1200 rub. for the photo report
We pay for photo reports on car repairs. Earnings from 10,000 rubles/month.
Write:
The muffler resonator is a part of the exhaust system whose task is to dampen low-frequency sounds arising from engine operation. It will be useful for every car enthusiast to know where the resonator is located and what possible problems he will have to face during its service. A breakdown of the exhaust pipe resonator is not critical, but it can cause a lot of inconvenience not only to the driver, but also to those around him. We will talk about all this in this material about how to eliminate problems that have arisen, how to dismantle and install the unit, as well as how to make a resonator with your own hands
Purpose of the resonator
First, let's figure out what a resonator is for . As mentioned above, it is part of the exhaust system of a car engine. Its main function is to dampen low-frequency sounds that arise during the exhaust process of gases and their entry into the gas exhaust system. There are two reasons why noise occurs in it:
- sound from expansion of gases;
- noise from vibration of exhaust system elements.
Along with a muffler, the tasks of a car resonator include reducing the speed of movement of exhaust gases. This becomes possible thanks to a physical law, according to which gases that move quickly in a narrow pipe, when they enter a large volume, lose their speed and, accordingly, energy. In the gas exhaust system, the resonator is located in front of the main muffler, being, in fact, the first link in the sound muffling chain of the exhaust system. That is, its main tasks are preliminary noise reduction and balancing of exhaust gas flow pulsations.
Some car owners call it the “middle muffler” (due to its physical location approximately in the middle of the bottom of the car) or the “second muffler.” However, this is not true because the exhaust system resonator and muffler have different operating principles.
The resonator of the car exhaust system also performs the function of freeing the engine exhaust from exhaust gases and creating uniform pressure in it. This ensures minimal resistance to the movement of exhaust gases, and it is possible to use almost all the useful engine power.
What it is
First, you need to understand what a resonator is in a modern car and what the purpose of this part of the exhaust system of a vehicle is.
A muffler resonator or simply a resonator is an integral part of the system responsible for removing exhaust gases from a running vehicle. Given the way this resonator looks, many people call it an additional muffler. It does look like a muffler, but it is not one. This is just part of the exhaust system.
Not everyone fully understands what a resonator is in a car with an internal combustion engine. It is often positioned as a unit to reduce the noise level of a running motor. But in fact, this is a secondary effect, which is achieved by performing the main function of the resonator. It consists of ensuring an even flow of exhaust gases throughout the vehicle exhaust system.
When the engine is running, regardless of the number of engine revolutions, so-called intermittent gas pressure parameters are formed in the manifold. Their frequency is largely influenced by the number of cylinders in the internal combustion engine and the revolutions made by the crankshaft. The resonator makes it possible to eliminate these intermittent parameters or pressure levels.
Resonator device
Structurally, the resonator consists of a perforated (drilled along the entire length within the device) pipe placed in a metal casing. The design also has a throttle hole designed to increase the efficiency of damping wave vibrations in the pipe. The internal cavity of the resonator is divided into two or more unequal parts by partitions located in a transverse plane to the pipe. Also, more modern exhaust resonators are designed with thermal insulation and/or sound insulation (often the same material) located under the housing and designed to reduce its temperature and/or sounds emanating from the device.
Internal structure of the resonator
The internal cavities have an unequal volume in order to ensure periodic narrowing and expansion of the flow of exhaust gases, which in turn equalizes their uneven pulsation. That is, each chamber has its own resonant frequency. In addition, they have a slight offset relative to the axis of the body. This is necessary to achieve a change in the direction of the exhaust flow. And internal perforation on the pipe is needed to dampen the large amplitude of sound waves that produce gases.
The efficiency of the resonator is influenced by the following factors:
- the degree of its wear, tightness;
- level of contamination from soot (the cleaner, the more effective);
- diameter (the larger the diameter of the device, the greater its efficiency).
