Every year, the automobile market offers a huge number of models, trim levels, and modifications to suit every taste and budget of the buyer. In addition to design, comfort and engine, there is a variety of transmissions on offer. More and more manufacturers are equipping cars with both manual and automatic transmissions. But if mechanics differ mainly in the number of steps and gear ratios, then with automatics the situation is more complicated. They are presented in several types, differing from each other in operating principle, design, and scope of application.
Most often, the buyer's choice falls on 2 types of automatic transmissions - classic automatic transmission and DSG, which is also called a “robotic” transmission. Let's look at each type in more detail and try to decide which one is better.
DSG box or automatic: how to determine the type of gearbox
Let's start with the fact that the hydromechanical automatic transmission has established itself as a reliable, durable and completely repairable unit. At the same time, many potential owners choose this type of gearbox even taking into account increased fuel consumption and a slight decrease in acceleration dynamics.
As for preselective robots, the DSG gearbox was initially presented as an alternative to classic automatic transmissions, combining the positive properties of a manual transmission and a classic automatic transmission.
On the one hand, the production of such a box is cheaper, which reduces the final cost of the car. The driver also receives almost imperceptible gear changes, high transmission efficiency, fuel efficiency and excellent acceleration dynamics.
It is for this reason (usually in the secondary market) that cars with DSG sell worse than those with automatic transmission and even a CVT. Buyers themselves often either refuse to purchase or try to reduce the price as much as possible, citing the possible need for serious repairs of such a box already at 100-150 thousand km.
Naturally, the car seller is not interested in a significant reduction in cost. If we remember that it is difficult to visually distinguish a DSG from an automatic, inexperienced buyers are often deceived by claiming that the car has a regular automatic transmission, DSG tiptronic, etc. Adding to the complexity is the fact that some models can be equipped with both DSG and a conventional automatic transmission.
As a result, especially if the lever is from a classic automatic, new owners often do not know what kind of transmission is actually installed on their car. So, in order to clearly understand which gearbox the car comes with, you need to be able to distinguish DSG from automatic transmission.
First of all, among the main distinctive features of the DSG are:
- the presence under the hood in front in the direction of travel on the gearbox of a black metal cover, similar to a sump. The cover is moved slightly to the side, located closer to the radiator of the cooling system. So, under the specified cover there is a mechatronics, which is an actuator that responds and controls the operation of the entire DSG box. The automatic transmission does not have such a cover;
- Also on the DSG on top of the box there is a rectangular heat exchanger, as well as an oil filter. If we compare the Aisin tiptronic and DSG, the heat exchanger of a classic automatic transmission is round in shape and there is no oil filter;
- An important difference between a DSG and an automatic is the information encrypted in the VIN code. By VIN you can determine the equipment, color of the car, type of internal combustion engine and transmission, etc. It would also be a good idea to study the stickers/placards on the body, marks in the service book, and instructions in the manual;
At the same time, we note that in some cases the answer to the question of how to distinguish a DSG gearbox from a conventional tiptronic automatic transmission is the presence of a characteristic rollback in a car with a DSG. By rollback it should be understood that when the owner puts the car in P mode on a slope and turns off the engine, without tightening the handbrake, the car rolls forward a little. In the case of an automatic transmission, this does not happen, since the shaft locking in the box in P mode works faster.
How to determine which gearbox is installed on a car
It is relatively simple to determine how different types of gearboxes differ in appearance - the six-speed gearbox has an oblong shape. At the same time, the seven-speed gearbox is elongated vertically. It is worth noting that in the absence of experience it is difficult to visually determine the type of transmission. In addition, it is not always convenient to look under the bottom of the car.
The easiest way is to get acquainted with the information of the official dealer and send a request to the manufacturer. Another good solution is to contact a certified car service center. Pre-check will avoid problems.
DSG 7
DSG 7
A further development of engineering was the DSG 7. Its design followed the path of simplification. The box is installed with engines whose torque is less than 250 Nm. The clutch has lost its “oil” bath and consists of two friction “dry” clutches. The innovation reduced the maintenance requirements of the box and its weight to 70 kilograms. The rest of the mechanism remains similar. DSG 7 is installed on: Volkswagen (Polo, Golf, Passat, Transporter, Caddy); Skoda (Fabia, Superb, Octavia); Audi (A3, Q3, TT); Seat (Ibiza, Leon, Altea).
