Alarm on a Priora is a serious issue; everyone is afraid for their car, trying to protect it to the maximum. The Priora is equipped with an alarm system from the factory - an immobilizer (immobilizer). On a Lada Priora car, it allows you to partially protect the car from theft. The immobilizer on the Prior is a factory anti-theft device combined with the car's electrical package, which is located under the center console. Owners immediately try to disable the immobilizer on their Priora, because they consider it archaic and prefer to install a more advanced alarm system on the car instead of the standard anti-theft one. Installing an alarm on a Priora will cost approximately 10,000 -17,000 rubles.
Disabling the immobilizer on a Priora is not easy. The engine is started by an electronic engine control system, which also blocks its operation when the immobilizer is turned on. And already in the electronic control unit of the car, in the place where the EEPROM circuits are stored, the process of data exchange with the immobilizer takes place, and at the ECU level there is a ban or permission to start the engine. You can turn off the alarm on a Priora yourself, but this requires knowledge of electronics and special tools.
What is an immobilizer for?
The immobilizer will allow you to start the engine only if the key is recognized in the ignition switch. This blocking device, by transmitting a signal to the ECU, can block sparking and fuel supply. The immo receives a signal from a key fob with a chip that sends a key recognition signal.
That is, even if an attacker fakes the ignition key itself, but does not fake the key fob, he will not be able to steal the car. An impulse is sent from the key fob chip, and without the key fob, the key is a plug for the ignition switch. Its work with the data of the electronic control unit is carried out in seconds, and during this time the immobilizer manages to determine the authenticity of the chip.
Protection functions and operational reliability
The standard Priora alarm system is not overloaded with additional functions. It does not have access to service options related to auto start, opening the trunk, or searching for a car in a parking lot. It will not inform its owner based on the indication from the key fob about the loss of communication with him. And even more so, it will not send all kinds of SMS messages about various machine malfunctions. Let the owners of Bugatti Veyron and Porsche 918 use GSM communication and GPS navigation services.
It is absolutely not worth using a gas adjustable wrench No. 3 as a torque gauge. The standard Lada car alarms have a different task. They don’t need to amaze the Priora owner’s colleagues with the ergonomics of the control key fob or autostart from a neighboring village. Their advantage is reliability and ease of setup without additional hassle and the involvement of related specialists. In addition, during its operation, the standard alarm system ensures the safety of specific areas of the machine:
- doors of a protected vehicle;
- car hood or trunk door;
- driver's door with lock cylinder;
- voltage at the terminals of the standard battery.
Lada Priora will give a fairly reliable alarm signal and will accompany it with flashes of turn signals when attempting to violate any of the zones protected by the standard alarm system. Such unauthorized access attempts include:
- desire to open any of the car doors, including the trunk or hood;
- turning an untrained key in the ignition lock of the Lada;
- any manipulations with the standard battery related to its connection or disconnection;
- when an additionally configured volume or shock sensor is triggered.
Important: if cases of incorrect operation of the car’s standard alarm system occur, you should first of all check the serviceability of the control key fob.
Operating principle of the immobilizer
The principle of immo operation is that while the engine is turned off, the ignition system is blocked, and when the key is inserted into the lock, it begins its work. One of the main elements of the immobilizer device - the antenna - uses an adapter to recognize the signal from the chip inside the key fob. If there is no key fob with a chip, the immo antenna will not receive the signal and the system will not work. After recognizing the key installed in the ignition switch, a positive signal is sent from the ECU to unlock the ignition system. The anti-theft system is completed within seconds and the vehicle is ready to start.
Causes of immobilizer malfunction
Sometimes the immobilizer of VAZ cars breaks down, and the driver cannot go anywhere in the car. Immo malfunction can occur for a number of reasons:
- Battery completely discharged;
- Technical difficulites;
- Software problems.
The worst way to kill an immo is to completely discharge the battery or simply disconnect the battery from the car's power supply. De-energizing the network will result in a chaotic code being written to the EEPROM circuit in the ECU, all settings will be lost, and the immobilizer will block engine operation.
Technical problems are problems with the boards, immobilizer antenna, or its adapter. The most common failure is a “burnt” board. You can accurately determine which part has failed using the anti-theft device diagnostics. It is important to monitor the immobilizer fuse in the Priora, because it serves as a consumable element in the overall chain. Exactly also a breakdown of electrical equipment can adversely affect the operation of the immobilizer. The problem may occur after replacing the engine or electronic control unit. When replacing the engine, it is worth installing a new ECU and a new immo chip.
Software problems are failures of the code recorded by a specialist. They can occur in EEPROM cells or the alarm key fob chip. If the operation of the ECU chip can be corrected using a computer, adapter and equipment, then the key fob chip will have to be changed. There have been cases of blocking due to interference from smartphones and other mobile devices.
Installation of hydraulic mounts on the VAZ 2106 2105 2107 2103 engine
My personal experience with installing hydraulic supports is described here. This resource cannot be used as a guide to action when installing hydraulic supports. When repeating such a procedure, you do everything at your own peril and risk.
