When operating a car with front- or all-wheel drive, the driver may hear a crunching sound when turning the steering wheel to the right or left. Often in this case the CV joint (constant velocity joint or just a grenade) crunches. The sound is characteristic and resembles a booming crack.
It is important to accurately determine:
- which CV joint crunches;
- the severity of the failure;
- Is it possible to get to the service station on your own?
The fact is that on each side there is an internal CV joint, as well as an external CV joint. For diagnosis, it is necessary to separately take into account some features and nuances. Read more in our article.
CV joint: what is it and how does it work
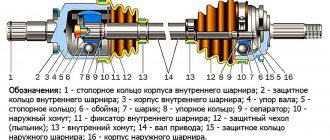
CV joint (constant velocity joint) is a part that transmits torque between axle shafts, while the angle between the axle shafts is constantly changing. CV joints are actively used in cars with front-wheel drive and all-wheel drive.
On the front axle the following are used:
- internal CV joint (internal CV joint);
- outer CV joint (outer grenade);
The inner CV joint is responsible for transmitting rotation from the gearbox to the shaft, while the outer joint transmits rotation from the inner one to the wheel. The use of these elements allows you to transmit torque and turn the drive wheels of the car.
Crunching is a characteristic sign of malfunction
CV joints are fairly reliable units, but they also fail. Problems with them manifest themselves in the form of distinct crunching sounds when performing maneuvers, knocking noises when turning the steering wheel, and vibrations (twitching) of the car when driving over uneven surfaces.
Experienced drivers call this unit more simply – a grenade.
If a crunch is a characteristic sign of a grenade malfunction, then other structural elements can also make knocking noises in the front of the car, so when they appear, you must first perform diagnostics and determine which component is faulty.
Moreover, even if there is complete confidence that something is wrong with the CV joints, you still need to find out which unit is problematic, because the drive design uses 4 such components (2 internal and 2 external, a pair for each left and right drive shafts).
Why does the grenade crunch?
In general, the constant velocity joint is a fairly reliable part. Natural wear and tear occurs over long runs (about 150-200 thousand km or more). However, in some cases, a part may fail earlier for certain reasons.
In this case, the main sign of problems with the joint is a characteristic cracking sound (often the CV joint crunches when turning). The crunch of a grenade can also be heard when accelerating a car (especially pronounced with the wheels turned out).
The main causes of CV joint crunching:
- operating a vehicle in difficult conditions (off-road, falling into potholes at high speeds, towing heavy trailers, transporting goods, etc.).
- aggressive driving, sudden acceleration and emergency braking (especially with the wheels turned out), taking sharp turns at high speed, etc.
- rupture of the CV boot, moisture, dirt and dust entering the mechanism (CV joint lubricant accumulates particles and begins to work like an abrasive, destroying the part). By the way, the vast majority of problems with CV joints are associated with damage to the boot;
To understand which CV joint makes a crunching sound when you turn the steering wheel, you need to carry out diagnostics. At the same time, it is not particularly difficult to quickly determine which CV joint is crunching. As part of the inspection, you should pay attention to some features.
- Crunching and squeaking noises are usually produced by the external grenade. You can check the CV joint by turning the wheels and starting active acceleration. As a rule, a not particularly strong crunch when turning will become louder. You should also pay attention to the steering wheel. If vibrations and slight jolts are felt on the steering wheel, this will also indicate problems with the outer joints.
- The inner CV joint usually does not crunch, but slightly taps when driving with the wheels evenly aligned in a straight line. In addition to driving on a flat road, when you hit potholes, the knocking intensifies. The fact is that the load on the inner CV joint is stronger depending on the depth of the hole under the wheels.
Steering column
In this mechanism, crunching can be produced from the following sources:
- The body is made of cheap plastic in inexpensive cars.
- Extraneous noise may come from the steering column coupling, which can be eliminated by adding a certain amount of lubricant, the type of which depends on what material the coupling is made of.
- The column crosspiece, called the driveshaft, rubs against the boot located near the driver's feet, where the column meets the engine compartment. A crunch may occur after repairs due to slight misalignment of parts. The problem is solved by adding lubricant or WD-40.
- The steering column may be bent. A squeak appears on the surface, auxiliary signs are: shocks, vibration on the steering wheel. This malfunction can be eliminated by replacing the entire mechanism with a new unit, although a slight noise indicates a minor malfunction.
When is a car's CV joint checked?
If the CV joint crunches, many drivers are interested in how long they can drive the car before repairing such a breakdown. In other words, how long can you drive if the CV joint crunches? There are several reasons why repairs are delayed:
- Constant velocity joints on some cars can be quite expensive.
- the crunching and knocking may not be strong, etc.;
First of all, the ability to operate the car depends on the severity of the breakdown. The more worn out the CV joint is, the sooner it needs to be replaced. In this case, knocking and crunching are indicators indicating the need for replacement.
