Recently, more and more new devices have appeared in cars, and the absorber is one of them. To comply with the Euro-3 environmental standard, all vehicles are required to have equipment that prevents the release of hazardous substances into the atmosphere that are formed as a result of fuel combustion.
The absorber is of greatest importance in capturing and processing waste vapors in the machine. Every car owner should know its structure and basic principles of operation.
How to properly remove the adsorber
In a car, the adsorber absorbs fuel vapor from the gas tank ventilation system and supplies it to the intake, because according to environmental standards, the gas tank must be isolated from the atmosphere.
From Wikipedia ;
Adsorber (from Latin ad - on, with and sorbeo - absorb) is a device for absorbing (thickening) a surface layer of a solid, called an adsorbent (absorber), of dissolved or gaseous substances, not accompanied by a chemical reaction. The adsorber is used in chemical, oil refining and other industries. The process occurring inside this apparatus is called adsorption.
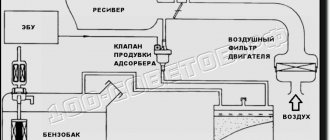
Gasoline vapor filtration system. The diagram is quite conventional, but it reflects the essence. Gasoline vapor from the tank passes through a carbon filter, is cleaned and supplied to the inlet through a solenoid valve controlled by the ECU.
Now the first question is - why filter gasoline vapors if they still go into the intake? The answer is simple - adjusting the internal combustion engine control program by adding the nth number of clean air at the inlet is much easier than making adjustments based on the fuel-air mixture (gasoline vapor from the tank) of an unknown proportion.
And now the answer to the main question - why delete it? So, although some manufacturers claim that this device will have enough resources for the entire life of the car, we know that they are lying)
In general, over time, the adsorber becomes clogged and stops passing air. As a result, we get excess pressure in the tank, which interferes with the normal operation of the fuel pump. In the cabin (sometimes under the hood) we get a periodic smell of gasoline, the vapors of which are squeezed out of the ventilation tube. And the engine starts running on a rich mixture due to lack of air.
Now guess how our country solves this problem? That's right, most people simply throw out the adsorber and turn off the system as shown in the diagram:
A fuel filter from a carburetor classic is usually placed on the tube from the gas tank, and the solenoid valve, through which clean air should flow into the engine, is simply shut off with a bolt.
In the picture I already wrote that this is wrong and here’s why. This method of removing the adsorber only partially solves the problem. Yes, the smell of gasoline disappears, the tank is ventilated, but no air is supplied to the intake and the engine continues to run on a rich mixture.
And now the following diagram:
And now it already shows how it SHOULD be done. The same filter from the classics is put on the hose from the valve to the adsorber, which now serves as an air filter and prevents dirt from getting into the receiver. This is how the fuel-air mixture is brought to normal parameters.
Well, now a couple of visual photos of what it all really looks like:
Everything is clear here, one tube goes to the gas tank, the second through the valve to the engine.
Enter your email and receive emails with new crafts.
Bottom part of the adsorber. There is a fitting for supplying air from the atmosphere so that a vacuum is not created in the adsorber.
So this is all done on my machine. I didn’t take a photo of the tube from the tank, it’s hard to get to it even without a phone
Source
Determining possible damage
We figured out why the adsorber is needed, now let’s determine the signs indicating its failure. Considering the quality of the fuel, at gas stations in our homeland this part is often contaminated and also bad.
Any malfunction of this mechanism can be easily determined by obvious signs:
- Damage to the absorber: problems with this mechanism in your car can be determined by a hissing sound when the reservoir is opened, which indicates the accumulation of excessive amounts of gasoline vapor.
When you open the lid, excess pressure appears in the container; there is a moment when the contact area with the external environment is small and through it the pressure is quickly “relieved” and the container “hisses”, like a bottle of soda.
If the problem is not “treated”, the tank will at some point catch fire with the lid on, in addition to repairing the tank, this promises serious (possibly criminal) liability, because it is impossible to predict where the lid will fly, the speed of which is comparable to the speed of a cannonball.
- Valve failure: There will be a reminder that the engine is unstable at idle, the car will randomly increase (decrease) the actual speed and stop.
If the adsorber breaks down, it is often removed completely; we’ll look at how to do this below, but there are no unnecessary parts in the car, it’s worth remembering. If you don't want to remove and gut the ECU, you can try to repair everything yourself. The weakest point in the absorption kit is the VAZ 2114 valve.
On the VAZ 2115 there was a decrease in speed when driving, the car was out of breath and stuck in motion, after stopping for a while the problem disappeared.
Before repairing, you need to make sure that the problem is here:
- Using a flat-head screwdriver on the motor cover, unscrew the fastener (be careful, the fastener is plastic, do not break it), then carefully remove the fasteners.