Skoda Octavia with DSG 7
All about the variator design
A variator is a type of automatic transmission. It is designed to smoothly transfer torque from the engine to the wheels and infinitely change the gear ratio within a fixed range.
Chain variator CVT
Often in the technical documentation for a car you can find the abbreviation CVT as a designation for the gearbox. This is a variator, translated from English as a “continuously variable transmission” (Continuously Variable Transmission).
The main task of the variator is to ensure a smooth change in torque from the engine, which makes the acceleration of the car smooth, without jerks or dips. The machine's power is used to the maximum, and fuel is consumed to a minimum.
Controlling a CVT is practically no different from controlling an automatic transmission, with the exception of stepless torque variation.
Briefly about the types of CVT
- V-belt variator. It has become the most widespread. This variator consists of a belt stretched between two sliding pulleys. The operating principle of a V-type variator is to smoothly change the gear ratio due to a synchronous change in the contact radii of the pulleys and the V-belt.
- Chain variator. Less common. Here, the role of a belt is played by a chain that transmits pulling rather than pushing force.
- Toroidal variator. The toroidal version of the transmission, consisting of disks and rollers, is also worthy of attention. The transmission of torque here is carried out due to the friction force of the rollers between the disks, and the gear ratio changes by moving the rollers relative to the vertical axis.
Toroidal variator
The parts of a variator gearbox are expensive and difficult to obtain, and the gearbox itself will not be cheap, and problems may arise with its repair. The most expensive option would be a toroidal box, the manufacture of which requires high-strength steel and high precision machining of surfaces.
Advantages and disadvantages of a CVT transmission
Both the positive and negative aspects of the variator have already been mentioned in the text. For clarity, we present them in a table.
| Advantages | Flaws |
| 1. Smooth car movement, stepless acceleration | 1. High cost of the box and its repair, expensive consumables and oil |
| 2. Fuel savings by using the full potential of the engine | 2. Unsuitable for high loads and difficult road conditions |
| 3. Simplicity and lighter weight of the box compared to a classic automatic transmission | 3. “Thoughtful effect” when changing gears (although, in comparison with a robot, the variator “slows down” less) |
| 4. Ability to drive at maximum engine torque | 4. Restrictions on installation on vehicles with high-power engines |
To ensure that the device does not fail the driver during operation, the following conditions must be observed:
- monitor the oil level in the transmission and change it on time;
- do not load the box during winter cold when starting to move, when towing a car and while driving off-road;
- periodically check the unit connectors and wiring for breaks;
- monitor the operation of the sensors: the absence of a signal from any of them can lead to incorrect operation of the box.
A CVT transmission is a new transmission system that has not yet been brought to its optimal state and has many shortcomings. Despite this, developers and designers predict a great future for it. CVT is the simplest type of transmission both in terms of technical design and operating principle.
Despite the apparent advantages of providing fuel economy and driving comfort, CVT transmissions are used quite rarely today and mainly in passenger cars or motorcycles. Let's see how things stand with the robot.
What's the difference between automatic transmission and dsg?
As you know, today automakers offer consumers a large number of automatic transmissions, taking into account the constantly growing demand for gearboxes of this type. In this case, the automatic transmission can be represented not only by a “classic” hydromechanical automatic transmission, but also by a robot, a variator, and also a preselective robotic gearbox with two clutches.
Also, the main modes and the actual performance in the cabin in relation to different types of automatic transmissions are often practically the same. This is done for ease of interaction. In other words, when buying a car, it can be difficult to determine which automatic transmission is installed in a particular case, since the automatic transmission lever (selector), panel and available modes may be the same.
Taking into account the fact that different types of machines have both pros and cons, and also differ in reliability and service life, in some cases it is important to understand exactly which box is on the machine. Next we will talk about how to determine whether it is an automatic or DSG, and what to look for.
