Imagine how many fewer accidents there would be if cars could stop instantly. Unfortunately, the elementary laws of physics say that this is impossible.
It is customary for car manufacturers to “boast” about another indicator: acceleration speed up to 100 km/h. Of course, this is also important. But it would be nice to know how many meters the braking distance will stretch. After all, it differs from car to car.
In this article we will talk about what every driver needs to know about braking distances in order to protect themselves on the road. Buckle up and let's go!
What is the braking distance of a car?
The braking distance is the distance that the car will travel after activating the brake system until it comes to a complete stop. This is only a technical parameter by which, in combination with other factors, the safety of the car is determined. This parameter does not include the driver's reaction speed.
The combination of the driver’s reaction to an emergency situation and the distance from the start of braking (the driver pressed the pedal) to the complete stop of the vehicle is called the stopping distance.
The traffic rules indicate critical parameters under which the operation of a vehicle is prohibited. The maximum limits are:
| Transport type: | Braking distance, m. |
| Motorcycle/moped | 7,5 |
| A car | 14,7 |
| Bus/truck weighing up to 12 tons | 18,3 |
| Truck weighing more than 12 tons | 19,5 |
Since the braking distance directly depends on the speed of the vehicle, the critical indicator is the distance covered by the vehicle mentioned above when the speed decreases from 30 km/h. (for motor vehicles) and 40 km/h. (for cars and buses) to zero.
A braking system that responds too slowly will always result in damage to the vehicle and often injury to those in it. For clarity: a car moving at a speed of 35 km/h will collide with an obstacle with a force identical to the impact of a fall from a five-meter height. If the speed of the car in a collision with an obstacle reaches 55 km/h, then the impact force will be identical to that of a fall from the third floor (90 km/h – a fall from the 9th floor, or from a height of 30 meters).
These research results show how important it is for a motorist to monitor the condition of the car’s braking system, as well as tire wear.
Brake system and its features
Each vehicle has its own time to stop. The brake system in the car sections works almost the same, the only difference is in the condition of the brake pads.
A certain vehicle will be able to stop for:
- Passenger cars – 12-13 seconds.
- Buses up to 5 tons – 13-14 seconds.
- Buses over 5 tons – 16-17 seconds.
- Trucks up to 3.5 tons – 15-16 seconds.
- Trucks from 3.5 to 12 tons – 17-18 seconds.
- Trucks weighing more than 12 tons – 17-18 seconds.
- Two-wheeled mopeds or motorcycles – 7-8 seconds.
- Motorcycle equipped with a trailer – 8-9 seconds.
- Passenger cars with a trailer – 13-14 seconds.
What is the braking distance formula?
There are special formulas that help the driver calculate the braking distance during emergency and normal braking. Of course, they are averages.
So, normal braking involves gently pressing the brake pedal, for example at a traffic light. In this case, we are guided by the formula:
(Speed in km/h: 10) * (speed in km/h: 10) = braking distance in meters
That is, if you are moving at a speed of 50 km/h, the braking distance will be approximately 25 meters. We count like this: 50/10 * 50/10 = 5*5 = 25.
During emergency braking, the resulting value is divided by two more. The formula looks like this.
(Speed, in km/h: 10) * (speed, in km/h: 10) / 2
Let's do the math using a specific example. Let's say you are again moving at a speed of 50 km/h and a situation occurs in which you urgently need to brake. We calculate the braking distance as follows: 50/10 * 50/10 / 2 = 5 * 5/2 = 12.5 meters.
You may say that in an emergency there is no time to count and you need to act. Yes, you are absolutely right. But there is one “but”. Each driver moves around the city at approximately the same speed. Therefore, you can learn the desired value in advance and build on it when needed. This simple life hack could one day save someone's life. So take note of it.
How to calculate the total stopping time and the final braking distance?
As we noted above, the driver needs time to make a decision to brake. That is, to react. Plus, it takes time to move your foot from the gas pedal to the brake pedal and for the car itself to react to this action.
There is a formula that averages out the driver's reaction path. Here she is:
(Speed in km/h: 10) * 3 = reaction distance in meters
Let's imagine the same situation. You are driving at a speed of 50 km/h and decide to brake smoothly. While you are making a decision, the car will travel 50/10*3 = 15 meters. We calculated the second value (the length of the actual braking distance) to be higher - 25 meters. As a result, 15+25 = 40. This is the distance your car will travel until you come to a complete stop.