- We remove the part and blow out the valve. If there is no air flowing through, the valve is working and the problem is elsewhere, but if air is passing through the valve, you have a problem.
A valve failure, in addition to an unstable idle, will soon introduce you to the CheckEngine and significantly increase fuel consumption.
Is it worth turning off the adsorber, pros and cons, possible consequences
Before turning off the adsorber in a car, it is important to understand how much this will affect the performance of the vehicle, including environmental ones, as well as driving safety.
In the article we will analyze the purpose and operating principle of the adsorber, where it is established, when it needs to be changed and whether it is possible to turn it off and drive without the device, how to properly remove it on a VAZ 2110, 2112, 2114, Lada Priora, Grant, Largus, Gazelle and whether it is necessary to flash the ECU after shutdown devices.
What is the correct name for an adsorber or absorber?
Both concepts exist in the world. But despite the fact that from the Latin “sorbeo” and “absorbeo” are translated almost identically: adsorber - (from Latin ad - on, with and sorbeo - absorb), and absorber - (from Latin absorbeo - absorb), the semantic load both words convey different meanings.
- In our case, we are talking specifically about an adsorber, since this is a device that, with its solid surface, absorbs gaseous or soluble substances without undergoing chemical reactions. There are periodic and continuous devices.
- And an absorber is a device that completely absorbs gases (vapors) inside, followed by a chemical reaction, as a result of which one of the substances is completely absorbed by a special liquid (absorber).
Therefore, for our situation, the first option will be correct.
Purpose and principle of operation
Adsorber - is a container filled with activated carbon, which acts as a filter element. This element is the main part of EVAP - Evaporative Emission Control (gasoline vapor recovery system).
The system has been integrated into the fuel system of cars with Euro-2 standards and higher. Those. you won’t see an adsorber on a VAZ classic or even a 2108 model, not to mention Moskvich, Volga 3110, etc.
The goal is to reduce harmful emissions into the atmosphere and eliminate gasoline odors in the car interior.
But despite the simplicity of the design, in addition to the housing and the filter element, the adsorber consists of:
- Branch pipes: air supply, vacuum, gasoline vapor removal.
- Separator - here the vapors are condensed and drained back into the tank.
- Gravity (emergency) valve – blocks the overflow of fuel when the machine overturns.
- The solenoid valve (or vacuum valve - for example, found on some Nissan models) is one of the important elements (details below).
- Other additional devices (depending on the car model).
Fuel vapors accumulating in the gas tank must go somewhere. In old cars they escaped into the atmosphere through a special tube. In modern vehicles, fuel tanks are isolated from the external environment.
Gasoline vapor, through a separate outlet pipe, enters the adsorber and condenses there in the form of fuel, which is returned back to the tank or to the intake manifold. In the first case, the process occurs with the engine turned off, in the second - with the engine running.
As soon as the car starts, the ECU sends a signal to the solenoid valve. The latter opens and the activated carbon (sorbent) is purged. Fuel vapors are “extracted” from the sorbent and immediately enter a special receiver and then into the combustion chamber.
To find out more about what an adsorber is, follow the link.
Adsorber - what is it? What is an adsorber for? Adsorber - malfunctions
With the advent of cars that meet the Euro 3 environmental standard, car designers were faced with the task of creating a device that traps hydrocarbon vapors in order to prevent their penetration into the atmosphere. So, an adsorber began to appear in the fuel system of many cars, including domestic ones. What is it and how does this part work? You will find out the answers to all these questions in our article.
Where it is located?
A part such as an adsorber is a small black can a few centimeters high. It is installed on almost all cars under the air intake on the right side of the engine compartment.
Adsorption Characteristics
What is an adsorber for? In general, adsorption is the process of absorbing gases using liquid or solid bodies. In our case, the main element that “absorbs” vapors in the fuel system is coal. Part of this device is filled with it.
Adsorber - what is it? Visual characteristics
The word “adsorber” itself translated from English means “to absorb”, “to absorb”. By its design, this part is an energy-absorbing plate. Externally, you may not immediately be able to tell that the bumper is not solid - inside it there is a special filler made of polymer materials.
This part of the device (bumper) is considered the main one and converts mechanical energy into thermal energy, which is then dissipated in the external environment. The plate located in the adsorber bears a lot of responsibility, which is why many manufacturers place such stringent requirements on its technical characteristics and the properties of the entire device as a whole.
The main material used in the manufacture of this element is cellular plastic or expanded polystyrene foam. Recently, manufacturers have begun to use glass beads. The quality of the material itself is also strictly controlled, since the health of many people depends on it. For this reason, the adsorber (you can see a photo of this device below) is equipped only with high-quality bumpers.