Peugeot 308 2009, 120 l. With. - Test Drive
Existing versions of DSG boxes
For the first few years, starting in 2003, the DSG-6 gearbox, which received the factory designation DQ250, was only available in conjunction with a transversely mounted engine under the hood, and the cars were equipped with front-wheel drive or all-wheel drive with a Haldex clutch, double wet » clutch (Wet Clutch).
DQ250
This transmission from the Volkswagen concern could be considered the only version that has six gears, but there is also a DQ400e model used in hybrid cars, for example, on the Skoda Superb Mk4 and Volkswagen Golf GTE.
Since the end of 2007, the Volkswagen automaker began equipping its cars with a preselective 7-speed DQ200 robot with a “dry” clutch (Dry Clutch).
The unit is designed to work with engines with a volume of 1.0 to 1.9 liters, mounted transversely, with a maximum torque of up to 250 Newton meters (models VW Polo/Golf/Caddy/Touran/Passat, Skoda Fabia/Octavia/Jetta). There is also a DSG-7 version (DQ200e) with the same type of clutch used on the Jetta Hybrid with the 1.4 TSI power unit.
All other robotic gearboxes produced by VW today come only with Wet Clutch, and all are seven-speed, but can be of different types depending on the engine location.
What other manual transmission models are there from Volkswagen (seven stages, “wet” clutch, for transversely mounted internal combustion engines):
- DQ500 - produced since 2009, mainly found on the Volkswagen Transporter, but can also be installed on Passat B8 (BiTDI), Multivan T5/T6, Tiguan, Audi TT RS and RS3;
- DQ380 - produced since 2014, used on Audi S3 and VW Golf-7 cars, widely distributed in China, in fact, it is a smaller version of DQ500 (VW Golf-7 GTI, Skoda Octavia-3, Octavia RS, Skoda Superb -3, Audi S3);
- DQ381 - exists since 2022, is an improved version of the DQ380, used on many cars built on the MQB platform. The DQ381-7A modification has been developed for all-wheel drive vehicles, and DQ381-7F for front-wheel drive vehicles.
Also, at the moment, there are three types of 7-speed “pre-selective” DSGs, designed to work with engines with a longitudinal arrangement:
- DL382 – start of production: 2015, found on Volkswagen Phideon, as well as on Audi A4 / A5 / A6 / Q5. At first, the gearbox was designed for a torque of up to 400 N*m, and from 2022 it began to be installed on the Audi A6/A7 in the 4K body with a torque rating of up to 500 N*m. There are two modifications: for 4WD – DL382-7Q, for 2WD – DL382-7F;
- DL800 – produced since 2015, used infrequently, the transmission can be found on the second generation Audi R8;
- DL501 (Audi S-tronic) – produced since 2008, installed on Audi Q5-Q7, RS5-RS6, A6-A7, A4 Allroad, A5 Cabriolet, designed for torque up to 600 N*m.
In the line of Volkswagen robotic gearboxes there is one not quite typical model - this is the 10-speed “robot” DQ511, which is similar in its mechanics to the DQ511.
VW Group Director Martin Winterkorn first announced the plan to release this transmission in 2013; according to the calculations of the German automaker, the transmissions were supposed to help reduce fuel consumption by up to 15%. But the gearbox never appeared in the production version; its use was abandoned in 2022.
Reviews
Konstantin, Moscow, 25 years old: Purchased a 2022 Nissan Qashqai with an automatic transmission. The impressions are positive, there are no problems. I constantly drive at speeds over 150 km/h outside the city. Many people blame the fragility of the transmission. I am completely satisfied with the purchase. Perhaps it's a matter of low mileage.
Victor, St. Petersburg, 29 years old: I bought a Nissan Teana with a CVT – 2015. After just a few thousand kilometers, a major overhaul was required. The cost of the chain was 30 thousand rubles. Work, other parts - another 35 thousand rubles. I operated the car carefully and did not drive it when it was cold. Perhaps the previous owner lied about the mileage and screwed it up. At the time of purchase, the speedometer showed only 120 thousand km.
