Only in 2016, AvtoVAZ, for the first time in history, chose energy efficiency over gasoline savings, so the developers of the VAZ 21179 engine were faced with tasks in order of importance:
- achieve high torques, even at low speeds;
- increase power and volume;
- increase resource and use high-quality attachments.
ICE 21179
Already at 1000 rpm, the engine shows the torque developed at the peak of the capabilities of previous versions of the internal combustion engine, and its maximum is 170 Nm at 3750 rpm. Under the hoods of the X-Rays and West there is now 122 hp. With. in a 1.8 liter internal combustion engine. With the resource, everything is not easy due to an obvious flaw in the designers - the insufficient size of the groove inside the main bearings.
Engine characteristics 21179
Initially, the plant management set the task of increasing the volume, so a standard boost was used - maintaining the cylinder diameter, increasing the piston stroke. The power drive 21127 used as a basis bends the valve, so version 21179 inherited this defect along with a high-life Gates belt to provide at least some guarantees against timing belt breakage.
The engine diagram remains the same:
- transverse, front-wheel drive;
- camshafts located at the top, 4 valves per cylinder.
Motor parts 21179
The developers have already made tuning in the engine:
- adding piston stroke;
- increasing the diameter of the valve while reducing the thickness of its rod to 5 mm;
- vortex supply of the air mixture into the combustion chamber.
Even with increased oil consumption, the internal combustion engine consumes it within 200 ml/1000 km. The factory manual contains a description of all changes in the design and parameters of the power drive.
Design Features
Despite the fact that the motor is lighter than previous versions, it uses large quantities of attachments, so overhaul and even normal maintenance on your own is a difficult task.
For example, the manufacturer provides for fixing the camshafts and crankshaft with special devices. To install them, he recommends removing most of the overhead and intake tract. Likewise, upgrading to increase power is also difficult since there is no free space under the hood.
Intake manifold Motor Super
As a result, the technical characteristics of modification 21179 are as follows:
| Manufacturer | AvtoVAZ |
| Engine brand | 21179 |
| Years of production | 2016 – … |
| Volume | 1774 cm3 (1.8 l) |
| Power | 89.7 kW (122 hp) |
| Torque moment | 170 Nm (at 3750 rpm) |
| Weight | 99.3 kg |
| Compression ratio | 10,3 |
| Nutrition | injector |
| Motor type | in-line |
| Injection | distributed electronically controlled |
| Ignition | electronic contactless microprocessor |
| Number of cylinders | 4 |
| Location of the first cylinder | TVE |
| Number of valves on each cylinder | 4 |
| Cylinder head material | aluminum alloy |
| Intake manifold | plastic manufacturer Motor Super |
| An exhaust manifold | catalyst |
| Camshaft | 2 pcs., marks on pulleys are offset by 2 degrees |
| Cylinder block material | cast iron |
| Cylinder diameter | 82 mm |
| Pistons | lightweight, manufacturer Federal Mogul |
| Crankshaft | from 11183 |
| Piston stroke | 84 mm |
| Fuel | AI-92 |
| Environmental standards | Euro 5/6 |
| Fuel consumption | highway – 5.8 l/100 km combined cycle 6.8 l/100 km city – 8.6 l/100 km |
| Oil consumption | maximum 0.2 l/1000 km |
| What kind of oil to pour into the engine by viscosity | 0W30, 0W40, 5W30, 5W40, 10W30, 10W40, 15W40 |
| Which engine oil is best by manufacturer | Liqui Moly, LukOil, Rosneft, Mannol, Mobil, Castrol |
| Oil for 21129 according to composition | synthetics, semi-synthetics |
| Engine oil volume | 4.4 l |
| Operating temperature | 95° |
| ICE resource | declared 200,000 km real unknown |
| Adjustment of valves | hydraulic compensators |
| Cooling system | forced, antifreeze |
| Coolant volume | 7.8 l |
| water pump | with metal impeller GBM |
| Candles for 21129 | BCPR6ES from NGK or domestic AU17DVRM |
| Spark plug gap | 1.1 mm |
| Timing belt | Gates, width 22 mm, service life 200,000 km |
| Cylinder operating order | 1-3-4-2 |
| Air filter | Nitto, Knecht, Fram, WIX, Hengst |
| Oil filter | catalog number 90915-10001 replacement 90915-10003, with check valve |
| Flywheel | increased damper size |
| Flywheel mounting bolts | box MT – M10x1.25 mm, length 26 mm, groove 11 mm box AT – M10x1.25 mm, length 26 mm without groove |
| Valve stem seals | code 90913-02090 inlet light code 90913-02088 exhaust dark |
| Compression | from 13 bar, difference in adjacent cylinders maximum 1 bar |
| XX speed | 800 – 850 min-1 |
| Tightening force of threaded connections | spark plug – 31 – 39 Nm flywheel – 62 – 87 Nm clutch bolt – 19 – 30 Nm bearing cap – 68 – 84 Nm (main) and 43 – 53 (rod) cylinder head – three stages 20 Nm, 69 – 85 Nm + 90° + 90° |
This is the manufacturer’s second engine with a similar volume, but for the first time the cylinders were bored out, and here an integrated approach was used to improve the performance of the engines.