Distance
- Three car lengths . Anyone traveling in urban areas must maintain a distance of at least 15 meters, or three car lengths.
- Half speedometer : for a safe distance outside of populated areas, pay attention to the speed of the car. In order to calculate a safe distance, divide by 2 the current speed shown by the speedometer. As a result, you will get the distance to other cars in meters. Example: At a speed of 70 km/h, you must keep at least 35 meters from the vehicle in front. Moreover, this applies to dry asphalt in the summer.
- Double distance : In case of poor visibility or bad road conditions, you should double the safe distance.
What factors influence braking and stopping distance?
We already wrote above that the length of the braking distance is influenced by many factors. We invite you to consider them in more detail.
Speed
This is the key factor. This means not only the speed of the car, but also the reaction speed of the driver. It is believed that everyone has approximately the same reaction, but this is not entirely true. Driving experience, a person’s health status, medication use, etc. play a role. Also, many reckless drivers ignore the law and are distracted by smartphones while driving, which ultimately can lead to catastrophic consequences.
Remember one more important point. If a car's speed doubles, its braking distance quadruples! The 1:1 ratio doesn't work here.
Road conditions
Undoubtedly, the length of the brake line is influenced by the condition of the road surface. On an icy or wet road it can increase significantly. But these are not all the factors. You should also be wary of fallen leaves, on which tires glide perfectly, cracks in the surface, holes, and so on.
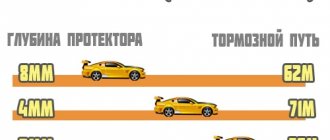
Tires
The quality and condition of the rubber greatly influence the length of the brake line. Often, more expensive tires provide better grip on the road surface. Please note that if the tread depth has worn off beyond the permissible value, then the rubber loses its ability to drain a sufficient amount of water when driving on a wet road. As a result, you may encounter such an unpleasant thing as hydroplaning - when the car loses traction and becomes completely uncontrollable.
To shorten the braking distance, it is recommended to maintain optimal tire pressure. Which one exactly - the automaker will answer this question for you. If the value deviates upward or downward, the braking line will increase.
Depending on the coefficient of adhesion of the tires to the road surface, this indicator will vary. Here is a comparative table of the dependence of the braking distance on the quality of the road surface (a passenger car whose tires have an average coefficient of adhesion):
| 60km/h. | 80 km/h. | 90 km/h. | |
| Dry asphalt, m. | 20,2 | 35,9 | 45,5 |
| Wet asphalt, m. | 35,4 | 62,9 | 79,7 |
| Snowy road, m. | 70,8 | 125,9 | 159,4 |
| Ice, m. | 141,7 | 251,9 | 318,8 |
Of course, these indicators are relative, but they clearly illustrate how important it is to monitor the condition of car tires.
Technical condition of the machine
A car can only go on the road in good condition - this is an axiom that does not require proof. To do this, carry out routine diagnostics of your car, make timely repairs and change the brake fluid.
Remember that worn brake rotors can double the brake line.
Distraction on the road
While the vehicle is moving, the driver has no right to be distracted from driving the vehicle and monitoring the traffic situation. Not only its safety, but the lives and health of passengers, as well as other road users, depend on this.
Here's what happens in a driver's brain when an emergency occurs:
- assessment of the road situation;
- making a decision - to brake or maneuver;
- response to the situation.
Depending on the driver's innate abilities, the average reaction speed ranges from 0.8 to 1.0 seconds. This setting concerns an emergency situation, rather than an almost automatic process when slowing down on a familiar stretch of road.
To many, this time period seems insignificant to pay attention to, but ignoring the danger can lead to fatal consequences. Here is a table of the relationship between the driver’s reaction and the distance traveled by the car:
| Vehicle speed, km/h. | Distance until the brake is pressed (the time remains the same - 1 second), m. |
| 60 | 17 |
| 80 | 22 |
| 100 | 28 |
As you can see, even a seemingly insignificant second of delay can lead to dire consequences. That’s why every motorist should never break the rule: “Don’t be distracted and stick to the speed limit!”
Various factors can distract the driver from driving:
- mobile phone - even just to see who is calling (when talking on the phone, the driver’s reaction is identical to the reaction of a person in a state of mild alcohol intoxication);
- watching a passing car nearby or enjoying beautiful scenery;
- fastening the seat belt;
- eating while driving;
- falling of an unsecured DVR or mobile phone;
- clarification of the relationship between driver and passenger.