For example, if the crunch is strong, it is better to change the joint immediately. The fact is that if the unit is completely broken (jamming, cracking of the body or balls falling out, etc.), you can get serious problems with other units, units and elements.
In turn, you can try to eliminate the symptoms of a malfunction at the initial stage using a maintenance method (lubricating the CV joint and replacing the boots). If there is no result, then you should prepare for the fact that with increased noise, knocking and crunching, the part will need to be changed. This can happen after 500-1000 km. after the first symptoms appear, or later.
At the same time, experts still do not recommend operating the car and subjecting the car to loads in the presence of such faults. This means that you can drive with a partially faulty CV joint for some time, however, the part should be replaced at the first opportunity and not delay the repair. If the signs of failure are serious (extreme noise and crunching), you should stop using it and replace the hinges.
How to check the outer CV joint
Having identified characteristic signs of a malfunction, an additional check of the CV joint is necessary. If you need to check the outer CV joint, there are some things to consider. The part is attached to the internal hinge through the axle shaft on one side, and attached to the hub on the other.
Considering that the hinge is a separator with balls, if the ball mechanism is damaged, a crunching sound appears. The case is also protected on top by a dust cover. If the boot is torn, moisture, dirt and dust get inside the CV joint and damage it.
In order to check the outer CV joint, you need to drive on a flat road, turning the wheels in one direction and the other until they stop. In the extreme positions of the steering wheel, you must press the gas. If the crunching intensifies, then the external grenade is faulty. In this case, a crunching sound when turning left will indicate that the CV joint on the right “passenger” side is faulty. If the sound appears in a right turn, in this case the left CV joint (on the driver’s side) crunches.
Checking the internal hinge
As for the inner CV joint, this element is structurally similar to a glass (there is an outer housing with bearings that move in three planes). The shaft is inserted into the gearbox, while the tripod with bearings is fixed to the axle shaft.
The design of the inner CV joint is extremely simple; the joint fails much less often than the outer one. However, the lack of lubrication in the inner CV joint and a torn boot can damage even such a reliable mechanism.
We also recommend reading the article on how to replace ball joints with your own hands. From this article you will learn about the features of replacing ball joints, as well as how to change ball joints correctly and what needs to be taken into account if such a replacement is performed.
To check internal grenades, you need to select a section of the road where there are holes and uneven spots. The main symptom of a faulty internal joint is a knocking sound when the wheel hits a hole. Please note that before checking, it is advisable to perform chassis diagnostics to rule out other possible causes of knocking.
There is another method of checking - you can load the rear axle of the car to such an extent that the “nose” of the car rises higher, and the axis of the inner CV joint deflects. If a knock occurs under such conditions, this means that the internal CV joint has failed.
Other verification methods
As part of diagnosing constant velocity joints, you also need to know another way to determine which CV joint is crunching. However, this method is only suitable for cars with a manual transmission. The tool you will need for checking is a jack.
- First, the car is placed on a level surface;
- The wheels are set straight and hung out;
- By tightening the handbrake, the engine starts in neutral gear;
- Then, after squeezing the clutch, first speed is engaged;
- Then, in the cabin, the gas pedal is pressed and the brake pedal is carefully pressed (a load is created on the CV joint).
We also recommend reading the article about what signs indicate problems with anti-roll bar bushings. From this article you will learn what stabilizer bushings are intended for, as well as when and why they need to be changed, and how to replace stabilizer bushings with your own hands.
If the inner CV joint breaks, knocking noises will be heard when you press the brake. If the internal CV joints are working properly, the engine will stall and there will be no extraneous knocking noises. Next, turn the steering wheel all the way to the left or right and press the brake. If a crunching sound is added to the knocking sound, the external grenade is also faulty. Using this method, you can check the CV joints on the axle shafts on both sides.
Steering wheel
A crunch or squeak is heard directly inside the car and has nothing to do with the steering mechanism. Most often, such a malfunction occurs in inexpensive brands of cars due to poor quality processing of body parts. The reason lies in the friction of the steering wheel on the plastic, the laxity of various fastenings, for example, signal delivery devices.
This malfunction does not require much effort to solve the problem. The steering wheel must be disassembled and removed; if necessary, the upper part of the plastic elements of the steering column must be cleaned.
Recommendations
As a rule, the main problem with CV joints is damage to the joint boots. For this reason, their condition must be constantly monitored at every maintenance. Even the slightest damage (cracks, tears, holes and other defects) is not allowed. If such defects are found, the CV joint boot must be replaced immediately. Please note that ignoring this rule leads to breakdown of this unit.