Problems
Not only reviews about the VAZ 21179 engine, but also its production cycle (it was produced in a very short time), indicate that this was not the most successful option for manufacturers. The main problems faced by owners are the following:
- Unfortunately, the power unit is characterized by increased consumption of lubricating fluid. There are quite a large number of opinions about the causes of oil burns. But most likely this is due to design features, since increased oil consumption can be overcome by boring the cylinders and achieving normal piston clearances.
- The oil pump in this internal combustion engine often jams, and the main reason that the pressure relief valve remains in the open position is the adhesion of combustion products on it. It is worth closely monitoring the lubricant pressure, since a drop in it can affect very rapid wear of the camshaft and crankshaft journals.
- There are also other breakdowns in the form of regular oil leaks from the camshaft plugs. Also, sometimes the fuel supply pipe can rub against the partition bracket, which can lead to a fire. The timing belt also often breaks.
Design nuances
The 21179 engine bears little resemblance to the basic version 21127, as both the design and appearance have changed:
- phasing of intake valves within ±30 degrees;
- hollow camshafts with cams using powder metallurgy;
- vortex air supply into the combustion chamber;
- cylinder cooling system (jacket);
- improved configuration and cylinder head gasket volumes;
- ShPG Federal Mogul;
- Korean pump;
- inclined drilling of oil channels in the crankshaft journals;
- polymer cylinder head cover and solid aluminum pan;
- flywheel for clutch 215 mm, which is recommended by the manufacturer.
Motor gaskets
ShPG from Federal Mogul
A distinctive feature of the ICE 21179 was a very complex and expensive overhaul, even when performed on its own in a garage.
Cylinder head
The cylinder head is made from aluminum, just like the base engine. But there is a significant difference - in the cylinder head of the VAZ-21179 there is a system of additional oil channels to the phase shifter control valve, originating from an additional oil supply point from the block between the first two cylinders. In this case, the valve acts as a solenoid that regulates the flow of lubricant into the chambers of the VVT system. The lubrication system has been improved - in the intake camshaft support, which had to be expanded for this purpose, there are two oil intake channels and one outlet. These channels are connected through an electrovalve in a certain way to the chambers of the phase shifter, which rotates under their influence. Possible oil leakage through the camshaft seals is resolved by installing drain holes in the front supports.
photo of VAZ-21179 block head
Pros and cons
The new power drive initially has a number of advantages:
- torque is increased, not only in the high speed range, but also at the bottom;
- oil pump performance has been doubled;
- camshafts are lighter, valve cross-section is increased;
- The displacement and engine power have changed significantly - 1.8 liters and 122 liters. pp., respectively;
- a phase distributor appeared on the intake camshaft;
- the intake and exhaust tracts have been improved, Euro-5 standards have been met;
- it is possible to finalize it to the Euro-6 protocol, planned for 2020.
Phase distributor
Exhaust tract
To replace the timing belt, it is necessary to remove half of the equipment under the hood. We come across defective valves from the German manufacturer Mahle, whose production facilities are actually located in China. Hence the increased oil consumption to 3 l/1000 km, then the cylinder head is replaced, which is very expensive (overhaul instead of maintenance).
The main bearing shells have a groove of less than 180 degrees; there are no counter grooves in the yokes. This single drawback is negated by the use of the latest higher-capacity oil pump, cooling channels between the cylinders and larger valve diameters.
Oil pump GMB
The use of high-quality parts from foreign manufacturers is not as clear as the designers intended:
- at any time after the European Union imposes sanctions against the Russian Federation, supplies may stop unilaterally;
- domestic industry is not yet able to provide such manufacturing precision;
- the engines will be equipped with a ShPG, low-quality timing belts and rollers, the service life will immediately decrease by half, that is, to 70 - 80 thousand kilometers.
Automatic tensioner
AvtoVAZ remains practically the only manufacturer in the world that, in principle, cannot provide the necessary precision in the manufacture of parts, which is why selective assembly is used on the assembly line, which indicates not advanced, but extremely poor technologies. It is easier for designers to “force the machine” to distinguish between the accuracy class markings of connecting rods and crankshaft main journals and bearings than to strictly adhere to one accuracy class, as in the entire civilized world.
Crankshaft 21179
As a result, the declared service life remains in question, since the lubricant used in the design of the main bearings will clearly be insufficient; scuffing of the crankshaft and overhaul are possible after 50,000 km.
Cylinder block
The material used for the cylinder block of the 21179 engine is traditional - cast iron. But the filling is not traditional, it is new: - in the cooling system - additional channels of the original cross-section between the second and third cylinders, to increase the efficiency of the system in order to increase the service life of the piston rings, which had high wear due to overheating of the inter-cylinder walls; - in the lubrication system - an additional oil channel, communicating with the main one, between the first two cylinders, for supplying oil in the cylinder head to the automatic phase distribution regulator, phase shifter;
photo of VAZ-21179 cylinder block
In which cars is it present?
The first in the manufacturer’s line, the 1.8 liter engine 21179 is installed in only two brands of cars from the AvtoVAZ manufacturer:
- Lada Vesta - since 2016, five-door, five-seater station wagon or sedan;
- Lada X-Ray - since 2016, five-seater, five-door hatchback.