December 2005
Having driven tens of thousands of kilometers on the Niva 21214, you get used to the quiet rumbling of the engine, so I wanted to install hydraulic compensators (hydraulic valve mounts) on the classics. Only hydraulic supports were installed; the hydraulic tensioner was not installed. Tensioning the chain once or twice a year is not a big problem. I recommend reading about the State Scientific Center in Niva-FAQ
To begin with, it should be recalled that there are hydraulic valve mounts and hydraulic chain tensioners manufactured by , as well as hydraulic valve mounts and a hydraulic tensioner standard for the 21214 engine (used on the VAZ 21214-20 and Chevy Niva). Initially, only Hermes products were known; with the spread of injection engines 21214, spare parts for them began to be produced.
The question is raised on the forums: is it necessary to install RV 21214? I found the answer on the website behind the wheel, but now the site has been redone and the link is not working, here is an excerpt from there: Does VAZ allow the installation of hydraulic valve thermal clearance compensators and a hydraulic chain tensioner produced by VAZ-2103 and 2106 engines?
The hydraulic chain tensioner produced by Hermes was not tested at VAZ. Hydraulic compensators or, in VAZ terminology, hydraulic supports of valve levers were tested at VAZ in 1992 and received the conclusion: “cannot be used on engines of the VAZ-2101 family during the warranty period.” The main reason at that time was unsatisfactory reliability. Later, in relation to hydraulic mounts from any manufacturer, it was revealed that the installation of such supports in combination with a camshaft not adapted to them leads to an unfavorable change in valve timing, causing: an increase in the speed of the valve seating, which negatively affects the reliability of the valves; an increase in fuel consumption at partial loads ; deterioration of exhaust gas toxicity indicators. Currently, VAZ-21214 engines use hydraulic mounts produced by YAZTA (Yaroslavl) in combination with the original camshaft 21214
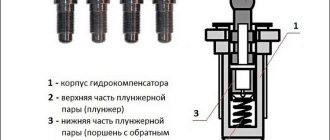
In order to forget about adjusting the valves (there is a micrometer with a rack, but I want something even better), I bought hydraulic mounts 21214 and an oil ramp from the Nivovsky store. The purchase price was 2875 ($100, December 2005) for 8 hydraulic mounts and an oil ramp. I bought the camshaft assembly and gear 21213 on the market at Energetikov a little earlier for 1500. For complete happiness, I bought a 21 head, a new valve cover gasket (30 rubles), a camshaft gear lock washer (5 rubles). For good loosening of the existing supports I used a 21 head , with the surface ground off from the end using a grinding machine (to cut off the chamfer of the head). The lever for turning the head is about 30 cm, there were no problems with turning it off. Next, the rocker springs and plates that were clamped by the supports are dismantled. Oil is sucked out from the wells under the supports using a syringe. Next, a ramp is installed and hydraulic supports are screwed into it. At this stage I took a photo:
After assembly:
tightening torque of hydraulic compensators on a Chevrolet Niva: The hydraulic supports are tightened with a torque of 2.1-3.0 kg (read in the VAZ manual), using a 24mm socket and a torque wrench!
Otherwise, the silumin housing of the oil supply ring can be crushed, and the possibility of jamming of the plunger in the hydraulic mount depends on the tightening torque, that is, the possibility of normal operation of the hydraulic mount, so on the Internet you can find recommendations to pull the hydraulic mount with a torque of 1.8-2.0 kg.
I bought RV 21214 assembled, but on the bearing housing I was confused by the number 2101-….. According to the catalog it should start with 21214. However, the middle support of the camshaft housing is lower than the rest, made for the oil sampling ring of the oil frame. Regarding this, I came across an excerpt on the Chevy forum, namely “15) Camshaft 21214 assembly.
The worst option is self-assembly with the Rostov bed. The best price-quality ratio IS STK. If you are offered a device without packaging, know that it is self-assembled (does not mean it’s bad, but it’s better to look for it in a package with a GCZCH sticker. I can assure you that the camshaft 21214 itself has not yet been counterfeited. Its body (bed) is another matter." Later in the Nivovsky store I asked why the bed came with the marking 2101, the seller replied, “Who will redo the casting mold to change the inscription?”
The question also arises whether to fill the oil line before assembly. I have not heard such a recommendation, incl. I didn’t read it in the Nivovskaya Murzilka either. In the Nivov book, when replacing hydraulic mounts, the following actions are noted: unscrew the hydraulic mounts, remove the oil from the wells with a syringe, the oil ramp is disassembled into parts, washed with gasoline and blown with compressed air, the seals in the ramp are replaced with new ones, and after lubricating with oil, the ramp is carefully assembled so as not to damage the seals.
Well, okay, the main result is this: I didn’t want to start right away, I had to remove the choke all the way. After starting, one valve rattled a little for about 30 seconds and then there was silence.
Results: negative: - decreased
idle, about 70 rpm - idle became a little less stable
positive: the engine cannot be heard. The loudest sound in the car is the sound of the heater fan and the noise of the tires. Just a thrill, a pleasure to drive! I didn’t feel any impact on the dynamics, I’ll say that it hasn’t changed and it definitely hasn’t gotten worse.