03.03.2022 3 133 Timing
Author: Victor
A gas distribution mechanism (GDM) is a unit that consists of many structural elements that work synchronously. In this article we will tell you what decoding is used for the timing belt and what the operating principle of the mechanism as a whole is.
[Hide]
The main reasons for drive belt failure
– Over-tensioning of the belt during installation. As a result, its material is subject to increased stretching, and the rollers and bearings of the mechanism are subject to increased pressure, which will lead to faster wear.
– Replacing the belt without replacing the rollers in a timely manner. As a rule, the interval for replacing the timing belt and its rollers is considered mutual, but some drivers do not do this in order to save money. The consequences of such savings can be very unpleasant.
– Operation in hot climates. If you drive a car in climate zones with high temperatures, manufacturers of rubber products strongly recommend replacing drive belts earlier than recommended.
– Violation of the tightness of the protective casing. The slightest amount of dirt, road dust or petroleum products gets into the gas distribution mechanism, its service life is significantly reduced.
– Relaxation of tension. During the operation of the car, it is recommended to check it with tension diagnostics halfway through the life of the belt. If weakening is detected, tightening should be done.
The most popular brands of Timing Belts
Domestic motorists most prefer the following belt companies - Dayco, Gates, Contitech, Bosch, Lemforder and Balakovo.
Information about manufacturers
Dayco is an Italian company founded in 1905 in Dayton, Ohio (USA). The main direction of the manufacturer is the production and development of drive belts, hinges and roller mechanisms. Country of origin: Italy.
Gates is the largest market leader in the production and sale of drive belts for various purposes. Products of this brand can be found not only in the automotive industry, but also in the computer, agricultural, metallurgical, etc. Country of origin: Belgium.
Contitech is one of several manufacturers that supply their products directly to new vehicles. In addition, the corporation produces various drive systems, air suspension mechanisms, car interior parts and fluids for technical purposes. Production is located in Germany.
Bosch is the oldest German company founded in 1886. The main direction of its products is considered to be the production of automobile spare parts, garden and construction equipment, household goods and power tools. Location: Germany, Gerlingen.
Lemforder is the largest German company, known to many car enthusiasts under the name ZF, producing steering, transmission, suspension and drive systems for various mechanisms. The company's products are also manufactured under the brands SACHS, LEMFORDER, BOGE and ZF PARTS. Country of location: Germany.
Balakovo is a domestic manufacturer of drive belts, producing rubber and technical products at the Balakovo plant. In addition, the manufacturer produces household parts, chemical and mineral mixtures. Timing belts of the Balakovo brand have found great popularity among owners of Russian cars. Country of origin: Russia.
Strength research results
The average replacement interval for the drive belt and gas distribution mechanism is considered to be 60 thousand kilometers. This indicator is considered very average. So, for example, on some cars, technical regulations require belt replacement at 70 and even 90 thousand km. But still, in the majority, these readings are close to 50-70 thousand
It is very important to note the fact that the gas distribution drive requires systematic monitoring and maintenance. And avoiding such basic procedures can lead to very disastrous results.
Important information about the timing belt mechanism
The GRS mechanism belt guarantees an elastic connection between both shafts, controls the process of opening/closing the valves and their synchronous operation. In a word, this is a very important element of the GDS mechanism and the car as a whole.
Timing belt from Toyota
Another function of the belt is to prevent the pistons and valves of the power plant from meeting each other, although they operate in the same spatial plane. For this reason, the reliability of the belt is extremely important, and if it breaks, the piston meets the valve and bends it. This inevitably leads to a thorough overhaul of the internal combustion engine.
The reliability of the belt, as mentioned above, depends directly on the release date and service life of the product. Replacement must be carried out periodically, constantly monitoring the condition of the part. It will be interesting to note that you can directly find out about the replacement frequency based on a specific car brand. You can see this in the technical documentation. On the other hand, craftsmen and experts recommend not to blindly believe the data, but to replace it every 50 or 80 thousand kilometers.
Article on the topic: KGB car alarm - reliable protection against theft
It will be useful to know that few foreign car manufacturers indicate a period for replacing a product of less than 120 thousand km. But dealers selling cars from the same manufacturer, on the contrary, advise changing the belt after the same 50-80 thousand km, taking into account the peculiarities of Russian roads.
If cracks appear on the belt, it should be changed immediately, this is true. But you should not do this, of course, if we are talking about microcracks. In this case, the product will definitely not break, since the belt, although rubber, is woven from metal rods. Thus, it is able to withstand shock loads repeatedly, while working for a long time.