This is due to the fact that the engine characteristics are more tailored to French gearboxes, which are not yet used on other manufacturer’s cars. In the future, equipment for Grant, Kalina-2, Largus and Lada 4x4 NG vehicles will be available.
AMT robot box for X Rey
Install sensors
Install phase sensor 2, Figure 13, and secure it with bolt 1. The tightening torque of the fastening bolt is 4…8 N∙m (0.4…0.8 kgf∙m) (replaceable Torx E8 head, wrench, extension, torque wrench).
Install valve 2, Figure 12, for adjusting the position of the camshaft and secure with bolt 1. The tightening torque of the fastening bolt is 5…8 N∙m (0.5…0.8 kgf∙m) (replaceable head 8, knob, extension, torque wrench) .
Install sensor 1, Figure 11, of the oil pressure warning lamp. The tightening torque of the sensor is 25…30 N∙m (2.5…3.0 kgf∙m) (replaceable high head 21, wrench, torque wrench).
Install detonation sensor 5, Figure 10, and secure with bolt 4. The tightening torque of the fastening bolt is 15…24 N∙m (1.5…2.4 kgf∙m) (replaceable head 13, wrench, extension, torque wrench).
Maintenance
The actual life of the internal combustion engine is still unknown due to the short service life of the first cars that rolled off the assembly line in 2016. However, to increase it, engine 21179 should be serviced according to the regulations below:
- 10,000 km means changing the filter/oil;
- twice as long, the alternator belt runs 30,000 km;
- after 45,000 km, change hoses/fittings and antifreeze;
- spark plugs and batteries are enough for 60,000 km;
- About 180,000 the original timing belt passes.
For 2022, the internal combustion engine device is considered the most advanced in the AvtoVAZ manufacturer’s line. In practice, his project had been considered since 2006, but was constantly postponed until the technical, economic and market situation in the Russian Federation finally developed favorably. That is, AvtoVAZ in this project prioritized the power output of the engine, and not economical fuel consumption, as was usually the case before.
Install crankshaft
Install and secure the cylinder block on a stand (electric or manual hoist, stand for disassembling and assembling units).
Select sets of main and connecting rod bearing shells according to tables 9 and 10, respectively.
Sets of main and connecting rod bearing shells for the repair crankshaft should be selected according to the amount of reduction in the diameter of the main and connecting rod journals.
The reduction amount is marked on the first cheek of the crankshaft (for example, K 0.25; W 0.50). The size marking of the set of inserts is applied on the packaging. In addition, on the repair size liners, the repair reduction value is marked on the outer surface (-0.25; -0.50; -0.75; -1.00).
Lubricate the main and connecting rod bearing shells, thrust half rings, as well as the main and connecting rod journals of the crankshaft with engine oil (motor oil).
Place the shells in the main bearing sockets of the block. Install the liners with grooves on the cylinder block in the bed of the main bearings, and the liners without grooves - in the main bearing caps.
Place the crankshaft in the main bearings and insert two thrust half-rings into the sockets of the middle support.
WARNING
. Install the thrust half-rings with the grooves to the thrust surfaces of the crankshaft. Install a steel-aluminum half-ring (part 2101-1005183) on the timing drive side, and a cermet half-ring (yellow, part 2106-1005183) on the flywheel side.
Install the main bearing caps according to the marks. The marks on the covers should be located on the side where the water pump is installed.
Install and tighten the main bearing cap bolts. The tightening torque of the fastening bolts is 70…86 N∙m (7.0…8.6 kgf∙m) (replaceable head 17, wrench, extension, torque wrench).
Check crankshaft rotation. The shaft should rotate freely and without jamming by hand. If the rotation is tight or there are jams, it is necessary to remove the crankshaft and repeat the operation to select a set of bearings.
Check the axial clearance of the crankshaft. Install rack 2 with indicator 3 on cylinder block 1, Figure 51. Place the measuring rod of the indicator on the crankshaft flange 4, as shown in Figure 48, and set the indicator scale to zero. Moving the crankshaft using screwdrivers 5, measure the axial clearance of shaft 4.
The axial clearance of the crankshaft should be within 0.06...0.26 mm. If the axial gap is more than 0.26 mm, adjust the gap by replacing the normal thrust half-rings with half-rings increased by 0.127 mm. Enlarged steel-aluminum half-rings are marked “P” on a steel base. The enlarged metal-ceramic half-rings are not marked and have a thickness of 2.44...2.49 mm (ShM-PV-8 tripod, ICh-10 indicator, 2 flat-head screwdrivers, MK 25-1 micrometer).
Causes of problems and solutions
In the very first Vesta and X-Ray models that came off the assembly line in 2016, motor 21179 has been in use for less than two years. At this stage, only two problems have been identified that are unique to this modification:
- increased oil consumption - insufficient quality of valves made in China, replacement with original Mahle parts is necessary;
- wear of the crankshaft and liners - poor lubrication due to manufacturer defects; replacement of the original yokes with versions of previous engines with a small groove and main bearing liners with a 180-degree groove is required.
Fuel rail
Other malfunctions are similar to 16 valve internal combustion engines of previous generations.
