The engine force, which is converted into the gearbox, is transmitted to the drive axles of the Chevrolet Niva not directly, but through the transfer case. It performs several functions:
- Distributes torque between axles, allowing them to rotate at different speeds.
- If necessary, it blocks the center differential, preventing wheel slipping.
- Allows you to change the gear ratio, increasing torque.
This key transmission element ensures high maneuverability on difficult road sections.
When to use low gear
How to use the transfer case on a Chevrolet Niva is a question that many owners of this car ask.
The Chevrolet Niva is a popular Russian SUV not only among extreme driving enthusiasts, but also for those who use the car for personal purposes. Everyone knows that the car is equipped with a transfer case, which is responsible for engaging the lock and downshift. It is worth noting that all this can be done even simultaneously and this is done using one lever. So, in order to use a lower gear, you need to shift the lever first to the right and then up, but of course, in order to engage in a higher gear, you just need to shift the lever back.
Note that the transfer case can be used to engage neutral gear, which will prevent the car from moving. You can engage the lock both in high gear and in low gear; to do this, you just need to switch the lever to the left.
There is a diagram on the shift lever. To engage a downshift, you need to move the lever to the right, up. To lock the differential, pull it all the way to the left. There are also Latin letters on the lever. So, L is a low gear, N is neutral, and H is high.
By switching the operating modes of the transfer case, you can adjust the behavior of the car in accordance with road conditions.
Low gear is used in two cases:
- It is necessary to ensure low speed. For example, if you need to drive onto a curb or other obstacle, you can engage a lower gear so as not to burn the clutch.
- Need high torque. A lower gear is engaged before overcoming steep inclines.
The differential lock is activated when driving off-road, where there is a high risk of slipping.
At the same time, it must be turned on before entering a difficult area.
In general, you need to use the transfer case like this:
- Driving on the highway. The differential is unlocked, the first speed of the RK is turned on.
- Overcoming climbs and obstacles on hard surfaces. The differential is unlocked and the reduced speed is engaged.
- Overcoming difficult snowy areas, mud, slippery climbs. Locking and reduced speed enabled.
For what purpose is a transfer case even needed, when does it make sense to engage the locking and downshift? Such seemingly simple, but at the same time serious questions will become clear when considering the following example. When driving on a country road on a hard surface, fourth gear is engaged. Suddenly, a large puddle with a soft, unreliable surface appears in front of the car.
It is worth noting that in order to engage a lower gear on a Niva Chevrolet, you need to stop - this is how the car’s differential is designed. But you don’t need to stop at all to turn the lock on and off. But is it worth using such additional and, without a doubt, useful functions of the machine often? Experienced drivers recommend using them in places where the dirt is not located on level ground, but with various potholes and the like.
Thus, the low gear of the Chevrolet transfer case is designed for comfortable off-road driving and overcoming various obstacles. In such a gear you need to drive slowly, you cannot accelerate sharply, because at this moment the wheels will receive a large load, as a result of which a real hole can form, from which it will be very difficult for the car to get out.
With this driving style, the motorist will better feel the movement of the wheels, as a result of which, when they “bury”, as evidenced by the chaotic movement of the car, it will be possible to immediately do something after overcoming the obstacle. Most often, this is done by changing the trajectory of the car.
It is also worth noting that when driving through sticky mud or deep puddles, you should never suddenly engage second downshift. At the same time, the torque increases, as a result of which the car can simply “choke”, stalling at the most inopportune moment.
Eliminate vibration with additional fasteners
Vibration in the body is the main “disease” of the Niva; it often occurs due to improper alignment of the transfer case. Most often, vibration occurs on VAZ 21213/21214 cars, since the transfer case is mounted only on two supports on the sides of the body; on the Chevrolet Niva, the transfer case is already installed on three supports.
- driveshafts are poorly secured;
- wheels are not balanced;
- there is play in the cardan crosspieces (vibration is especially affected by play in the rear driveshaft crosspieces);
- The vibration comes from the engine itself.
Vibration when starting off on a Niva can also occur for the following reasons:
- the mounting supports of the transfer case have become loose;
- The rubber on the RK supports themselves broke.
Installing the third support of the transfer case on VAZ 21213/21214 vehicles allows you to reduce the level of vibration of the transfer case; with this support it is easier to center the transfer case. The part can be purchased at auto stores or made yourself. The finished product comes with three long studs (for model 2121); to install the third support on this machine, you will need to unscrew the short studs from the transfer case housing and install new studs from the kit. We carry out repairs as follows:
- dismantle the front passenger seat in the cabin;
- remove the floor tunnel lining;
- in the cabin we move aside the carpet covering the body amplifier (in front of the handbrake lever);
- remove the transfer case (alternatively, you can simply hang it up, but removing the third support makes it easier to install);
- We attach the bracket of the new support to the body of the RC;
- we install the transfer case in place, center it in the optimal position, and fasten the side supports;
- we combine the third support with the body, drill two holes in the bottom;
- Using washers, bolts and nuts (from the kit) we attach the support to the bottom of the body.
Vibration is eliminated more effectively by installing a subframe under the transfer case. You can also make such a device yourself or buy a finished product at a car store.
