Error codes Kalina 8 valves caused by incorrect ignition activation (0300)
- 300 – misfire or no spark for all pistons;
- 301/302/303/304 – similar to the previous number with clarification for each boiler sequentially;
- 325 – problems with the functioning of the DD;
- 327/328 – the mixture detonation sensor does not work correctly;
- 335/336 – failure or incorrect information is received from the DPKV unit;
- 337/338 – similarly with touching ground or other wires;
- 340 – wire break or DRF has failed;
- 342/343/346 – incorrect operation of the phase distribution indicator, possible short circuit;
- 351-354 – poor contact to the ignition coils, or damage to the wiring, for all boilers in series;
- 363 - dry pistons, no gasoline or oxygen, possible blockage or air bubble in the line.
What does error code P0301 mean?
Most gasoline cars have 4-6 cylinder engines. During operation, a spark plug fires sequentially in each cylinder, which ignites the fuel mixture. At the moment of ignition, a micro-explosion occurs, the energy of which is transferred to the crankshaft, which transfers it further to the transmission.
If misfires occur in more than one cylinder, this increases or decreases engine speed. If such fluctuations are 2 percent or more, the engine control unit will record an error code P0300 in its memory.
If the percentage of such fluctuations is in the range from 2 to 10 percent, then the “Check Engine” will light up on the dashboard. If the Check Engine light starts blinking, this indicates that the number of misfires exceeds 10 percent and further operation of the vehicle can lead to serious damage. The P0301 error code indicates that the misfire is occurring in the first cylinder.
Checking and replacing the VAZ 2114 phase sensor: step-by-step instructions
The VAZ 2114 camshaft sensor is one of the most important measuring instruments of the fourteenth, which, through a pulse signal, transmits information about the current engine operating cycle to the car’s brains. Based on the information received, the electronics adjusts the timing of supply and ignition of the fuel mixture in the engine cylinders.
A normally functioning DF is the key to the correct functioning of the engine, which achieves the optimal ratio of the amount of fuel consumed and the operating power of the power unit.
From this article you will learn the main causes of DF malfunction and how the failure of the device affects the operation of the car. The technology for replacing the DF on the VAZ 2114 will also be examined in detail.
Features of the VAZ 2114 phase sensor
Peripheral system used (2000)
- 70-71 – the channel size diagnostic valve is faulty (jammed);
- 100 – break in the PDZ line;
- 101 – similar value to the previous paragraph;
- 102/103 – short circuit of the remote control control line;
- 105 – control unit failure;
- 122/123 – incorrect pedal position signal;
- 127/128 – similar to the above code;
- 187/188 – excessively rich or lean mixture at idle;
- 135 – sensors A and B, designed to control the position of the remote control, do not respond correctly;
- 138 – similar value for the corresponding accelerator lever position sensors;
- 176 – throttle drive position failure;
- 178 – complete failure of adaptation of the above block;
- 187/188 – incorrect mixture formation;
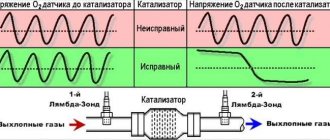
- 270/271 – lack of reaction of DK2 to enrichment or depletion of the mixture after the catalyst;
- 301/304/307/310 – short circuit of the ignition coil for all cylinders, respectively;
- 500/501 – incorrect generator power readings.
Lada Kalina errors, interpretation for automatic transmission (р0000)
- 720 – failure of the output shaft rotation sensor;
- 717 – turbine rotation sensor;
- 705-706 – no selector signal or multiple values;
- 973/974 – solenoid on/off, open circuit or short circuit to ground;
- 962/963 - the same element responsible for pressure - there is a break or short circuit;
- 740/743 – LOCK UP SOL open or closed;
- 17AB/AA – L/C SOL;
- 17АЭ/AD – 2-4/B SOL;
- 17B1/B0 – H/C and L and R/B;
- 1735-1738 – the 1st-4th gear lock is closed, respectively;
- 744/1744 – LU CLUTCH;
- 731-734 – incorrect ratio for positions 1-4;
- 17A0-A4 – reverse and forward gears do not work alternately in accordance with the last digit of the code;
- 711-713 – network malfunction or DTM failure;
- 863 – connection failure with the diagnostic computer;
- 062F – memory error;
- 1701 – main controller power failure.
