install a split gear and install any other improved camshaft from a 214 Niva like an Estonian or OKB.
Recommendation No. 3 When changing oil, use flushing and flushing oils, this will extend the life of hydraulics.
Recommendation No. 4 Additionally, it will be necessary to install an automatic chain tensioner (this will be discussed in a separate article)
Recommendation No. 5 Before the first start, get ready to adjust the ignition; for me it ran 100 degrees counterclockwise.
1. Now I am not bothered by the noise of the valves. While the engine is running, you can hear the chain and rotation of the gearbox input shaft. 2. Lack of constant maintenance of the timing mechanism. 3. The car began to start better and switched to diesel when the ignition was turned off.
Alternative.
My neighbor, who has owned a Niva-Chevrolet for more than 10 years, advised us to replace them completely with simple adjusting bolts from our domestic “classics”. He himself had already changed the hydraulic lifters 2 times until he was advised to do so in one of the services. Since then he hasn't had any problems.
Having gone to the service center, I consulted with specialists. They confirmed to me that on Niva they make such a replacement quite often and then do not return to them with problems.
It is not a problem to purchase adjusting bolts. In a store nearby they cost 800 rubles for 8 pieces. The problem was finding plates for them and springs for the rocker.
But this matter was resolved quite simply by disassembly, and cost 300 rubles for everything including bolts!
The service work, including adjusting the bolts and replacing the valve stem seals, cost me 1,000 rubles. Total issue price is 1300 rubles. + hour of time.
You can do it yourself, but the prospect of removing the camshaft and then installing it correctly, to be honest, did not appeal to me.
Diagnosis of GCC
Listening to knocks and monitoring the dynamics of the VAZ 2107 engine is, of course, a useful habit. But you still have to roll up your sleeves and drive the car into the garage. After all, for an accurate diagnosis, you need to get the device and inspect it personally.
- Remove the valve cover.
- Using a special wrench, rotate the crankshaft so that the cylinder piston is in the compression stroke.
- Try pressing the rocker arm on the intake valve.
If the rocker arm easily gives in to your efforts, the hydraulic compensator requires replacement.
You can also check the functionality of the hydraulic supports using a screwdriver. If you press on a faulty mechanism, it will give play.
VAZ 2110: replacing hydraulic compensators yourself
Replacing hydraulic compensators of a VAZ 2110
It is necessary to objectively understand that the engine of any car always heats up during its operation. Another question is what the degree of heating is. It is worth noting that it is primarily determined by the intensity of the motor’s functioning. On a VAZ 2110, replacing hydraulic compensators is quite commonplace for an experienced motorist. Before understanding the reasons that lead to replacement, it is necessary to consider the essence of the device itself. Replacing the hydraulic compensator on a VAZ 2110 is done with your own hands using the step-by-step instructions presented below.
How to install a hydraulic compensator on a VAZ 2107
Before starting work, prepare the following tools:
- new parts;
- set of keys and sockets;
- torque wrench;
- Screwdriver Set;
- rags;
- New timing cover gasket.
Follow these steps in order:
- Remove the air filter.
- Remove the carburetor.
- Remove the distributor. The valve cover must be completely free to operate.
- Using a 38mm wrench, rotate the crankshaft so that the camshaft mark aligns with the protrusion on the bearing housing.
- Secure the chain to the sprocket with a wire to prevent it from falling into the engine.
- Bend the bolt stopper on the camshaft sprocket and unscrew the fasteners.
- Using a socket, unscrew the camshaft mount and remove it.
- Remove all rocker arms and springs. Find a way to label each rocker so you can put it in place when you assemble it!
- Unscrew the adjustment bolts and their bushings.
- Blow out the oil rail with a compressor.
- Remove the locking elements from the hydraulic compensators.
- Install the CV joints through the ramp and tighten them slightly.
- Tighten the hydraulic compensators to a torque of 2 to 2.5 kg/m.
- Install a new camshaft from 21214.
- Remember to place the oil rail ring on the first stud.
- Follow the camshaft tightening sequence as shown.
- Make sure that the oil line takes a shape that does not interfere with the installation of the valve cover.
- Install and tighten the camshaft gear.
- Install the carburetor, distributor and air filter.
As you can see, the work can easily be done with your own hands in the garage. An experienced master will take no more than two hours to complete everything.
How do hydraulic compensators work?
Preliminary preparation includes the following manipulations:
- Removing the air filter housing and element.