Engine malfunctions and repairs Lada Vesta 1.8
The appearance of heavier models in the AvtoVAZ range, such as Vesta and X-Ray, necessitated the development of a more powerful and high-torque engine than the usual 1.6 liter. This issue was resolved by adding an additional 200 cc to the Priora 21126. A similar experiment has already been carried out and everyone remembers the Lada Priora 1.8 with an engine from Super-Auto. But the new engine 21179 is different from previous versions. This engine uses an old cylinder block from Priora, 197.1 mm high, with a slightly improved cooling system and an oil channel for the phase shifter. New pistons with a diameter of 82 mm and a height of 26.7 mm, a new crankshaft with a piston stroke of 84 mm, and connecting rods of 128 mm were installed. The weight of the connecting rods and pistons is approximately the same as the 126th engine. All together this made it possible to obtain a working volume of 1.8 liters. We covered it all with a modified cylinder head 21126, installed on an adapted metal gasket. For the first time in Togliatti, a variable valve timing system on the intake camshaft from INA was used. The adjustment range is 30 degrees, the camshafts themselves are hollow and significantly lightweight. Lightweight, enlarged intake and exhaust valves are installed, the diameter of the intake is 31 mm, the exhaust is 28 mm, the diameter of the stem is reduced to 5 mm. This head received an improved cooling system, modified channels, and new valve springs. Engine 21179 bends valves, like other recent AvtoVAZ engines:, etc. The engine control unit on the M86 was also changed (as on Vesta), an electronic throttle valve, more efficient injectors, a new oil pump, a modified oil pan, a new pump, and an improved exhaust manifold were used. Unlike 21129, the 21179 engine uses a regular plastic intake manifold without changing the length. All this made it possible to obtain an increase in power and torque throughout the entire range; in numbers it looks like 122 hp. at 6050 rpm, torque 170 at 3750 rpm. The timing drive uses a toothed belt; it is advisable to replace the belt approximately every 90 thousand km.
For Lada models of older families, this engine will be called 21176, on Nivas it will also be called 21174. Based on the 179, the 21238 engine is being developed, with a variable valve timing system on both camshafts.
Problems and disadvantages of Lada 21179 engines
This motor has only recently been used and there is no information yet on its reliability. It is known that the first models were characterized by increased oil consumption. We will keep an eye on this engine and in the future we will describe all the troubles that owners may encounter.
Engine tuning
As standard for the AvtoVAZ manufacturer, engine 21179 has a potential of at least 150 hp. With. However, tuning is complicated by the following factors:
- M86 control unit - it is very difficult to change the internal combustion engine settings online;
- exhaust tract - the diameter of the manifold is narrowed for Euro-5 standards, it is almost impossible to install a “spider”.
Electronic throttle
Motor 21179 is initially already a factory tuning of versions 21127 and 21129, so without the ability to configure controllers, rarely anyone manages to upgrade it on their own.
Thus, the 21179 engine for 2022 is the best version of the 16-valve power drive with a DOHC two-shaft design. All components have undergone changes, with the exception of control controllers and spark plugs; spare parts from foreign companies are widely used, which is not entirely correct at the time of EU sanctions against Russia.
If you have any questions, leave them in the comments below the article. We or our visitors will be happy to answer them
Piston group
For the VAZ 21179, lined pistons with a diameter of 82 mm and a height of 26.7 mm, connecting rods of 128 mm, and a crankshaft providing a piston stroke of 84 mm were developed. The weight of the kinematic piston-connecting rod pair, when compared with the previous modification 21126, has remained virtually unchanged and is approximately similar to the 126th engine.
The height of the piston crown has increased by 1.3 mm compared to a similar 1.6 liter unit. To increase the piston stroke in the cylinder, engineers had to reduce the length of the connecting rod to 128 mm, the lower head of which is made according to the breaking principle.
The crankshaft, as well as the cylinder block, are produced at the auto giant’s own production facilities. The connecting rod and piston group is produced by the partner company Federal Mogul - Vostok, which is located in Tolyatti, which minimizes logistics costs. All elements are made from lightweight materials, which has a positive effect on the characteristics of parts and components. A special graphite coating is applied to the piston skirt, which increases engine life; the shape of the skirt has been changed to increase the contact patch. The piston rings are the same as on other engine models in the series, with the exception of the oil scraper rings, which are coated with chrome.
Can't we stand on the price?
The cylinder block (BC) is the most labor-intensive part, requiring a significant amount of metal-cutting, mainly automatic equipment. Its replacement or modernization requires huge financial investments. Therefore, when designing the engine, an emphasis was placed on the maximum use of serial parts in the design, primarily such labor-intensive parts as the BC.
What would it mean, for example, to replace a cast iron block with an aluminum one? This would entail a revision of the entire technological chain: instead of existing foundry lines, it would be necessary to purchase expensive injection molding machines. How will this affect the cost, and therefore the selling price? After all, aluminum is more expensive than cast iron.
Its processing is carried out using other cutting modes, so all metal-cutting equipment must be replaced or radically modernized. For these reasons, it was decided to make do with little bloodshed.
The new engine was based on the design of the VAZ-21127 or 21129 engine, differing only in the firmware. These are 16-valve units with a displacement of 1.6 liters, which are installed on the Priora, Kalina, Granta models.
