The vehicle's on-board network is powered by a lead-acid battery with thick or liquid filler. The performance of the battery is affected by both normal wear and negative factors, in particular, the level and density of those components decreases. liquids. When the electrolyte level decreases, it is necessary to add liquid, depending on the measurement results. This will restore capacity and extend the life of the battery.
Adding electrolyte to the battery is necessary when its level decreases.
Why do you need to add electrolyte to the battery?
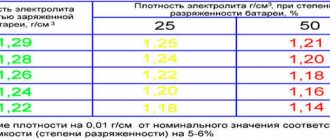
There are standards that determine the normal density of the electrolyte. The indicator is affected by the season, ambient temperature, and battery age. For example, for the central zone of the Russian Federation, a density of 1.25-1.3 g/cm3 is considered normal. If the battery is frozen or overheated, the density will most likely change, as a result the battery will discharge faster, and as a result, the car may simply not start in the morning and will not be charged from the car’s generator.
If you correctly add electrolyte to the battery, the problem will be solved, unless the reason lies in the natural wear of the battery plates or problems in the vehicle’s on-board network.
If the density has dropped
What to put in the battery? In this case, you cannot add water. This will only make the situation worse. The only correct solution is to fill the electrolyte. Before the operation, it is necessary to make a control measurement. It is produced by the same hydrometer. If the value obtained is 1.25 grams per cubic centimeter or lower, it is worth increasing it by using a new electrolyte. The density of the latter should be about 1.27 grams. What volume should I use? Using a syringe, you need to pump out as much of the old liquid as possible from the first jar and pour it into a measuring cup or test tube. It is important for us to find out how much solution was removed from the first jar. This amount needs to be written down somewhere in a notepad. The volume of the new solution should be half that of the one we removed.
Checking the fluid level
Notches for checking the electrolyte level.
You can determine whether electrolyte needs to be topped up in the battery by looking at the control marks on the body
batteries. The marks are located inside or outside the housing. Some battery models have a viewing window made of transparent material. The notches determine the minimum and maximum technical level. liquids. During normal operation the value is in the middle. Manufacturers prohibit the use of batteries with abnormal electrolyte levels.
If there are no notches, they do not allow you to accurately determine whether electrolyte can be added to the battery or not, a glass tube will be required for measurements. To test, you need to clean the battery from dirt and dust, unscrew the plugs, and insert the tube until it stops. Next, the other side is clamped with a finger, so that the liquid remains inside the tube.
As an alternative, you can use a folded sheet of paper for measurements, determining the level by the moistened part.
The level is determined visually. This method does not allow obtaining accurate results, but it is sufficient to ensure the operation of the battery. If the liquid is below normal, it is necessary to add distilled water or electrolyte; if it is higher, pump out the excess using a pear.
The maintenance-free battery has a sealed case where access to the banks is not provided. Accordingly, to check the electrolyte volume you will need to drill holes, which is highly not recommended.
Distillate selection
If you fill the battery with ordinary water (including collected rainwater), the active mass of the plates will very quickly become unusable. To extend battery life, use only high-quality distilled water. To check the quality, consider the simplest characteristics of the distillate:
- electrical conductivity. Distilled water, unlike ordinary water, does not conduct electricity. You can check the water by measuring the resistance with a multimeter - for distillate it will be equal to infinity;
- no traces after boiling. For the test, drop water on a clean A4 sheet or heat it on a glass surface/piece of foil. After the distillate has evaporated, there should be no halos or stains left on the surface.
Video: HOW TO ADD ELECTROLYTE OR WATER INTO THE BATTERY | WHAT NOT TO DO
What can you add to the battery?
To determine what to add to the battery, you need a special measuring device - a hydrometer. This is a glass tube with a bulb, inside of which there is a float. A scale indicating the density is applied to the outer wall.
Verification algorithm:
Checking the electrolyte level with a hydrometer.
- Charge the battery to 100%.
- After fully charging, wait 3-5 hours for the chemical reaction inside the cans to normalize.
- Unscrew the plugs (if the battery is maintenance-free, drill holes in the housing).
- Immerse the hydrometer in the jar and scoop up the electrolyte with a bulb.
- Take measurements in each section one by one.
When to add electrolyte and when to add water?
Under normal conditions, the hydrometer scale shows 1.27-1.30 g/cm3. If the density is less, it means there is a lack of sulfuric acid in the battery, if there is more distilled water. In a standard operating scenario, sulfuric acid from the electrolyte is practically not consumed, so distilled water is often poured into the jars.
It is not recommended to fill in excess fluid above the level - this can lead to the release of acid into the engine compartment.
