Before we begin, it is necessary to make a small digression. No one can deny the fact that the fuel pump in a car’s design is one of the most important elements. Without which the car will not function, and malfunctions will lead to unstable engine operation.
It is worth noting that gasoline pumps can be divided into mechanical and electric. However, this article will not discuss mechanical fuel pumps due to the fact that they were used on older cars and cannot be found in modern cars.
How does an electric fuel pump work?
In the Photo: submersible fuel pump with a disassembled glass
Operating a car fuel pump
As we have already found out, a gas pump is a simple and unpretentious device. However, due to its compact size and high load, the pump requires special conditions for its operation. Firstly, its durability depends on the quality of the fuel, or more precisely on its cleanliness and the performance of the filtering system. Therefore, refueling with dirty, poor quality or contaminated fuel should not be allowed. Any specks of dust or particles can affect the integrity of the mechanisms.
To do this, it is necessary to regularly inspect fuel filters and screens that do not allow foreign elements to pass through. In addition, modern cars use submersible pumps, which are located directly inside the tank and are cooled by the fuel itself. Therefore, it is unacceptable to operate the car on an empty tank; overheating will certainly cause pump failure.
Symptoms of malfunction
Firstly, failure to comply with the rules for cleanliness, quality and availability of fuel in the tank will lead to pump failure, but other malfunctions associated with the fuel pump may also occur. But first, you need to understand the symptoms that will indicate a fuel pump failure.
First of all, you should pay attention to the unstable operation of the motor. The reason for this may be insufficient pressure in the fuel system due to the pump. At the same time, the car may gradually lose power or drive sharply, either normally or not at all.
Another sign of a malfunction or imminent breakdown of the fuel pump is the appearance of noise in the rear of the car. Strong buzzing sound from the fuel pump. Especially when you turn on the ignition, this is the first signal to replace it. Moreover, if you didn’t even pay attention to his work before.
In the Photo: The process of replacing a submersible fuel pump
Another sign of unstable operation is problems starting the engine. However, in such a situation there can be many reasons. From problems with the wiring of the entire car, to a malfunction of the motor itself or the electronic part of the control unit.
And the main sign of a malfunction is the complete inability to start the car, and complete silence in the fuel tank area when the ignition is turned on and attempts to start the engine.
How to find a breakdown
To start troubleshooting, you will have to know the entire structure of the fuel system. After all, a breakdown can occur not only in the fuel pump, but also in other elements of the fuel system. The entire fuel supply circuit consists of: a fuel tank with a fuel pump, fuel carrying pipes and hose, a fuel filter, injectors or other injection system and a return circuit of the fuel system.
If there is a suspicion of a drop in pressure in the fuel system, then the malfunction could occur in one of these elements. Next we will briefly go through each of them.
Fuel tank
In most modern cars, the fuel tank is a sealed container with a pressure release valve. However, the pressure in the tank is maintained and helps the entire system operate. But there are cases when the valve in the tank cap stops functioning normally and pressure disappears in the fuel tank or excess pressure accumulates. In this case, the entire system may not work correctly.
In addition, the tank may leak due to damage or corrosion. In this case, in addition to increased consumption and loss of pressure in the tank, there is a high probability of fire.
Fuel pump malfunction
The device itself can fail for a number of reasons:
• The gasoline pump has already exhausted its service life and the membrane with all its elements is not capable of pumping the required amount of fuel and maintaining the nominal pressure in the system.
• The valve responsible for maintaining constant pressure in the fuel system has failed and is constantly leaking fuel. Because of this, the engine does not receive enough gasoline and power decreases.
• The clogged mesh at the inlet to the fuel pump has become very dirty and has stopped passing a sufficient amount of fuel. In this case, in addition to reducing engine power, the fuel pump itself begins to work with increased load, which leads to rapid breakdown.
In the Photo: Filter mesh clogged with various dirt
• Also, the electrical wiring to the fuel pump may be damaged, or the contacts on the terminals of the device itself may be oxidized. But first of all, you should check the fuse in the cabin unit. If you successfully replaced the fuse with a new one, and it burned out again, you will have to carefully check the electrical wiring.
Symptoms of a faulty fuel pump
Fuel pump for VAZ
Actually, these are rather two stages of the same malfunction, although it happens that malfunctions in the operation of the fuel pump do not lead to its complete failure. Especially when these failures are caused by some extraneous factors. And so, the fuel pump either simply fails or does not work at all. These are all his breakdowns. Another thing is that there are many breakdowns of other elements, which in their symptoms are very similar to fuel pump breakdowns.
