It is important for every driver to remember that his car cannot stop instantly. To do this, he will need a certain time, which is influenced by a large number of factors. Traffic rules require maintaining a safe distance between your own car and the car in front in order to have time to brake if necessary. To know the magnitude of this distance, you need to have an idea of the braking distance. In addition, many people confuse two concepts - braking and stopping distance.
What does braking distance depend on?
The indicator under consideration is not a constant value and can vary for a number of reasons. All factors influencing the braking distance can be divided into two large groups: driver-dependent and driver-independent. Reasons beyond the control of the person driving include:
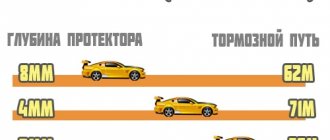
It is easy to guess that in rain, snow or ice, the distance required to stop a car will be greater than on dry asphalt. Braking will also take a long time when driving on smooth asphalt, to which stone chips have not been added. Here the wheels have nothing to catch on, unlike rough surfaces.
Note: it is worth noting that poor quality of the road (potholes, potholes) does not lead to an increase in the distance required to stop. The human factor plays a role here. Trying to save the suspension, drivers rarely reach high speeds on such roads. Accordingly, the braking distance here is minimal.
Factors depending on the driver or owner of the car:
- brake condition;
- system design;
- presence of ABS;
- type of tires;
- vehicle load;
- movement speed.
Modern assessment methods
Technological progress does not stand still, and today it is often possible to determine speed quite simply.
Two data sources help with this:
- DVR data. Almost all models of these devices also record the speed of the vehicle. A special sensor detects the moment of collision and resets the data to memory; it is impossible to delete it from there;
Is it possible to determine the speed of a car from video footage? How to do it? Watch the video:
- GPS/GLONASS. They also help to estimate speed, but not at the moment of impact, but only a few seconds before it.
Considering that today DVRs are ubiquitous, determining the speed of a car has become easier, and often does not even require additional expertise.
However, these methods are not always suitable. In this case, you will have to measure speed using more classical methods.
When and how measurements are taken
Braking distance calculations may be required in the following cases:
- technical testing of the vehicle;
- checking the capabilities of the car after modifying the brakes;
- forensic examination.
As a rule, the formula S=Ke*V*V/(254*Fs) is used in the calculation. Here S is the braking distance; Ke – braking coefficient; V₀ — speed at the start of braking; Фс – coefficient of adhesion to the coating.
The coefficient of road adhesion varies depending on the condition of the surface and is determined according to the following table:
| Road condition | Fs |
| Dry | 0.7 |
| Wet | 0.4 |
| Snow | 0.2 |
| Ice | 0.1 |
The Ke coefficient is a static value and is unity for all the most common passenger vehicles.
Example: how to calculate the braking distance of a car when the speedometer shows 60 km/h in the rain? Given: speed 60 km/h, braking coefficient – 1, adhesion coefficient – 0.4. We count: 1*60*60/(254*0.4). As a result, we get the figure 35.4, which is the braking distance in meters.
The table shows how many meters the car will continue to move until it comes to a complete stop. It should be taken into account that no other indicators are taken into account (turns, potholes on the road, oncoming traffic, etc.). It is doubtful that in real conditions on an icy road, a car will be able to slide for a kilometer without encountering a pole or bump stop.
