The gearbox design in the Lada Kalina model has a rather complex design, but it will still be useful for the owner to know the main features of the gearbox design. For the budget “Russian”, the manufacturer has provided the possibility of equipping it with a five-speed transmission.
Many owners pour out complaints about the Lada Kalina gearbox, because when switching, they observe a creaking sound coming from the unit. This is explained by the fact that the developers placed special type synchronizers on the gears of all forward gears. It is these components that “give” themselves away with a characteristic creaking sound. Adjustment or replacement can help here, as a result of which the creaking effect disappears. To perform this repair correctly, you will need a gear shift diagram.
The vast majority of buyers are inclined to purchase Lada Kalina, which have a manual transmission. Note that these boxes are equipped with any of the engines used, be it an 8-valve version or a modification with a 16-valve head.
Gearbox Features
If we talk about the features of the Lada Kalina 2 gearbox, then it is worth mentioning the locking solenoid.
It was installed specifically to prevent the driver from accidentally engaging reverse gear while moving forward. You will not be able to engage reverse gear if the electrical network of the solenoid is interrupted or if it fails. If you find such a malfunction, then repair is needed
But it is important to get to the parking lot
Unscrew the solenoid from the box and install the rod lock plug in its place. You will take it in a special repair kit; every driver should carry it with him. This will help you get to the garage or get to the repair shop. You need to drive carefully. Be careful not to shift into reverse instead of first gear.
Replacing the Lada Kalina gearbox: why is it needed and how to replace it correctly
If the circumstances were not the most favorable, and you still had to resort to replacing the Kalina gearbox, you need to know the correct sequence for dismantling the transmission.
A car requires some maintenance with constant use. If it is not followed, the mechanisms begin to break down. This can happen with the gearbox on Lada Kalina. Replacing the gearbox on Kalina is carried out strictly according to the regulations.
What to consider when choosing a box
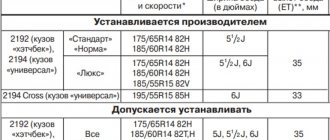
Technical characteristics of Lada-Kalina (VAZ-1117, 1118, 1119)
When selecting a new transmission, there are a number of nuances that need to be taken into account. These include shape, size, torque and more. But you can pick up almost any of the front-wheel drive Lada.
Shape and dimensions
All front-wheel drive Lada cars are similar to each other. Manual transmission 2108 appeared on models 2108, 2109 and 21099. Subsequently, it migrated to 2110, 2111, 2112, 2113, 2114, 2115 in a slightly modified form for different needs. The Priora received a modified box from the “ten”. “Kalina” and “Granta” are very similar to the “nine” in their design, therefore the dimensions and shape are identical. “Automatic” and “robot” were specially developed for these cars, so it’s the same here. Any will do.
Permissible torque
The Kalina’s torque is about 120-148 Nm, the G8’s is 79-186 Nm. The 2108-2112 transmission was designed for higher torque. Starting from 2113 to “Kalina” and “Grants” the torque dropped and the gearbox became a little weaker.
Is it possible to change one type of box to another without major modifications?
To switch from one type of gearbox to another, modifications to the vehicle are necessary. When switching from an automatic to a manual, the price is not too high, because you need to purchase:
This procedure will cost no more than 30 thousand rubles.
When replacing it back, the cost of the work carried out increases and can reach 10 thousand rubles (excluding the cost of the box). This is the case if you want to install an automatic gearbox instead of a manual one. If desired, everything can be interchanged; the main thing is to approach this issue competently.
Source
Design features, gearbox design on the Lada Kalina Lada Kalina VAZ 1118
Light on the road: characteristics and rules for replacing Lada Kalina headlights
The input shaft 29 (Fig. 5.2) of the gearbox is made in the form of a block of drive gears, which are in constant engagement with the driven gears of all forward gears. The secondary shaft 25 is hollow, with a removable drive gear 3 of the main gear. On the secondary shaft of the gearbox there are driven gears 16, 18, 19, 21, 23 and synchronizers 17, 20, 24 for forward gears. Front bearings 4, 31 roller shafts, rear 22, 28 - ball. Under the front bearing of the secondary shaft of the gearbox there is an oil sump 5, which directs the flow of oil into the secondary shaft and further under the driven gears.