How to troubleshoot P0301
The cause of the misfire should be fairly easy to determine if the problem is persistent.
Check spark plugs, ignition coils, distributor
Spark plugs can tell you a lot. Signs of sparking on the ignition coil, distributor cap, or rotor may also indicate a faulty part.
A faulty spark plug coil is usually checked by replacing the coils between the cylinders. They look to see if the misfired cylinder has changed or remains the same.
Compression, marks, fuel pressure, lean mixture
Compression, timing marks and fuel pressure can also be checked. The engine may need to be checked for air leaks.
Short-term fuel control (STFT) and long-term fuel control (LTFT) must be checked using a diagnostic scanner or an ELM327 adapter with Torque software. This is necessary to make sure that the air-fuel mixture is not lean.
Often, a faulty mass air flow sensor (MAF) causes the engine to run lean, causing random misfires.
Checking the cooling system pressure can help identify a leaking head gasket.
Exhaust gas recirculation
If the misfire only occurs at idle, the EGR valve and purge valve should be checked as either one may be stuck open.
Valve mechanism
You may need to check your valve adjustments, as out-of-adjustment valves can cause misfire on cold starts, which is a fairly common problem in some older Honda engines.
Faulty valvetrain mechanical parts, such as worn camshaft lobes or a stretched timing chain, can also cause an engine to misfire.
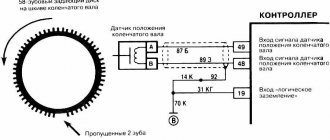
Sometimes a broken or damaged tooth on the crankshaft or camshaft sensor gear can cause a misfire. If you suspect a crankshaft position sensor (CPS) or camshaft position sensor (CPS), checking the signal with an oscilloscope may help.
Once the problem is fixed, the misfire code will disappear after some driving time.
Previous Post Trouble P0131 - Oxygen Sensor Voltage Low (Bank 1 Sensor 1) Next Post Trouble P0341 - Camshaft Position Sensor Range/Performance
Causes of error P0343
A high signal level from the camshaft position sensor may indicate various breakdowns. Most often the error occurs for reasons such as:
- The camshaft position sensor is faulty or dirty;
- Contacts and terminals are faulty or oxidized;
- The sensor connector is damaged or dirty;
- Broken or broken wiring;
- Low battery charge;
- The electronic engine control unit has failed.
The code may also appear in other cases. But most of them are rare. Many of the above breakdowns can be identified by visual inspection of parts or testing them with a multimeter. External damage is usually easy to detect by eye. The presence of poor contact or open circuit will be shown by appropriate measurements. And the corresponding indicator on the car’s dashboard can also indicate a poor battery charge. In addition, a discharged battery may also indicate a malfunction of the generator, which is determined by checking with a tester. Therefore, identifying such breakdowns will not be difficult for the car enthusiast himself. The most difficult thing to diagnose is ECU failure. Without relevant experience, it is not easy to determine them. Therefore, if you suspect a malfunction of this device, it is recommended to contact an automobile electrician.
Signs of a faulty phase sensor
If the phase sensor fails completely or partially, the electronic control unit forcibly switches the engine to paraphase fuel injection mode. This means that the timing of fuel injection is carried out according to the readings of the crankshaft sensor. As a result, each fuel injector injects fuel twice as often. This ensures that a fuel-air mixture is formed in each cylinder. However, it is not formed at the most optimal moment, which leads to a drop in engine power, as well as excessive fuel consumption (albeit small, although this depends on the specific engine model).