If the belt weakens, that is, its tension decreases, this will lead to problems in the operation of the internal combustion engine. It will negatively affect the dynamics of the car, its traction, noise and starting. It is precisely these signs that will indicate a loose belt or wear in the first place.
All car manufacturers unanimously recommend replacing the tensioner roller and pump simultaneously with replacing the rubber-metal belt. The cost of carrying out this work is quite high, and the complexity is not questioned, but otherwise it is extremely difficult to ensure reliability.
It will be useful to know that some cars are equipped with timing belts with reinforced metal cord. It is better to buy them, since the service life is noticeably higher than usual.
Timing faults
Main malfunctions of the gas distribution mechanism:
- Reducing compression and popping in pipelines. As a rule, it occurs after the appearance of carbon deposits, shells on the surface of the valve, and their burnout, which is caused by a loose fit of the intake and exhaust valves to the seats. Factors such as cylinder head deformation, breakage or wear of springs, jamming of the valve stem in the bushing, and a complete lack of space between the rocker arm and the valves also have an impact.
- Reduced power, engine tripping, and metallic knocks. These symptoms appear because the intake and exhaust valves do not open completely, and part of the air-fuel mixture does not enter the combustion chamber of the cylinder. The consequence of this is a large thermal gap or breakdown of the hydraulic compensator, which causes a malfunction and improper operation of the valves.
- Mechanical wear of parts, such as: crankshaft guide bushings, camshaft gears, as well as camshaft displacement. Mechanical wear of parts, as a rule, occurs when the engine has been operating for a sufficient period of time and the engine is operating within critical limits.
- Engine failure also occurs due to wear of the toothed belt, which has its own warranty period, the chain, which becomes less efficient after a long period of operation and constant exposure to it, the chain guide and the toothed belt tensioner.
How to find out the production date
Belt storage time matters as the material ages and becomes less reliable. The production date is indicated on the packaging and on the belt itself. There is no unity here. You have to refer to tables that are easy to find on the Internet.
For example, Contitech indicates the date in a natural way, with two digits for the day and month, and four digits for the year. And Gates marks the week with two digits and the last digit of the year.
Purpose and types of timing belts
The job of the timing belt is to transmit torque from the engine crankshaft to the fan, gas distribution mechanism, generator and other components, the exact composition of which depends on the car model. The most common at the moment are timing, V-belts and poly-V-belts. Timing belt
is the most complex structurally, but also the most effective.
A broken belt can be a serious disaster for a car engine, since it drives the gas distribution mechanism, and its sudden stop can cause damage to the valves and cylinder head. Before belts, internal combustion engines used chains. Replacing them made it possible to somewhat simplify and lighten the engine, as well as improve its noise characteristics. But the timing belt needs constant monitoring of condition and tension.
Chain or belt drive
To ensure the rotation of the two shafts, belts or chains are used. Chain transmission was originally used in cars. Chains can have from one to three rows of links, everything depends on the power of the power unit.
Chain: advantages and disadvantages
The advantage of the chain is its long service life. Its stretching is compensated by a specially installed tensioner. Compared to a strap, it lasts much longer.
The chain needs to be replaced only if it is significantly stretched or damaged and breaks, which happens quite rarely.
This is the only advantage of chain transmission.
Disadvantages of such devices:
- The use of a chain affects the noise level of the power unit. Single-row chains don't make as much noise, but two- and three-row chains are louder. Their use contributes to the rather noisy operation of the machine's engine.
- Cylinder blocks that use a chain are more complex in design. Because of this, the procedure for replacing the product becomes much more complicated, since the car owner needs to have direct access to the crankshaft.
Belt: pros and cons
The main advantages of belt drives:
- If the engine is equipped with a timing belt, then such a product will operate much quieter. The driver can only hear one sound when the power unit is operating - the faint knock of valves.
- Easy to replace compared to chain drive. If you are prepared, you can change the belt yourself.
Flaws:
- Low service life of the drive compared to chain transmission. As a result of prolonged use, the strap breaks, and this can cause serious malfunctions. Eight-valve engines practically do not suffer from breaks. In the case of engines equipped with 16 valves, the elements themselves may bend as a result of a break. This will lead to the need for major repairs, the cost of which will be significantly higher than replacing the strap. Sometimes a reduction in service life and a broken belt leads to the formation of cracks in the cylinder head or the cylinder block itself. The only solution to the problem is to install a new cylinder head, and the gasket also changes.