But the safety and health of people depends not only on this. In order for the adsorber to perform its functions efficiently on a VAZ Kalina car, it is necessary to reduce the risk of damage to the rear bumper to zero. This part is a power element, and it is it that “bears the blow” that can cause mechanical damage. And if the device is broken or punctured, it can no longer be allowed to be used. This is because with each blow the adsorber (including the 2110 VAZ) loses its ability to absorb emissions.
Adsorber - what is it? About the design
This part consists of several structural elements:
- Front steam pipe.
- Several hoses.
- Purge valve.
- Vapor separator and fuel drain pipe.
- Gravity valve.
- Canister tubes and purge valve.
- Adsorber.
Principle of operation
The adsorber's action algorithm is as follows. Fuel (gasoline) vapors that form in the tank, due to their properties, rise upward and, due to the absence of any container at the neck, first enter the separator. This is where the condensation process takes place. That is, the vapor turns back into liquid and flows back into the tank. The part that did not have time to transform from a gaseous substance into a liquid substance ends up in the adsorber itself. Here the system absorbs these excesses using activated carbon.
It is worth noting that this process occurs only when the engine is turned off. Otherwise, the system will open the canister purge solenoid valve to perform purge. In this case, all gasoline vapors that formed in the tank and did not have time to turn into a liquid state are blown out through the intake pipe of the internal combustion engine and burned.
Where is it installed?
As a rule, the adsorber is installed under the hood on the right in the direction of travel of the car, for example, in the VAZ 2110 it is in the form of a barrel.
In other cars, it can be square and installed to the left of the engine (in the direction of travel), under the air duct (Lada Granta), the vacuum brake booster (some Nissan models) or in the radiator area. For VAZ 2114 it is located near the battery and air filter.
On the Volkswagen Passat B3, the adsorber is located under the air filter on the right side in the direction of travel.
Other vehicles - see your model's owner's manual.
How to disable or remove the adsorber on a car and do you need to reflash the ECU?
You need to understand that when the adsorber is removed, the solenoid valve is turned off, which is directly connected to the controller and controlled by the latter.
This will lead to error p0443, which we already mentioned above. The tubes are also silenced, in particular the one that goes to the intake manifold.
What is the disadvantage of such a shutdown?
The fact is that through the tube that goes to the intake manifold, air is constantly sucked in; even in idle mode, the so-called small purge of the adsorber occurs. At high speeds from 1500 – 2000 and above there is a lot of purging.
In the ECU firmware, constant air leaks and the flow of fuel vapor are taken into account when forming the air-fuel mixture, despite the fact that all this goes past the mass air flow sensor, the causes of the malfunction of which can be found out by clicking on the link.
If you plug the pipe, which many people do, a certain amount of air will not flow into the intake manifold bypassing the ECU, but the latter still takes them into account.
That is, the controller takes into account one volume of air, but another (smaller) one actually enters. As a result, the amount of fuel is generated by the ECU based on more air than is supplied. This leads to an over-enrichment of the air-fuel mixture.
As a result, the engine does not work correctly, because the mixture is constantly over-enriched where it is and is not needed, and fuel consumption increases.
It is also worth talking about the transient mode of operation of the engine, which can manifest itself when approaching an intersection, a traffic light, lying to a policeman, at the moment when the gas is released.
At this moment, a failure may occur - a decrease in speed below idle. The engine seems to choke, it doesn’t have enough air, the reason is an over-enriched mixture. After a few seconds, the situation is resolved electronically.
Therefore, it would be correct to disable the adsorber in the following ways:
- After removing the device, install a nozzle with a diameter of 1 mm into the tube that goes directly past the mass air flow sensor. This will, at least partially, solve the problem, since only air without gasoline vapors will be supplied in doses.
- The ECU is being reflashed (difficult). If it is impossible to remove the Check error, you may need engine chip tuning, which is expensive.
- Dismantling the entire system except the solenoid valve, which operates idle.
- By installing a resistor (valve emulation) in the electrical circuit at 200 - 250 Ohms and 2 watts. To do this, bend the legs of the resistor and insert them into the valve chip. We secure everything with electrical tape. But this doesn't always help.
How to check the valve
In order not to struggle with symptoms in the future, the valve is checked periodically. You can notice that it is not working properly by its characteristic sounds. Many people think that the clicking sounds when an internal combustion engine is running are made by the rollers or timing belt, but a similar sound can also be produced by the adsorber valve when it is not functioning properly. In order to check whether it really makes the appropriate sounds, just press the gas pedal. If the sound does not change when you press the gas pedal, then this is the reason.
In order to understand how to correctly diagnose a device, you need special equipment.
In order to make sure that the adsorber valve is faulty, you can pay attention to the characteristic symptoms:
- When the engine is idling, there are noticeable dips;
- The inside of the car smells of gasoline;
- When the gas tank cap is opened, a hissing sound is heard;
- The engine runs poorly.