In order to install the subframe, the transfer case must be removed. It is more convenient to carry out such work in a pit; we carry out repairs as follows:
- leave the car in neutral gear;
- disconnect the propeller shaft from the transfer case, it is advisable to mark the driveshaft flange and the drive shaft so that during installation, align the driveshaft according to the marks - this way, the occurrence of unnecessary vibrations is eliminated;
- dismantle the muffler mounting bracket;
- remove the gearbox traverse;
- jack up the transfer case, remove the side fastenings of the transfer case;
- We treat the places where the subframe fits to the body with Movil;
- place the subframe on the gearbox studs;
- we mark the attachment points of the subframe on the side members, drill holes, attach bolts to the body;
- we tighten all fastenings, except for the transfer case supports themselves;
- we perform alignment of the steering wheel;
- Finally tighten the transfer case supports.
It should be noted that installing an additional support or subframe on the steering wheel does not always lead to the desired effect; in some cases, vibration only increases.
Forced unlock
Sometimes it happens that the lock gets stuck - it cannot be turned off even when the car is completely stopped. The situation is quite common for the Chevrolet Niva. How to solve it? There is a sure way. To do this, engage reverse gear, accelerate a little and turn off the differential lock while driving.
What to do in such a situation? It is necessary to turn on the first speed and try to turn off the unit again. Moving back and forth will solve the problem of a stuck differential. In general, it is recommended to turn on the center lock only in serious off-road conditions. At the intersection of dirt roads and sand dunes, a downshift is sufficient.
How to change gears and transfer case Niva VAZ 21213, 21214, 2131 lada 4×4
(see also on this topic Driving a car and What is all-wheel drive, as well as Niva driving techniques)
TRANSFER CASE SHIFTING
Transfer case levers and their positions
The gear shift lever in the transfer case can occupy the following positions:
H - low gear;
N - neutral position;
B - top gear.
The differential lock lever in the transfer case can occupy the following positions:
P - differential unlocked;
B - differential is locked. When the lever is moved to this position, a warning light comes on in the instrument cluster, warning that the differential is locked.
NOTE Shifting from low to high gears and locking the differential can be done while driving with the clutch disengaged.
It is recommended to engage low gear in the transfer case after the vehicle has come to a complete stop and with the engine disconnected from the transmission.
To overcome difficult sections of the road, block the differential in advance. Do not lock the differential when the car's wheels are slipping. After overcoming such sections, unlock the differential - driving the car on good roads with a locked differential shortens the life of the power transmission mechanisms, increases tire wear and fuel consumption, and when braking the car can lead to skidding.
SHIFTING TRANSMISSION GEARS
Gear shift diagram (also printed on the handle)
Before driving, check the position of the transfer case levers - it must correspond to the road conditions. Start driving in first gear and, as the crankshaft speed increases, move to higher gears in a timely manner.
In time and in accordance with the road situation, change to a lower gear in the gearbox, avoiding overloading the engine.
To move in reverse, press the gear shift lever, pushing it all the way down and move it to the position corresponding to engaging reverse gear. Engage reverse gear only when the car is completely stopped.
Video
lada-niva.ru
When to downshift?
How to use the transfer case on a Chevrolet Niva, why and when to turn on low and lock? This seems like a trivial but serious question. It's simple. Just imagine, you are driving along a country road in fourth gear - the road is wonderful, but then a deep puddle appears in front of you, where, naturally, the road surface is soft and the car will sink. To do this, you need to stop and engage a lower gear. You are not mistaken, but you really need to stop.
The whole reason is that there is a center differential that simply will not allow you to switch from high to low and back. Why do you need a downshift at all?
Just imagine - you need to drive along a soft or heavily polluted section of the road. For example, you are driving in second gear and begin to feel that the car is heavy and something is slowing it down, you switch to first, but it is still hard for it, that’s what a lower gear is for.
The first downshift is like half the first upshift, that is, if you shift to the second downshift, you get the first upshift.
As a rule, low gear is designed for off-road use. When the low gear is on, you need to drive and it is advisable not to accelerate sharply, because at this moment the wheels receive a large load and can make a fatal hole that will not allow you to move further.
In this case, the car allows you to feel the movement of the wheels and if they start to dig in, you will immediately understand it by the chaotic movement. In this case, if you notice in time that the car is starting to slip, you can do something to avoid an ambush, for example, change the trajectory.
Also interesting: LADA Niva Travel – Technical characteristics – Simferopol-Lada: LADA dealer in Simferopol (Republic of Crimea)
It is worth paying attention to the fact that if you are driving through deep puddles or sticky mud, then in no case should you sharply switch to the second lower gear, since the car may simply “choke” when the torque increases, which means it will become difficult for it and it will simply stall at the most inopportune moment.
If you are driving, for example, in third gear and feel that the car is becoming heavy, then you should immediately switch to second or even first, so as not to stall in the most dangerous place.
Operating a vehicle in different modes
A lower gear is engaged when it is necessary to increase torque. An example would be driving up a steep slope or driving through sticky ground. To overcome difficult areas, the lock is activated. To achieve a clearer and more fixed engagement, you need to wait for the moment of slipping, and then, with the clutch disengaged, move the lever to the left. While locked, you can only travel a limited distance at a speed of no more than 40 km/h.
When to use and how to disable blocking
It is preferable to enable forced blocking in various modifications of the Niva in the following situations:
- The blocking must be turned on in advance if you have to overcome a difficult route.
- On sharp climbs uphill or when driving downhill.
- While crossing terrain with a top layer of sand.
- When you have to drive on snow drifts or an icy road.
Wheel locking is not necessary when driving quietly on a flat road within the city. Grip on asphalt surfaces will be decent, and traction will be distributed evenly by default.
What is the purpose of blocking?
This mechanism contains shafts and gears. The differential is intended to distribute torque from the engine to the wheels. In Niva, the main driving wheels are the rear ones. With the help of a differential, the wheels can spin at different speeds , for example, when cornering. In this case, one wheel travels a small radius, and the other – a large one. If there were no differential, the wheels would begin to slip, which would cause increased tire wear.