As for the signs of a fuel pump malfunction, there can be a lot of them, and as already mentioned, they may coincide with symptoms of problems in other components and systems of the car. Therefore, we will describe only the most common and most characteristic of these symptoms.
- the car does not start or stalls frequently;
- engine troits;
- extraneous noise in engine operation;
- drop in engine power;
- absence of characteristic noise when the fuel pump operates;
The signs are very eloquent, but it’s not always possible to understand what they are talking about. And here we cannot do without methods for diagnosing the fuel pump.
Gasoline supply problems - common symptoms
Malfunctions of the fuel supply system are conventionally divided into 2 categories:
- The combustible mixture is not supplied to the cylinders at all.
- Gasoline is supplied intermittently or under insufficient pressure.
In the first case, the engine does not start and does not engage the starter during rotation, that is, it does not show signs of life. In such a situation, it is always easier to determine the cause of the breakdown.
When insufficient fuel enters the cylinders, the following symptoms appear:
- starting the power unit “from cold” is very difficult, the engine seizes and “sneezes”, it starts in 3–10 attempts;
- idling is unstable, the engine “troubles”;
- dynamic acceleration becomes impossible - a sharp opening of the throttle causes a long dip and deceleration;
- when the driver releases the accelerator pedal, the engine often stalls;
- The car has difficulty climbing hills and accelerates slowly when fully loaded.
The cause of the above phenomena may be a malfunction of the fuel pump or other elements of the system, and the primary symptoms are almost the same. To carry out an accurate diagnosis, you need to understand how the car's power system works.
How to determine if a fuel pump is faulty
Be that as it may, most of the signs indicating a fuel pump malfunction may indicate problems in other systems and components of the machine. The car is malfunctioning - maybe the spark plugs, maybe the ignition, maybe some sensor is acting up. Extraneous noise in the engine can generally be caused by various breakdowns. Even when the engine stalls immediately after starting, you cannot blame only the fuel pump. For example, without readings from the crankshaft position sensor, the ECU can stop the pump, which is quite a normal car reaction to such a problem. And even a decrease in pressure in the system can be caused by leaks in the fuel lines, breakdown of the bypass valve and other failures.
Similar symptoms not related to the fuel pump
The symptoms that appear due to a lack of fuel in the supply line are quite typical and are very similar to problems with other systems. How to eliminate possible problems using the elimination method:
- Unscrew and inspect the spark plug skirts. When there is not enough fuel, the electrodes remain clean or become covered with a white coating. This is further evidence of a malfunction in the power system.
- Replace spark plugs. If they wear out, they create a similar effect - failures, difficult starting, and a drop in engine power.
- Check the functionality of the throttle position sensor (TPS) and idle air control.
- Measure the compression in all engine cylinders. Due to excessive wear, the naturally aspirated engine is unable to create the required pressure and vacuum; the mixture burns poorly, which is why identical symptoms occur.
Preventing fuel pump malfunctions
What should you pay attention to so that the fuel pump runs as long as possible? First of all, this is the quality of the fuel and, of course, timely replacement of the fuel filter. If the gasoline you fill contains various foreign inclusions, this will most likely negatively affect the condition and service life of the fuel pump, and not only it. Therefore, it is not worth saving on the quality of fuel, since such savings then result in very significant expenses for car repairs.
Monitor the fuel level in the tank. The fact is that the fuel pump is cooled by the same gasoline that it pumps. Accordingly, if there is little fuel, or the pump runs idle, it may overheat and therefore fail. Knowledgeable people also advise cleaning the gas tank at the appropriate time and not neglecting this procedure. This is, perhaps, all the prevention of problems with the fuel pump.
Preliminary checks
Before checking your fuel pump, review this checklist. This includes some obvious things and often forgotten common maintenance problems that can turn into false diagnoses.
- Check for fuel in the tank. If the engine turns over but does not start, make sure there is actually fuel in the tank.
- Listen to the noise of the fuel pump. You can usually do this test yourself from inside the car. When you turn the ignition key to the ON position (engine off), you will hear the fuel pump come to life for approximately 2 seconds. If you cannot hear the pump running, seek help from an assistant and follow these steps:
- Remove the fuel tank cap.
