The ignition coil is part of the vehicle's ignition system. It converts the 12 volt battery voltage to high voltage to create a spark in the spark plug. The spark ignites the air-fuel mixture in the engine cylinders.
Most modern cars have an individual (plug) ignition coil per cylinder. Usually it is installed directly above the spark plug, as on this VAZ engine in the photo.
In some vehicles, the ignition coils for all cylinders are combined into one coil pack. In older cars with a distributor (distributor), one coil is used for all cylinders. Check out this example of an engine with a single ignition coil:
Ignition system diagram
In the general scheme of the ignition system, the coil is located between the battery and the ignition distributor, followed by spark plugs. A breaker (in old cars) or an ECU is connected in parallel with the coil to regulate the charge supply - in new ones. A direct low-voltage current from the battery (or generator) is supplied to the coil. The breaker handles periodic breaks in the circuit (more on this a little later, in the description of the operating principle). The coil generates a high-voltage current, which is supplied to the desired spark plug through a distributor. Regardless of what control system is used in the car (mechanical or electronic), the ignition circuit does not change in principle, but is only improved in form.
Scheme of operation of an ignition system with a coil
If any element of the system fails, this immediately affects the operating mode of the engine. That's why the reel is so important.
Photo gallery
Photos of different types of devices are presented in this section.
Classic machine short circuit
Individual short circuits for each candle
Dual type device
Purpose of the ignition coil
Ignition of the fuel-air mixture in the combustion chamber of a gasoline engine is carried out using an electric spark generated by a spark plug. However, it is quite difficult to create a spark of sufficient strength, because gasoline mixed with air is a good dielectric, and it is not easy for even a short spark breakdown to occur in it. The problem can be solved only by applying a powerful electric pulse with a voltage of tens of thousands of volts to the spark plug. Where can you get that kind of voltage in a car, even for a short fraction of a second?
This problem is solved using a special device - an ignition coil, or bobbin. An ignition coil is a component of a vehicle's ignition system that converts low-voltage direct current (6, 12, or 24 volts depending on vehicle type) from the battery or alternator into a short electrical pulse of up to 35,000 volts. The pulse from the coil is supplied to the spark plug, a spark appears in its spark gap, which achieves the goal - ignition of the fuel-air mixture.
Today, ignition coils are used in almost all cars with gasoline engines or gas-powered engines. Reels are used with equal success both in ignition systems of traditional circuits (contact with a distributor, contactless with thyristors) and in modern electronic ignition systems. Because there is no simpler, more reliable and efficient way to create a high-voltage electrical pulse.
How does it work
The principle of operation of the ignition coil is based on the basic physical laws that were taught in school. It can be characterized as follows: a low-voltage type voltage is sent to the primary winding. All this creates a magnetic field. Sometimes this voltage can be cut off by a breaker, which causes a sharp reduction in the magnetic field along with the formation of an electromotive force in the turns of the coil.
If you believe the physical law regarding electromagnetic induction, then the magnitude of the electromotive force that arises in this way is proportional to the number of turns in the circuit winding. This can explain the fact that a high voltage pulse is formed in the secondary coil, because there are a large number of turns there. This impulse is sent to the spark plug. Moreover, this process is not typical for the individual type, since this type is installed directly on the candle.
It is thanks to this impulse, transmitted by a coil, that a spark occurs between the electrodes of the spark plug, which causes the fuel-air mixture to ignite. And at the moment when the occurrence of this spark is simply necessary, the contacts in the distributor-breaker open. At the same moment, the primary winding circuit breaks. A high-voltage current appears at the central contact of the coil, after which it is sent again - to the contact opposite which the slider electrode is located at that particular moment. After all this, the circuit is closed, and the impulse passes to the spark plug belonging to one of the cylinders.
A small recommendation: the coil does not particularly welcome long-term loads, so it is better to turn on the ignition for a long time when the engine does not start. This is a proven fact, the implementation of which will help to maximize the duration of the described mechanism.