When driving on a straight road, the thrust from the engine is distributed evenly between the wheels. If one wheel starts to slip, for example on ice, then the differential transfers more force from the engine to it. This mechanism is mainly installed on the drive axle. Niva has it at:
- Rear and front axles.
Video about how the cross-axle differential lock works on a Niva Chevrolet
A few words about the Chevrolet Niva transfer case
I think it’s time to talk about the transfer case of the Chevy Niva, because those who just bought this car, at the very beginning of use, do not really know how to use the transfer case, what the rules are, and in general, when to lower the gear and when to lock it. Let's figure it out now. It’s a pity, of course, that I didn’t record a video on today’s drive along a fairly washed-out road. Well, never mind, I’ll record it and show it clearly on video. For now, in words.
In general, the transfer case switches to a lower gear, as well as to lock, and it is possible and even necessary to do this at the same time. It’s convenient on the Shevik - this is done with one lever.
Turn it down - right up. Add lock - Pull the lever all the way to the left. Look at the switch handle, it's written there. Letter designation - L(low) - low, N - neutral, H(high) - high, that is, normal.
Well, now we’ll figure out when it’s better to turn it down, and when to also lock it. And how to do it correctly.
It looks something like this - we are driving across the field in normal second/third gear. Suddenly there is a terrible puddle ahead. We stop and turn down the car.
You may ask - how long does it take to turn on the blocking and then turn it off? There is another nuance here - very often, many owners of the Chevrolet Niva have a problem with the blocking - it does not turn off. It just jams and that’s it, you have to drive on the highway with the blockage. This, you understand, is very harmful for the machine and in such cases you must turn it off.
In bright sunny weather it is sometimes difficult to see. Be careful. Well, about turning off the center wheel - I managed to turn it off just when reversing. Needless to say, now I turn it on only in the most dire cases. In the rest of the others, lower gears are quite enough for me.
Just today I went to the lake to check if the ice had melted. The road was washed out, the snow had already melted and turned into liquid mud, and it’s not safe to drive through such mud on my AT tires. It feels like it’s being dragged in all directions, but the most important thing is that I’m driving, I don’t get stuck, and sometimes the ruts were almost to the very bottom; when you shuffle, it always becomes unpleasant)) After some short drives, the car looked “military-like” - all covered in mud , went to the city - people look around))
And here’s another observation of mine: it’s better to drive through mud slowly but surely. This applies to lower gears - if the mud is serious, then I always drive in first, pushing hard, trying to feel the wheels spinning in the mud. If you accelerate a little, you can immediately “burrow”, this is the case when there is no hard covering under the liquid mud.
Well, a lot, of course, depends on the tires. Sometimes, if the tires are toothy, it is useful to accelerate so that the tread cleans itself. For Nivka and Shevik I highly recommend Cordiant Offroad tires, and if you have a little more money, then imported ones - Kumho and of course Hankuk Dinapro MT. Imported tires are more comfortable and are better for driving on the highway because they are soft. Well, in terms of cross-country ability, everything is also very cool here - after all, the tires are a Mud Terrain class, which means they are simply designed for mud.
When you turn on the second lower gear, the car accelerates, but if you get into a mud hole, there is a risk that the engine will “choke” (it is very difficult to spin the wheels in the second gear when stuck) and you will stall. Needless to say, stalling in a deep puddle can be dangerous. Therefore, if you decide to overcome a puddle or muddy area with acceleration (very often this makes sense), then be prepared in the middle, if you suddenly start to fall through, immediately switch from 2 to 1 low, so as not to stall.
All this knowledge - when to go in first and when in second, when to turn on the lock and when not necessary - all this comes with experience. You’ll ride in the mud and you’ll already begin to understand that it’s better to take the puddle over there with acceleration without locking, and that clay hill with potholes - only at 1 lower gear and with the locking on. Think with your head first, and don’t rely on the car to pull it out. The Chevrolet Niva is an excellent car, if you don’t be stupid.
I remember when we were making our way to an abandoned village, we got to one really dangerous place, and there was a UAZ standing there and didn’t dare to drive through. We scouted around and decided that we would pass. And we drove by, leisurely, pushing hard, without particularly accelerating.
Therefore, one more rule (which I always adhere to) - if the place is dangerous, there is a risk of getting stuck, then get out of the car, poke it with a branch, find out the depth of the puddle, rut, feel for a solid place where you can drive. This is the job of the navigator, so let your partner get out of the car and don’t be lazy. Spend 5 minutes on reconnaissance so that you don’t have to spend several hours later getting out of an ambush.
Why enable blocking?
An SUV is a car that is not afraid of difficulties. Chevy Niva is an all-wheel drive car. The presence of a lock allows it to become an even more powerful and reliable off-road friend. When you turn on the lock, those wheels that are easier to work with work.
When you turn on the lock
As a rule, both axles work at 50%, that is, one wheel on the front axle and one on the rear axle work.
For example, the question of how to use the transfer case on a Chevrolet Niva is relevant when your car begins to slip even when the lock is turned off. In this case, those wheels that are stuck are slipping and as a result they get buried even more. When the lock is turned on, those wheels that have not skidded begin to work and thereby pull the car out of the mud or ice surface.
Rules for applying blocking on Niva
To ensure that the locking mechanism lasts for a long time, use the following rules:
- It is necessary to switch the transfer case when the Niva does not move.
- The differential can also be engaged while the vehicle is moving.