- Place your ear close to your throat.
- Have an assistant turn the ignition key to the ON position, but do not start the engine.
- You should hear a whirring sound coming from the tank for about two seconds. This is the sound of the fuel pump turning on. This means the pump is receiving power and responding.
- If you do not hear this sound, but the engine starts when you try to start it, there may be a problem with the fuel pump electrical circuit. Check the pump fuse, fuel pump relay and, if necessary, wiring and other related sensors that the engine control module (vehicle ECM) relies on to turn on the fuel pump, such as the camshaft position sensor.
- Check the car's computer for stored diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) in the computer that may indicate the direction of the problem.
- If you think there is an electrical problem and the fuel pump fuse is good, try switching the fuel pump relay with another similar relay in your vehicle and try starting the engine.
- On some vehicle models, insufficient engine oil pressure prevents the engine from starting to prevent engine damage. Check all stored DTCs. If necessary, the vehicle repair manual for your specific vehicle make and model will help you perform this check.
- Make sure the timing belt is in good order. If the engine turns over but does not start and the engine is using the timing belt, check that the belt is still in place or not loose. On average, a timing belt has a service life of about five years. On some models, checking the timing belt is a simple procedure. By removing the cover or pulling it slightly, make sure the belt is in place. If so, have a helper crank the engine while you watch the belt. Make sure the belt moves smoothly.
- Check if the fuel filter is clogged. Have you changed the fuel filter according to your car manufacturer's service schedule? Check the service interval for this filter in your vehicle's owner's manual or vehicle repair manual. Replace the filter if necessary to ensure that you are not dealing with a fuel filter that is not allowing fuel into the engine.
- Check the vacuum line to the fuel pressure regulator (FPR). Disconnect the vacuum line from the fuel pressure regulator (FPR). This is a small metal cylinder connected to the fuel rail. Make sure that the vacuum line is free of fuel and that it is completely dry (if possible, perform this check with the engine idling). If the inside of the vacuum hose is wet, it is sucking fuel from the pressure regulator because the diaphragm is torn. Replace the fuel pressure regulator.
We recommend reading: The car jerks during acceleration, why and what are the reasons
Fuel pressure regulator on the fuel rail (bottom assembly).
- Make sure there is fuel in the fuel lines. On EFI models you can do this by pressing the Schrader valve or "test port". You will find a valve somewhere along the fuel rail that holds the fuel injectors in place. Cover the valve with a rag and use a small screwdriver to press down on the valve. Use a rag to catch any leaking or splashing fuel. If there is fuel in the line, this simply confirms that the fuel pump is delivering fuel, although not necessarily in the right amount.
- On throttle body injection (TBI) models, you can see fuel being sprayed into the throttle body by removing the air filter housing and observing the injector while an assistant starts the engine.
- If your system does not have a Schrader valve and the engine will not start, remove the fuel pump fuse and crank the engine for a few seconds. Disconnect the fuel line from the fuel rail and route the end of the line into a fuel container (if it is a steel line, you can connect a short length of hose to the line). Turn the key to the ON position or crank the engine. If the pump is delivering fuel, it is working, but this does not confirm that the pump is delivering enough fuel, although if the pump is not delivering fuel, you may have a clog, a restriction in the fuel line, a problem with the fuel pump electrical circuit, or a faulty pump.
Tip 1: When the engine stalls after a few minutes of running
If the engine stalls within a few minutes of starting and does not start until the engine cools, perform the following check as soon as the engine stalls:
- Open the hood and pull out the spark plug wire.
- Grasp the wire using insulated-handled pliers.
- Position the tip of the wire about a half inch to an inch from the bare metal motor or metal bracket (a grounded location is required).
- Have a helper crank the engine or use the remote starter switch.
- Is there a spark coming from the end of the wire?
- If there is no spark, you may have a bad ignition coil. If it sparks, you may have a bad fuel pump.
Tip 2: Check the inertia switch
Ford vehicles - and some others - use an inertia switch to shut off the fuel pump when the vehicle is involved in a collision. But other events can trigger the switch:
* Hit the bumper
* Driving through a pothole
* Even a small bumper bump in a parking lot
So check your vehicle's owner's manual or vehicle repair manual to find out where the switch is located and how to reset it if necessary.