Symptoms of a faulty phase sensor are:
- fuel consumption increases;
- the toxicity of exhaust gases increases, the smell of exhaust gases will be felt, especially if the catalyst is knocked out;
- the engine begins to operate unstably, most noticeably at low (idle) speeds;
- the acceleration dynamics of the car, as well as the power of its engine, are reduced;
- the Check Engine warning light is activated on the dashboard, and when scanning errors, their numbers will be associated with the phase sensor, for example, error p0340;
- at the moment the engine starts in 3...4 seconds, the starter spins the engine “idling”, after which the engine starts (this is due to the fact that in the first seconds the electronic control unit does not receive any information from the sensor, after which it automatically switches to emergency mode, based on data coming from the crankshaft position sensor).
In addition to the above symptoms, often when the phase sensor fails, problems arise with the vehicle’s self-diagnosis system. In particular, at the moment of starting, the driver is forced to turn the starter for a little more time than usual (usually 6.10 seconds, depending on the model of the car and the engine installed on it). And at this time, self-diagnosis of the electronic control unit occurs, which leads to the formation of corresponding errors and transfer of the engine to emergency operation mode.
Malfunctions of the phase sensor on a car with HBO
It is noted that when the engine is running on gasoline or diesel fuel, the unpleasant symptoms described above do not appear so acutely, which is why many motorists often use cars with a faulty phase sensor for a long time. However, if your car is equipped with gas equipment from the fourth generation and higher (which uses its own “smart” electronics), then the engine will work intermittently, and the driving comfort of the car will sharply decrease.
In particular, fuel consumption will increase significantly, the air-fuel mixture may be lean or, conversely, enriched, and engine power and dynamics will significantly decrease. All this happens due to a mismatch between the software of the electronic engine control unit and the LPG control unit. Accordingly, when using gas-cylinder equipment, the phase sensor must be changed immediately after its breakdown is detected. Using a machine with a damaged camshaft position sensor is harmful in this case not only to the engine, but also directly to the gas equipment and its control system.
Device design
The phase sensor of the Priora and any other car is an integral mechanism, the functions of which include obtaining all kinds of information about the engine operating cycle, as well as transmitting a signal to the electronic control unit using special pulses. The sensor design consists of 2 parts.
This is a Hall effect sensing element and a small transducer. The sensitive element responds to changes in the magnetic field. The sensor is located at the end of the cylinder block, not far from the air filter. There is a metal disk on the camshaft that is necessary for the sensor to function properly.
How does a mechanic diagnose a P0300 code?
When diagnosing this error code, a mechanic will do the following:
- Reads all data and error codes stored in the PCM memory using an OBD-II scanner
- Clear error codes from the PCM memory and test drive the vehicle to see if P0300 appears again
- Determines which cylinders are misfiring
- Check the wires connecting the ignition coils to the spark plugs for wear and damage
- Check spark plugs for wear and damage
- Check the ignition coils, as well as wires and connectors for corrosion and damage
- If necessary, replace spark plugs, ignition coils, as well as related wires and connectors
- If the P0300 code appears again after replacing the above components, check the fuel injector and fuel delivery system
- Check the ignition distributor cap and slider for wear and damage
- If there are other error codes stored in the P0300 code, the PCM will clear any existing errors and test drive the vehicle again to determine if the P0300 error code appears again.
- If the P0300 error appears again, check the compression in the cylinders.
- If the P0300 code persists, the problem may be a faulty PCM. In this case, the module may need to be replaced or reprogrammed.
Common errors when diagnosing code P0300
The most common mistake when diagnosing a P0300 code is to rule out a failed cylinder, fuel injector, or PCM.
It is also a mistake to not look at other error codes that appear along with the P0300 code. If you do not resolve all present errors, this may cause the P0300 code to appear again.
Is it possible to drive with P0343?