- To ensure efficient and long-term operation of the device, it is advisable for the Niva driver to turn on the lock from time to time. Once a week in winter is enough.
And also interesting: Niva transfer case: howl, vibration, hum » PERMANENTLY getting rid of extraneous sounds
Where is the lever responsible for switching located? Pay attention to the area between the wings located in front, there are 2 levers there. One makes it possible to change gears at the gearbox, the other successfully controls the transfer case.
The basis of the transfer case is a gearbox, which includes 2 stages. The control lever comes directly from it, you can move it forward and backward - this is how the gear is changed on the Niva. The direction of movement of the lever to the left and right allows you to activate the differential lock and vice versa to disable it.
Step-by-step instructions for removing the manual transmission and gearbox on a Niva Chevrolet
- And so, first of all, we disconnect the negative terminal from the battery.
- Next we will need to disassemble the center console. I will not explain in detail how this is done, if you cannot do this yourself, then it is better for you not to continue working, but to turn to specialized services.
- We remove it and bring it to this form:
- Unscrew the exhaust pipe from the manifold and disconnect the upper oxygen sensor.
- After we have done this, we lift the car on a lift to make it more convenient for us to work. If this is not possible, then you can work from the pit.
- Next, drain the transmission oil from the gearbox and transfer case, as well as from the rear and front gearboxes.
- Here we see our transfer case, it’s all covered in oil.
- Photo of the gearbox, also covered in oil.
- Next comes a very important point: the drain plugs are all magnetized and after we unscrew them, we carefully inspect them for the presence of foreign particles.
- In our case, there are metal particles on the transfer case plug and on the rear gearbox plug. This means that there is something that has fallen apart and we continue to disassemble the car.
- Next, you need to disassemble the following parts: rear cardan, front cardan, unscrew the rubber couplings on the intermediate cardan.
- Now we remove the sensors from the gearbox and transfer case.
- We disconnect the bracket going from the gearbox to the exhaust pipe and the upper front shield going above the exhaust pipe.
- We place the transmission jack under the transfer case and unscrew the supports on one side and the other.
- Unscrew this bolt on the engine mount.
- We lower the transfer case, and now we can easily remove the intermediate cardan.
- We disconnect two terminals from the transfer case. And we let her go calmly.
- Now we can remove the intermediate shaft from the transmission. Remove the sealing ring from it.
- Next, remove the clutch slave cylinder, starter and move it to the side.
- Now unscrew the two bolts from the side of the casing.
- Then there are two bolts on the left side, one is located behind the tab of the second on the right side.
- Next we need to unscrew the rear bracket holding the gearbox.
- Now lower the gearbox and remove it.
- It is recommended to immediately check the clutch disc together with the basket.
Razdatka, "Niva-Chevrolet": technical features of the device
For hunting and fishing, the Niva is an indispensable car. It is famous for its maneuverability and simple design. Of course, over the years the model has become significantly outdated. But there is an option to buy a Chevrolet Niva. This is a more modernized car with a pleasant appearance and no less good off-road performance. What is the secret of cross-country ability? It's simple - a transfer case is installed on a Chevrolet Niva. Its structure, principle and modes of operation are discussed further in our article.
| Type | Mechanics |
| Number of gears | 4 |
| For drive | front |
| Engine capacity | up to 1.6 liters |
| Torque | up to 116 Nm |
| What kind of oil to pour | Lukoil TM-5 80W-90 |
| Lubricant volume | 1.35 liters |
| Change of oil | once every 50,000 km |
| Replacing the filter | every 50,000 km |
| Approximate resource | 150,000 km |
Transfer case purpose
If you create a permanent all-wheel drive in a car and provide constant torque on the driveshafts of the rear and front axles, then such equipment is capable of overcoming obstacles such as off-road, but no more. However, the car will not be suitable for driving on the highway at relatively high speeds.
- There will be an excessive load on the parts that distribute the moment along the axes.
- Fuel consumption will increase.
- There will be a rubber eating effect.
The transfer case on a Chevrolet Niva car performs two functions at once. It ensures the distribution of torque along the axes with the possibility of supplying it to both axles simultaneously.
The transfer case also converts torque, increasing it by lowering the speed in gear. Here, transmission means a pair of gears that are in mesh and have a certain gear ratio. These two functions can be performed together or separately.
Varieties
There are several types of these elements:
- Equipped with coaxial drive shafts. This type is used on many SUVs. It gained such popularity due to the use of a single main gear for both axles.
- With a misaligned driven shaft. There is no intermediate shaft here. The advantages of this system are high efficiency and noiselessness. Also, this box has a low curb weight.
- With drive axle drive blocking. It is also installed on the Chevrolet Niva. Here it is possible to use all the torque without slipping the wheels, which is very important when driving off-road. The front axle engages only on difficult sections of the road. On asphalt surfaces, the SUV has a single-wheel drive (only the rear axle works). This allows you to reduce fuel consumption and, if necessary, increase cross-country ability (when the drive “closes”). There is also an interaxle forced locking.
The design of the car provides for the presence of a transfer case, similar to the unit that is installed on the VAZ 2121. In this case, the so-called small-module RK with single-row or double-row bearings are used.
About 1000 copies of the Chevrolet Niva modification FAM-1. They were equipped with gearboxes from Suzuki Grand Vitara combined with a transfer case.
How to use a transfer case in a field, box design
The relatively complex scheme for distributing torque from the internal combustion engine to the wheels is explained by the universal purpose of the Niva 2121 - if used correctly, it can be used comfortably in the city and along muddy country roads. Such properties are ensured by the presence of a transfer case with a center differential lock, complementing a 4- or 5-speed manual transmission, depending on the year of manufacture. The lever located closer to the dashboard is responsible for turning off/on the center differential, the second “small” lever controls the range multiplier and has 3 positions: high and low rows, as well as neutral.