Video on the topic
The fuel pump is one of the main components of a car. Without it, it is simply impossible to start the engine, much less operate it. Therefore, if you have any problems starting or operating the engine, you first need to check the fuel pump. To find out how to check a gas pump, you must first determine the basic principles of operation of this unit and possible breakdowns. As a rule, the fuel pump is not repaired and is replaced by a working one. However, it is necessary to identify that this is where the problem lies.
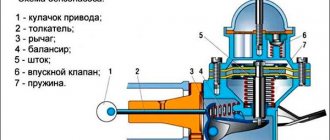
How does an electric fuel pump work?
To constantly maintain the correct pressure in the fuel rail, the electric fuel pump must always operate when the ignition is turned on. The uninterrupted supply of fuel to the combustion chambers of the engine depends on it.
As soon as you get into the car and turn the key in the ignition, this unit immediately starts working - even before the starter starts cranking. When you turn off the engine, the fuel pump also turns off - this ensures safety in emergency situations and in case of an accident. Excess fuel is released back into the tank through a special bypass valve.
Having a given pressure in the fuel rail, it is easy to dose the fuel supply to each specific cylinder: at the right moment, the “brains” of the car send a command to one or another injector, its solenoid valve opens for a few milliseconds, and the fuel flows by gravity into the combustion chamber through tiny holes. All the car's ECU needs is to calculate the time during which the injector valve should remain open. When the pressure in the rail drops, the fuel supply is disrupted, which leads to numerous problems, which we will discuss below.
The principle of operation of the fuel pump
Schematic diagram of a fuel pump
The main function of a fuel pump is to transfer fuel from the tank to the engine. In injection engines, the fuel pump is connected to the fuel rail, and in carburetor engines - to the carburetor. In this case, it is necessary not only to pump fuel, but also to provide a certain pressure. Too high pressure leads to increased richness of the mixture and high fuel consumption. Too low pressure leads to a lean mixture and a drop in power. Both the first and second cases negatively affect the engine life. That is, the fact that the gas pump pumps fuel does not indicate its full serviceability.
Design and operation of fuel supply
The system that provides the engine with the required amount of gasoline operates according to the following algorithm:
- After turning on the ignition, the electric fuel pump starts, raising the pressure in the line after itself to a certain level. The electrical power supply circuit of the unit is protected by a fuse.
- The fuel pressure regulator (common abbreviation - RDT) is located on the line after the pump and limits the upper pressure threshold, dumping excess fuel back into the tank through a separate pipeline.
- When the crankshaft is rotated by the starter and the engine continues to operate, fuel enters the fuel rail, mixes with air and is directed to the injectors built into each cylinder. The amount of mixture supplied to the combustion chambers is controlled by an electronic unit.
- On the way to the fuel rail, gasoline goes through 2 stages of filtration. The first is a mesh installed in the tank on the suction pipe of the pump, the second is a fine filter on the gas supply line.
Reference. In various car models, 2 schemes are used for installing the RTD and laying the return pipeline - in the engine compartment or directly in the gas tank. In the first case, the standard fuel pressure in the system is 2.7...3.0 Bar, in the second - 3.8...4 Bar.
A common mistake made by ignorant car enthusiasts: if the combustible mixture does not enter the cylinders, then the fuel pump is definitely not working. Knowing the design of the fuel supply, we can assume other problems:
- the protective fuse in the electrical circuit has blown, the pump is in good working order, but does not receive power;
- the primary or secondary filter is clogged (sometimes both at once), fuel flows in small quantities or does not flow at all;
- the pressure regulator has become unusable, dumping the lion's share of the fuel back into the tank, the engine gets nothing;
- One or more injectors have failed.
To accurately determine the source of the problem, you need to check the operation of the electric fuel pump and other elements. It is not necessary to go to a service station - diagnostic work can be carried out in your own garage.
When should you check your fuel pump?
It is necessary to check all potentially faulty components one by one, and the fuel pump first.
Problems when starting and running the engine are not always associated with the fuel pump. Sometimes the signs of a fuel pump breakdown are the same as those of a faulty fuel pressure regulator , injectors or jets, spark plugs and high-voltage wiring. Even experienced specialists who know by heart all the signs of a “dying” pump cannot unambiguously determine the type and cause of the breakdown the first time, and it is necessary to check all potentially faulty components one by one. In this case, the fuel pump is usually checked first. In this case, there are two types of malfunction - the fuel pump does not work at all or does not produce the required pressure. In the first case, the malfunction can be recognized by ear, since it should start when the ignition is turned on. In the second case, you need to know how to check the pressure of the fuel pump. Here you need to use a special pressure gauge. We list the main symptoms of a fuel pump malfunction:
- the engine does not start;
- the engine is unstable;
- the engine lacks traction during sharp acceleration;
- The engine lacks traction at low speeds.