The differential is two-satellite. The preload in the differential bearings is adjusted by selecting the thickness of the ring 13. The driven gear 12 of the main gear is attached to the differential box flange. A master ring 7 of the magnetoelectric speed sensor is installed on one of the axles of the differential box.
The gearbox control drive consists of gear shift lever 11 (Fig. 5.3), a ball joint, rod 10 and a gear selection mechanism (installed in the gearbox housing).
The reverse gear lock is controlled by a solenoid mounted on the gearbox housing, which, in turn, is controlled by switch 13 mounted on gear shift lever 11.
On a Lada Kalina car, the gear selection mechanism is made as a separate unit and is attached to the plane of the clutch housing inside the gearbox.
In housing 9 (Fig. 5.4) of the gear selection mechanism, two axes are fixed. Axle 3 is equipped with a three-arm gear selector lever 2 and two locking brackets 7 and 11. The other axis 1 passes through the holes of the locking brackets, securing them from turning. Shoulder b
three-arm lever 2 is used to engage forward gears, arm
a
is used to engage reverse gear, and the third arm is affected by the lever of the gear selection rod, connected through a cardan joint to rod 10 (see Fig. 5.3) of the gearbox control drive. On axle 6 (see Fig. 5.4) there is a fork 8 for engaging reverse gear.
Rice. 5.4. Gear selection mechanism:
1 - guide axis of locking brackets; 2 — three-arm lever; 3 — axis of the gear selector lever; 4, 10 - spring; 5 - retaining ring; 6 — reverse fork axis; 7, 11 — locking brackets; 8 — reverse gear fork; 9 — housing of the gear selection mechanism; a - arm of a three-arm lever for engaging reverse gear; b - arm of a three-arm lever for selecting forward gears
Rice. 5.3. Gear shift drive Lada Kalina VAZ 1118:
1 - damper bushing; 2 — spacer sleeve; 3, 16, 20 — nuts; 4, 8, 18 — bolts; 5 — protective cover; 6 — retaining ring; 7 — ball joint housing; 9, 21 — coupling clamps; 10 — transmission control drive rod; 11 — gear shift lever; 12 — clamp for fastening the wiring harness; 13 — reverse gear lock control solenoid switch; 14 — gear lever handle; 15 — washer; 17 — cover of the gear lever handle; 19 — jet thrust
Rice. 5.2. Gearbox Lada Kalina VAZ 1118:
1 — clutch release bearing; 2 — guide sleeve of the clutch release bearing; 3 - main gear drive gear; 4 — roller bearing of the secondary shaft; 5 - oil sump; 6 — satellite axis; 7 — speed sensor master ring; 8 — axle gear; 9 — differential box; 10 — satellite; 11 — clutch housing; 12 — driven gear of the main gear; 13 — adjusting ring; 14 — tapered roller bearing of the differential; 15 — axle shaft seal; 16 — driven gear of the 1st gear of the secondary shaft; 17 — synchronizer of 1st and 3rd gears; 18 — driven gear of the second gear of the secondary shaft; 19 — driven gear of the third gear of the secondary shaft; 20 — synchronizer for 3rd and 4th gears; 21 — driven gear of the fourth gear of the secondary shaft; 22 — ball bearing of the secondary shaft; 23 — driven gear V of the secondary shaft transmission; 24 — 5th gear synchronizer; 25 - secondary shaft; 26 — rear cover of the gearbox housing; 27 — drive gear of the 5th gear; 28 — ball bearing of the input shaft; 29 — input shaft; 30 — gearbox housing; 31 — roller bearing of the input shaft; 32 — input shaft oil seal; 33 - breather
What is a tachometer for?
Any “self-respecting” car has such a device as a tachometer. For many experienced drivers, it is obvious what I will write about now, but there are often people who have never thought about the presence of a tachometer or its purpose. It is usually located next to the speedometer and shows, pardon the expression, the engine speed