Vitaly, Voronezh, 27 years old: Acquired a Skoda Octavia 2 with a DSG robotic gearbox in 2022. Very smooth ride, soft acceleration. I covered 100 thousand km in a year. Work on the chassis and transmission is only routine. There are no problems. Very pleased with the purchase!
How to use dsg
There are no special instructions for using dsg boxes. The transmission is automatic, user intervention in its operation is minimized, so it is almost impossible to influence the life of the gearbox to increase or decrease it.
There are a number of rules, following which you can slightly extend the operation of the box until it is repaired, even indirectly.
- When changing gears, you must depress the brake all the way. Weak pressure does not allow the disks to fully open and leads to their wear;
- If the stop does not exceed one minute, you should not switch the rocker to the neutral position; in traffic jams it is advisable to use the “S” mode and coast;
- It is not recommended to move away using slippage;
- The hand brake must be applied without releasing the foot brake pedal;
- Modes must be switched smoothly, with a short pause between switches;
- For the DSG 6 gearbox, timely oil changes play a significant role; it must be changed in conjunction with the filter, every 60,000 km;
- If the car is stuck or stuck in the mud, when freeing it, the gear shift lever must be set to the neutral position.
It may seem that the DSG box imposes many restrictions on the operation of the vehicle.
By choosing it, the driver receives comfort and safety, and this is important
What do automatic transmissions and DSG have in common?
- Automation . Both transmissions are automatic and the driver does not need to be distracted by squeezing the clutch, shifting the lever, or adjusting the gas pedal. This is especially important for drivers who have just received a driver's license and have not yet acquired sufficient skills in driving a manual transmission.
- When the transmission is in good condition, switching occurs smoothly, comfortably, without jerking.
- The modes and their letter designations are identical.
Automatic transmission or torque converter
This is a classic version of an automatic transmission. Most often among car enthusiasts the question arises regarding which gearbox will be better: automatic or conventional manual. And it’s difficult to give an answer, because not everything is so simple. Having looked at the strengths and weaknesses of a manual transmission, you also need to look at the characteristics of an automatic transmission.
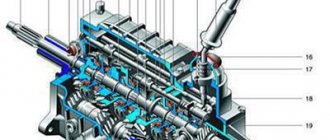
Automatic transmission cross-section
A classic automatic transmission operates on the basis of a torque converter. This is a special unit that switches planetary gears. As for the torque converter itself, it plays the role of a clutch in the structure of the automatic transmission, thereby replacing the need for the driver to depress this pedal and change gears manually, as happens with a manual transmission.
The system is quite complex, but it makes it possible to switch gears automatically. Moreover, the electronics does this at the optimal moment, taking into account the load and driving conditions of the vehicle.
A drawback is the need to change gear oil more frequently. But this is far from the most difficult procedure that you can do yourself. Modern and high-quality automatic transmissions prove that they can serve for a long time and reliably, sometimes eclipsing even old proven manual transmissions in terms of service life and resource.
Traditional automatic transmissions have several main advantages.
Service life or resource. The classic machine works confidently, efficiently and does not require complex maintenance or regular repairs. For a modern automatic transmission, a mileage of 400-500 thousand kilometers is not the limit. The car can travel such a distance if the box is maintained in accordance with the regulations and high-quality consumables are used
The main attention should be paid to the quality of ATF lubricant, that is, automatic transmission oil. Comfort level. Gear shifting is carried out not only almost imperceptibly, but also without driver participation
He doesn’t need to constantly pull the handle, squeeze the clutch, or dose the gas correctly so that the car doesn’t suddenly stall when starting or during a maneuver. Despite the emergence of new subcategories of automatic machines, the classic torque converter is still at a high level in terms of comfort. Simplicity of the device. Yes, the system is more complicated than in the case of mechanics. But not so much as to make independent maintenance or repair impossible. Many motorists successfully maintain automatic transmissions on their own, saving significant money. Resistance to loads. This is the prerogative of newer automatic transmissions, which provide the ability to automatically control very powerful engines. Even in extreme conditions, an automatic transmission often behaves better than a manual transmission. The driver is focused on the road and overcoming obstacles, without being distracted by the gearbox selector. Suitability for repair. Automatic transmissions are definitely repairable. They have typical faults, but all of them have been studied a long time ago, so repairing a classic torque converter will not cost much. This is more expensive than a manual transmission, but significantly cheaper compared to other types of automatic transmissions.