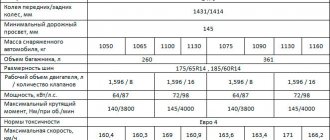
And their cylinder block is used from unit 21126, installed on the VAZ-2170 LADA Priora. The table shows as a comparison the main characteristics of the new engine, its predecessor and its closest competitors.
| Parameter name | Engine make | |||
| VAZ-21127 | VAZ-21129 | HR16DE | VAZ-21179 | |
| Automobile model | LADA Kalina, LADA Granta | LADA XRAY, LADA Vesta | LADA XRAY, LADA Vesta | LADA XRAY, LADA Vesta |
| Working volume, cm³ | 1596 | 1596 | 1598 | 1774 |
| Compression ratio | 11,0 | 10,5 | 10,7 | 10,3 |
| Power, l. With. | 106 | 106 | 114 | 122 |
| Torque, Nm | 148 | 148 | 156 | 170 |
Basics
As mentioned above, the developers took the BC from the 126th engine. At the same time, the increase in working volume was ensured by increasing not the diameter of the cylinders, but the stroke of the pistons, which is again explained by the desire to reduce alterations of the main body part. At first glance, the differences are invisible (and at second glance too). However, the developers have put a lot of effort into adapting the block to new conditions:
- An additional vertical oil channel appeared between the 1st and 2nd cylinders to supply oil to the phase-regulating device (“phaser”), which was not present on previous engines.
- During testing of the unit, increased wear of the piston rings was discovered. It turned out that this was caused by insufficient cooling of the inter-cylinder jumpers. The problem was solved by drilling additional inclined holes intersecting in the body of the jumpers (in the shape of the letter V).
- Automatic selective control of main bearing beds was introduced with the application of appropriate markings on the end of the block (3 size groups).
- The location of the engine serial number was moved from the rear end of the block to the left side. This is done so that the number can be read when the unit is installed longitudinally (on all-wheel drive vehicles).
- Finally, in order for the 1.8 engine to fit both on Vesta (VAZ platform) and on XRAY, Largus (B0 platform), threaded holes were added to the front end of the block for attaching the right engine mounting bracket.
Operating conditions and factors affecting oil consumption
Exceeding the engine fluid consumption rate should alert the car owner. Lubricant consumption may increase in engines with significant wear. In any case, engine oil consumption must be periodically monitored. Insufficient mixture in the lubrication system leads to malfunctions, which are usually followed by the need for expensive repairs.
Lubricant consumption depends on several aggregate indicators:
- characteristics of the condition of the internal combustion engine (this includes not only age, power, cylinder displacement and degree of wear, but also the climatic conditions in which it is operated, timely technical inspection and a number of other factors);
- filter condition (clogged or damaged will increase flow);
- type of internal combustion engine design (oil consumption depends on the type of fuel resource and the method of its supply);
- technical characteristics and quality indicators of motor fluid.
The reason for the high consumption of engine oil in the engine may be due to operating conditions, increased load, external unfavorable factors and excessive levels of lubricant in the system.
Install the intake module
Install the lower crankcase ventilation hose onto the cylinder head cover pipe and secure with a clamp (pliers).
Install new seals for 5 gas channels on module 4, Figure 8, inlet.
Insert the lower crankcase ventilation hose into the hole in the intake module.
Install the intake module to the cylinder head. Screw in and tighten two bolts 7 and three nuts 8 securing the intake module with washers.
The tightening torque of bolts and nuts is 21…26 N∙m (2.1…2.6 kgf∙m) (replaceable head 13, wrench, extension, torque wrench).
Install two washers 2, screw in and tighten the two upper nuts 1 securing the intake module to the cylinder head. The tightening torque of the nuts is 3…5 N∙m (0.3…0.5 kgf∙m) (replaceable head 10, wrench, extension, torque wrench).
Attach the fastening elements of the injector wiring harness to the intake module.
Install a new seal 3 of the throttle pipe.
Install the throttle pipe 3, Figure 7, on the intake module and secure it with three nuts 1 with washers 2. The tightening torque of the intake module mounting nuts is 5…8 N∙m (0.5…0.8 kgf∙m) (replaceable head 10, knob , extension cord, torque wrench).
Install tube 2, Figure 6, with oil level indicator 1 assembly and secure with screw 3 with washer 4 (Phillips screwdriver).
Oil consumption standards after 2022
In February 2022, AvtoVAZ sent information letter No. 23-20 to the heads of the dealer network “On the appeal of consumers with the defect “increased oil consumption” of LADA car engines.” It states that when operating vehicles, consumers may complain of “blue smoke at the exit of the exhaust system, increased oil consumption.” During the warranty period, to assess the need for engine diagnostics, by analogy with the applicable f. Renault has established and included in the new Operating Manuals for LADA vehicles a control value for oil consumption, which is no more than 0.5 liters per 1000 km
vehicle mileage. There is also an addition to the actual oil consumption, depending on the influencing factors, recommendations to consumers on reducing oil consumption when operating vehicles.
At the same time, it is indicated that IP No. 62-12, No. 48-17 (discussed above) should be considered invalid.