- Removing the throttle cable. It is installed on the gas distribution mechanism cover. You can install hydraulic compensators on a VAZ-2107 (carburetor). They are installed not only on injection engines.
- Rotate the crankshaft so that the distributor is installed in such a way that the marks on the sprocket and the housing align.
- Flaring the washer under the camshaft sprocket mounting.
- Unscrewing the fastening bolt.
- Unscrewing the camshaft pastel fastening nut, then dismantling it along with the rockers. Be sure to mark in which places they were installed - when assembling, mount them in the same way.
- Complete dismantling of the camshaft, unscrewing the adjusting cams.
After the preparatory work, you need to cut off the tide, which is located near the second valve - it will interfere.
Engine disassembly
First of all, you need to completely remove the air filter housing along with the pipe so that they do not interfere. Next, remove the throttle, after which you need to remove the valve cover. The camshaft gear will have to be removed, so we reduce the risks on the gear and bed, unscrew the nut securing the gear and remove it.
The gear needs to be secured so that the timing chain does not fly off, otherwise it will not be so easy to put it in place. Now unscrew the nuts securing the camshaft bed and remove it together with the shaft. After this, you need to remove the plungers (levers) and number them in order so as not to confuse them during installation, unscrew the adjusting bolts and their bushings. You need to pump out the maximum amount of oil from the bushing seat using a regular syringe and clean the wells with a dry, lint-free cloth.
Sources
- https://7vaz.ru/tjuning/gidrokompensator-na-vaz-2107.html
- https://sto-AvtoStroy.ru/avto-lada-drugoe/gidrokompensatory-vaz.html
- https://AutoClub174.ru/lada-drugoe/ustanovka-gidrokompensatorov-na-vaz-2106.html
- https://7road.ru/drugoe/ustanovka-gidrokompensatorov-na-vaz-2107.html
- https://semerkavaz.ru/dvigatel/gidrokompensatory-na-vaz-2107/
- https://MySummerCar.ru/drugoe/ustanovka-gidrokompensatorov-na-vaz-2107-inzhektor.html
- https://soloserv.ru/avto/kak-ustanovit-gidrokompensatory-na-vaz-2107
- https://RoomAvto.ru/novosti/ustanovka-gidrokompensatorov-na-klassiku.html
- https://bumper.guru/klassicheskie-modeli-vaz/grm/grm-2107/gidrokompensatoryi-na-vaz-2107.html
- https://avto-lover.ru/drugoe/gidrokompensatory-na-vaz-2106.html
- https://www.vazdriver.ru/ustanovka_gidrokompensatorov/ustanovka_gidrokompensatorov_na_vaz2107_vaz2106_na_lyuboy_klassicheskiy
[collapse]
Do new hydraulic compensators need to be bled before installation?
We have already talked about the design, operating principle and replacement of hydraulic compensators, but we consider it necessary to revisit this topic and address the question - how to bleed hydraulic compensators? This procedure is considered mandatory and must be performed both after replacing the hydraulic compensators and in the event of their cleaning. Bleeding hydraulic compensators allows you to remove excess air that has entered its cavities. This must be done to ensure unimpeded access of oil to the HA.
Why do hydraulic compensators knock?
To begin with, I would like to note that if the compensators are knocking, this indicates that they are not working correctly, most likely they are out of order, or something is wrong with the engine lubrication.
Actually, the main reason lies in the quality and level of the oil, although there are a lot of mechanical faults.
- Not enough oil. This also happens, it is not pumped effectively into the channels and therefore is not pumped inside the plunger pair, that is, the required pressure is not created inside
- The channels in the cylinder head or the hydraulic compensator itself are clogged. This happens due to untimely oil changes, it burns and deposits form on the walls, which clog the channels; the oil cannot effectively pass into the compensator.
- The plunger pair has failed, often it simply jams
- The plunger ball valve has failed
- Carbon deposits on the outside of the plunger body. He physically does not allow him to rise and compensate for the gaps
Of course, sometimes they knock because there is carbon deposits in the system, then you just need to remove them and wash them, and their performance may be restored. BUT with high mileage, they break (depletion appears) and require replacement.
I want to repeat again - you need to understand that the operation of the hydraulic compensator depends on the quality of the oil and its timely replacement. You need to pour only high-quality synthetics and my advice to you is to change the lubricant a little more often than prescribed, for example, after 15,000 km, change after 10 - 12,000 km. They will last longer.