| Speed | Dry | Rain | Snow | Ice |
| km/h | meters | |||
| 60 | 20,2 | 35,4 | 70,8 | 141,7 |
| 70 | 27,5 | 48,2 | 96,4 | 192,9 |
| 80 | 35,9 | 62,9 | 125,9 | 251,9 |
| 90 | 45,5 | 79,7 | 159,4 | 318,8 |
| 100 | 56,2 | 98,4 | 196,8 | 393,7 |
| 110 | 68 | 119 | 238,1 | 476,3 |
| 120 | 80,9 | 141,7 | 283,4 | 566,9 |
| 130 | 95 | 166,3 | 332,6 | 665,3 |
| 140 | 110,2 | 192,9 | 385,8 | 771,6 |
| 150 | 126,5 | 221,4 | 442,9 | 885,8 |
| 160 | 143,9 | 251,9 | 503,9 | 1007,8 |
| 170 | 162,5 | 284,4 | 568,8 | 1137,7 |
| 180 | 182,2 | 318,8 | 637,7 | 1275,5 |
| 190 | 203 | 355,3 | 710,6 | 1421,2 |
| 200 | 224,9 | 393,7 | 787,4 | 1574,8 |
We determine the speed of cars in an accident by their rotation
↓ Read in full ↓ ... so, in order to check the reliability of the solution to any theoretical problem, you need to try to solve it from the end ... which I suggest to all of you, dear humanists, if you want, of course (for the theorist, with the name KTN - not at all, because , as this has been verified by almost fifteen years of experience, it is useless, and if anyone wants, I can quite reliably substantiate and explain this) ... well, yes, now we are not talking about that at all ... the respected theorist ended with the fact that people like him, if I may say so , not exactly scientific delights, “take place in the courts”... in this regard, I would like to emphasize that they certainly “pass”, because the court, as often “taking advantage of its complete misunderstanding of the essence of the issue, made a certain decision” ©... I repeat, and this is objective and not at all offensive - such delights can make an impression only for people who are not entirely knowledgeable in this area of knowledge, but who probably have knowledge in completely different areas, that is, in the humanities... further from the end of that type of theoretical problem... with using an irrefutable rule about the inevitable existence of certain errors in expert calculations, determined by the expert’s forced choice of various kinds of parameters, although acceptable, but not at all reliably proven to exist in any road transport situation, and quite clearly stated by the “founder” - V.A. Ilarionov, without being at all refuted in any way or by anyone, like plus or minus seven percent for each expert calculation, the calculations given by the theorist are not worth a damn, not even in relation to the possibility of a judicial resolution that is absolutely abstract, invented by him, such as for example, a traffic situation... further, the theorist for some reason forgot, or maybe did not bother to find out, that speed is a vector differential and the blunt addition of scalar quantities of any speeds contradicts objective physical laws, since, to obtain a real picture of any interaction, one should operate precisely with vectors (their (velocities) or with graphical or analytical-digital operations on them in the parameters of the required arithmetic - addition, subtraction, multiplication) ... and in the same section from the end (like the sixth) - I can’t remember at all, obviously so the same with I. Newton himself, the possibility of determining the magnitude of the force acting on any material body through speed, but only through acceleration coupled with its (body’s) mass... and in the same connection - I just can’t understand how this is possible a kilogram multiplied by a meter squared and multiplied by a second to the minus first power, divided by a meter, results in newton multiplied by a second, and also subsequently divided by kilograms, although with an applied conversion factor - it turns out to be kilometers per hour, i.e., a unit of measurement of linear speed of movement... according to the second section of the theoretical sophistication - if we count from the moment and point of collision, as is generally accepted among experts, then, at the final (or initial - xs) speeds of movement of both cars determined by the theorist, both the initial angular velocity and the time of their movement to their final positions after the collision will be somewhat different... and who actually reliably told that theorist that the process of each of the cars moving to their named positions until the very end was accompanied by their reversal - but couldn’t will the turn end somewhat earlier than these vehicles stop?... the following, about choosing the value of the coefficient of adhesion of rubber tires to the supporting surface in a lateral (transverse) relationship, I already wrote to the theorist elsewhere, however, I repeat - the coefficient of adhesion of rubber tires to the surface in the lateral (transverse) direction, defined in various sources as (0.8 - 0.9) * by the same coefficient, but in the longitudinal direction, is valid only if the wheels are loaded with braking or torque, i.e. is determined by the presence of other forces that stabilize the possibility of rotation of the wheels of the car... it is quite obvious that in almost any collision of vehicles, without the presence of any traces left by their wheels, it is not possible to reliably assume the condition of the presence of the named moments, since the driver’s legs, like as a rule, they fly off the control pedals upon impact... thus, the unloaded wheels of the car, in any case, tend to rotate and the coefficient of their adhesion to the supporting surface, both longitudinally and transversely, also invariably tends to the value of the rolling resistance coefficient... well and the next thing - I was very pleased with the method used by the theorist to determine the distances of movement of the center of mass of each of the cars by mathematical resolution using the rules of a right triangle... in this regard, I would like to ask those in the know - doesn’t PC-Crash allow the possibility of stupid and trivial scale measurements such a movement?.. well, and the type at the end (or at the beginning, as asked), of what has been said, I would like to ask the theorist - how, in what reliable way and with what degree of error, during collisions, the type of which he chose as the type An example of a solution that is not of good quality, it should be noted, is a certain theoretical problem, the mutual position of vehicles at the moment of their initial entry into contact is determined (the angle between the directions of the longitudinal axes), as well as their location on a local section of the supporting surface (permissible - the roadway and its boundaries) at the mentioned moment?... although, frankly aware of the complete lack of intelligible answers from the theorist from the results of previous (more than a decade and a half ago) communication with him, I am inclined to classify almost all the questions raised as rhetorical... that’s why... lol
How to increase the intensity of deceleration
From the above, it became clear what is called the braking distance and what this indicator depends on. However, is it possible to reduce the distance required to stop a car? Maybe! There are two ways to do this - behavioral and technical. Ideally, the driver combines both methods.