How to check the functionality of the pump?
If the engine is absolutely “dead”, follow this algorithm:
- Turn on the ignition without turning the starter. A working electric fuel pump should respond with a quiet but distinct buzzing sound coming from the rear row of seats. If there is no sound, go to the next step.
- Using the car's operating instructions, find the number of the fuse that protects the pump's power circuit. Try replacing it; if unsuccessful, check the wiring and clean the contacts from oxides.
- If previous manipulations did not produce results, you need to measure the fuel pressure in the fuel rail.
Pressure measurement is also practiced when identifying symptoms of insufficient fuel supplied to the cylinders of the power unit.
To take measurements and compare signs of a breakdown with a fuel pump or other element, you need to reset the initial fuel pressure in the system, no matter how low it turns out to be.
If the pressure is below normal, proceed to find out the reasons according to the recommendations:
- There are pressure surges in the range of 0.2...0.3 Bar at idle - look for a problem in the filters. Surely the coarse mesh or secondary element is clogged.
- Use pliers to pinch the return line hose coming out of the RTD. The gasoline pressure should increase to 5 Bar, with the new pump - to 6 Bar. If the readings are 4 Bar or lower, the cause should be sought in the regulator or the pumping unit itself.
- The best way to identify a fuel pump malfunction is to exclude other parts of the system and take a measurement directly at the outlet fitting. If the pressure gauge shows 5 Bar, the unit is working properly and you need to change the RTD, which dumps half of the fuel into the tank.
To measure the pressure at the outlet of the electric fuel pump, you will need to remove the rear seat, dismantle the service hatch and connect a pressure gauge to the supply fitting of the unit. Here you may need adapters in the form of plastic clamps or threaded tubes.
Before changing the pressure regulator, make sure that the gas lines and filters are of normal capacity. Due to refueling with low-quality fuel, even the flow area of 8–10 mm tubes can become clogged. Then the pressure gauge on the ramp and pump will show different values, and the RTD will regularly drain excess fuel into the tank.
The main causes of fuel pump failure
The coarse filter is clogged
Old and new fuel pump coarse filter
A clogged filter is brown in color because its cells are completely clogged with sediment.
The most common problem that causes the fuel pump to not pump is a clogged coarse filter. This filter is usually installed in the tank immediately before supply to the pump itself. This is where primary fuel filtration occurs. This malfunction can be determined visually. A clogged filter is brown in color; the cells in its mesh are almost completely clogged with sediment. Even a working pump cannot pump fuel through such a filter; as a result, the required pressure is not provided in the system. The coarse filter must be replaced. Its cost is low (about 50 rubles). However, replacing it takes time and a set of tools. First you need to remove the fuel pump itself, which is usually screwed to the tank. Before removing the fuel pump, you need to disconnect the terminal on the battery. Then the fuel pump is removed and the filter is removed from it. The filter itself is installed on the pump manually, without tools. It is recommended to change the coarse filter every 20 thousand. However, it can become clogged much faster. This depends on the quality of the fuel and the condition of the fuel tank. It only takes one refuel with low-quality fuel at an untested gas station to clog the filter. It can also easily become clogged with rust if the tank is already old and susceptible to corrosion.
What types of fuel pumps are there for cars?
All existing fuel pumps can be roughly divided into two groups: mechanical type pumps and electrical systems. Mechanical devices do not have their own motor; they are mounted on the engine and connected to one of the constantly rotating systems. Such devices have been used before; they do not provide normal pressure maintenance. Also, similar devices are used in some diesel engines as a system for maintaining pressure (paired with an injection pump).
Electric pumps work on a different principle. They are autonomous, driven by electricity, and pump up pressure even before the driver starts the car. If you read the instructions, many manufacturers recommend not starting the car until most of the icons on the dashboard have gone out. This not only allows the on-board computer to boot up, but also gives the fuel pump time to build up the required pressure for safe starting.