- The need to replace the tension roller along with the belt. In some cases, car owners also need to change the water pump device and a set of washers. The service life of the strap is on average about 60 thousand km. But if you take into account the difficult conditions of use and the presence of defects in many spare parts, experts recommend changing the belt earlier.
Timing belt repair process
It is often necessary to carry out maintenance of the gas distribution mechanism. The main problem is wear of the journals, shaft cams and increased clearances in the bearings. In order to eliminate the gap in the crankshaft bearings, it is repaired by grinding the bearing journals and deepening the oil supply grooves. The necks need to be ground to repair size. After completing the repair work to restore the crankshaft, you need to check the height of the cams.
There should be no even the slightest damage on the supporting surfaces under the crankshaft journals, and the bearing housings must be free of cracks. After cleaning and washing the camshaft, be sure to check the gap between its journals and the hole in the cylinder head support.
The chain must not have any mechanical damage and be stretched by more than 4mm. The timing chain can be adjusted: unscrew the locking bolt half a turn, turn the crankshaft 2 turns, then turn the locking bolt all the way.
Consequences of a broken timing belt
The main task of the timing belt is to connect the camshaft and crankshaft, allowing the valves to open and close in synchronization with the operation of the pistons. The belt should rotate the camshaft at a speed exactly half the speed of crankshaft rotation.
This is important for the normal operation of the internal combustion engine.
If the timing belt
jumps off or breaks, the piston is guaranteed to hit the open valve, bending it, which leads to expensive engine repairs. It should be noted that engines with such design features are installed in the vast majority of cars produced today.
Causes of breakdowns
The most common failures of this unit seem to be a phase break or loss. This leads to engine stoppage and serious damage requiring expensive repairs. The most likely causes of breakdowns include excessive wear, jamming of the tensioner pump or shafts, as well as insufficient tension.
Ways to eliminate them
The troubleshooting procedure is significantly different and depends on the cause of its occurrence. Most often, the belt needs to be tensioned to its optimal condition, which can be done using an appropriate mechanism. However, if there is a break or other serious damage, the timing belt may need to be replaced.
The procedure is quite simple and involves the following steps:
- Remove the front wheel to gain access to the crankshaft pulley.
- Remove the power steering belt, alternator, spark plugs and pump mechanism.
- Remove the pulley and the right engine support.
- Remove the worn timing belt and install a new one in its place.
Next, you will need to repeat all the operations in reverse order, installing the dismantled components on the car one by one. Thanks to its simple design, such manipulations can be done with your own hands, significantly saving on the services of specialists.
How not to buy a fake
Currently, the auto parts market is literally overflowing with counterfeit products. Timing belts are no exception. Moreover, they counterfeit not only products belonging to expensive brands, but also mid-priced spare parts
Therefore, when choosing a particular timing belt, you need to pay attention to its quality and follow a few simple rules that will help minimize the likelihood of purchasing a counterfeit
- Make purchases in trusted stores. Regardless of what timing belt you are going to buy, cheap or expensive. It is best to contact an official representative of the manufacturer of the specific timing belt.
- Study the packaging carefully. Self-respecting companies always spend a lot of money on high-quality printing. The printing on the boxes should be clear, and the images should not float. In addition, the product description must contain no grammatical errors. It is desirable that the packaging also have a hologram (although not all manufacturers apply it).
- Carefully examine the belt and other elements from the repair kit. Directly on the outside of the belt there is always information about its purpose and characteristics. In particular, the brand, sizes, etc. are indicated. In addition, there should be no delamination, inclusions of foreign particles or other damage on the rubber.
Some manufacturers are introducing online verification of packaging originality. To do this, codes, drawings, QR codes or other information are applied to its surface, with the help of which a counterfeit can be clearly identified. This is usually done using a smartphone with internet access. Another option is to send an SMS with a code from the package.
Remember that a fake belt will not only not work for the time (mileage) allotted to it, but will also not properly ensure the operation of the gas distribution mechanism and other engine elements, the movement of which it ensures. Therefore, buying an original is the key to long-term operation of both the belt and the engine.