- Behavioral method - you can reduce the braking distance if you choose a low speed on slippery and wet roads, take into account the degree of load of the car, and correctly calculate the braking capabilities of the car depending on its condition and model year. Thus, a Moskvich developed in 1985 will not be able to brake as effectively as a modern Hyundai Solaris, not to mention more respectable and technologically advanced models.
- Technical method - a method of enhancing braking capabilities, based on increasing the power of the braking system and the use of auxiliary mechanisms. Manufacturers of modern vehicles actively use such methods of improving brakes, equipping their products with anti-lock braking systems, braking assistance systems, using more efficient brake discs and pads.
It should be remembered that reducing the time required to stop is one of the ways to ensure a safe trip. Therefore, every driver must constantly monitor the technical condition of his “iron horse”, promptly maintain and repair the braking system. In addition, it is important to choose the driving speed taking into account the surrounding situation: time of day, road condition, car model, etc.
Very fast cabbage. Filled and ready
Cabbage is tasty and full of vitamins. Crispy!
Recipe
We take three kilograms of cabbage at the rate.
- Shred the cabbage.
- Grate three large carrots on a coarse grater.
- Squeeze 3-4 cloves of garlic from the garlic.
- Mix everything.
Making the marinade:
- We put one and a half liters of water on the fire.
- Add 200 grams of sugar, 3 tablespoons of salt (without top).
- Then, 250 gr. sunflower oil.
- When it boils, pour in 200 gr. vinegar 9%.
- It should boil for 2-3 minutes.
- The marinade is ready.
Formulas for calculating stopping and braking distances, as well as safe distances.
In the theory exam there is a question about the average reaction time of a driver, the correct answer to which is 1 second. The traffic police tickets also contain a question related to safe distance. There are questions regarding braking. But, as they say, a theory is a theory, which, alas, as a rule, has nothing in common with practice.
Firstly, what you taught in the tickets is a theory based on averages and various studies. In fact, the driver's reaction time, stopping and braking distance depend on many factors and cannot be accurately calculated for all cases. Nevertheless, every driver should be able to calculate these parameters at least approximately.
P O P U L A R N O E:
PodR >A bicycle is good, but with a roof and even a motor, it’s absolutely cool! Lightweight, comfortable, economical and covered with a tent on top for protection from rain and wind... a lot of positive things can be said about the development from JMK-Innovation - PodRide.
Many similar homemade products, as shown in the photo, are made all over the world, and there are even small-scale projects.
To work on the Internet you need a program - a browser.
You can use the Internet on your computer using standard Opera, but on your phone it will be more convenient to use Opera Mini.
Opera Mini is one of the world's popular browsers that works great on almost any phone. Read more…
Car braking distance
Braking distance is the distance that the vehicle will travel between the driver's contact with the brake pedal and the vehicle coming to a complete stop. It is also worth understanding the differences between “normal braking” and “emergency braking”. In particular, we must not forget that weather conditions affect braking distances. If there is snow on the road, the braking distance naturally increases.
Here is the formula for calculating the braking distance:
Calculation example: imagine that you are driving at a speed of 50 km/h in the city and approach a pedestrian crossing along which children are walking. Calculation: (50 km/h : 10) x (50 km/h : 10) = 25 (meters). Thus, the braking distance of your car is 25 meters. Therefore, you must take into account the length of the braking distance in order to calmly start braking in a timely manner and stop before the pedestrian crossing.