Things to keep in mind about these types of fuel pumps:
- vacuum type - the device is similar in design to the old mechanical type, but is driven by an electric drive, which ensures autonomy; it is almost never used in modern cars;
- roller - in such a complex the rotor rotates, which creates a suction effect in the pump body, the cycle is repeated continuously while the car engine is running;
- gear - a design option similar to the previous type, but a rotor gear is used as the main working mechanism;
- centrifugal - a popular type that works by rapidly rotating special blades, creating excess pressure and maintaining its relative stability;
- plunger - a complex and rare option for gasoline engines; in most cases, a similar design is found on diesel engines as an injection pump; its reliability is very dependent on the quality of production.
It is also possible to conditionally divide all fuel pumps into remote and submersible. The remote ones are mounted in the engine compartment, on the bottom of the car, in the cabin along the direction of the fuel lines. Submersibles are mounted in the tank along with all the necessary electronics. The advantage of remote equipment is that it is much easier to access. Submersible systems often require removal of the tank, but some manufacturers have implemented the ability to service the pump from inside the cabin.
Also, each manufacturer tries to develop their own changes to the design of pumps, making them unique. This often leads to a number of problems. For example, there are known difficulties in operating fuel injection pumps on Ford cars after changing the standard design of the high-pressure pump to proprietary equipment. Opel, GM, Peugeot had the same problems, but very few diesel engines from these manufacturers were sold in Russia.
Which fuel pump to install on a VAZ 2114
On the VAZ 2114 and others of this family, they are installed from Bosch or Denso, since the original fuel pump only comes complete with a module (article 21102-1139009-02). Other manufacturers may be preferred only for reasons of economy.
| Manufacturer | vendor code | Average price, rub. |
| SAT | STFP06 | 799 |
| MEAT DORIA | 76416 | 1056 |
| DENSO | DFP0105 | 2504 |
| BOSCH | 80453453 | 2899 |
Tool required for work
- 10mm wrench;
- Screwdrivers “+” and “-“;
- Construction hair dryer;
- Passatizhi;
- Fuel container.
Repair of fuel pump VAZ 2114/2115
When repairing the fuel pump, we will proceed from the fact that we have already removed the fuel pump from the tank. How to properly dismantle the device will be written below, but we will dwell in more detail on the description of the progress of the repair work:
You will need to remove the protective cup from the module - to do this, you will have to pry the cup latches with a screwdriver, and the fuel pump will come out freely.
We unscrew the two screws from the fuel pump housing that secure the fuel level sensor, then disconnect the cable of wires coming from the sensor and put it aside.
Next, you will need to disconnect the filter mesh from the pump using a flat-head screwdriver.
To complete the disassembly, you need to remove the housing itself from the device - there is a cotter pin on the surface that needs to be pulled out.
Models of fuel pumps for VAZ 2114/2115 cars
VAZ 2114/2115 cars are equipped with 1.5 cm 3 and 1.6 cm 3 gasoline engines with a distributed injection system. A submersible electric fuel pump is used to supply fuel. It is part of the fuel module installed at the top of the gas tank (under the rear seat). In addition to the pump, the module includes a fuel accumulator (cup), a coarse filter and a fuel level sensor with a float.
To supply fuel in VAZ 2114/2115 cars, a submersible electric fuel pump is used
The VAZ 2114/2115 fuel pump is a conventional DC electric motor in a sealed housing with a one-way valve at the outlet. An impeller of a special shape is located on the electric motor shaft. Its rotation ensures the fuel supply.
The fuel module includes a fuel pump, a fuel accumulator, a coarse filter and a fuel level sensor
The fuel pump is powered from the vehicle's on-board network. The electrical circuit of the pump, protected by a fuse, is closed using a separate relay.
Electric fuel pumps for VAZ cars are produced by both domestic (Utes, SAAZ, Pekar) and foreign companies. The latest modifications of the VAZ 2114/2115 are equipped with BOSH pumps, which are distinguished by their high reliability, long service life and relatively low price.
Design of the electric fuel pump VAZ 2114/2115
Catalog numbers of standard fuel pumps for VAZ 2114/2115:
- 2112–1139009–12 - for engines with a volume of 1.5 cm 3;
- 2112–1139009–01 - for engines with a volume of 1.6 cm 3;
- 580453453 (BOSH) - for engines with a volume of 1.5 and 1.6 cm 3.
These models differ in operating pressure. The former are capable of creating a pressure of 2.8–3.2 kPa in the fuel system, the latter - 3.7–3.9 kPa. BOSH fuel pumps are rated at 3.5 kPa.