In fact, it is impossible to make a complete list of all the factors that can distract a driver from driving. In view of this, everyone should be attentive to the road, and passengers will benefit from the habit of not distracting the driver from driving.
State of alcohol or drug intoxication
The laws of most countries around the world prohibit driving under the influence of drugs or alcohol. This is not because drivers are prohibited from enjoying life to the fullest. The braking distance of the car depends on this condition.
When a person is under the influence of drugs or alcohol, his reaction is reduced (this depends on the degree of intoxication, but the reaction will be slow in any case). Even if the car is equipped with the most advanced systems and braking assistants, pressing the brake pedal too late in an emergency situation will lead to an accident. In addition to braking, a drunk driver reacts more slowly to the need to perform a maneuver.
What is the braking distance at speeds of 50, 80 and 110 km/h.
As you can see, due to the many variables, it is impossible to create a clear table describing the exact stopping distance of an individual vehicle. This is influenced by both the technical condition of the car and the quality of the road surface.
Average braking distance data for a passenger car with a working system, high-quality tires and normal driver reaction:
| Speed, km/h. | Approximate braking distance, m. |
| 50 | 28 (or six car bodies) |
| 80 | 53 (or 13 car bodies) |
| 110 | 96 (or 24 cases) |
The following conditional situation shows why it is important to stick to the speed limit and not rely on “ideal” brakes. To stop in front of a pedestrian crossing from a speed of 50 km/h to zero, a car will need a distance of almost 30 meters. If the driver violates the speed limit and moves at a speed of 80 km/h, then when reacting at a distance of 30 meters before the crossing, the car will hit a pedestrian. In this case, the speed of the car will be about 60 km/h.
As you can see, you should never rely on the reliability of your car, but it is correct to follow the recommendations, because they are taken from real situations.
Traffic rules and speed
In order to keep the braking distance as short as possible and in accordance with the table above, you should adhere to the traffic rules and recommended speed.
- So, in populated areas you should not exceed the speed of more than 60 kilometers per hour, and in courtyards and residential areas you should not drive more than twenty kilometers per hour.
- For buses carrying children, there is a limit on all roads - sixty kilometers per hour.
- The same speed conditions must be observed for vehicles that have people sitting on special benches in the back. Buses, whether intercity or small, as well as motorcycles are allowed to travel no more than 90 kilometers per hour.
- All other buses, as well as category “B” cars that tow a trailer , can drive no more than 90 kilometers per hour on highways.
- The same rules apply to semi-trailer trucks. But on other roads these vehicles can travel no more than 70 kilometers per hour.
- Cars and trucks (if the gross weight does not exceed three and a half tons) can drive on highways at a speed of 110 kilometers per hour, and on all other roads - no more than 90 kilometers per hour.
What determines the average braking distance of any car?
To summarize, we see that the braking distance of any car depends on a combination of such factors:
- vehicle speed;
- machine weight;
- serviceability of brake mechanisms;
- tire adhesion coefficient;
- quality of the road surface.
The driver's reaction also influences the car's stopping distance.
Considering that in an emergency the driver's brain needs to process a lot of information, sticking to the speed limit is the very first commandment, the importance of which will never stop being talked about.
When and how measurements are taken
Braking distance calculations will be needed when a vehicle is being examined after a serious accident (forensic examination), during technical testing of the car, and also after upgrading the braking system.
There are various online calculators with which the driver can independently check these parameters of his car. An example of such a calculator can be found at this link . You can use this calculator right on the road. The main thing is to have Internet access. A little later we will look at what formulas can be used to calculate this parameter.
How to increase the intensity of deceleration
First of all, the effectiveness of deceleration depends on the driver’s attentiveness. Even the best braking system and a full range of electronic assistants are not capable of changing physical laws. Therefore, in no case should you be distracted from driving by making phone calls (even if a hand-free system is used, the reaction of some drivers may slow down significantly), texting or looking at beautiful landscapes.
An equally important factor is the driver’s ability to anticipate an emergency situation. For example, when approaching an intersection, even if there is a secondary road adjacent to the main road and there is a “Give Way” sign on it, the driver needs to be more concentrated. The reason is that there are motorists who believe that the size of their car gives an advantage on the road, regardless of the signs. In such situations, it is better to be prepared for emergency braking than to later find out who should yield to whom.