Over time, given the progress of automatic transmissions and the emergence of new varieties, it is already relevant to ask what is better: an automatic or robotic gearbox.
This is due to the fact that the classic machine is gradually losing its relevance. This can be explained by increased environmental requirements and the need to reduce fuel consumption as much as possible. Plus, the creation of automatic transmissions remains expensive, while other alternative technologies are actively becoming cheaper.
Many auto experts are confident that the classic automatic machine will soon cease to exist. And its place will be taken by CVT and robotic gearboxes. Whether this will actually happen or not, time will tell.
Which is better: DSG 6 or 7
DSG type gearbox is a robotic transmission unit. For the first time, Skoda and Volkswagen began to use this type of box in their cars en masse. We must remember: DSG and automatic are not the same thing. In this case, the driver's participation in changing gears is not required. The abbreviation DSG stands for relatively simply:
- in English - Direct Shift Gearbox;
- in German – Direktschaltgetriebe.
Main advantages and features of DSG type boxes:
- there is practically no gap between different gears;
- ease of control - no need to operate three pedals (gas, clutch, brake);
- fuel is consumed more efficiently - 10% less than when driving a manual or conventional automatic transmission.
It is worth noting: some boxes allow gear shifting not only in automatic modes. But also manually. This option is not available on all models. It should be noted that the design principle of the DSG box is almost completely consistent with the usual mechanical one. The main difference from a conventional manual transmission is the presence of two clutches at the same time. When changing gears, one of the clutches disengages. The second, on the contrary, turns on.
DSG device
It is in this way that the transmission torque is switched. Based on what was written above, it becomes clear that there are also two transmission shafts. In fact, the DSG is two boxes at once:
- for even gears;
- for odd gears.
The two boxes themselves work simultaneously. When you start moving, two gears are engaged simultaneously - first and second. But at the same time the clutch on the second one is disabled. At the moment of gear shifting, the clutch of the first gearbox is disengaged. The second clutch is turned on. All other gears are switched in a similar manner.
DSG clutch
Many owners wonder: why is a gearbox of this type called robotic - when the switching process is 100% automatic? The reason for this is the microprocessor system used to change gears. This is what distinguishes the box in question from a regular automatic machine. The gears are switched using conventional synchronizers. But the forks are driven by special hydraulic cylinders.
The clutch drive itself on the DSG is also turned on and off by hydraulic elements. A special unit – mechatronics – controls all processes occurring inside the transmission. The block includes the following main components:
- electronic;
- hydraulic;
- electrical.
The work of mechatronics consists of analyzing data from special sensors - they monitor the speed of rotation of the shafts at the input and output of the box, oil temperature and many other characteristics. The device in question is programmed. Specialist developers have written a special program for controlling electrohydraulics.
Appearance of mechatronics
Today, the automaker Skoda uses 2 different types of DSG preselective gearboxes - 6 and 7. Version 6 was released a little earlier, in 2003. But it continues to be used to this day. Version 7 - released in 2006. The first thing that distinguishes these gearboxes is the number of gears. It corresponds to the markings (6 and 7, respectively).
Another important difference between the DSG 6 (the model is marked as VW02E) is the “wet” clutch. All basket discs are constantly in a special oil bath. Moreover, such oil simultaneously solves two problems - cooling and lubrication. Which also has a positive effect on the clutch life. The box marked 6 is used on more powerful engines. She can easily “digest” a thrust of 325 Newtons. Allowed for use with 3.2 l 250 hp engines.
The DSG 7 box operates on a “dry” clutch; this model is marked as VW 0AM. Its cost is slightly less. A gearbox of this type is initially developed for low-power engines - with a torque of less than 250 hp. Moreover, this version of the box requires less oil and saves up to 10% of fuel. Often used for crossovers. It is difficult to determine which is better - wet or dry. Each box was designed to solve specific problems. Owner reviews of both types are positive.