Why is downshift needed?
It is difficult to imagine a transfer case without the main functional component - a reduction gearbox. Positioning the lever in the rear direction reduces the transfer case value to 1.2.
By fixing the lever at the front, the gear ratio can be increased to 2.1. The lever in neutral indicates gear ratio 0.
To use the lock installed on the Niva effectively, use the following recommendations from experts:
- When driving on good quality road surfaces, install the front transfer handle at the front and the rear at the rear.
- The front handle is moved back if the road becomes slippery. Once the slippery area has been passed, switch the levers to normal mode.
- If the Niva is stopped, the lock may not engage when the clutch is depressed. This occurs due to the alignment of the teeth with the gear teeth. What should you do in this case? Moving as if on a turn, engage the lock. The differential will turn and the gear teeth will come closer to the teeth. If turning off is difficult, do it while the vehicle is moving, maintaining a minimum speed and squeezing the clutch.
Tips for owners
To make driving your car comfortable, read some important points:
- The usual, standard arrangement of the front and rear handles is forward and backward, respectively. Movement in this mode can and should be carried out in areas characterized by even and smooth surfaces.
- Locking the differential by switching the front handle to the rear position is best on roads characterized by increased slipperiness. This measure will give Niva stability. It is worth understanding that after overcoming the problem area, the handle will need to be returned to its original position.
- As noted earlier, downshift should be activated before a potential obstacle, but not while the car is already stuck.
- It is worth understanding that activating the lock when the vehicle is stationary is sometimes impossible, even if the clutch is depressed. This may be caused by the clutch teeth hitting the gear teeth. In this case, you can try to activate the lock by starting to drive slowly and make a slight turn. If problems arise with disabling the lock, it is recommended to perform the same procedure with the clutch depressed and the steering wheel slightly rocked.
Also interesting: Niva pickup: technical specifications and tuning for model 2329
Enabling the differential lock
On the Chevrolet Niva it is possible to turn on all three differentials at the same time
. Thanks to this, the vehicle’s cross-country ability increases several times when driving off-road.
As already mentioned, the differential assembly consists of shafts and gears. With their help, the traction force is automatically distributed between the drive wheels. The differential is locked using a blocker (clutch)
. In this case, when the driver turns on the forced locking, the wheels “become” connected to each other. This helps ensure that they rotate evenly.
Differential assembly
If the center lock is forcibly engaged, then the front ones are also rigidly connected at once, which guarantees an even distribution of traction to all four wheels. Thus, the vehicle’s cross-country ability will be increased several times.
, which makes the Chevrolet Niva a real SUV.
How to turn on all-wheel drive on a Niva
The Niva has permanent all-wheel drive. What does this mean? What the Niva all-wheel drive scheme means is that it always works - all four wheels constantly receive rotational energy from the engine through the cardans and differentials.
The information that on a Chevrolet Niva and Niva 4x4 you can turn off and turn on all-wheel drive with a lever is a very common myth . This version is sometimes voiced even by managers of Lada dealers - supposedly the transfer case lever connects the front axle, connecting all-wheel drive. In fact, the Niva has permanent all-wheel drive, not plug-in one!
The most common argument in favor of the wrong theory is why, with the transfer case turned off, if you hang one wheel on the Niva, the car will not move? For example, in this video they talk about the “floating” and unstable all-wheel drive of the Niva.
Whether the Niva has permanent or non-permanent all-wheel drive (see from time mark 2.40)
The answer is simple - because this car, in both generations, uses free, non-locking differentials. How it works - read the corresponding material. Therefore, when the wheel is suspended, all the engine power is spent on its rotation, and the other three wheels practically do not rotate.
Why then does turning on the transfer case lever help when off-road? Is it because it “turns on” the Niva’s all-wheel drive? No, this lever locks the center differential. As a result, the engine power is not sent to the wheel that spins the easiest (in accordance with the principles of the differential), but is distributed equally between the axles. And one of the axles is able to pull the car out.
By the way, if a Niva has a wheel stuck/slipped on each axle, the car will not be able to get out of this situation. In this case, only blocking each of the wheel differentials would help, but this car does not have it. Although such a device can be installed additionally.
Therefore, there is no need to ask the question “how to turn on all-wheel drive on a Chevrolet Niva, Niva 2121 or 4x4, because it is already turned on. But you need to use the locking capabilities of the center differential. Let's look at how further.
Gear Modes
Let's take a closer look at how to use the transfer case on a Chevrolet Niva. It serves to switch to a lower gear and also blocks the center differential; this can be done at the same time. In order to engage a lower gear, you need to shift the lever to the right and up; to lock the lever, you need to pull it to the left all the way. The handle has the following designation:
- Low(L) - decrease;
- N-neutral;
- High(H) - normal, increased.
You can switch the transfer case from low to high while driving. To do this, you need to squeeze the clutch twice.
Low gear is engaged at a speed of no more than 5 kilometers per hour, or after a complete stop. In order to overcome a steep climb, or when driving where there is soft ground, so that the vehicle speed is minimal and at the same time stable, a lower gear must be engaged in advance. For example, if you are driving on a flat road in second or third gear, and a bad section of road appears in front of you, you need to stop and shift to a lower gear.
It is not recommended to turn on the center differential at high speed, since the car may skid strongly at the moment of switching. It is advisable to block where there is a slippery surface and the wheels begin to slip.