Muffler functions in the exhaust system
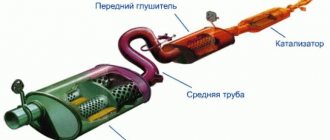
In the engine exhaust system, the muffler is installed after the catalyst (for a gasoline-powered car) or the particulate filter (for diesel engines). In most cases, there are two of them:
- Preliminary (muffler resonator) - designed to roughly suppress noise and stabilize fluctuations in the flow of exhaust gases leaving the engine. It is installed first, which is why it is often called "front". One of its main functions is the distribution of exhaust gases in the system.
- Main muffler - designed for final noise suppression.
Location of the muffler in the exhaust system
In practice, the design of a car muffler provides the following exhaust transformations leading to noise reduction:
- Changing the cross-section of the exhaust flow. This is realized due to the presence of chambers of different sections in the design, which allows you to absorb high-frequency noise. The principle of the technology is simple: first, the moving flow of exhaust gases narrows, which creates some acoustic resistance, and then expands sharply, as a result of which the sound waves are dissipated.
- Exhaust gas redirection. It is carried out by partitions and displacement of the axis of the tubes. When the exhaust gas flow is turned at an angle of 90 degrees, high-frequency noise damping is achieved.
- Changes in gas vibrations (interference of sound waves). Achieved due to the presence of perforations in the tubes through which the exhaust passes. This technology allows you to dampen noise of various frequencies.
- "Self-absorption" of sound waves in a Helmholtz resonator.
- Absorption of sound waves. In addition to chambers and perforations, the muffler body contains sound-absorbing material that insulates noise.
Problems with the resonator
Like any part, a car resonator periodically fails. After all, it passes through exhaust gases having a temperature of several hundred degrees Celsius. And in combination with the aggressive chemical elements contained in the escaping gas mixture, this leads to gradual burning of the metal parts of the system.
The main signs of resonator failure are:
- Deterioration of the muffler and exhaust system . This is manifested by increased sound coming from the exhaust pipe, especially low frequency sounds (roar).
- The appearance of exhaust gases from under the bottom of the car . This is a clear sign of depressurization of the resonator or other parts of the gas exhaust system.
- The presence of a characteristic rattling metallic sound from the resonator . It appears due to the fact that one (or more) of the internal components of the device burns out. Usually in such cases he “hangs out” or breaks away and rumbles in one of the cells.
- Significant drop in engine power . Due to a malfunction, the throughput of the resonator decreases significantly, so it dampens uneven pulsations of exhaust gases worse or not at all. And this gives feedback on the deterioration of the power unit.
If you encounter one or more of the above signs of a resonator malfunction, you need to inspect its operation as quickly as possible
How to check the catalyst?
Engine power depends on the condition of the catalyst. If there are characteristic symptoms of a breakdown, you should definitely check it. This can be done in light (by dismantling) and for back pressure or CO content without removing Read more
Shoots the silencer
Does your car engine need to shoot at the muffler? Then it’s worth checking the ignition system, fuel supply or timing marks. Find out the reasons and how to get rid of popping sounds from the muffler Read more
Components of the structure
As previously noted, the appearance of resonators is very similar to mufflers. Because of this, they are easy to confuse for a beginner. And more experienced motorists call resonators small or additional mufflers.
In fact, structurally this is a rather complex element, including several layers. Moreover, each of these layers is responsible for performing a specific function.
If you get acquainted with the structure of car resonators in cross-section, you can really notice a significant external resemblance to the standard standard muffler of a vehicle.
It is worth making some clarifications regarding how the muffler resonator is arranged in a car:
- the design is presented in the form of several chambers, which are separated from each other by a special mesh;
- This structure allows you to constantly narrow and expand the flow of exhaust gases. It is important to note that the gas comes out in sharp jerks. The resonator evens out these jerks, which allows you to obtain a uniform flow of exhaust gas at the output;
- the chambers inside are slightly offset, which allows you to change the direction of exhaust movement, thereby smoothing out uneven pulsation;
- Exhaust frequency damping occurs due to internal perforation. With its help, the noise level is reduced.
An automobile resonator performs its tasks thanks to a design that provides for the presence of a large number of closed cavities connected to each other using a pipeline and many perforations, that is, holes.
The holes provided by the design make it possible to cause multi-frequency vibrations that change due to friction.