Outdated car models had such coils, the voltage from which was supplied to all spark plugs at once using an ignition distributor. The latter mechanism turned out to be not reliable enough, and therefore in modern cars they began to actively use systems with individual coils belonging to each individual spark plug. In this regard, the sparking energy increased, and the level of radio interference created by the ignition system, on the contrary, decreased. Also, the use of this system made it possible to say goodbye to the need to use high-voltage wires, which often turn out to be unreliable.
The coil, as the most important element of the overall ignition system, needs special attention and care. Therefore, this should not be neglected and should be expected until the last moment, until only this mechanism fails, but also the entire ignition system, and later the car. So I recommend that you always find time to carry out at least basic diagnostics of the car and the ignition system in particular, especially if the principle of its operation is now known. And may the car never fail.
Diagram of the operation of an ignition coil in a car
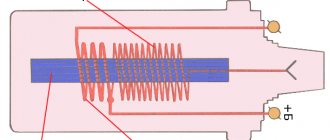
Ignition coil device
The basic design of the coil remains the same for all modifications and design features.
The device of the simplest ignition coil
- Internal central core made of steel plates insulated together to reduce eddy currents.
- The primary winding is made of thick (approximately 0.8 mm in cross-section) wire wound in 250-400 turns.
- The secondary winding, consisting of a thin wire (approximately 0.1 mm in cross-section), wound in 20-25 thousand turns. On average, the ratio of the number of turns between the primary and secondary windings is approximately 1:150 to 1:200.
- Outer ring core, also known as magnetic circuit.
- Terminals: two for low voltage current (from the battery and to ground) and one high voltage.
- Housing, filler (filled with transformer oil or epoxy compound).
The primary and secondary windings are insulated from each other, and in expensive models there is insulation between the layers of turns. This is done in order to avoid voltage breakdowns.
Video: Individual ignition coil VAZ
Something else useful for you:
- What is the heat rating of spark plugs?
- How to choose the best spark plugs?
- How to replace spark plugs?
Since current heating of the windings is possible during operation of the coil, transformer oil is used for cooling, which fills the housing cavity. Its cover fits tightly to the body, so the coil is non-separable. If it malfunctions, it cannot be repaired either.
The input and output voltage of the coil are not the main characteristics with which you can check its serviceability. The performance of the coil is checked by the resistance of its coil. In this case, the resistance of each coil may be different. For example, a coil may have a resistance of the first winding of 3.0 Ohms, and a resistance of the secondary winding of 7000-9000 Ohms. A deviation during measurement from these values will indicate a coil malfunction. And since it cannot be repaired, it is simply replaced.
The design of a general type coil has been described above. It is installed on all cars that have a battery, contactless and electronic ignition system, and are equipped with a distributor that directs the impulse from the coil to the desired cylinder.
Design differences between individual coils
This type of coil is used in electronic systems. They work the same way as the classic ones. Its structure also has high and low voltage windings. But there are also differences: in an individual coil, the primary winding is inside the secondary; the presence of two cores - internal and external.
The first is located inside the primary winding. The second one is around the secondary. The high voltage winding of the individual ignition coils is equipped with a special diode. Its purpose is to cut off high voltage currents.
Individual coils are divided into 2 types: compact and rod. They differ in the structure of the core. The latter have the ability to combine 4 pieces. The result of the coil's activity is the formation of one spark in one complete cycle. This explains the need to synchronize all coils relative to the engine camshaft.
Types of coils
Today, there are a sufficient number of types of ignition coils that can be installed both on old domestic cars with carburetor engines and on more modern cars with direct fuel injection.
Housing ignition coils are installed on vehicles with mechanical ignition distribution, where the distributor, rotating, supplies high-voltage voltage to each spark plug in a certain sequence. This method of switching and voltage distribution is not used in the modern automotive industry due to its short service life and low reliability.
A coil with electronic ignition distribution, or a distribution coil, does not require an additional contact cascade breaker for its operation, because with the development of technology in microelectronics, it has become possible to integrate such an ignition breaker into the coil itself. This coil is suitable for cars with mechanical ignition distribution.