These include:
- Switching the transfer case should only be done when the car is not moving.
- You can also engage the differential while the vehicle is moving.
- You can switch to a lower gear while the car is moving.
- To ensure long-term and uninterrupted operation of the differential, it is necessary to periodically turn it on, especially in winter. This should be done once every 7 days.
Also interesting: Chevrolet Niva instrument cluster tuning
Among domestic car enthusiasts, the Chevrolet Niva is a fairly popular SUV that appeals not only to fans of extreme driving, but also to fans of measured driving outside the city. Many people know that one of the features of a car of this brand is the presence of a transfer case in it.
Using this unit, you can enable downshifting, locking, or two functions at the same time, depending on the conditions. The question of how the Niva Chevrolet transfer case should be used correctly is of interest to many happy owners of such a vehicle and those who only intend to purchase it.
It should be immediately noted that you can engage both the lock and the transmission at the same time using the Chevrolet lever that changes gears. So, the lever shifts to the right, and then immediately up to engage a lower gear. To switch back to higher, the lever should simply be moved back.
Using a Niva Chevrolet transfer case, in addition to the above, neutral gear is also engaged, while the car will remain reliably in one place. The lock can be engaged at any time - in normal gear, in low gear - just switch the Chevrolet lever to the left.
This mechanism can operate in five modes:
- Neutral is on.
- The differential is unlocked when the "lowering" is turned off. In this case, the torque is distributed in a ratio of one to two.
- The differential is locked when overdrive is engaged. Here, torque distribution is carried out automatically, depending on the quality of wheel grip on the road.
- Downshift is engaged and the differential lock is disabled. The transfer of forces occurs in the same ratio as in the first case.
- The differential is locked and the gearbox is engaged. In this case, all axles are rigidly locked together, including the axle shafts. Torque is produced unevenly, depending on the type of road surface (dirt, sand, etc.). In this mode of operation, the best cross-country ability of the vehicle is achieved. But driving with a constantly engaged downshift and with locks will not work. This increases the load on the transfer case bearings. The Chevrolet Niva will soon require serious intervention in the transmission. Fuel consumption also increases significantly, which greatly eats up the tires.
Differential
In the absence of a differential mechanism, this would cause detrimental consequences, such as wear and damage, because the result would be the following: when turning, one wheel would be in a slip state, and the second would simply rub against the road surface. The design features of the Niva transmission provide for the presence of 3 differentials. They are located in each of the bridges and in the transfer mechanism.
When the car moves on a flat road and in a straight line with differentials, the traction force is divided equally between all 4 wheels. If there is insufficient adhesion of the wheels to the surface or slipping occurs, the differentials will redistribute the load on the slipping and sliding wheel so that the first receives more force, and the second, accordingly, less.
We have already mentioned UAZ. Despite many similarities, it should be understood that the VAZ’s all-wheel drive is made in the “pat-time” style. This means that when connected, the axes are firmly connected to each other, and rotation occurs at the same speeds. This device imposes some restrictions on the use of all-wheel drive - it can only be used in cases where road conditions allow slipping. In cases with hard asphalt roads and highways, it is recommended to switch the car to single-drive mode.
Sometimes you can come across a misconception about why a small handle is needed next to the shift lever on a Niva. Some car owners believe that it is needed to connect front-wheel drive. However, the front-wheel drive of this car is permanently connected. As is the rear one. Cars of the Niva family have permanent all-wheel drive. The handle actually serves to switch the operating modes of the differential of the transfer mechanism.
In the “forward” position, the differential operates as usual, but if you move it back, the differential is locked, and the forces from the motor are applied to the differentials of the axles, which makes the drive more rigid. It is worth noting that there are also special types of locks for front and rear axles.
Niva Chevrolet transfer case control: device, how to turn it on and off?
The engine force, which is converted into the gearbox, is transmitted to the drive axles of the Chevrolet Niva not directly, but through the transfer case. It performs several functions:
- Distributes torque between axles, allowing them to rotate at different speeds.
- If necessary, it blocks the center differential, preventing wheel slipping.
- Allows you to change the gear ratio, increasing torque.
This key transmission element ensures high maneuverability on difficult road sections.
The Niva 2121 transfer case has manual control with a lever-type mechanical drive. The shift lever swings in the longitudinal direction and is performed on an axis that is installed in the bracket eyes in front of the transfer case. Friction is reduced by pressed plastic bushings into the holes of the lever.
The lower part of the lever is inserted into a groove on the rod, and fixation occurs using a figured spring. The other end of the rod, in turn, is connected to a fork, which moves the shift clutch. The rigidity of this connection is ensured by the bolt. The rod at the outlet of the transfer case is sealed with an oil seal, and dirt and dust are protected with a rubber corrugation. The entire switching drive is fixed in the set position by a spring-loaded ball that fits into special grooves in the rod.
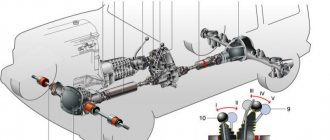
Design and principle of operation of the Niva 2121 transfer case
The transfer case mechanism includes more than 60 independent parts, which is confirmed by the presented drawing. Therefore, it is quite prudent to name the main elements and their purpose.
- Housing Differential housing Shafts Couplings Seals Pinions Gears Flanges Levers
A pair of gears are tightly seated on the drive shaft, one of them (large) is intended for high gear, the second (small) is responsible for low gear. They have serrations with straight and oblique profiles. The first ones are in contact with the coupling, the second ones - with the intermediate shaft. The inclusion of one or another row causes the coupling to move along the hub in the horizontal direction, after which it is connected to the gear on the transfer case drive shaft.