Driving with code P0343 is possible, but not recommended. There is a possibility that the engine will suddenly stop without being able to start it again. This is fraught with unpleasant consequences, especially on a long journey. In addition, driving with such a problem is uncomfortable. But the error does not have any impact on safety and controllability. Therefore, there is no ban on the operation of such a machine. But, despite this, it is recommended to carry out independent diagnostics and repairs within a reasonable time or contact a car service to carry out these works.
Source
Interruptions in the air supply to the internal combustion engine (0101)
- 102 – damage or malfunction of the mass air flow sensor;
- 103 – short circuit in the MAF wiring;
- 112/13 – failure or incorrect operation of the fuel mixture temperature sensors in the intake manifold;
- 115-116 – violation of antifreeze t° sensors – there is no cooling of the system or the main airflow is not working properly;
- 117-118 – open circuit of the coolant temperature sensor power supply/short circuit;
- 122/123 – defect in cable insulation at the TPS;
- 130/131 – error/break in DC circuit No. 1;
- 132 – short circuit of sensor No. 1 PCV;
- 133/134 – the air sensor connection is broken (sometimes it’s enough to clean the terminals and connector) or the wiring is damaged;
- 135 – malfunction of heater DK2;
- 136 – contact with the body of the DK2 highway;
- 137/138/140 – uncontrolled signal DK2 or break of the corresponding line;
- 141 – failure or interruption of heating of DC2;
- 171/172 - violation of mixture formation in the first case - depletion, for the second - excessive enrichment.
How to Diagnose DTC P0300?
Once a P0300 code is detected, a professional auto mechanic will perform the following steps. You can do the same thing yourself.
Connect your car charger
The charger is extremely important when diagnosing the P0300 code. Because troubleshooting requires that the ignition remain on, and this can lead to battery discharge
As a result, additional error codes will appear, which will complicate the search. A car charger will help preserve your battery's charge.
Connect OBD2 scanner
An OBD2 scanner is required to scan and resolve the P0300 code. With the help of it, you can track the issues related to the error and also troubleshoot them easily.
For cars manufactured before 1996, an OBD1 scanner is used. If the car was manufactured after 1996, use an OBD2 scanner.
Check wiring
Before replacing any part, first make sure all wires and connections are in good condition. Visually inspect the wiring, check for corrosion and correct if necessary.
Check the spark plugs
Spark plugs do not wear out quickly. But if a cylinder is misfiring, it's a good idea to check the spark plugs and notice any signs of trouble.
If the spark plug appears to be faulty, replace it. As part of regular maintenance, you should change the spark plugs every 30,000 km. You should also check the ignition coils!
Inspect the distributor cap
If you replaced the spark plugs, but the problem persists, check the fuel injectors for defects. If you have an old car, check the ignition distributor cap.
Check other error codes
If the OBD2 scanner detects more than one fault code, take the necessary measures to diagnose and resolve them. After doing this, check if the P0300 code returns.
Replace engine control unit
If you have checked everything above, but the error does not go away, there is a possibility that the problem is related to the control unit (PCM). It may need to be re-flashed or replaced.
How to fix the problem?
To fix the problem, you should reset the error and repeat the diagnostics after a couple of days. It is advisable to use an OBD2 scanner. If the code does not disappear, you should check the parts and assemblies of the “four” described above. Sometimes, to eliminate the malfunction, it is enough to clear the sensor of oil and clean the contacts. This procedure can be combined with replacing the timing belt and engine lubricant. In this case, it is useful to eliminate the reason for its contact with an electrical component. If the sensor fails, it should be replaced. Broken or damaged wiring must be repaired. To restore the battery's charge, sometimes it is enough to charge it well with a charger and clean the terminals, but you may need to buy a new battery or repair the generator if the problem is in it.
The ECU, if broken, must be replaced. This is one of the most unpleasant and expensive breakdowns associated with this error. Fortunately, it is rare.
Causes of misfires
Ignition coils
Bad ignition coils are a common problem on many vehicles, including BMW, Ford, Hyundai, Mazda, Nissan, Volkswagen and GM. A faulty ignition coil needs to be replaced.