As for the location, this element of the exhaust system is installed directly between the intake manifold or converter and the standard muffler.
But the location may be slightly different. This depends on the specific vehicle model and manufacturer.
It is important to understand that the gas produced in the engine during combustion of the air-fuel mixture has a high temperature. In this case, the function of the car resonator is to reduce it, reducing the thermal load on the muffler and the exhaust system elements coming after the resonator.
Now as for what temperature is at the outlet of the combustion chamber and under what thermal loads the small muffler operates. Depending on the specific vehicle system, temperatures can reach over 650 degrees Celsius. After combustion, the exhaust gas goes to the intake manifold at extremely high temperatures.
When reaching the car muffler resonator, the temperature does not drop so much. Therefore, it is extremely important that the resonator is made of high-quality and heat-resistant materials. When the resonator itself operates efficiently, it contributes to a drop in temperature, due to which the load on the muffler is significantly less. This extends its service life and preserves the integrity of the entire automotive exhaust system.
Resonators or additional mufflers are classified depending on the type of engine they are used on.
Therefore, there are 2 main types of devices.
- Designed for installation on two-stroke engines. If the vehicle is equipped with such a motor, which is not so common these days, then the resonator becomes a mandatory element of the exhaust system layout. If the resonator is missing, this will immediately lead to an increase in the amount of fuel consumed. The operation of the motor will change for the worse, speed and power will decrease. This is due to the fact that not only exhaust gas will be removed, but also incompletely burned fuel. Hence the drop in speed parallels the increase in fuel consumption.
- Resonators installed on four-stroke power plants. In the case of such engines, the resonator may not be beneficial to the car, but may create certain additional problems. Removal allows you to increase the engine power level by approximately 15%. Experienced motorists believe that on four-stroke engines the resonator only interferes with the normal operation of the engine. Yes, if you remove it, the power will actually increase. But at the same time, the environmental friendliness of the vehicle will deteriorate, and the exhaust will begin to pollute the environment. Therefore, 4-stroke engines still have resonators that allow them to achieve the required environmental standards.
Checking the resonator
When identifying the problems listed above, every motorist should know how to check the resonator . This will not only normalize the operation of the engine and exhaust system, but also increase the comfort of using the car, including for the people around you.
To check, you will need an inspection hole (if you don’t have one, you can jack up the car). Diagnosis is made using visual inspection. During the process, it is necessary to carefully examine the integrity of both the device itself and the pipes connected to it (especially at their joints).
A clear sign of a problem is the formation of condensation in the cooling resonator, after which it begins to drip to the ground. This means that its body has lost its tightness and must be repaired, or better yet, replaced. You can check for condensation after some time, when you turn off the engine (to allow the resonator body to cool). Note! Some car enthusiasts, when making resonators on their own, specially drill a hole in its body to remove moisture . Therefore, if you bought a car with a similar resonator, then this testing method will not work for you.
Also, the integrity of the resonator body can be determined by the presence of exhaust gases leaving it. This also indicates depressurization and the need to replace it. This fact can be checked with the car engine running by looking under the bottom. To be sure, you can ask an assistant to “turn on the gas” at the same time so that more exhaust gases pass through the system. Also, suspicion of depressurization is caused by the appearance of smoke from under the bottom of the car while driving or when parked with the engine running.
Types of automotive resonators
When choosing an exhaust system resonator, you need to know what types they are and what materials they are made from. Currently, automotive resonators made of aluminized steel and stainless steel . The former are distinguished by their low price, but short service life. Their body is made of thin steel, coated with aluminum on top to prevent corrosion. However, this anti-corrosion composition is not durable. Therefore, we do not recommend that you buy an exhaust resonator made of aluminized steel. It is better to buy a car resonator made of stainless steel. This material has a smoother surface (that is, creates a minimum of turbulence in the system), and is also more resistant when working under extreme temperatures.
DIY resonator
Before designing and assembling a resonator of your own design, you need to understand one simple thing. The thicker the material from which the exhaust system is made (including the resonator), the more effective the fight against vibrations and resulting noise will be. It is for this reason that the exhaust manifold, which is the first to receive gases from the cylinder head, has such an impressive weight.