The intermediate position turns off the gearbox (the gearbox is open), and the vehicle cannot be moved in this mode. The front helical gear on the intermediate shaft is used to control the differential. The locking is engaged, or the rigid coupling of the drive shafts of both axles, is carried out through a clutch. The design is typical for modifications 21213 and 21214, and the latter is additionally equipped with a speed sensor drive.
In the operating state (with the transfer case reduction gear connected), the gear ratio in the first stage changes from 4.4 to 7.83, the second - from 2.52 to 4.58, the third - from 1.63 to 2.9, in the fourth - from 1.2 to 2.14, fifth - from 0.98 to 1.75, which is expressed in an increase in traction on the wheels.
Overcoming a deep puddle
Often a dispute arises between motorists about how best to cross a ford with a transfer case. Some people prefer to “fly” into a puddle from acceleration, others prefer to downshift. If you get into a mud pit, there is a high risk of water hammer - water gets into the cylinders through the filter, and the engine “chokes.”
To exclude this, many install a special snorkel. But you can do without it. A deep puddle should be overcome in second low gear. This is done so that in case of trouble (when the car starts to fail) you can switch to first gear in time and not stall. If you enter the water from acceleration (which is a better decision), remember that the wheels may get stuck in the middle of the journey. The engine power is not enough to turn the wheels - the car stalls, and the engine experiences a hydraulic shock.
Rules for using differential
These include:
- Switching the transfer case should only be done when the car is not moving.
- You can also engage the differential while the vehicle is moving.
- You can switch to a lower gear while the car is moving.
- To ensure long-term and uninterrupted operation of the differential, it is necessary to periodically turn it on, especially in winter. This should be done once every 7 days.
Shift lever location
In the interior of the Niva Chevrolet, there are two levers between the front seats . Using one of them you can change gears in the gearbox, and using the other you can control the transfer case.
Differential shift lever
The transfer case is based on a gearbox consisting of two stages . The control lever comes out of it into the cabin. He can move forward or backward. At the same time, it switches on/off downshift. If the lever is moved left or right, it can turn the differential lock on/off.
Gear shift and transfer case diagram
Downshift: what does it give?
The main component of the transfer case is the reduction gearbox . If the control lever is in the rear position, then the number of transfer cases decreases and is 1.2 . When the lever is in the forward position, the gear ratio increases. It will already be 2.1 . When the lever is in the neutral position, the gear ratio is equal to .
The differential is an integral part of the all-wheel drive mechanism in any car. It is recommended to use it only when the car is moving off-road.
Other problems
Quite often, car owners do not know how to use the transfer case on a Niva, and may encounter the fact that the center lock does not turn off, and they have to drive along the highway in this mode, which negatively affects the car. In order to switch the transmission to normal mode, you need to switch to reverse gear and accelerate a little, and while reversing, try to dislodge the lock. If this doesn't work, you can try to do the same thing, only while moving forward.
To avoid transmission problems, Niva car owners must adhere to the following rules:
- Try not to change gears while slipping;
- If the lock switches with difficulty, there is no need to apply excessive force;
- When a difficult-to-pass section has been overcome, it is necessary to unlock it again, since on a flat road in this mode at high speeds the car’s controllability deteriorates, and the service life of the entire transmission decreases.
Here are the basic rules by following which you can significantly extend the life of the gearbox on a Chevrolet Niva.
Sometimes there is a knocking sound in the transfer case. The Chevrolet Niva is a more reliable car than the VAZ-2121, but such malfunctions should not be ruled out. The first thing you should pay attention to is the driveline. Previously, Nivas had crosses, the play in which caused a lot of noise and vibration.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4k93vmooYNM
During the operation of off-road vehicles, parts and components of the transfer case gradually become unusable due to wear. Most often, the following interruptions in the operation of the mechanism occur:
- The front axle does not engage.
- The transfer case is overheating.
- Leaks and increased oil consumption of the transfer case.
- Unauthorized disabling of the front axle.
Description of possible problems with the transfer case
During the operation of off-road vehicles, parts and components of the transfer case gradually become unusable due to wear. Most often, the following interruptions in the operation of the mechanism occur:
- The front axle does not engage.
- The transfer case is overheating.
- Leaks and increased oil consumption of the transfer case.
- Unauthorized disabling of the front axle.
Changing the oil in the transfer case Niva 2121
To ensure the performance of the vehicle, it is necessary to carry out timely maintenance. Changing the oil is included in the mandatory list of machine maintenance work. To change consumables in the Niva 2121 transfer case, you will need 0.8 - 1.5 liters of gear oil.
The frequency of replacing lubricating fluid is equal to 45,000 km of distance traveled. The first procedure is carried out after 60,000 km, and then in accordance with the established schedule.
The procedure for changing the oil in the transfer case of a Niva SUV:
- warm up car systems and mechanisms, to do this you need to start the engine and drive a short distance;
- install the machine on an overpass or over a special inspection hole;
- clean the filler and drain plugs of the transfer case from dirt and dust;
- place a container under the drain to collect waste material;
- unscrew the plugs and drain the liquid;
- remove metal fragments, shavings, splinters and other wear elements;
- screw in the plug;
- pour into the washing liquid (about one liter);
- start the engine;
- move the lever through the transfer case gears with slight delays;
- turn off the engine;
- drain the flushing composition;
- fill the transfer case with new oil;
- check the oil level;
- if necessary, add the required amount.
For the transfer case of the Niva 2121 SUV, transmission oils of the famous brands Mobil, TNK, Castrol of the GL-4 class are most often used.