Candles
If the spark plugs have not been changed for more than 15 thousand km, replacing them would be a good idea. Worn spark plugs require higher voltage to produce a spark, which puts more stress on the ignition coils.
Some car manufacturers update ignition coils during vehicle production.
If one of the ignition coils has failed and the manufacturer has updated the part, then the auto mechanic may recommend replacing all ignition coils with updated ones as a precaution.
Carbon on valves
In many modern vehicles, especially those with direct fuel injection, carbon buildup on the intake valves and injectors can cause misfire.
Some mechanics may recommend cleaning the valves with a special spray or foam, as this is cheaper and sometimes helps. A more effective option is to clean the intake valves manually.
Watch the video on how to clean the valves:
Clogged fuel injectors also need to be cleaned or replaced. This repair is expensive because it requires more labor. It is necessary to remove the intake manifold and some other parts.
Air leak
Vacuum leaks, as well as a stuck EGR valve or purge valve, can cause misfires that mostly occur at idle but go away at higher rpms.
Adjustment of valves
In some older Honda vehicles, misfire can be caused by improperly adjusted valves. The misfire may be more noticeable when the engine is idling after a cold start.
As valve system parts wear, valve clearances change. To compensate for this, the valves in many Honda engines must be adjusted at recommended intervals.
Timing belt
Sometimes an engine may misfire if the timing belt or chain were not correctly aligned when replacing the timing belt. If the problem occurs after replacing the timing belt or chain, the first step is to check the timing marks.
Oil leak
In many high mileage vehicles, oil leaking into the combustion chamber due to worn valve seals and oil rings can foul the spark plugs and cause a misfire.
Often, misfires appear at idle, but disappear after increasing the speed. Blue smoke is another symptom of oil leakage into the combustion chambers.
Water
In many older vehicles, cleaning the engine compartment or driving through deep puddles can cause the engine to misfire as water gets into the ignition parts and causes short circuits.
Replacing the spark plugs and ignition wires often solves the problem. Ignition coils that have cracks or signs of sparking should also be replaced. In older vehicles with an ignition distributor (distributor), the distributor cap and rotor are also replaced.
Description of the causes of error P0300
When an engine misfires, high concentrations of hydrocarbons (CH) enter the exhaust pipe. High concentrations of CH can lead to increased exhaust emissions. High concentrations of CH can also cause the temperature of the three-way catalytic converter (TWC) to rise, which in turn can cause damage to the TWC. To prevent this increase in exhaust emissions and limit the potential for thermal damage, the ECM monitors the frequency of misfires. When the temperature of the catalytic converter reaches the thermal breakdown point, the ECM turns on the MIL. The ECM monitors misfires using the crankshaft position sensor (CPS) and camshaft position sensor (CMP). The SMR sensor is used to detect misfiring cylinders, and the SCR sensor is used to measure deviations in crankshaft speed. The number of misfires is counted when the crankshaft speed deviation values exceed preset thresholds. The ECM turns on the MIL and records a DTC if the frequency of misfires exceeds the threshold and may result in increased exhaust emissions.
| DTC No. | DTC Detection Condition | Faulty area |
| P0300 | Simultaneous misfire detected in several cylinders (diagnosis logic for 2 trips) |
|
| P0301P0302P0303P0304 | A misfire was detected in one of the cylinders (diagnosis logic for 2 trips) |
If DTCs are set for different misfired cylinders, but DTC P0300 is not set, it means the misfires were detected and stored at different times. DTC P0300 is set only when misfiring cylinders are detected at the same time.
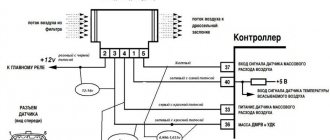
CONNECTION DIAGRAM
Ignition system connection diagram.
How to replace a spark plug?
Replacing the spark plug is a simple task and you can do it at home. Before changing spark plugs, make sure the engine temperature is low.
Step 1: Open the hood and locate the spark plug
Open the hood and you will see several wires running in the engine compartment. The spark plugs are located in the engine at the end of these wires.