Variable speed drive
The essence and meaning of the operation of a CVT transmission, which is designated as CVT, is no different from any other transmission. The essence of the device is to convert the torque that comes from the power unit to the wheels.
But a distinctive feature of the variator is that the torque is transmitted steplessly. A certain range of regulation is provided here. It is this characteristic that significantly distinguishes a classic automatic transmission from a variator.
As for the abbreviation CVT, it stands for Continuously Variable Transmission. This name can be translated as a transmission or gearbox with continuously varying torque.
You already roughly understand how CVTs differ from automatic transmissions and what the main difference is between them. But this is objectively not enough to give preference to either of the two options.
Also, the difference between a variator and a classic automatic transmission lies in its design features. There are 3 main types of CVT, which are:
- chain;
- V-belt;
- toroidal.
If we talk about passenger cars, then the most popular and widespread are V-belt varieties of CVT gearboxes.
- The V-belt variator includes a V-belt. It is located directly between two sliding pulleys. While the vehicle is moving, these pulleys are constantly compressed and unclenched, thereby providing changes in the gear ratio. The main task of the variator is to create a smooth and stepless change in torque. Such systems are actively used in passenger cars, snowmobiles, two-wheeled vehicles, etc.
- The next type of CVT is chain CVT. Power transmission here is carried out due to the beveled ends of the axis of the chain links. And the pulling force itself is transmitted using a special chain. Such variators are not widespread, although they are sometimes found.
- Toroidal variators replaced pulleys with cone-shaped discs. And instead of a belt, special rollers were used here. They are characterized by the fact that they can transmit quite a large torque. But in order to create such parts for the layout of the CVT box, it is necessary to use high-strength steel. This has a negative impact on cost, which is why many automakers have abandoned the idea of installing such CVTs in their vehicles.
Given the obvious differences in design and operating principle, it is easy to understand what the difference is between the two types of gearboxes under consideration. At the same time, an automatic transmission and a CVT are a worthy solution, each of which has its own strengths and weaknesses.
If we talk about the advantages characteristic of CVT or continuously variable transmissions, then the main advantage here is the provision of a continuous change in torque. There is no delay moment, which is typical for automatic transmissions, where the transition from one gear to another occurs. The stepless and continuous nature of the variator contributes to other advantages in the form of more efficient fuel consumption and improved dynamic characteristics of the engine. Cars with CVT consume less fuel and provide better acceleration dynamics.
At the same time, the variator also has some obvious disadvantages. Let's start with the fact that CVTs are not designed for use on high-performance engines. Installation on a car with increased power does not allow the potential of the box to be used. It will quickly deteriorate and wear out.
CVT can be considered a relatively new development in the field of automobile transmissions. Therefore, engineers have not yet figured out how to increase the stability of the variator to high loads, towing and active driving at high speeds. Under such conditions, the CVT belt quickly wears out and the entire transmission breaks down. Repairing and restoring a CVT is quite expensive, often exceeding the cost of repairing a classic automatic machine.
CVT device
DSG or CVT which is better?
Autoreview magazine decided to find out which gearbox is better? For tests with a full cycle of measurements, they chose the following two-pedal cars: Lada Granta Cross 1.6 station wagon (106 hp) with AMT-2 “robot”, Skoda Rapid 1.4 TSI liftback (125 hp) with DSG preselective, Hyundai sedans Solaris 1.6 (123 hp) with automatic transmission and Renault Logan 1.6 (113 hp) with CVT. The latest transmission has recently begun to be installed on LADA Vesta and XRAY Cross.
What do the boxes have in common?
In conjunction with both gearboxes, a dual-mass flywheel must be used, which increases smoothness and also eliminates slight nodding when stopping at a traffic light. It also participates in the general algorithm for switching to downshifts. From sixth gear, the box can switch to second, while lingering for a few seconds at fifth speed in a parallel row.
Otherwise, the boxes are specialized aggregate units that have a small margin of safety for successfully processing engine torque. Their installation will be similar for both boxes. The location of the wires and guides allows for replacement in the shortest possible time.