However, when choosing a material, you should not overdo it and choose too massive blanks. Otherwise, the mass of the resonator will be significant, and this will affect the dynamic characteristics of the car and the load on its chassis.
There are a number of reasons why car owners make their own exhaust resonators. One of them is to reduce the noise that a standard factory muffler produces. Usually, for this purpose, an additional resonator is installed in the exhaust system. The second reason is the manufacture and installation of a direct-flow car resonator . Its features are as follows:
- reduction in engine power loss (actually insignificant, about 5.10%);
- changing the sound background of the engine and exhaust system (for lovers of low sound).
To make a direct-flow resonator you will need:
- a set of locksmith tools;
- welding machine (it is advisable to use modern semi-automatic machines or inverters);
- angle grinder with a set of cutting and grinding discs.
The design of the resonator will differ depending on the materials used and the imagination of the car owner. We offer you one of the options for self-manufacturing a direct-flow automotive resonator :
- Pre-prepare the pipe that will serve as the internal base of the resonator. It should be the same or slightly larger diameter than the factory one. Make sure that it can be easily welded to the existing system in the future, so do not choose a diameter that is too large (unless it is possible to connect the pipe using a flange).
- Next, you need to drill holes in this pipe, similar to the stock resonator.
- After this, you need to find a pipe with a slightly larger diameter (about 3.5 cm) that will serve as the outer casing. Its length needs to be made smaller (depending on the design, on average by 5.10 cm on each side).
- The plugs necessary to seal the housing at the ends are made. For this, sheet metal is used, where the outer diameters of the large and small pipes are drawn. Afterwards, the blanks are cut out and processed using a grinding machine.
- A pipe with a larger diameter is placed on a pipe with a smaller diameter, and the cavity between them is filled with glass wool (or better yet, modern mineral wool with good heat and sound insulation characteristics).
- Next, you need to weld the ends around the edges of the pipe with a large diameter using pre-made plugs.
- After welding work, clean the seams using an angle grinder. After this you should paint them.
- The last stage is welding the new resonator into the car's exhaust system. After carrying out the work, also clean the welding seams.
Tuning the exhaust system of VAZ 2114
As practice shows, the task of absolutely any truly effective tuning of the exhaust system is to reduce the resistance of the exhaust gases produced by the power unit. The modified exhaust gas removal system has a much lower level of resistance compared to the standard system, which significantly increases the rate of gas release. In turn, this leads to increased engine performance and, in particular, to a certain increase in its power.
As a rule, the first thing professional “tuners” pay attention to is the intake manifold. By the way, this element is also called a “spider” for its peculiar shape.
An upgraded intake manifold is installed instead of the standard one, ensuring the removal of gases from each of the working cylinders of the engine. Accordingly, the gases do not mix, but are discharged directly into the pipe.
Removing the catalyst
In addition to installing a more advanced exhaust pipe, fans of fast driving very often resort to complete dismantling of the catalytic converter. The motive for this decision is simple - removing the “obstacle” in order to increase the throughput of the exhaust system. Of course, this significantly increases the exhaust toxicity level. However, the toxicity of the exhaust (without a catalyst) fits well within the framework approved by current legislation. That is, operating a car without a catalytic converter is completely legal.
It should be noted that if the catalyst is removed, a slightly different element is installed in its place - a flame arrester. Structurally, this flame arrester is a piece of pipe of the same length and with the same fastening method as the catalyst
At the same time, a small wire “washcloth” is located inside the flame arrester, which eliminates the occurrence of micro-fires.
At the same time, in order to prevent rapid destruction due to corrosion, the body of a homemade flame arrester must be painted with a special heat-resistant anti-corrosion paint.
Unfortunately, modern industry does not produce flame arresters for domestically produced cars. That is why those who want to modify the exhaust system make it themselves. In principle, there is nothing complicated about this - you just need to know how to use a cutting machine (“grinder”) and a welding machine.