Pull the wire and you will see the spark plug installed.
Step 3: Remove the candle
Insert the spark plug wrench and turn to loosen the spark plug
Remove the old spark plug and note its condition
Step 4. Install a new spark plug
Using the same spark plug wrench, install the new spark plug and tighten it correctly. Then connect the wire as it was before. All is ready.
Diagnostics on an eight-valve engine
Please note that sensors for 8 and 16 valve engines are not interchangeable. Therefore, when purchasing, pay attention to this nuance. To diagnose phase sensors, you must perform the following manipulations:
- Connect a 13.5 Volt constant voltage source to contact “E”.
- There should be a voltage of 0.9 V at pin “B”.
- After bringing a metal object to the active part of the device, the voltage will decrease to 0.4 V.
- If you remove the metal device, the voltage will return to 0.9 V.
Symptoms of a faulty camshaft sensor
Just like any part or component in your vehicle, this CMP sensor will eventually, sooner or later, simply stop working due to wear and tear. This happens anyway once its maximum service life has expired. This usually occurs due to wear on the internal wire wrap or a component associated with it.
Usually, in this case, the engine in the car begins to work intermittently, and the signs of a malfunction can vary in different ways, i.e. depending on the type of sensor wear. For example, the same connector in a sensor may wear out, the same internal circuitry in the sensor may fail, or a component associated with the sensor may fail.
On some types of cars, if the camshaft position sensor is faulty, the transmission may be locked in one of the gears and will be locked until you turn off the engine and start it back. This can be repeated with a certain cyclicity.
If the camshaft sensor begins to behave incorrectly while the car is moving, i.e. work, then you can immediately feel that your car has begun to move jerkily and at the same time lose speed.
If the camshaft sensor fails, you may experience a noticeable loss of power from the engine itself. For example, your car simply cannot accelerate over 60 km/h.
The engine in the car may stall intermittently, and all this is due to a malfunction of the CMR sensor.
If the sensor fails, you will notice poor engine performance, it will have a loss of dynamism, misfires will begin when the ignition is turned on, jolts during acceleration, popping noises in the exhaust system, etc. irregularities in work.
On some car models, if the camshaft sensor is faulty, the ignition spark may completely disappear, which will ultimately lead to failure and the engine being unable to start.
After your car's computer detects a malfunction of the camshaft position sensor, which, as you understand, will lead to the appearance (lighting) of the “Check Engine” indicator on the dashboard. After detecting poor operation of the CMR sensor, the computer will automatically record the sensor’s “error code” in its memory. To accurately determine the cause of the malfunction of this camshaft sensor, it is necessary to conduct computer diagnostics of the car, i.e., by thus connecting special equipment to the diagnostic connector of the car. Next, using a special computer program, you can read the “error code”. Below, dear motorists, we present to you a table of diagnostic “error codes” that are directly and directly related to wear on the camshaft sensor.
When error P0300 occurs
The P0300 code appears when the problem is related to the ignition. The error code can be determined in the range P0300-P0312. The code values directly depend on the number of cylinders and the malfunction in each of them. For example, error code 0301 indicates a misfire in the first cylinder, and so on. When checking with a scanner, it will display a warning message about random multiple misfires on the cylinders. If the error is indicated as 0300, the problem is general sparking.
Error code on display
Nevertheless, it is the 300th code that is recorded by the scanner only when there is a failure in sparking in several cylinders at once. The failure is not stored in memory instantly, but only 210 seconds after the next operation at idle; at medium speeds, the error rate should be no less than once every 75 seconds. In this case, an ignition error in several cylinders is indexed only when more than 3.25% of all flashes are missed. If a specific cylinder is to blame, then we will see another version of this code - 0301, 0302 or 0303, if we are dealing with a three-cylinder Daewoo Matiz engine.
Interesting on the topic: The most extravagant cars of rock stars that we didn’t know about
On which cars is this problem most common?