Here's what was added to the car's owner's manual:
Actual oil consumption
. Oil consumption is provided for by the engine design and cannot be equal to zero, otherwise the engine will be destroyed. Oil is consumed primarily through piston rings and valve seals, the purpose of which is not an absolute seal, but to meter oil penetration to ensure lubrication. A small amount of oil is also consumed through the crankcase ventilation system. Operating oil consumption depends on many factors:
- compliance by the consumer with operating conditions during the vehicle break-in period and, accordingly, the quality of running-in of engine friction surfaces;
- viscosity-temperature properties of the oil used;
- quality of the oil used;
- frequency of oil changes;
- ambient temperature;
- the amount (level) of engine oil maintained by the owner;
- driving style of the car owner (engine operating modes);
- driving routes used by the owner.
Recommendations for reducing oil consumption
:
- Strictly follow the recommendations for running in the car and engine (see the subsection “Operating a new car” in the “Driving a car” section) to ensure optimal running-in of the cylinder-piston parts, the surface quality of which significantly affects oil consumption.
- Use high-quality fuel that ensures the safety of parts of the cylinder-piston group.
- Use high-quality motor oils for reliable lubrication, cooling and removal of natural wear products from friction surfaces without the formation of unnecessary deposits of sludge, varnish and carbon deposits.
- Follow recommendations to match the viscosity-temperature properties of the oil to environmental conditions to maintain optimal lubrication conditions.
- Maintain the oil level between the MIN and MAX marks.
- Observe the oil change intervals.
- Carry out engine maintenance regularly.
- Drive the vehicle at moderate engine speeds, with smooth acceleration, within the permitted speed limits. Because oil consumption is higher, the higher the load and engine speed.
- If possible, minimize the frequency of using the engine braking mode (driving with the accelerator pedal released and with the gearbox in low gear, when the wheels rotate the engine through the transmission).
- Choose rational routes that minimize the number of stops, starts, and accelerations.
Oil consumption standards after 2022
In February 2022, AvtoVAZ sent information letter No. 23-20 to the heads of the dealer network “On the appeal of consumers with the defect “increased oil consumption” of LADA car engines.” It states that when operating vehicles, consumers may complain of “blue smoke at the exit of the exhaust system, increased oil consumption.” During the warranty period, to assess the need for engine diagnostics, by analogy with the applicable f. Renault has established and included in the new Operating Manuals for LADA vehicles a control value for oil consumption, which is no more than 0.5 liters per 1000 km
vehicle mileage. There is also an addition to the actual oil consumption, depending on the influencing factors, recommendations to consumers on reducing oil consumption when operating vehicles.
At the same time, it is indicated that IP No. 62-12, No. 48-17 (discussed above) should be considered invalid.
Here's what was added to the car's owner's manual:
Actual oil consumption
. Oil consumption is provided for by the engine design and cannot be equal to zero, otherwise the engine will be destroyed. Oil is consumed primarily through piston rings and valve seals, the purpose of which is not an absolute seal, but to meter oil penetration to ensure lubrication. A small amount of oil is also consumed through the crankcase ventilation system. Operating oil consumption depends on many factors:
- compliance by the consumer with operating conditions during the vehicle break-in period and, accordingly, the quality of running-in of engine friction surfaces;
- viscosity-temperature properties of the oil used;
- quality of the oil used;
- frequency of oil changes;
- ambient temperature;
- the amount (level) of engine oil maintained by the owner;
- driving style of the car owner (engine operating modes);
- driving routes used by the owner.
Recommendations for reducing oil consumption
:
- Strictly follow the recommendations for running in the car and engine (see the subsection “Operating a new car” in the “Driving a car” section) to ensure optimal running-in of the cylinder-piston parts, the surface quality of which significantly affects oil consumption.
- Use high-quality fuel that ensures the safety of parts of the cylinder-piston group.
- Use high-quality motor oils for reliable lubrication, cooling and removal of natural wear products from friction surfaces without the formation of unnecessary deposits of sludge, varnish and carbon deposits.
- Follow recommendations to match the viscosity-temperature properties of the oil to environmental conditions to maintain optimal lubrication conditions.
- Maintain the oil level between the MIN and MAX marks.
- Observe the oil change intervals.
- Carry out engine maintenance regularly.
- Drive the vehicle at moderate engine speeds, with smooth acceleration, within the permitted speed limits. Because oil consumption is higher, the higher the load and engine speed.
- If possible, minimize the frequency of using the engine braking mode (driving with the accelerator pedal released and with the gearbox in low gear, when the wheels rotate the engine through the transmission).
- Choose rational routes that minimize the number of stops, starts, and accelerations.
Oil consumption standards after 2022
In February 2022, AvtoVAZ sent information letter No. 23-20 to the heads of the dealer network “On the appeal of consumers with the defect “increased oil consumption” of LADA car engines.” It states that when operating vehicles, consumers may complain of “blue smoke at the exit of the exhaust system, increased oil consumption.” During the warranty period, to assess the need for engine diagnostics, by analogy with the applicable f. Renault has established and included in the new Operating Manuals for LADA vehicles a control value for oil consumption, which is no more than 0.5 liters per 1000 km
vehicle mileage. There is also an addition to the actual oil consumption, depending on the influencing factors, recommendations to consumers on reducing oil consumption when operating vehicles.
At the same time, it is indicated that IP No. 62-12, No. 48-17 (discussed above) should be considered invalid.