Moving towards each other
Tasks involving movement towards each other (counter movement) are one of the three main types of movement tasks.
If two objects move towards each other, then they get closer:
To find the speed of approach of two objects moving towards each other, you need to add their speeds:
The speed of approach is greater than the speed of each of them.
Speed, time and distance are related by the path formula:
Let's look at some problems involving oncoming traffic.
Two cyclists rode towards each other. The speed of one is 12 km/h, and the other is 10 km/h. 3 hours later they met. What was the distance between them at the beginning of the journey?
It is convenient to formulate the conditions for motion problems in the form of a table:
1) 12+10=22 (km/h) approach speed of cyclists
2) 22∙3=66 (km) was between the cyclists at the beginning of the journey.
Two trains are heading towards each other. The speed of one of them is 50 km/h, the speed of the other is 60 km/h. Now there are 440 km between them. In how many hours will they meet?
1) 60+50=110 (km/h) speed of approach of trains
2) 440_110=4 (h) time after which the trains will meet.
Answer: in 4 hours.
Two pedestrians were 20 km away from each other. They went out at the same time towards each other and met 2 hours later. The speed of one pedestrian is 6 km/h. Find the speed of the other pedestrian.
1) 20_2=10 (km/h) speed of approach of pedestrians
2) 10-6=4 (km/h) speed of another pedestrian.
Driver reaction time and path
Driver reaction time is the time that will pass from the moment the driver detects a danger on the road until the start of taking measures to prevent it.
The driver's reaction path is the distance the vehicle will travel from the moment the driver detects a hazard on the road until the brake pedal is pressed.
Here is the formula for calculating the distance a car will travel when the driver reacts to danger:
(Speed in km/h: 10) x 3 = reaction distance in meters
Calculation example: imagine that you are driving at a speed of 100 km/h along a country road and suddenly an elk runs out onto the road. Calculation: (100 km/h: 10) x 3 = 30 (meters). That is, after you react to a danger on the road, your car will travel about 30 meters. Add to this the braking distance of the car.
Attention: these rules are not scientifically correct formulas and provide only approximate values!
Forecast of the maximum speed of a car in gear:
| 1st gear: | 23.68 | km/h | 24.43 | km/h |
| 2nd gear: | 36.34 | km/h | 41.52 | km/h |
| 3rd gear: | 52.47 | km/h | 58.01 | km/h |
| 4th gear: | 69.1 | km/h | 73.3 | km/h |
| 5th gear: | 90.21 | km/h | 93.04 | km/h |
| 6th gear: | No | km/h | No | km/h |
* For slicks marked in inches, enter only R wheels (you do not need to enter the width and profile).
By default, the calculator for calculating gearbox ratios shows the characteristics of the S4C (gearbox #1) and S9B (gearbox #2) boxes. I chose these boxes not by chance, because... the first was installed on the Civic EK9, and the second is considered the longest manual transmission for B-engines.
You can change tire sizes, engine speeds, gear ratios and the main pair at your discretion. The calculator is a universal tool, so you shouldn’t get hung up on the fact that it only works on gearboxes designed for Honda. He will also calculate the box of a VAZ without any problems.
Attention ! The gearbox and maximum vehicle speed calculator is provided for informational purposes only and does not guarantee 100% reliable data!
There are several topics on the forum dedicated to Honda gearboxes, from which you can find out the gear ratios for the calculator. The information is not complete yet, but over time, through the efforts of the community, we will update the topics and make a complete selection of characteristics:
– Gearbox and gear ratios for B series engines; – Gearbox and gear ratios for K series engines; – Gearbox and gear ratios for H series engines; – Gearbox and gear ratios for F series engines. –
At the end of the post, I would like to note that when installing wheels of a larger diameter or tires other than the stock size on a car, the speedometer will not provide entirely correct data. Few people send it for calibration in order to take accurate readings; in 99.999% of cases, car owners leave everything as is. To find out how much the speedometer is “deceiving” you, the blog has another useful tool:
Thank you for your attention and special respect to all those who shared the link to the post
PS Following a long-standing tradition, do not forget to subscribe to updates of the project and our public VKontakte, tell friends about the project, share links to interesting posts online, leave detailed comments on the topic, retweet, like, click on “I like”, add posts in Google Plus and . And of course, the MOST IMPORTANT thing - I invite everyone to the forum of Honda lovers. Since the last post, a lot has changed, and so has the forum. I'm waiting for everyone on the forum
Source: www.mytyper.ru
Car stopping distance
Stopping distance is the distance traveled by a vehicle from the moment the driver detects a danger on the road until the car comes to a complete stop.