A dual-spark ignition coil allows spark plug voltage to be generated simultaneously in two engine cylinders per crankshaft revolution, without the need for coordination between the ignition system and the camshaft. It is advisable to use such coils only in engines with an even number of cylinders, for example, for an engine with four cylinders you will need two coils, with six - three, respectively, with eight - four.
Double spark ignition coil
The "smart" plug ignition coil is single-spark and is installed directly on each spark plug. The design and functional characteristics of such a coil make it possible to avoid the use of high-voltage wires in the system, but it requires connecting clamps (terminals) designed for high voltage. Due to their compactness, these coils are used in cars with a small amount of free engine compartment space, but compact does not mean ineffective. The plug coil can easily compete with its brothers.
Plug-in ignition coil device
The advantages of the reel are:
- The widest range of ignition timing settings.
- Diagnosis of misfires from the primary and secondary windings.
- Spark extinguishing in the secondary circuit using a high voltage diode.
Such devices are used for engines with any number of cylinders, but synchronization with the position of the camshaft using an appropriate sensor is strictly required.
Requirements for modern ignition coils
Requirements that apply to all modern short circuits:
- Simplicity of design. The simpler the short circuit is, the easier it is to install and maintain in the future. With a simpler device, the consumer will be able to independently diagnose in case of problems.
- Small dimensions and weight.
- High service life. The reliability of the device will ensure a long service life.
- Reliable protection against humidity and elevated temperatures. It is important that the design of the reel, as well as the materials used for its production, are resistant to elevated temperatures and moisture. This will ensure effective operation of the short circuit when weather conditions change and exposure to the aggressive environment characteristic of the engine compartment. The vapors that come from fuel and engine fluid should not harm the device or its body. If the structure body is damaged, this will lead to a deterioration in the functioning of the short circuit as a whole.
- Precision fit of the device, as well as resistance to short circuits. The design of the short circuit must be made so that its dimensions are sufficient to remove heat and ensure temperature stability.
Technical characteristics of ignition coils
The main characteristics of the devices are shown in the table.
| Characteristic | Description |
| Inductance | This parameter determines the ability of the short circuit to accumulate electricity and is measured in Gn. The energy collected inside the primary element of the device is proportional to the inductance value. The higher the inductance value, the more energy the mechanism can accumulate |
| Transformation parameter | Determines how much a short circuit can increase the magnitude of the primary voltage. The primary element receives 12-volt voltage from the battery, and when the circuit is opened, the current will drop from 6-20 amperes to 0. As a result of the current change, voltage appears on the primary component, and the transformation parameter determines how much this value has increased. This value is determined by the ratio of the number of turns in the secondary and primary devices |
| Short circuit resistance value | The primary coil device has a resistance of about 0.25-0.55 Ohms, and the secondary - from 2 to 25 kOhms. The magnitude of the spark formation power, as well as its energy, is inversely proportional to the resistance parameter in the primary component. The higher this value, the lower the amount of energy and power that is generated when a spark is applied. |
| spark energy | This parameter is about 0.1 joule and is consumed over 1.2 ms. In the spark plug itself, energy appears as a result of the formation of an arc charge when a breakdown occurs between the electrode elements. The voltage value on the parts is determined by the diameter of the spark plug, as well as the gap between the electrode components and the material from which it is made. This value is also affected by the temperature and pressure in the combustion chambers of the internal combustion engine, and the composition of the combustible mixture. For efficient operation of spark plugs, the voltage generated in the short circuit will be one and a half times greater than the voltage required to ensure breakdown |
| Breakdown voltage parameter | The breakdown itself is formed between the electrode components of the spark plug if the voltage across them and the breakdown correspond to each other. The operating parameter is determined by the gap between the electrodes, the pressure parameter in the combustion chambers, as well as the temperature of the combustible composition. When starting the internal combustion engine cold, this value should be greater, this will allow breakdown and the appearance of a spark discharge. This is important because the fuel and air in the engine are still cold. |
| Number of sparks appearing per minute | To calculate the number of sparks in one minute, you need to know the crankshaft speed, as well as the number of cylinders in the internal combustion engine. The spark value can be calculated by dividing the number of revolutions multiplied by the number of cylinders. And divide the resulting indicator by the number of engine cycles |
Service life and malfunctions of ignition coils
Theoretically, modern ignition coils have a service life of 60-80 thousand vehicle kilometers. However, actual performance largely depends on operating conditions. There can be many reasons for malfunctions:
- Short circuit on the windings.