Myths and truth about fake belts
There is a common myth among inexperienced car enthusiasts that if there is a seam on the timing belt, then the product is defective. Actually this is not true. Almost all belts have this seam, since their manufacturing technology implies its presence. At the factory, belts are produced by cutting a wide roll with the appropriate geometric parameters, the ends of which are sewn with strong threads
Therefore, you do not need to pay attention to the presence of a seam. Another thing is to evaluate its quality or the numbers indicating the number of such a band
The next myth is that Teflon-coated timing belts are white. Actually this is not true! Teflon itself is colorless, therefore, when it is added during the manufacturing process of the belt, it will not in any way affect the color of the final product. Whether the belt is Teflon or not must be clarified separately, in the technical documentation for it or directly from the sales consultant.
A similar myth is that the surface of a Teflon belt is supposedly always labeled Teflon. This is also untrue. Information on the composition of the timing belt components must be clarified additionally. For example, many belts that are actually made with Teflon do not outwardly indicate this.
Conclusion
Choosing one or another timing belt is always a compromise of several decisions. It is advisable to install the same belt on the car engine that was originally provided by the manufacturer as the original one. This applies to both its technical characteristics and the manufacturer. As for specific brands, their choice largely depends on the price-quality ratio, the range presented, as well as simply availability in stores. You should not buy frankly cheap belts, since they are unlikely to last their intended life. It is better to buy original products or their high-quality analogues from the middle or higher price range.
Decoding the symbols on the belt
The belt configuration contains a number of important geometric and technological characteristics, without which it will not work correctly on a particular engine:
- number of teeth;
- tooth and cavity profile;
- belt width;
- tooth pitch, that is, the distance between adjacent repeating geometric points;
- materials and technologies used in production.
Not all of them are reflected in the factory markings on the product. But attempts at standardization are already being made. There are standards from the international organization ISO, but even they are ambiguous. Fortunately, there are no particular difficulties in understanding dimensional data, so even scattered notations are easy to understand.
the ISO encoding in the form of 5 digits, the letter “x” and two or three more digits contains information about the tooth profile code (the first two digits), the number of teeth (three more), and after the letter - the rounded width in millimeters. There is enough information to exclude gross errors.
Some of the manufacturers use their own markings, but they are also understandable. The data is the same, number of teeth, width, profile designation. There is no need for a more complete set of information; belts are selected according to the catalog numbers of car and spare parts manufacturers; cross-matching tables are available on the websites of companies and trade organizations. It is worth checking the markings only for additional verification.
Technologies for manufacturing parts are described in information materials of large companies. The same standard size can be in different designs, which determines the strength of the product, durability and cost.
Gas distribution mechanism with lower camshaft
The gas distribution mechanism of an engine with a lower camshaft is shown. The gas distribution mechanism is overhead valve, with a gear drive and two valves per cylinder.
Figure 5 – Gas distribution mechanism with a lower camshaft
1 – camshaft; 2 – valve; 3, 20 – bushings; 4 – spring; 5 – rocker arm; 6 – axis; 7 – screw; 8 – rod; 9 – pusher; 10, 11, 12 – gears; 13 – neck; 14 – eccentric; 15 – cam; 16 – cracker; 17, 19 – washers; 18 – cap
Classification or types of timing belts
Engines may have different gas distribution mechanism layouts. Consider the following classification.
According to the location of the camshaft
There are two types of camshaft position:
With a lower position, the camshaft is located in the cylinder block next to the crankshaft. The force from the cams is transmitted through pushers to the rocker arms, using special rods. They are long rods and connect the pushrods at the bottom to the rocker arms at the top. The lower location is not considered the most successful, but it also has its advantages. In particular, a more reliable connection between the camshaft and the crankshaft. This type of arrangement is not used on modern engines.
Lower camshaft and timing device
In the upper position, the camshaft is located in the cylinder head (cylinder head) directly above the valves. In this position, various options for influencing the valves can be implemented: through pushers, rocker arms or levers. This design is simpler, more reliable and compact. The overhead camshaft position has become more widespread.
By number of camshafts
In-line engines may have one or two camshafts. Engines with one camshaft are abbreviated SOHC (Single Overhead Camshaft), and those with two camshafts are abbreviated DOHC (Double Overhead Camshaft). One shaft is responsible for opening the intake valves, and the other for opening the exhaust valves. V-engines use four camshafts, two for each cylinder bank.
Maintenance of crank crankshaft and timing gears
Main works:
- checking the stability of the condition and tightening the fastenings (fastening work) of the engine mount to the frame, the cylinder head and the oil pan to the block, the flanges of the intake and exhaust pipelines and other connections;
- checking the technical condition or operability (control work) of the crank and distribution mechanisms;
- adjustment work and lubrication.