Here's what was added to the car's owner's manual:
Actual oil consumption
. Oil consumption is provided for by the engine design and cannot be equal to zero, otherwise the engine will be destroyed. Oil is consumed primarily through piston rings and valve seals, the purpose of which is not an absolute seal, but to meter oil penetration to ensure lubrication. A small amount of oil is also consumed through the crankcase ventilation system. Operating oil consumption depends on many factors:
- compliance by the consumer with operating conditions during the vehicle break-in period and, accordingly, the quality of running-in of engine friction surfaces;
- viscosity-temperature properties of the oil used;
- quality of the oil used;
- frequency of oil changes;
- ambient temperature;
- the amount (level) of engine oil maintained by the owner;
- driving style of the car owner (engine operating modes);
- driving routes used by the owner.
Recommendations for reducing oil consumption
:
- Strictly follow the recommendations for running in the car and engine (see the subsection “Operating a new car” in the “Driving a car” section) to ensure optimal running-in of the cylinder-piston parts, the surface quality of which significantly affects oil consumption.
- Use high-quality fuel that ensures the safety of parts of the cylinder-piston group.
- Use high-quality motor oils for reliable lubrication, cooling and removal of natural wear products from friction surfaces without the formation of unnecessary deposits of sludge, varnish and carbon deposits.
- Follow recommendations to match the viscosity-temperature properties of the oil to environmental conditions to maintain optimal lubrication conditions.
- Maintain the oil level between the MIN and MAX marks.
- Observe the oil change intervals.
- Carry out engine maintenance regularly.
- Drive the vehicle at moderate engine speeds, with smooth acceleration, within the permitted speed limits. Because oil consumption is higher, the higher the load and engine speed.
- If possible, minimize the frequency of using the engine braking mode (driving with the accelerator pedal released and with the gearbox in low gear, when the wheels rotate the engine through the transmission).
- Choose rational routes that minimize the number of stops, starts, and accelerations.
History of origin
Motor 21179 was already in the minds of the engineer much earlier than you can imagine. Even at the end of the USSR, developers began to think about the Lada C project and its power units. Even then, engineers “knew” this motor by its features and power characteristics. But the difficult economic situation of that time and the collapse of the USSR forced the engineers to completely forget the Lada-Ts project.
And now, after a long time, when Boo Anderson comes to the post of general manager of AvtoVAZ, the project is raised and developed again.
The main task was to create an engine with good low-end torque, which AvtoVAZ lacked for a confident, comfortable ride. “Tractor” 8-cl engines have long since become obsolete, but the new 16-cl engines had a more “sporty” character. The situation was corrected by the then 21127 engine, now 21129, which is installed on Vesta, Xray, and other AvtoVAZ models. Due to the intake receiver with variable geometry installed on it, the torque from the bottom began much earlier, unlike the Prioromotor (21126), and its shelf was much further, right up to the cutoff. But with the start of production of a sedan with a larger mass - the Vesta, and the Xray hatchback - the need for low-end engines reappeared.
The engine was run in and tested for a long time. As a result, during the testing process it turned out that the rings were already stuck at 4t.km., as a result, the heat zone was increased and the problem disappeared.
Nissan HR16DE engine with 110 hp power. It copes well with its task on front-wheel drive. But if you have all-wheel drive, it will strain, get hot, eat a lot and not drive.
Another factor in the creation of the 21179 motor is economics and politics. Because the Nissan engine, although it is assembled here, still belongs to Nissan. And in the event of an unfavorable economic situation, an increase in exchange rates, the cost of its production and sale may simply be unprofitable.
Start of production of motor 21179
Back in 2014, there were rumors about the possible production of a 1.8 liter engine with phase shifters. And yet it became a reality. Previously, OPP and its subsidiary Super-Auto were already engaged in the construction and installation of a 1.8 liter engine with index 21128, which was installed in Priora Sport. But that engine did not have a special resource.
Oil sump volume
This point will be useful for those who are going to change the engine oil. With different transmissions, the volume of oil poured into the engine is also different.
VAZ 21129 manual transmission Renault (cast crankcase) = 4.4l
VAZ 21129 robot (stamped crater) = 3.2 l
The engine resource is 200 km. But in practice, you need to monitor the condition of the roller, pump and timing belt, because if individual valve elements jam, they will meet the piston group, and then both will come to an end. In addition, during the impact of these elements, it is not uncommon that the crankshaft bends slightly. You can drive with such a crankshaft, but there will be huge oil consumption.
Sliding bearings, their types and role in the operation of internal combustion engines.
Main and connecting rod bearings are two types of plain bearings. They are produced using the same technology and differ from each other only in the inner diameter (for connecting rod liners this diameter is smaller).
The main task of the liners is to convert translational movements (up and down) into rotational ones and ensure uninterrupted operation of the crankshaft so that it does not wear out prematurely. It is for these purposes that the liners are installed under a strictly defined gap, in which a strictly specified oil pressure is maintained.