Moreover, if the CV joint crunches, this indicates critical wear. In practice, the problem can be “preserved” by updating the joint lubrication. However, this does not allow us to talk about the reliability and durability of the unit after such maintenance.
We also add that the maximum load on the CV joint is created if the driver accelerates heavily with the wheels turned out. If there is such an opportunity and you need to overcome an obstacle (for example, driving onto a curb or accelerating sharply when turning), it is better to put the wheels as straight as possible in order to reduce the load on the CV joint.
Power steering
In the steering mechanism where it is mounted, this is the noisiest mechanism. When you turn the steering wheel of a stationary car, it produces a specific noise. An increase in this sound indicates that the fluid level in the power steering is insufficient. This issue is resolved by adding fluid to the expansion tank.
Other extraneous sounds in the form of whistling or creaking indicate serious malfunctions. Their causes may be wear of the power steering belt, or its weakening, penetration of air into the system, or breakdown of the power steering pump. It is advisable to identify and repair them in car repair services.
There was a crunching sound when turning the steering wheel
As we have already described above, the cause of the crunching in most cases is the CV joint. Let's figure out why it starts to crunch.
The device of this spare part is shown in the photo below. In the widest part there are balls (as in bearings) and each such ball has its own seat, which breaks due to wear over time. Therefore, in certain positions of the wheel, the ball leaves its seat, which causes contact with the rotating parts with a characteristic crunch, and sometimes the wheel jams.
Types of CV joints, their design features
The most common types of CV joints in the design of front-wheel drive passenger cars are ball and tripoid.
The former are often used on the outside, the latter as internal hinges. On some models, ball devices may also be installed exclusively.
The design of these types of CV joints differs, and significantly. The tripoid assembly consists of an outer casing of a certain shape, on which there is a drive shaft end stop (thanks to it, the drive is connected to the gearbox).
The housing contains a tripoid with rollers, mounted via a splined connection on the drive shaft.
Ball CV joints are partially similar in design to conventional bearings - there are two cages between which the balls are located in the separator.
The outer ring of the unit is its body, on which another shaft end is attached (it is installed in the wheel hub). The inner race is mounted on the drive shaft by means of a spline connection.
The transfer of force from the inner race to the outer one in such a hinge is carried out by balls, which are located in special grooves on the working surfaces of the races.
These same grooves allow the balls to move longitudinally, thereby ensuring transmission of rotation when the drive shaft and end switch are positioned at an angle relative to each other.
A tripoid CV joint is structurally simpler, and therefore more reliable, but it is used only as an internal hinge. This is due to its operational characteristics - they allow significant longitudinal movements of the tripoid relative to the body (provides a change in the length of the drive), but at the same time it is limited in the angle of rotation of the limit switch relative to the shaft.
In ball joints, the angle of rotation is much larger, so it is better suited for use on the outside of the drive, but such a unit does not provide significant longitudinal movements.
Due to their more complex design, very harsh operating conditions and location (near the wheel), ball CV joints are more susceptible to wear and malfunction; they are smaller in size than their tripod counterparts.
Both types of CV joints are made with high precision, so there are no backlashes in them. But during the operation of the car, the working surfaces of the hinge gradually wear out, which leads to the appearance of backlashes, which are the main cause of unit failure. The wear situation is aggravated by dirt getting inside the joint.
Elimination of crunches and knocks, restoring the operation of CV joints
How to find out which CV joint is crunching - we figured it out, now about the measures that should be taken to fix the problem, since it is undesirable to operate a car with problematic joints.
One of the disadvantages of CV joints is their non-repairability, that is, if the joint crunches, then it is worn out and requires replacement. The only thing that can be done is to “extend the life” of the node and delay its replacement.
Since the main reason for the appearance of crunches is dust and dirt, when they appear, you should immediately inspect all the anthers for damage. If none are found, we determine which CV joint is crunching using one of the above methods.
After identifying the problematic hinge, we try to extend its service life. To do this you need:
- Remove the drive from the car;
- Disassemble the CV joint;
- Thoroughly wash all components with gasoline, solvent or other means (white spirit, etc.);
- Apply new CV joint grease or equivalents (see above) and assemble the hinge;
- Install a new boot;
- Install the rebuilt drive on the car.
At the initial stage of wear, these measures are enough to get rid of the crunches, but they will eventually return (when the wear intensifies) and then the hinge will have to be replaced.
Conclusions that suggest themselves
As you can see, there are plenty of reasons for the occurrence of third-party noise in the front suspension area. However, most of them do not pose any danger to the further operation of the vehicle. Despite this, experienced auto mechanics advise carrying out a full diagnosis of all elements of the chassis when noise occurs in the suspension area, because only during this process can the condition of all component components be fully assessed.
Restoring the front suspension is not difficult, so any car owner can independently carry out repair work, during which damaged parts will be replaced.