VAZ 2121 Niva has established itself as a reliable and versatile Soviet SUV. In 1977, the first domestic all-terrain vehicle rolled off the assembly line, which, unlike ordinary passenger cars, the VAZ 2121, had all-wheel drive and increased cross-country ability. The Niva transfer case design was developed by experienced AvtoVAZ designers in order to increase the functionality and versatility of the vehicle both when driving off-road and in city conditions.
The need to use a differential device lock and disable it on a Chevrolet Niva
On a Chevrolet Niva SUV, in some cases it may be necessary to forcibly block the cross-axle differential. Typical situations of its forced blocking:
- on roads with extremely difficult conditions;
- on routes with the possibility of wheel slip (these may be steep slopes in mountainous areas);
- on roads with dry sandy surfaces;
- on roads covered with a layer of snow or ice crust.
In all of the above cases, the differential is forcibly locked before entering such a highway. When the Chevrolet Niva moves on a regular asphalt road, there is no need to block the cross-axle differential device. This is explained by the fact that the wheels adhere well to the road surface, and the torque between all wheels of the vehicle will be distributed evenly. In this case, you will need to disable the differential lock.
What is a differential and what is it used for?
The differential has the form of a mechanical installation with a set of planetary gears and shafts. It is designed to distribute torque from the engine of a Chevrolet Niva car to the drive wheels, which are mounted on the same axle. This allows the wheels of the car to spin at different speeds. Rotating the wheels at different speeds is very important when turning a car, when one wheel passes a small radius and the other a large one. In the absence of a cross-axle differential, this would lead to spinning (slipping) of the wheel, which covers a smaller radius. A single wheel slipping would cause the vehicle to skid and increase tire wear.
When a car moves in a straight line at a constant speed, then the thrust from the engine to the wheels is distributed evenly. This helps both drive wheels rotate at the same speed. When one of the drive wheels slips, the differential automatically distributes the traction force from the engine. At the same time, the force on the slipping wheel increases and decreases on the stationary one. Typically, cars have only one differential installed in the drive axle. There are three of them installed on Shevik:
- Two differentials are installed in the front and rear axles of the car, which allow the drive wheels to rotate on the same axle at different speeds.
- The third is central (interaxial action). It helps distribute torque from the engine to both axles of the vehicle.
Chevrolet Niva differential lock
SUVs, including the Niva, have the ability to lock all three (cross-wheel locks are installed optionally) differentials. Thus, the vehicle’s maneuverability in harsh off-road conditions increases many times over.
When one wheel of the car slips, through the differentials, traction force will be transmitted from the engine to this wheel. All other wheels will be at rest, since the traction force will not act on them. Thus, the car will be immobilized. For example, while one wheel is slipping in a hole, the remaining wheels will be at rest. This means that all the traction force will be transferred specifically to the slipping wheel and will contribute to its rotation.
The purpose for which forced differential locking is turned on is to unite the drive wheels with each other, while ensuring their rotation at the same speed. Blocking makes it possible to make maximum use of the traction force transmitted from the car engine.
The operating principle of the differential lock on a Chevrolet Niva. As you know, a differential consists of gears and shafts, which make it possible to automatically distribute torque from the engine to the wheels. Forced differential locking prevents the gears from rotating, which is achieved using a special locking clutch. Thus, when the lock is manually engaged, the driving wheels of the car are rigidly connected to each other. This connection allows the wheels to rotate at the same speed. When the center differential lock is engaged, the drive shafts of the front and rear wheels are rigidly connected to each other, thereby providing uniform torque to the front and rear axles. The vehicle's cross-country ability increases, which makes it possible to be the first of its kind in SUVs. When the traction of the car's wheels is better, the more traction power the car will receive.
When is it necessary to use a differential lock?
Not all cars have the ability to lock the differential, which makes these cars more vulnerable off-road. And sometimes it happens that now it would be useful to have two axles on a car. The Chevrolet Niva is a unique car that has great cross-country ability on all types of off-road and even mountain surfaces. Forced blocking is used in the following cases:
- When the vehicle overcomes difficult road sections. The blocking is activated prematurely, before entering such a road.
- On steep slopes or mountainous areas where there is a possibility of wheel slip.
- When driving on a dry sandy road.
- When the road is covered with a layer of ice or snow crust.
How to determine whether the differential lock is engaged on a Chevrolet Niva
You can determine whether the inter-wheel differential device is locked without even leaving the Chevrolet Niva interior. Let's look at how to do this:
- Find two control levers between the passenger and driver's seats:
- gear shift lever (with long handle);
- machine transfer case control lever (with short handle);
- move the transfer case control lever forward - this will engage a lower gear to the drive axles of the wheels from the gearbox.
- Move the transfer case control lever back - this will disengage the downshift.
- Move the transfer case control lever left and right. This will switch the blocking of cross-wheel differential devices:
- to the left - switch on;
- to the right - shutdown.
How to properly use the cross-axle differential locking functions on a Chevrolet Niva
When using a differential lock on a Chevrolet Niva, experts recommend adhering to several rules.
Rule No. 1 - the specifics of switching the transfer case to lower gears. This switching must be done when the vehicle is stopped.
Rule No. 2 - enable the differential locking process. This is only possible when the car is driving non-stop.
Rule #3 – Downshift. This action is allowed to be performed without stopping the Chevrolet Niva.
Rule No. 4 – ensuring optimal operation of the cross-axle differential. To do this, the driver will need to periodically switch the differential device lever on the transfer case. Frequency – once a week (especially in the winter season).