Removing and installing the resonator
Many motorists are interested in a natural question - how to remove the resonator ? The answer to this question will vary depending on the brand of car. However, in general, the algorithm is simple and will be approximately as follows:
- it is necessary to disconnect the resonator pipes at the points of their connection with the exhaust gas removal system (front, on the engine or catalyst side, and at the rear, on the muffler side);
- remove the resonator from its suspensions, with the help of which it is attached to the bottom of the car;
- dismantle the resonator with its pipes.
How to replace a Renault Logan resonator
Installing a new device is done in the reverse order. When removing the resonator, it is important not to damage the O-rings that connect its pipes to the rest of the exhaust system.
As an example, we present to your attention two video instructions demonstrating the replacement of the resonator on popular Renault Logan cars and front-wheel drive VAZ 2110, VAZ 2111, VAZ 2112, VAZ 2114, VAZ 2115, Kalina, Priore, Grante.
Finally
Partial or complete failure of the car exhaust system resonator is not a critical failure . Diagnosing a resonator failure is not difficult even for an inexperienced car owner. This is indicated by a loss of power, the spread of exhaust gases under the bottom and/or into the cabin, and an increase in background noise when the engine is running. Please note that the car can be used case, however, we still recommend that you do not delay repairs, since driving with a burnt-out resonator can lead to failure of other elements of the vehicle’s exhaust system.
Hello everyone, I’ll try a little bit today)
The desire to make a small exhaust has settled in my head for a long time. But it never got to him. And recently, I came across a jar from a friend of mine, which had been lying idle in the garage for quite some time.
This is the bank. It stood on the exhaust of an old chord, and according to a friend, it sounded interesting at the bottom, and almost stopped sounding at the top. I studied what kind of can it was, but it turned out that it was not a muffler at all, but a resonator from a turbovag)) My friend was no less surprised than I was, because once upon a time this exhaust was made for him in some good tuning studio)) in general there are pitfalls all around and divorces))
But still, it was decided to try to weld it) All the work took about an hour, the original nozzle remained in place, but now it sticks out a little. In my opinion, it looks very good.
The sound actually appeared, the car began to grumble at the bottom and disappeared somewhere after 3.5 thousand revolutions. It resonates a little in the ears at 1.5 thousand, and this despite the fact that it is not loud at all. If I don’t like the ride with this configuration, I’ll change it) that’s all) I’m attaching videos with sound)
The exhaust systems of modern cars are becoming more complex and sophisticated. This is due not only to the fight for a clean environment, but also to the general trend towards reducing vehicle noise.
Elements of the exhaust system operate under difficult conditions. High temperatures, combined with aggressive environmental influences, have a significant destructive effect. Therefore, some parts of the exhaust system become unusable over time.
Nowadays there is a large variety of spare parts for exhaust systems on the market. There is a general trend towards unification and interchangeability of spare components for the exhaust line. Manufacturers are increasingly moving away from the principle of producing components for a specific car model, as this has proven to be impractical.
Today, many manufacturers strive to produce universal spare parts, the installation of which requires minor modifications to the exhaust tract. This applies to components such as resonators and flame arresters. Unification of the production process has reduced the cost of spare parts. But for the consumer, the reduction in the cost of the spare part itself is offset by the need to rework the exhaust tract with welding and cutting work.
Exhaust system VAZ 2114 stock and hound
Children are the flowers of life, and they don’t necessarily need to understand the intricacies of exhaust systems, but the kid made the right verdict - if it makes noise, it means it’s a hound, that is, a sports one. It's time for grown-up guys to understand the difference between stock exhaust systems, reconfigured and mutilated, which are only suitable for scaring away non-migratory bird species. Not everyone, however, understands this, or does not understand it quite correctly, so we decided to look into this delicate exhaust issue so that the concepts of “direct flow”, “crab 4-2-1” and other magic spells of tuners acquire a meaningful outline.
To implement this plan, you must first understand the standard exhaust system of the car, because its tasks include not only noise suppression. In fact, the 2114 exhaust system is a complex complex that solves a lot of problems. Noise suppression is only one of them, and not the most important for the engine. The pipe should not choke the engine, but work in balance with the intake system and fully comply with the design features of a particular engine. Precise tuning of the exhaust system is impossible without deep knowledge, laboratory conditions and precision instruments, so talking about tuning it in a garage is pointless. And that's why.