The problem with code P0343 can occur on different machines, but there are always statistics on which brands this error occurs more often. Here is a list of some of them:
- Audi (Audi a4, Audi TT)
- BMW
- Cadillac (Cadillac SRX)
- Chery (Chery Amulet, Jagi, M11, Tiggo)
- Chevrolet (Chevrolet Avalanche, Aveo, Lacetti, Traverse)
- Chrysler
- Citroen (Citroen C4)
- Dodge (Dodge Ram)
- Ford
- Geely (Geely MK)
- Hyundai (Hyundai Accent)
- Kia (Kia Rio, Sportage)
- Lexus
- Mercedes
- Opel (Opel Corsa)
- Peugeot (Peugeot 308)
- Skoda (Skoda Octavia)
- Toyota (Toyota Camry)
- Volkswagen (VW Beatle, Jetta, Passat, Tiguan)
- VAZ 2110, 2111, 2112, 2114, 2115
- Volga Chrysler, 31105
- Gazelle Chrysler, 405
- Lada Vesta, Granta, Kalina, Largus, Niva, Priora
- UAZ Patriot
With fault code P0343, you can sometimes encounter other errors. The most common are: P0030, P0036, P0124, P0332, P0335, P0336, P0340, P0341, P0342, P0345, P0346, P0347, P0348, P0349, P0365, P0366, P0367, P0368, P0369, P039 0, P0391, P0392, P0393 , P0394, P0606, P2122, P2138.
Sources used:
- https://elm3.ru/diagnostika/oshibka-p0343
- https://autonevod.ru/obd2-codes/p0343
Self-diagnosis
The easiest and most common way to diagnose error codes on a VAZ Kalina is to search using the on-board network. The procedure looks like this.
Insert the key into the lock cylinder. Next, hold down the RESET key and, without releasing it, turn on the ignition. In this case, the device will automatically switch to diagnostic mode. At the same time, all the indications will light up, and the instrument arrows will make a full circle.
You should pay attention to the arrows and indicators - if any diode does not light up, you need to check the device for which the element is responsible. On the right steering column lever there is a button for scrolling through the options - you need to scroll to the required position (error codes). Next, the display will show the general error number; to reset the index, you need to hold RES for three seconds.
Note! The indicated sequence is relevant for Lada Kalina of the first and second modifications.
The position of the error codes will show one of the indices on the display:
- “2” – there is a surge in the BS power supply – a possible short circuit in the wiring;
- “3” – rupture of lines, or failure of the float inside the gas tank;
- error 4 Lada Kalina says that the coolant temperature sensor is broken or malfunctioning;
- “5” – the thermometer has gone astray, the element may be damaged or the circuit may be broken;
- “6” – exceeding the maximum permissible temperature of the internal combustion engine block, while the acoustic alarm is working;
- “7” – exceeding the permissible pressure thresholds inside the oil line;
- “8” - on a Lada Kalina car, error 8 appears when there is a malfunction of the calipers or a breakdown in the hydraulic drive line;
- “9” – critical voltage drop in the battery;
- “E” – incorrect reading or display of the EEPROM information module.
To return to the original part, it is enough to hold RES for 30 s. The disadvantage of this method is minimal accuracy - the procedure shows in which direction to look for a breakdown, but not a specific node. So, it is possible to understand exactly where the failure occurred only by the following method.
Causes of error P0300
- Worn or damaged spark plugs
- Worn or damaged spark plug wires and/or ignition coils
- Damage to the distributor cap (if equipped)
- Worn or damaged ignition distributor runner (if equipped)
- Fuel injector damage
- Clogged pipes or valve of the exhaust gas recirculation system
- Incorrect ignition timing setting
- Vacuum leak
- Low fuel pressure
- Damage to the cylinder head gasket
- Distributor cap wear
- Camshaft position sensor malfunction
- Malfunction of the crankshaft position sensor
- Air flow sensor malfunction
- Oxygen sensor malfunction
- Throttle Position Sensor Malfunction
- Malfunction of the catalytic converter
- PCM malfunction
Replacing the phase sensor VAZ 2114 8 valves
Having determined that the DF is faulty, you can begin to replace it. The process is easy enough that you will only need a ratchet wrench with a 10 mm head to do all the work yourself.