If you want to calculate a car's stopping distance, you must add to the car's braking distance the distance covered during the driver's reaction time. Here's how to do it:
The first value in the expression is the driver reaction path traveled by the car while the driver is reacting to a hazard on the road. The second expression is the formula for calculating the braking distance. In order to calculate the stopping distance of the vehicle, it is necessary to add both results together.
Calculation example: you are driving your car at a speed of 50 km/h. Calculation: (50 km/h : 10) x 3 = 15 meters of distance the car will travel when responding to a danger on the road (50 km/h : 10) x (50 km/h : 10) = 25 meters will be the braking distance of the car. As a result, adding both values, we find that the stopping distance of the vehicle will be 40 meters.
Attention: these rules are not scientifically correct formulas and provide only approximate values!
Calculation of speed during examination
To expertly determine the initial speed of a machine, specialists use the formula:
Va = 0.5*tз*j + √2Sь*j,
Where
tз – time during which the vehicle speed slows down, s;
j – deceleration constant at the moment of braking, m/s2 (determined by reference, based on GOST 25478-91);
Sу – length of the trail during braking, m.
On a dry road, j is equal to 6.8 m/s2, so the skidding speed of a car braking at a distance of 21 meters is 64.5 km/h.
After the driver begins to react to the environment, the car goes through the so-called stopping distance until the speed is completely zeroed.
So = (S1 + S2 + S3 + S4) = (t1 + t2 + 0.5*t3)*Va + Va/2j,
Where
t1 – driver reaction;
t2 – delay of the hydraulic drive of the brake system;
tз – increase in deceleration.
The time interval t4 (full stop time) is calculated as the ratio of the skidding speed Vу to the deceleration j. The time until the deceleration rate increases depends on three indicators:
- type of drive;
- road surface condition;
- vehicle weight.
To determine it, half should be subtracted from the initial speed Va until the minimum speed tз*j is established. Thus, the total time of the dynamic part of an accident for a car is t0 = t1 + t2 + t3 + t4 = T + Va/j, s.
Attention! The deceleration increase time for a pneumatic drive is longer than for a hydraulic drive. It increases with the curb weight of the vehicle and the coefficient of adhesion.
Distance
- Three car lengths . Anyone traveling in urban areas must maintain a distance of at least 15 meters, or three car lengths.
- Half speedometer : for a safe distance outside of populated areas, pay attention to the speed of the car. In order to calculate a safe distance, divide by 2 the current speed shown by the speedometer. As a result, you will get the distance to other cars in meters. Example: At a speed of 70 km/h, you must keep at least 35 meters from the vehicle in front. Moreover, this applies to dry asphalt in the summer.
- Double distance : In case of poor visibility or bad road conditions, you should double the safe distance.
Overtaking formula: how to calculate the distance required for a maneuver?
In order to solve a question regarding time, distance and speed, it is necessary to create an equation.
To overtake a passenger car, it is necessary, as a rule, to move 30 m ahead relative to that same car. 30 meters is the conventional length of three cars, that is, the distance to which you must rush forward in the oncoming lane.
How much do you need to speed up? If you accelerate at 30 km/h, the entire maneuver will take 3.6 seconds. If you take the speed higher, you risk losing control and exceeding the speed limit.
Overtaking time (sec) = How far to go (m) / 0.28 x Speed difference (km/h)
Of course, you won’t be doing calculations while driving, so we have prepared this table for you. Evaluate the numbers - 10 seconds in the oncoming lane is too much. Add 20-30 km/h, overtake in 3-5 seconds and continue driving calmly.
How long does it take to overtake a car?