Turns and maneuvers on the road must be performed with equal concentration, especially taking into account blind spots. In any case, the driver’s concentration affects the reaction time and, as a result, the deceleration of the car. But no less important is the technical condition of the vehicle, as well as the presence of additional systems that increase braking efficiency.
Also, if the driver chooses a safe speed, this can significantly reduce the braking distance of the car. This concerns the actions of the driver.
Additionally, it is necessary to take into account the load of the machine, as well as the capabilities of the braking system. That is, the technical part of the vehicle. Many modern car models are equipped with various amplifiers and additional systems that significantly reduce the reaction path and the time it takes for the car to come to a complete stop. Such mechanisms include brake boosters, the ABS system, as well as electronic assistants that prevent frontal collisions. The installation of improved brake pads and discs also significantly reduces the braking distance.
But no matter how “independent” the car’s electronics or reliable brake system actuators were, no one canceled the driver’s attentiveness. In addition to the above, it is extremely important to monitor the serviceability of the mechanisms and carry out scheduled maintenance in a timely manner.
Stopping and braking distance of a car: what is the difference
Braking distance refers to the distance a car will cover from the moment the driver presses the brake pedal. The beginning of this path is the moment the brake system is activated, and the end is the complete stop of the vehicle.
This value always depends on the speed of the vehicle. Moreover, it is always quadratic. This means that the braking distance is always proportional to the increase in vehicle speed. If the vehicle speed is twice the speed limit, the car will come to a complete stop at a distance four times the average.
This value is also affected by the weight of the vehicle, the condition of the braking system, the quality of the road surface, as well as tread wear on the wheels.
But the processes that affect the complete stop of the car include a much longer period of time than the time it takes for the brake system to respond. Another equally important concept that affects the deceleration of a car is the driver’s reaction time. This is the period of time during which the driver reacts to a detected obstacle. For the average motorist, it takes about one second between detecting an obstacle and pressing the brake pedal. For some, this process takes only 0.5 seconds, while for others it takes much longer, and they activate the brake system only after two seconds.
The reaction path is always directly proportional to the speed of the car. The reaction time of a particular person may not change, but depending on the speed, during this time the car will cover its distance. These two quantities: braking distance and reaction path together form the stopping distance of the car.
Getting the car out of a skid
Skidding is a process in which the rear of the car deviates from the main trajectory to the right or left. In the event of a severe skid, it is possible that the car may spin on the roadway and be thrown off the road.
A car skidding on a slippery road can be caused by one of three reasons:
- Sharp braking;
- Sharp acceleration with wheel slipping;
- Sharp turning of the steering wheel at too high a speed, which does not correspond to the condition of the road.
It is important to know! To get out of a skid, you must first eliminate the reason why it occurred - stop braking, ease your pressure on the gas pedal, or turn the steering wheel in the opposite direction.
After the cause of the skid has been eliminated, the driver can only restore the correct trajectory. This is done differently on different types of cars.
However, in any case, the main action is to turn the steering wheel in the direction of the skid. To quickly turn the steering wheel to a sufficient angle, you need to hold it slightly above the middle of the steering wheel.
It is important to know! During a skid, you can only use the steering wheel and the gas pedal. Under no circumstances should you press the brake and clutch pedals.
On rear-wheel drive vehicles (trucks, as well as Mercedes and BMW cars), you need to smoothly release the gas and turn the steering wheel properly in the direction of the skid. When the trajectory begins to recover, turn the steering wheel back to a smaller angle.
On front-wheel drive cars (most passenger car models), you need to set the steering wheel in the direction you want the front wheels to move and gradually apply the gas so that the rear axle, which has deviated to the side, does not try to “overtake” the front wheels.
On all-wheel drive vehicles (jeeps, SUVs), you need to turn the steering wheel, as on a front-wheel drive car, and try to find an intermediate position of the gas pedal at which the trajectory will begin to recover.
How to calculate the total stopping time and the final stopping distance?
It is impossible to carry out accurate calculations on an abstract car. Often the braking distance is calculated based on what this value was for a particular car at a certain speed. As we have already said, the increase in braking distance is quadratic to the increase in vehicle speed.