- Coil overheating.
- Wear due to long-term use or increased vibration.
- Charging time exceeded. Most often this happens when the car battery does not provide the required voltage level.
- Depressurization of the main components of the engine and fuel system.
- Damage to the body.
In modern cars, the on-board computer signals a coil malfunction by turning on the Check Engine indicator on the dashboard. In addition, signs of malfunction are:
- Deviation of the resistance of the transformer windings from the standard value. Diagnosed using a tester.
- Intermittent or complete failure of one or more engine cylinders, reducing engine power.
- Deterioration of internal combustion engine performance in cold (frosty) weather or high air humidity.
- Engine failure when the gas pedal is suddenly pressed.
- Poor vehicle acceleration.
Due to the design features, repairing ignition coils is impossible, and if problems are detected, they are simply replaced with new ones. It is better to diagnose the condition and replace them in service centers, since the operation of the engine and the vehicle as a whole depends on the accuracy of the operation of this element of the ignition system.
Video “Self-diagnosis of short circuit operation”
The MotoDalnoBoy channel talked about the causes of malfunctions and also showed ways to check the coil using a tester.
Replacing the ignition coil
If the coil malfunctions and cannot be restored, it must be replaced. You can buy exactly the same original one, or you can choose a similar one, but their characteristics should not differ by more than 20-30 percent, and also have the same fastening and design. For example, for domestic cars VAZ-2108 - 2109 with electronic coils 27.3705 from a domestic manufacturer, coils 0.221.122.022, which are not much different in parameters, are suitable. In this case, the spread of parameters will be from 10 to 15%.
To summarize, it can be noted that when writing the article, real information was used about the problems that each driver faced. All coils are practically the same from each other in terms of their operating principle, but not all of them are interchangeable, for example, coils with mechanical ignition distribution cannot work with contactless distribution and vice versa.
Questions on the topic
Filter:AllOpenSolvedClosedWaiting for response
What is the price of an ignition coil for Mazda 6? Answered by User Answered 10 months ago • Ignition system
27 views 1 answer. 0 vote.
Trouble with car, problem with Infiniti FX coils Answered by User answered 10 months ago • Ignition system
28 views 1 answer. 0 vote.
Which coil can replace the Ford Fiesta Mk1 1.1 ignition coil? Answered by User Answered 10 months ago • Ignition system
35 views 1 answer. 0 vote.
How to check the ignition coil of a Hyundai Santa Fe Classic? Answered by User Answered 10 months ago • Ignition system
50 views 1 answer. 0 vote.
Are the ignition coils burning out on your Toyota Corolla? Answered by User Answered 10 months ago • Ignition system
37 views 1 answer. 0 vote.
Ask a Question
Conclusion
One of the important components in a car is the bobbin, which creates high voltage to produce a spark. If dips appear in the engine’s operation, it begins to stall and simply run unstably – this could be the cause. Therefore, it is important to know how to check the ignition coil correctly, and if necessary, using the old-fashioned method, in the field.
Sources
- https://VazNeTaz.ru/katushka-zazhiganiya
- https://www.avtoall.ru/article/4555827/
- https://AvtoMotoProf.ru/obsluzhivanie-i-uhod-za-avtomobilem/chto-iz-sebya-predstavlyaet-katushka-zazhiganiya-avtomobilya/
- https://SwapMotor.ru/ustrojstvo-dvigatelya/katushka-zazhiganiya.html
- https://avtozam.com/elektronika/pusk/printsip-raboty-katushki-zazhiganiya/
- https://TechAutoPort.ru/dvigatel/sistema-zazhiganiya/katushka-zazhiganiya.html
- https://ZnanieAvto.ru/fire/katushka-zazhiganiya-sxema-ustrojstvo-i-podklyuchenie.html