Video tutorial on replacing the VAZ exhaust system
Resonator or flame arrester
Car owners are often faced with a choice: resonator or flame arrester?
A resonator is an integral part of the exhaust system, the main purpose of which is to suppress resonance phenomena, equalize the flow of exhaust gases and reduce noise. Made from heat-resistant stainless steel.
There are many different resonator designs. Each engine has its own parameters. One of the main characteristics is internal volume. Important parameters are the number of chambers and the type of communication between them (through perforated holes in pipes, through pipes offset relative to each other, or through holes in the walls of the chambers). Resonators are also divided according to the type of internal contents:
- hollow;
- with packing made of heat-resistant materials.
The principle of operation is as follows. Exhaust gases, depending on the engine speed, enter the resonator with a certain pulsation. Once inside the resonator, they follow a developed route with a constant change in direction and division of the main flow into smaller directions. As a result, the initial impulse dissipates. A more uniform movement of gases is created with a relatively small amplitude of pressure changes.
The main difference between a flame arrester is its direct-flow design. A high-quality flame arrester is made of stainless steel. The central pipe is perforated with a calculated frequency and hole diameter. The body is often made of two layers. This is done to increase reliability (if one layer is damaged, the second will not allow gases to escape) and to achieve even greater noise suppression efficiency.
The internal space of the case is filled with heat-resistant materials. It can be a metal or mineral filler. Its main task is to freely pass gases through itself, breaking them into as small streams as possible.
A flame arrester, unlike a resonator, is capable of operating for a long time under the influence of higher temperatures. Therefore, it is advisable to install it in places located close to the exhaust manifold.
Exhaust gases have a wave-like flow structure with areas of high and low pressure. When a portion of high-pressure exhaust exits into the flame arrester, gases penetrate through the holes into the housing packing. There they are divided into smaller flows and cooled. When a low pressure area approaches, the exhaust gases exit the packing and are added to the flow. In this way, the pulsation amplitude decreases, which leads to the elimination of resonance phenomena. Cooling is also carried out, which has a beneficial effect on subsequent elements of the exhaust system.
In general, the functionality of the resonator and flame arrester are similar. The differences are that the flame arrester can withstand a greater temperature load, and the resonator does a better job of suppressing resonance phenomena and reducing noise. Based on this, we can conclude that it is more expedient to install a flame arrester instead of exhaust system elements located closer to the manifold. It is better to install the resonator in the second half of the exhaust system.
Features of operation and types of mufflers
There are two types of mufflers used in modern cars: resonant and direct-flow. Both can be installed in conjunction with a resonator (pre-silencer). In some cases, a straight-through design can replace a front muffler.
Resonator device
Structurally, the muffler resonator, which is also called a flame arrester, is a perforated pipe located in a sealed housing, divided into several chambers. It consists of the following elements:
- body (has a cylindrical shape);
- thermal insulation layer (exhaust gases have a very high temperature);
- blind partition (to turn the flow of gases);
- perforated pipe;
- throttle (allows you to change the cross-section of the exhaust gas flow).
Resonant muffler design
Unlike the preliminary muffler, the main resonant muffler is more complex. It consists of several perforated pipes installed in a common housing, which are separated by partitions and located on different axes (see Fig. Silencer in section):
- front tube with perforation;
- rear tube with perforation;
- inlet pipe;
- anterior partition;
- middle septum;
- posterior septum;
- exhaust pipe;
- body (oval section).
Thus, a resonant muffler uses all types of transformation of sound waves of various frequencies.
Features of a direct-flow muffler
The main disadvantage of a resonant muffler is the effect of creating back pressure, which occurs as a result of redirecting the flow of exhaust gases (when it collides with partitions). In this regard, many motorists tune the exhaust system by installing a direct-flow muffler.
Direct flow muffler
Structurally, the direct-flow muffler consists of the following elements:
- sealed housing;
- exhaust and inlet pipe;
- perforated pipe;
- soundproofing material - fiberglass is most often used, which is resistant to high temperatures and has good sound-absorbing properties.