But there are also statistical averages. It is accepted that an average-sized passenger car at a speed of 10 km/h has a braking distance of 0.4 m. If we take this ratio as a basis, then we can calculate the braking distance for vehicles moving at a speed of 20 km/h (the value is 1.6 m) or 50 km/h (the value is 10 meters) and so on.
To more accurately calculate the braking distance, you need to use additional information. For example, if we take into account the degree of tire resistance (the friction coefficient for dry asphalt is 0.8, and for an icy road - 0.1). This parameter is substituted into the following formula. Braking distance = square of the speed (in kilometers/hour) divided by the friction coefficient multiplied by 250. If the car is moving at a speed of 50 km/h, then according to this formula the braking distance is already 12.5 meters.
To obtain a specific figure for the driver's reaction path, there is another formula. The calculations are as follows. Reaction path = car speed divided by 10, then multiplied by 3. If we substitute the same car moving at a speed of 50 km/h into this formula, then the reaction path will be 15 meters.
The car will come to a complete stop (the same speed of 50 kilometers per hour) in 12.5+15=27.5 meters. But these are not the most accurate calculations.
Thus, the time of complete stop of the vehicle is calculated by the formula:
P (full stop) = (multiplier of the braking efficiency coefficient and initial braking speed divided by the multiplier of free fall acceleration and the coefficient of longitudinal adhesion of tires to asphalt) + driver reaction time + response period of the brake system drive + multiplier of the braking force rise time by 0.5.
So, as you can see, the determination of a complete stop of a car is influenced by many factors, which can be completely different depending on the situation on the road. For this reason, once again: the driver must always control what is happening on the road.
Different braking conditions
Let's consider the following conditions:
- wet asphalt, snow, ice,
- dry asphalt.
Dry asphalt
On dry asphalt, the tire's adhesion coefficient is 0.7–0.8. This is an excellent indicator.
Wet asphalt, ice, snow
On wet asphalt the coefficient of adhesion is 0,4–0,5.
Determining car speed using braking distance
It is quite difficult to calculate using the formula. To determine the speed of the car, you can use special online calculators. You can find such an online calculator in a search engine.
Online calculators are designed taking into account all requirements. They take into account all the data and formulas.
You only need to enter the following data:
- braking trace length,
- type of road surface,
- vehicle load level,
- car type,
- movement speed.
Next, the online calculator will do all the work for you.
Now let's look at the formula for determining the speed of movement. Formula : 0.5 x t3 x j + √2Syu x j.
Description:
- Syu is the length of the trace,
- j - this symbol indicates the deceleration of the vehicle when braking,
- t3 is the increase in deceleration of the car,
- Va is the initial speed of the machine.
How to increase the intensity of deceleration
To minimize braking distance in different circumstances, the driver can use one of two methods. A combination of these methods would be best:
- Driver discretion. This method assumes the driver’s ability to anticipate dangerous situations and choose a safe speed limit and the correct distance. For example, on a flat and dry road, the Moskvich can be accelerated, but if the road is slippery and winding with a large flow of cars, then in this case it would be better to reduce the speed. Such a car will brake less effectively than a modern foreign car. It is also worth paying attention to what braking technique the driver uses. For example, in a car that is not equipped with any assistance system, such as ABS, pressing the brake hard all the way down often results in loss of traction. To prevent the car from skidding on an unstable road, it is necessary to use engine braking in a low gear and intermittently press the brake pedal.
- Car modification. If a car owner equips his vehicle with more efficient elements on which braking depends, then he will be able to increase the intensity of the deceleration of his car. For example, you can improve braking efficiency by installing better brake pads and discs, as well as good tires. If the car allows you to install additional mechanisms or even auxiliary systems (anti-lock braking, braking assistant), this will also reduce the braking distance.
Fuel economy
When driving two identical cars along the same route, different drivers will use different amounts of fuel. The art of economical driving consists of many secrets. Here are some simple rules:
- Keep your car in good condition;
- Refuel with quality fuel;
- Use first gear only when starting from a stop and on very steep inclines;
- Do not delay shifting gears when accelerating. The last gear is the most economical;
- To reduce speed smoothly, do not use the brake pedal, use engine braking;
- Try to avoid unnecessary braking and stopping.
It is important to know! Pressing the gas pedal sharply always leads to excessive fuel consumption and harms your car. Any braking converts useful energy intended to move the car into useless energy that impedes this movement. Especially a lot of energy is lost during sudden braking.