Now let’s watch a short detailed video.
I’ll end here, sincerely yours, AUTOBLOGGER.
(
41 votes, average: 4.61 out of 5)
Similar news
Timing chain or belt. What is better, which mechanism drive to choose? .
The timing chain knocks (rattles), whether cold or hot. How to determine.
Why does a car drive poorly in hot weather? Details + video version
Manual pumping of hydraulic compensators
This procedure is carried out only when the hydraulic compensators are removed from the engine. To pump, it is necessary to place the hydraulic fluid with the plunger facing up into a container with oil. The oil level should be approximately along the line of the middle cut of the hydraulic fluid. After this, press the HA plunger with your finger. You will notice dirty oil starting to come out through the valve. It is necessary to press the plunger until the oil released from the valve becomes clean.
This process is a quick manual pumping of the HA. There is also the option of pumping a disassembled hydraulic compensator, but this process takes a long time.
In conclusion, let us remind you of one more important detail: after replacing the hydraulic fluid on the engine, it is necessary to change the oil and strictly check its level. If there is not enough oil in the engine, the necessary pressure will not be created in the system, which pumps engine oil through the channels into the main fluid chamber. In this case, the hydraulic compensator will become airy and start knocking again during operation.
Diagnostics and replacement of hydraulic compensators
When one or more main valves fail, a knock similar to a valve valve appears. This sound travels well in metal, so a phonendoscope is used to determine a faulty hydraulic compensator. An analogue of this device can be made independently from a steel rod about 700 mm long and 5-6 mm in diameter. A beer can with the top cut off is attached to one end of the rod, and a wooden handle is attached to its middle. By placing your ear to the can and alternately placing the free end of the “phonendoscope” against the head of the block in the area of each compensator, the faulty one is determined by ear by the increased knocking. The “suspicious” HA should be dismantled and checked.
You can remove the main body from the seat using a magnet. If this fails (the main body is “stuck” or jammed), it is removed with a puller, having first welded a rod with a hook to it. Some hydraulic compensators can be disassembled, which allows you to determine the degree of wear of internal parts. Disassembly should be done with extreme care so as not to damage the surfaces of the mating elements.
The hydraulic supports are disassembled after removing the retaining ring; the internal parts of the hydraulic pusher are “shaken out” by gently tapping its body on a metal surface. The contaminated compensator is washed in acetone or another solvent.
Visual inspection allows you to detect external damage to the end surface of the hydraulic compensator exposed to loads (potholes, scratches or scuffs). During operation, a depression may even form on it.
There is another simple and effective way to monitor the condition of a dismantled main body: after filling with oil, it should not shrink when hand force is applied. Otherwise, it is faulty and must be replaced. An efficient main body, compressed in a clamp, exhibits significant resistance and slightly reduces the length only after 20-30 seconds.
When to change hydraulic compensators: signs
It is important to pay attention to indirect signs of problems with hydraulic compensators. If the oil level and its quality are normal, then the following symptoms indicate faulty oil coolers:
- strong knocking in the valve mechanism when cold;
- after warming up the knocking does not disappear;
- the knocking intensity decreases with increasing engine speed;
- Changing the oil and flushing the oil system does not solve the problem.
You can accurately determine that the Chevrolet Niva hydraulic compensators need to be replaced after removing the camshaft. In such a situation, it is necessary to disassemble the engine, remove compensators, perform troubleshooting or immediately make a complete replacement, etc.
What are the types of hydraulic compensators?
These devices are widely used in timing systems. However, their analogues are also used in chain tensioning, the so-called “ timing chain ”. For this period of time, only 4 designs are used.
- Hydraulic pusher. Often used on modern cars to adjust the gap between the valve and the camshaft
- Hydro support
- Hydraulic support for installation in levers and rocker arms. Mainly used on old timing mechanisms
- Roller hydraulic pusher
All 4 types can be found on various designs, although “hydraulic mounts” were often used earlier in engines. Now everything is more. It’s a little clear about the types, now let’s learn more about how they work.
A little history
Hydraulic compensators have replaced less efficient mechanical regulators of gas distribution mechanisms. As a rule, a regular engine valve, say on a classic VAZ 2105 - 2107 engine, does not have a hydraulic compensator, so it often had to be adjusted, on average after 10,000 kilometers. Valve adjustment on VAZ 2105 - 2107 was done manually, that is, you had to remove the valve cover and set the gaps using a special feeler gauge, which varied in thickness, which means you could choose it for your mileage.