Fastening works
To prevent the passage of gases and coolant through the cylinder head gasket, it is necessary to periodically check the head fastening with a torque wrench with a certain force and sequence. The tightening torque and sequence of tightening the nuts are set by automobile factories.
The cast iron cylinder head is attached when the engine is hot, and the aluminum alloy head is attached when it is cold.
The need to tighten the fastening of aluminum alloy heads in a cold state is explained by the unequal coefficient of linear expansion of the material of bolts and studs (steel) and the material of the head (aluminum alloy). Therefore, tightening the nuts on a hot engine does not ensure the required tight fit of the cylinder head to the block after it cools down.
The tightening of the crankcase sump mounting bolts is also checked in accordance with the sequence to avoid crankcase deformation and leaks. alternately tightening diametrically opposed bolts.
Monitoring the condition of the crankshaft and timing gear
The technical condition of these mechanisms can be determined:
- by oil consumption (waste) during operation and pressure drop in the lubrication system;
- by changes in pressure (compression) in the engine cylinders at the end of the compression stroke;
- by vacuum in the intake manifold;
- by the amount of gases breaking into the engine crankcase;
- leakage of gases (air) from the cylinders;
- presence of knocks in the engine.
Oil loss in a low-wear engine is insignificant and can be 0.1-0.25 l/100 km. With significant general engine wear, waste can reach 1 l/100 km or more, which is usually accompanied by heavy smoking.
The pressure in the engine oil system must be within the limits established for the given engine type and the type of oil used. A decrease in oil pressure at low crankshaft speeds of a warm engine indicates the presence of unacceptable wear on the engine bearings or a malfunction in the lubrication system.
A drop in oil pressure on the pressure gauge to 0 indicates a malfunction of the pressure gauge or pressure relief valve.
Increased pressure in the lubrication system can occur as a result of high viscosity or clogging of the oil line.
Compression serves as an indicator of the tightness of the engine cylinders and characterizes the condition of the cylinders, pistons and valves. The tightness of the cylinders can be determined with a compression gauge.
Compression is checked after preheating the engine to 70-80 ºС with the spark plugs turned out. Having installed the rubber tip of the compression gauge in the hole of the spark plug, turn the engine crankshaft 10-12 revolutions with the starter and record the readings of the compression gauge. The check is repeated 2-3 times for each cylinder.
General arrangement of the gas distribution mechanism
The timing device includes the following components: valves, valve drive, timing shaft and camshaft drive. The valve that supplies air to the cylinders consists of a rod and a plate.
The valves are located in the cylinder head, and the place where the valve comes into contact with the cylinder head is called the seat. Valves are inlet and outlet. The diameters of the discs of these valves vary. This is done to ensure more complete filling of the cylinders.
The spring keeps the valve closed, and pressing the rod keeps it open. A spring is secured to the rod using a plate. To avoid resonating vibrations on the valves, it is possible to install two springs with a lower stiffness coefficient and opposite winding. The vast majority of internal combustion engines have a pair of exhaust and a pair of intake valves for each cylinder.
However, there is an engine timing mechanism with three intake and two exhaust valves. The number of valves is directly proportional to the size and complexity of the internal combustion engine.
The gas distribution mechanism drive opens the valve and transmits force to the valve from the distribution shaft. There are two main types of actuators: roller levers and hydraulic tappets.
Roller levers are preferred because they have higher efficiency due to minimized friction losses and relatively lower weight.
The roller lever has two supports: on one side there is a valve stem, on the other there is a hydraulic compensator or a ball joint, depending on the design. The hydraulic compensator consists of a cylinder, a check valve, a piston with a spring and oil channels.
Camshaft device
There are two options for the location of the shaft in the block head: single-shaft and double-shaft schemes. The second one is preferred. In addition, 4 shafts are installed in the V-shaped internal combustion engine - a pair for each row. The camshaft is powered by the crankshaft through a drive that rotates at half the speed of the crankshaft.
Chain, belt and gear drives can be used to drive the distribution shaft. The first two types use a camshaft, which is located in the cylinder head, and the third, which is located in the cylinder block.
Chain and belt drives are used in the timing belt with the same frequency. The timing belt is less reliable and therefore less durable. However, the chain is heavier than the belt, which means it requires additional tension. This is achieved by installing tension rollers and dampers that dampen vibrations.
The timing chain consists of a single-row and a double-row roller chain. Toothed chains that interact with specially shaped teeth are gaining popularity. In addition to the camshaft, the chain mechanism is used to drive the balancer shafts and the oil pump.