Speed difference
Time to overtake
Did you like the article? Subscribe to the channel to stay up to date with the most interesting materials
Determining speed by analyzing the resulting deformations
This method is used most rarely, since in itself it is quite controversial . Today only a small number of experts resort to it.
The reason for this lies in the lack of accurate and proven methods for calculating speed based on damage received by a car. Typically, users of this method usually give speed indicators down to tenths, which casts doubt on their veracity.
The formation of deformations is influenced by a huge number of factors, including the condition of the car’s tires, the presence or absence of ABS, the distribution of load in it, the design, the service life of the car, etc.
Very often this data is simply discarded, and some of it is simply impossible to take into account. Also, as a result of aging, the metal of the body can deform in different ways. These are not all the factors that should be taken into account when calculating speed.
The huge amount of required data, as well as the often impossibility of establishing it by expert means, does not allow the widespread use of this technique in everyday practice.
Typically, many car owners are confident that analysis of car damage is the main method of determining its speed at the time of an accident, insisting on conducting such an examination.
How is traceological examination carried out? Read more here.
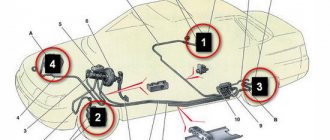
Where does the brake fluid go - sources of leakage?
Crack in the brake fluid reservoir
First of all, inspect the tank itself, this may be the reason. Do not rush to immediately disassemble the floor of the car in order to find the cause of the brake fluid leak. In general, it is best to look for the source of the malfunction by following the characteristic traces of leakage; they will show you the location, as well as the cause of the leakage of the fuel fluid.
Violation of the integrity of the brake cylinder
If your brake cylinder is leaking, the fuel fluid level will constantly drop, and under the car after long periods of inactivity, as a rule, there will be stains of fuel fluid on the asphalt. In order to confirm or refute this assumption, it is necessary to perform an inspection. To do this, remove the wheels and carry out a visual inspection of the front discs, check for any leaks on the calipers. If you have drum brakes on the rear wheels, you will also have to remove the drums. A leak in the rear brake cylinder is most often associated with damage to the rubber seals; they may be of poor quality or cracked over time. In winter, this problem is very urgent, the seals “dull” and leakage of fuel fluid occurs.
Damage to the brake hose
To establish this malfunction, a visual inspection will also be sufficient; you can touch the hoses with your hands to make sure they are in good condition. If the hoses feel hard to the touch or crack when bent, replace the hoses with new ones. Check for leaks on the hoses; they must be completely dry. Sometimes it happens that the brake hose simply flies off the fitting, in which case you need to put it in place and secure it using special clamps or replace the hose with a similar one, only of a smaller diameter.
The main brake cylinder (GTC) is faulty
In this case, it is necessary to inspect the gas turbine housing; in most cases, the leak occurs precisely because of the seal. A crack may form in the rubber seal, which causes fuel fluid leakage. Other scenarios are also possible, for example, when the brake fluid goes into the “vacuum reservoir”, while there are no signs of leakage outside; in order to detect this malfunction, it is necessary to remove the brake master cylinder. After removing the brake cylinder, remove it from the “vacuum chamber”, if you find a leak inside the “vacuum chamber” - completely replace the entire brake cylinder.
Start the engine, put it in neutral and apply the brake. If the cause of the brake fluid leak is in the hydraulic drive, the pedal will gradually “fail”. If you press the brake pedal and it reaches almost to the floor, the problem will be associated with a malfunction of the brake circuit.
After completing all repair work, it is MANDATORY to bleed the brake system. Also consider the fact that brake fluid is hygroscopic, so it must be changed after a certain period of time.
Issues discussed in the material:
- Where does the brake fluid go?
- How to detect a leak
- How to fix a brake fluid leak yourself
- Is it possible to get to your destination if brake fluid leaks on the road?
The braking system of a car operates using brake fluid (BF). An expansion tank is provided for it, on the body of which there are marks, by which you can find out what the volume of fluid is in the brake system. The lowest permissible level is marked min, and the highest, accordingly, is marked max. The brake system will operate normally when the fluid level is between these two marks. Some drivers prefer to add brake fluid to the maximum value.
If you see that its level drops sharply, and brake fluid leaks are found on the wheels, this is a signal to urgently take action; driving a car with such a malfunction becomes dangerous.