What is a robotic gearbox?
A robotic gearbox on a car means something between a manual transmission and an automatic transmission. In fact, a robotic gearbox is a “mechanics” equipped with an automatic clutch and the ability to change gears. The operation of this type of unit does not depend on the driver, but on the functioning of the control electronic module. While driving, the driver only needs to correctly transmit incoming data to ensure proper operation of the gearbox. Before buying a car with such a unit, it is recommended to understand the basic characteristics and operating principle of the device.
Robotic gearbox device
Schematic structure of the structural components of manual transmission
To understand what it is, you need to understand the structure of the unit. Additional elements intended for squeezing the clutch, as well as switching and selecting speeds, are called actuators.
The robotic transmission is equipped with its own control system, made in the form of a control unit, as well as several controllers. These sensors are designed to interact with the block. A robotic gearbox is fundamentally different from traditional automatic transmissions and CVT transmissions.
Robot gearboxes, like mechanical ones, are equipped with a clutch. ATF gear oils are not used in these types of units.
Depending on the car manufacturer, the robotic transmission can be equipped with one or two clutches:
- if there is only one clutch, then it is a single-disk unit;
- if two, then the transmission is considered preselective.
The main components of the robotic unit:
- The checkpoint itself.
- Actuators or servos. Designed for squeezing the clutch and activating speeds.
- The control module, which is a microprocessor unit. Used to process and transmit commands.
- External controllers. The number of sensors may vary depending on the machine manufacturer.
We recommend understanding the structure of the robotic unit in more detail using the example of a six-speed gearbox equipped with two clutches. The unit is designed as a manual gearbox, but is equipped with two drive pulleys. One of these elements is installed inside the other. The outer pulley has an internal cavity into which the inner component is installed. The outer pulley contains the gears for driving the second, fourth and sixth speeds, and the inner pulley contains the gears for the first, third, fifth and reverse gears.
Each shaft of the robotic gearbox is equipped with a separate clutch.
Actuators or servos
Actuator devices can be electrical or hydraulic. The electric type of elements is made in the form of an electric motor with a gearbox, and the hydraulic type is considered a hydraulic cylinder. The rod of the latter is connected to the synchronizer device. The main purpose of the actuator elements is to mechanically move the synchronizer components, as well as activate and deactivate the clutch.
Control module
The control module is a microprocessor unit on which external controllers are installed. These sensors are involved in the electronic engine control system of the machine. The transmission sensor interacts with controllers from the power unit and other systems, for example, ABS. The control module can be combined with a microprocessor engine control unit, but the transmission will operate according to its own algorithm.
The Carvizor channel spoke in detail about the structure and design features of manual transmission.
Features of a robotic gearbox
The electric clutch drive operates via an electric motor as well as mechanical speed. The operation of the hydraulic drive is based on special cylindrical devices, which are controlled by an electromagnetic valve. Sometimes a robotic unit can be supplemented with an electric motor, which is used to move cylindrical elements and is designed to support the functioning of the hydromechanical module. This device, equipped with a drive, is characterized by a long speed switching, which can be up to half a second.
Compared to a hydraulic device, the unit does not require constant support of the required pressure level to operate. In some Opel models, hydraulic units are characterized by a fast speed switching cycle, providing switching in 0.06 seconds. But such robots are usually installed on sports cars.
DSG box or automatic: how to determine the type of gearbox
So, we’ve sorted out the internal structure of classical and robotic machines. You ask me how to distinguish these checkpoints by appearance.
Selection and self-installation of multilock on automatic transmission
Please note the following methods for determining DSG:
- presence of mechatronics in manual transmission. It is enclosed in a black lid that looks like a tray. It stands in front of the machine, closer to the cooling radiator;
- VIN – vehicle code. It indicates the type of gearbox;
- if you install a car with a DSG on a slope and do not put the handbrake on, the car will roll towards the slope of the surface;
- DSG gears shift faster than with conventional automatic transmissions;
- The heat exchanger of the robotic box has a rectangular structure.