If this gap increases, the engine oil pressure in it becomes less, which means that the journals of the gas distribution mechanism, crankshaft, and other important components wear out much faster. Needless to say, too much pressure (reduced clearance) also does not bring anything positive, since it creates additional obstacles in the operation of the crankshaft, it can begin to jam
That is why it is so important to control this gap, which is impossible without using a torque wrench in repair work, knowledge of the necessary parameters that are prescribed by the manufacturer in the technical literature on engine repair, as well as observing the tightening torque of the main and connecting rod bearings. By the way, the tightening force (torque) of the connecting rod and main bearing cap bolts is different
Please note that the given standards are relevant only when using new sets of parts, since the assembly/disassembly of a previously used unit due to its wear and tear cannot guarantee compliance with the required clearances. Alternatively, in this situation, when tightening the bolts, you can focus on the upper limit of the recommended torque, or you can use special repair bushings with four different sizes, differing from each other by 0.25 mm, provided that the crankshaft is ground until the minimum gap between rubbing elements will not be 0.025/0.05/0.075/0.1/0.125 (depending on the existing gap and the repair product used)
Examples of specific tightening torques for connecting rod and main bearing cap bolts for some VAZ family vehicles.
| Automobile model | Bed cover tightening torque, N*m (kgf.m.) | Tightening torque of connecting rod bearings, N*m (kgf.m.) |
| VAZ 2108 | 69,0–84,0 (6,9–8,4) | 44,0–54,0 (4,4–5,4) |
| VAZ 2106 | 68,31–84,38 (6,97–8,61) | 43,32–53,51 (4,42–5,4) |
| Lada Priora | 68,31-84,38 (6,97-8,61) | 43,3-53,5 (4,42-5,46) |
Tuning a car VAZ 2110, 2111, 2112 Ten - Camshaft
Remove the camshaft gear pulley (see Composite camshaft drive pulley for an eight-valve engine).
To avoid losing the pulley key, remove it from the camshaft groove.
Using a 10mm wrench, unscrew the nut securing the rear timing belt cover.
Using a 10mm wrench, unscrew the two nuts securing the throttle cable bracket to the receiver...
...and remove the bracket.
Using a Phillips screwdriver, loosen the clamps securing the two crankcase ventilation outlet hoses and remove the hoses from the valve cover fittings.
Using a Phillips screwdriver, loosen the clamp securing the crankcase ventilation supply hose and remove the hose.
Using a 10mm wrench, unscrew the two nuts securing the valve cover.
Remove the valve cover.
Rubber sealing bushings are installed in the valve cover holes.
Remove the valve cover gasket.
Using a 10mm wrench, unscrew the two nuts securing the ends of the ground wires to the studs of the cylinder head plug and remove the wires from the studs.
Use a 10mm wrench to unscrew the two nuts...
...and one bolt securing the plug.
...and its O-ring.
Using a “13” wrench, evenly in several steps (until the pressure of the valve springs is removed), unscrew the ten nuts securing the camshaft bearing housings.
Remove the front one from the studs...
...and the rear camshaft bearing housings.
Moving the rear timing belt cover slightly away from the cylinder head, remove the camshaft.
Remove the camshaft oil seal.
We install the tuning camshaft in the following sequence.
We clean the mating surfaces of the cylinder head and bearing housings from sealant and oil.
Lubricate the bearing journals and camshaft cams with engine oil. We place the shaft in the cylinder head supports so that the cams of the first cylinder are directed upward (the figure shows the position of the cams of the first cylinder when the camshaft is placed in the cylinder head supports).
On the surfaces of the cylinder head that interface with the bearing housings in the area of the outer supports, apply a thin layer of sealant (arrows).
We install the bearing housings and tighten the nuts securing them in two steps.
Pre-tighten the nuts in the sequence shown in the figure until the surfaces of the bearing housings touch the cylinder head.
In this case, it is necessary to ensure that the installation sleeves of the housings fit freely into their sockets. We finally tighten the nuts to a torque of 21.6 N.m (2.2 kgf.m) in the same sequence.
After tightening the nuts, carefully remove any remaining sealant.
After lubricating the working edge of the new oil seal with engine oil, press it into place with a suitable piece of pipe.
We install the camshaft timing belt and timing belt. (See Composite camshaft pulley for eight-valve engine).
Turn the crankshaft clockwise until the timing marks on the camshaft sprocket and the rear timing belt cover align.
Then we turn the crankshaft another 40-50° (2.5-3 teeth on the camshaft pulley).
In this position of the shafts, we use a set of feeler gauges to check the gaps at the first...
... and the third camshaft cam.
The clearance between the camshaft lobes and the washers should be 0.20 mm for the intake valves and 0.35 mm for the exhaust valves. The clearance tolerance for all jaws is ±0.05 mm.
If the gap differs from the norm, then install a device for adjusting the valves on the studs of the camshaft bearing housings.
We introduce the “fang” of the device between the cam and the pusher.
We rotate the pusher so that the slot in its upper part faces forward (along the direction of the car).
By pressing the lever of the device, we recess the pusher with the “fang”...
...and install a clamp between the edge of the pusher and the camshaft, which holds the pusher in the lower position.
Move the lever of the device to the upper position.
Using tweezers, pry the adjusting washer through the pusher slot and remove it.
If you do not have a device for adjusting the valves, you can use two screwdrivers.
Using a powerful screwdriver, leaning on the cam, press the pusher down. By inserting the edge of another screwdriver (with a blade at least 10 mm wide) between the edge of the pusher and the camshaft, we fix the pusher.
Use tweezers to remove the adjusting washer.