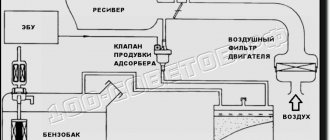
The timing belt does not require lubrication and, accordingly, is installed openly on the pulleys. The ridges on the inner surface of the belt engage the teeth on the pulleys, which creates rotation. The elliptical gear used on TDI engines reduces traction forces and also reduces torsional vibrations of the distribution shaft.
In addition to the camshaft, the gear mechanism drives the oil and fuel pumps, as well as the coolant pump. It is also necessary to say that the timing belt has a limited resource - 100-150 thousand km. The VAZ 2106 will have even less life.
And here is a video about the timing belt:
https://youtube.com/watch?v=6heSaiyAjaU
What happens if the marks shift?
Now turn on your imagination, because you will have to imagine the complex process that occurs when the marks are shifted. If the gas distribution mechanism drive is installed and configured correctly, taking into account all the marks, then the engine will operate ideally. But what happens if the belt suddenly slips a few teeth? Yes, this happens quite often; even a toothed belt can slip on a pulley if it is loosely tensioned.
And literally the following will happen: the movement of the pistons in the cylinders and valves will occur asynchronously. Decoding the timing belt says that intake and exhaust must occur in a timely manner, depending on the position of the pistons. Consequently, the intake stroke will start earlier or later, similar to the exhaust stroke. The air-fuel mixture will not enter in a timely manner; at best, its ignition will occur in the middle position of the piston in the cylinder. In other words, complete chaos begins in the engine. And all this happens due to the fact that some belt has jumped several teeth.
Breakage features for 8- and 16-valve vehicles
It should be noted that the more complex the design of the motor, the more serious the consequences will be for it if the belt breaks. So, on conventional 8-valve internal combustion engines, you can get away with simply replacing the device. At the same time, on a 16-valve engine it is necessary to completely restore damaged valves and pistons (that is, replace them). But this does not mean that driving 16-valve cars is very dangerous and that they are unsuitable for long journeys. If you regularly monitor its external condition, you will definitely not be in danger of a belt break.
Also, when inspecting the gear element, it is recommended to pay attention to the condition of the camshaft and crankshaft seals for leaks, and also to check the serviceability of the tension rollers. Remember that the malfunction of these elements significantly affects the life of the belt
What is the purpose of the belt?
The timing belt is a part whose purpose is to act as a connecting link.
Thanks to the timing belt, the camshaft and crankshaft work synchronously, which contributes to the proper functioning of the engine as a whole. This is the need for using a strap.
Markings on the strap
Let's look at a few examples of translating the timing belt decoding:
Table: Belt markings
Manufacturers may label their products differently. The table shows how to decipher the timing values.
What does the timing belt look like and where is it located?
We have already figured out what this element is, now let’s talk about where it is located. On most modern cars, the timing belt is located in the front part of the engine compartment, namely between the engine cylinder block and the radiator. Depending on the make of the car, this part may be hidden or already visible after opening the hood. But even a “disguised” belt is very easy to get to, since car manufacturers carefully consider its location. The maximum that needs to be done is to remove a couple of plastic protections or a decorative cover (the latter is mounted on most luxury cars). Externally, the timing belt (you can see a photo of this mechanism below) is a closed-type rubber toothed rim. The teeth themselves are made from the inside of the element. Also note that car manufacturers do not produce universal belts. They are selected for each car separately.
Principle of operation
The operation of the gas distribution mechanism is difficult to consider separately, in isolation from the engine operating cycle. After all, its main task is to open and close the valves in time for a certain period of time. Accordingly, on the intake stroke, the intake valves open, and on the exhaust stroke, the exhaust valves open. That is, in fact, the mechanism must implement the calculated valve timing.
Technically it happens like this:
- The crankshaft transmits torque through a drive to the camshaft.
- A cam on the camshaft pushes a pushrod or rocker arm.
- The valve moves inside the combustion chamber, allowing access to fresh charge or exhaust gases.
- After the cam goes through the active phase of action, the valve returns to its place under the action of the spring.
It is also worth noting that during a full operating cycle, the camshaft makes 2 revolutions, alternately opening the valves in each cylinder, depending on the order of their operation. That is, for example, with a 1-3-4-2 operating scheme, at the same moment in time, the intake valves will be open in the first cylinder, and the exhaust valves in the fourth. In the second and third the valves will be closed.