Main Differences
The DSG is structurally different from the automatic. An automatic is a fully automatic design, a robotic gearbox is a semi-manual gearbox. Although the speeds are switched thanks to the automatic transmission installed in the box, the driver controls the gear in which the car will move at the moment.
Now classic hydraulic automatic machines are produced, with a built-in tiptronic function, where the driver can also control the gears. Read more about tiptronics and mechatronics here so you don’t get confused about the differences between automatic transmission and DSG further.
The machine consists of the following components:
- torque converter;
- planetary gear;
- valve body
Design features of the robot:
- 2 primary (internal and external) and 2 secondary shafts;
- control module called “Mechatronic”;
- double clutch. One operates only on even gears, the other on odd ones.
You will say that these are all internal structures and only an experienced mechanic will understand their difference. Next, I will reveal to you the external secrets that distinguish these two types, which are identical in appearance and at the same time different in design and interaction with the engine and wheels.
You will understand, for example, how to distinguish a DSG from an automatic on a Skoda Octavia. In general, read below for the main differences.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=i0FU1sxq7HY
How to distinguish a DSG from an automatic
The shape of the variator box and automatic transmission is significantly different:
- CVT – more compact;
- Automatic transmission is an elongated “log” shape.
Impressive dimensions are ensured by the presence of a torque converter. It is worth noting: not every driver, especially without experience, will be able to visually distinguish the design of an automatic transmission from a CVT. This is why you should:
- read the technical documentation for the vehicle;
- go through text drive.
It should be noted: when using a CVT in a transmission, it will be impossible to feel the gear shift. In turn, the automatic uses a multi-stage transmission. But the switching process is completely automatic. You can determine the type of transmission installed simply by the sound:
- The CVT emits a smooth, continuous hum during operation;
- AT – makes corresponding sounds when switching.
It should be noted: some automakers specifically install special sound sources in their CVTs. They allow you to hear switching sounds, changes in rotation speed and load. The DSG differs from the automatic one visually, in characteristics and in many other nuances. It is difficult to determine the technical condition on your own, without using special instruments. It is advisable to involve specialists in such work.
When will DSG7 be discontinued?
Volkswagen doesn't talk about this. There are concerns that the box will last long enough on the assembly line, since DSG6 has been used since 2003. There are also examples of long life of frankly unsuccessful nodes. For example, the French 4-speed automatic DP0 and its numerous derivatives: DP1, DP2, AL4, which do not tolerate overheating and are distinguished by a rare “dullness” in motion. It has been used with various modifications since the early 90s, and is still installed on Renault Sandero, Duster, Nissan Almera and even on the relatively expensive Peugeot 408.
Unfortunately for motorists, now manufacturers generally care very little about the reliability of cars. The main vector of their development now is ecology. In order to save one hundred grams of gasoline per 100 kilometers, various dubious technologies are being introduced, often reducing the overall life of the car, such as direct injection, increasing turbocharging pressure or the compression ratio in the cylinders.
Gearboxes are a relatively dead-end branch of development, and DSG, paradoxically, is now at the pinnacle of progress, as it ensures efficiency (and therefore the coveted environmental friendliness). The fact that the unit “lives” on average 150 thousand kilometers is of little interest to anyone. Manufacturers are not at all interested in the existence of a secondary market - they dream of people buying only new cars and throwing old ones in the trash.
Therefore, sad as it may be, with DSG7 we have every chance of living for another 5-10 years without any major changes. And everyone will continue to pretend that this is how it should be.
Andrey Chepelev, Bibika.ru
What's bad about a robot?
The “robot” suffers greatly from slipping - it quickly overheats and breaks down. If a car with such a gearbox gets stuck in snow or mud, you should not try to get out by rocking. It is best to put the box in neutral and carefully tow the car out.
Interesting materials:
What is the difference between monologue and dialogue? What is the difference between a neurologist and a neurologist? What is the difference between forward and reverse polarity? What is the difference between pvp and pve? What is the difference between shellac and gel? What is the difference between sausages and sausages? What is the difference between Viber and Telegram? What is the difference between vintage and antique? What is Raskolnikov's worst punishment? What is the meaning of the film White Sun of the Desert?