If adjustments are not made, the car engine begins to make noise, dynamic characteristics decrease, and fuel consumption increases. After 40 - 50,000 kilometers, the valves generally should have been changed. That is, mechanical valve adjustment, to put it mildly, has outlived its usefulness, it was necessary to do something, to improve the design, so to speak.
So on front-wheel drive VAZ engines, they began to install mechanical pushers in front of the valve. To exaggerate, a large “cap” was simply put on top of the valve; it has a larger diameter (than the old design), and therefore wear was much reduced, because it is much more difficult to wear out a larger diameter than a small one. But adjustment still remains, of course not every 10,000 kilometers, much less often, but it is still recommended to do it. This usually happened by placing repair “washers” of increased height. Mechanical adjustments are quite effective and are still used by some manufacturers; adjustment with washers is recommended no earlier than 40 - 50,000 kilometers (if we talk about our VAZs); on some foreign cars the pushers last even longer. The big advantages are the simplicity of the design, unpretentiousness (semi-synthetic oils can be poured), as well as the relative cheapness of the design. The disadvantages can be noted that when the “washers” on top were worn out, the engine began to work noisier, the dynamic characteristics dropped and the consumption increased. What was needed was a design that automatically adjusted the gap.
And now, mechanical valve adjustment has been replaced by a completely new technology. Everything is simple here - now you don’t need to adjust the valves manually, hydraulic compensators will do everything for you. They themselves will set the required engine valve clearance, due to which the engine life is increased, power is increased, fuel consumption is reduced, and the mechanism runs for quite a long time - 120 - 150,000 kilometers (with proper maintenance). In general, a step forward.
How to bleed hydraulic compensators
Hydraulic compensators absorb the gaps existing between the working areas of the camshaft, rods and rocker arms, without taking into account the temperature regime and the degree of wear of the components. But sometimes blockages occur inside the parts and in this case they require bleeding. How to bleed hydraulic compensators yourself?
You should take into account that the hydraulic compensator is located between the valve end and the pusher. Remove the cover installed on the engine of the machine, clean the crankcase ventilation valve using a special carbspray.
How to bleed hydraulic compensators
You should also plug the spark plug wells using cleaning material or rags. Next, use a screwdriver to pry off the part located above the hydraulic compensator. Then you should carefully pull it off the hydraulic compensator, without being afraid that this part will fall out of your hands (it can be easily installed back). Pull out the hydraulic compensator using pliers. The device should come out without much difficulty. Try to make a simple device that you will use for pumping. To do this, prepare a syringe, then put a dropper on it. As a cleaning agent, use a product called “SHUMMA”. This substance should be poured into a syringe, after which foam should form, followed by its transformation into liquid. Place the other end of this homemade dropper on the hydraulic compensator, in the place where there is a hole. After which you can start pumping it by simply pressing the syringe so that the cleaning agent (“SHUMMA”) gets into the hydraulic compensator.
How to bleed hydraulic compensators - you can carry out similar manipulations several times and blow them out using carbspray. You need to pay attention that while bleeding the hydraulic compensator, liquid should flow out of the side hole in it. Complete the next step for the purpose of prevention. For this purpose, the hydraulic compensator should be placed in a vessel filled with the special product “SHUMMA”. Leave the device to soak in this position for about one hour, then repeat the bleeding process. When working with these devices, do not forget that hydraulic compensators are non-separable units, so you cannot fill them with oil. That's why you should repeat the bleeding process again, only without SHUMMA, but with oil. Next, place the hydraulic compensator in a small container filled with oil for one hour. When this time has passed, it must be taken out and pumped again.
We advised you how to bleed hydraulic compensators yourself, try it!
How to bleed hydraulic compensators video Did you like the article? Share with your friends on social networks!
Automatic pumping of hydraulic compensators
- It is necessary to start the engine and ensure its operation in the range of 2-3 thousand revolutions, no less, for 4 minutes. After this, the engine should idle for about 30 seconds.
- Then, the engine must be turned off for 1 minute.
- We start the engine again. If the knocking noise disappears, it means that the hydraulic compensators have been pumped and everything is fine. If the knock is still present, the procedure must be repeated about 5 more times. If there are no technical problems with the motor, the knocking of the main engine will disappear.