First, let's figure out where the VAZ 2114 phase sensor is located. It is located on the right side of the engine compartment, near the air filter. It is secured to the cylinder block body with one screw.
Replacement of the VAZ 2114 phase sensor is carried out in the following sequence:
- Open the hood and disconnect the power terminals from the fourteenth battery;
- Disconnect the wire block from the DF;
- Using a 10mm wrench, unscrew the screw fixing the sensor on the cylinder block;
- We remove the DF from the mounting socket.
After dismantling the old device, inspect it visually; perhaps the cause of its malfunction is metal dust magnetized on the DF body. If found, wipe the device with a cloth and reinstall it. If it does not come to life and the on-board computer continues to generate errors, the sensor needs to be replaced.
The new camshaft position sensor of the VAZ 2114 is installed in a similar way. As you can see, the work here only takes 10-15 minutes (replacing the VAZ 2115 phase sensor is carried out using the same method).
Important: when installing the DF into the mounting socket to seal the fixation, it is prohibited to use any sealing agents, since the device is located in an environment with a constantly changing temperature regime, in which the sealant will simply melt and bring you a bunch of additional troubles with the engine.
There are often cases when, even after installing a new DF, errors 0350 or 0343 continue to be displayed on the on-board computer of the fourteenth.
There are two possible scenarios for the development of events. You may have come across a faulty DF (even salespeople in auto stores say that if for 10 domestically produced phase sensors there are 5 workers, without manufacturing defects, this is already good).
Checking the functionality after replacement is carried out using a multimeter, as described in the previous section of the article. If the tester data corresponds to the indicators of a fully working sensor, then the problem is not with it. Errors 0350 and 0343, indicating a faulty DF, can also occur due to a timing belt that is stretched or has slipped by 1-2 teeth, or a loose crankshaft gear.
What Causes Code P0301
- spark plug of cylinder 1 is damaged or worn
- Damaged or worn spark plug wire and/or ignition coil
- The ignition distributor cap is damaged or worn.
- the “slider” of the distributor (ignition distributor) is damaged or worn out
- Fuel injector of cylinder 1 is dirty or damaged
- The EGR valve tubes or the valve itself are clogged
- Incorrect ignition timing (late or early ignition)
- leakage of vacuum tubes
- low fuel pressure
- Damaged cylinder head gasket(s)
- distributor cap is cracked
- camshaft position sensor faulty
- crankshaft position sensor is faulty
- The mass air flow sensor (MAF sensor) is faulty
- faulty oxygen sensor (lambda probe)
- Throttle position sensor is faulty
- the catalytic converter (catalyst) is faulty
- faulty engine control unit
What does P0301 mean?
P0301 (and other P030X codes such as P0302, P0303, etc.) are simpler than you might expect. Because the ECU has already determined which cylinder has the problem, saving you the diagnostic headache.
The last digit of the P030X code indicates the number of the misfired cylinder. P0302 is a misfire on cylinder 2, P0303 is on cylinder 3, and so on.
The P0300 code indicates a random misfire. This means that several cylinders are misfiring randomly. Codes P0300 through P0308 are called misfire codes.
If you have one of these errors, you need to fix the problem as quickly as possible. If you drive your vehicle in this condition, you will damage the catalytic converter.
Symptoms of error P0343
If this DTC is detected, the following symptoms may also be present:
- Problems starting the engine. It may start with difficulty or not at all;
- Sudden stop of the power unit. The car stalls while driving or stopping for a short time. In this case, the engine may not start again;
- Reduced engine power;
- Misfire in cylinders.
Signs may be constant or appear periodically. Often all symptoms or only some of them are present.