In practice, a straight-through muffler has the following operating principle: one perforated pipe passes through all chambers. Thus, there is no noise suppression by changing the direction and cross-section of the gas flow, and noise suppression is realized solely through interference and absorption.
Due to the unhindered passage of the exhaust through the direct-flow muffler, the resulting back pressure is very low. However, in practice this does not provide a large increase in power (from 3% to 7%). On the other hand, the car has a characteristic sports car sound, since the noise-absorbing technology present in it only eliminates high frequencies.
The comfort of the driver, passengers and pedestrians depends on how the muffler works. So, during prolonged use, increased noise can cause serious inconvenience. Today, installing a direct-flow muffler in a structure for a car moving within city limits is an administrative violation that threatens with fines and an order to dismantle the device. This is due to exceeding the noise limits specified by the standards.
The operation of the engine in vehicles, if we talk about internal combustion engines, is associated with the production of quite loud noise. But the driver, his passengers, and people on the street practically do not hear this noise effect.
This was not always the case. The first cars running on internal combustion engines were very noisy and created a lot of smoke, and therefore this became a real problem. But after some time they came up with a solution.
Every modern car is necessarily equipped with a muffler. Already from the name it becomes obvious that the main function of mufflers is to dampen and suppress noise and sounds arising from a running engine.
The exhaust system is quite complex, despite the apparent simplicity of its functions. It consists of several elements, one of which is a resonator. Car enthusiasts have questions regarding it. They are interested in what it is, why it is installed and what tasks it performs in the operation of the exhaust system and the entire car.
Flame arrestor instead of a resonator
There are several main reasons for resonator failure:
- mechanical damage due to an impact in the body area or under the influence of vibrations when the integrity of the rubber suspensions is violated;
- burnout of the body or internal structural elements;
- destruction of the internal structure.
Signs of resonator failure are as follows:
- a characteristic cutting sound (with minor leaks) or roar (when there is serious damage);
- rattling noise coming from the body;
- exhaust smell in the cabin;
- exhaust gases escaping from under the car.
Car owners often wonder whether it is possible to install a resonator instead of a flame arrester. It all depends on the design features of the exhaust system of a particular car. It is also necessary to take into account the experience of producing such a replacement on similar cars.
In most cases, installing a flame arrester is suitable to replace the central resonator, which is installed behind the catalyst or particulate filter. In this area, the exhaust gases are still at a high temperature. And the main muffler follows the central resonator. Therefore, installing a flame arrester here will not have a significant effect on the increase in noise output and will function properly, reducing resonance and participating in the cooling of exhaust gases.
Installing a flame arrester instead of the main resonator is impractical. Except in those cases when the exhaust system is modified into some kind of sports version. Then it makes sense to install a stronger instead of a muffler. At the same time, the noise output will increase, and echoes of resonant phenomena may appear.
How to repair a muffler
There are 2 options for resolving this issue. Option 1 involves purchasing a new muffler resonator, and option 2 involves completely upgrading it. You can do all this yourself. When repairing the muffler resonator, you should pay attention to the design features of this part of the system, select the appropriate material, and ensure the tightness of the resulting structure. To solve problems that arise with the resonator, you must first think through a plan for the work that is supposed to be performed. If you have no welding experience, it is advisable to contact a professional.
%rtb-4%
Resonator, flame arrester instead of catalyst
Most car owners in Russia, when problems arise with the catalyst, choose the path of removing it and installing a replacement. This is due to a loyal attitude towards violating environmental standards, as well as the low cost of such a replacement. The new catalyst is expensive. Installing a replacement is much cheaper.
Instead of a catalytic converter, it is most advisable to install a flame arrester or stronger. This is due to operating conditions near the engine. High temperatures can quickly damage the resonator. Especially if it is hollow.
An exception is the installation of a resonator in exhaust system designs with multiple catalysts. Here you can implant a resonator instead of the last catalytic converter. It is usually located at a considerable distance from the engine and by the time it reaches it, the exhaust gases have cooled and lost kinetic energy.