Pure electrolyte is used both to increase the density and to completely replace the process fluid in the battery banks - the filling volume depends on the battery model.
Application of sulfuric acid and its grade
In general, alkali can be used as an electrolyte in some types of car batteries. For example, nickel-cadmium or nickel-iron type batteries. There is also a group of gel batteries AGM and GEL, where the electrolyte is in a bound state. But this is the same solution of sulfuric acid. It’s simply either put into a gel state using additives (GEL), or glass fiber is impregnated with it (AGM). The most common today are lead-acid car batteries with liquid electrolyte. Therefore, we will talk specifically about an aqueous solution of sulfuric acid intended for pouring into the battery.
Electrolyte
Distilled water
Sulfuric acid is used in a variety of sectors of the national economy. For example, it is used to clean the metal surface before coating; it is used in the preparation of various synthetic dyes. In addition, sulfuric acid is in demand in the production of fertilizers, explosives, pharmaceutical industry, and oil refining.
Sulfuric acid is widely used in the production of lead-acid batteries for cars. The acid concentration in the electrolyte is 30-35 percent (wt.). The rest is distilled water. You cannot use regular tap water because it contains salts of various metals. If they get into a car battery, it will significantly shorten its service life.
In the domestic sphere, a concentration of H2SO4 of 30 percent is sufficient, but in the industrial sphere, sulfuric acid of a higher concentration is often used. Concentrated sulfuric acid is produced in two stages. At the first stage, the concentration is brought to 70 percent, and then increased to 98 percent. Sulfuric acid of this concentration is most suitable for subsequent storage. It is possible to obtain a concentration of 99 percent, but later due to the loss of SO3 it decreases to 98.3 percent. There are main grades of sulfuric acid, which are listed below:
- Tower or nitrous. Concentration 75 percent. The density of this variety is 1.67 g/cm3. This variety received its name due to the production method in lined towers using the nitrous method. The roasting gas with sulfur dioxide (SO2) is treated with nitrose (H2SO4 with added nitrogen oxides). The chemical reaction produces nitrogen oxides and acid. In this case, oxides constantly circulate in the production cycle;
- Contact. Concentration from 92.5 to 98 percent. The density of the variety is 1.837 g/cm3. This grade is also produced from roasting gas, which contains SO2 dioxide. During the reaction, it is oxidized to SO3 upon contact with a solid vanadium catalyst;
- Variety Oleum. Concentration 104.5 percent. The density is 1.897 g/cm3. The variety is a solution of SO3 in sulfuric acid (H2SO4). The ratio of SO3 is 20 percent, H2SO4 is 104.5 percent;
- High percentage oleum. The concentration is 114.6 percent, and the density is 2.002 g/cm3;
- Rechargeable. The concentration is from 92 to 94 percent, and the density is 1.835 g/cm3.
Features of maintenance-free batteries
Most batteries on sale are of the maintenance-free type. This decision has both positive and negative sides. In particular, if there is a need to add electrolyte to the jars, you will need to drill the battery case, which breaks the seal and automatically voids the factory warranty. The channels are made with a sharp awl all the way to the lead electrodes. The width of the hole must be sufficient so that a hydrometer tube can be inserted inside, which is necessary to determine the density of the electrolyte and what liquid to pour into a maintenance-free battery.
If the density is normal, but the level needs to be changed, a bulb or syringe will be required. Top up, depending on the hydrometer readings, with distilled water or pure electrolyte. To ensure normal operation of the battery, the technical level. liquid should be 10-15 mm above the edge of the electrode. Thus, it will be completely immersed in liquid, even when the car is parked on a slope, as a result, normal operation is ensured, and the possibility of oxidation of the plates associated with contact with air is eliminated.
Adding electrolyte to a maintenance-free battery.
Upon completion of the procedure for topping up each battery tank, it is recommended to pump the battery, thus speeding up the mixing of acid and distilled water. The IP should be shaken carefully, and under no circumstances should it be turned on its side - this leads to sludge getting between the electrodes, which reduces the service life. The next stage is a control measurement of the level and density of the electrolyte. If there is not enough fluid, it is refilled to the normal value.
The last step is to seal the holes with sealant and fully charge the battery.
Complete electrolyte replacement
To completely replace the electrolyte in a battery, you will need to go through several steps:
The battery plugs can be unscrewed with a coin.
- Place the car on a level surface, and before turning off the power, make sure that the driver has service codes from the radio and other equipment necessary to unlock them.
- Open the hood, remove the mounting cover, remove the terminals, wipe the body from dirt, dust, and electrolyte residues.
- Unscrew the cans (for a maintenance-free battery, drill holes).
- To pump out the liquid, take a medical syringe or a rubber bulb with an extension tip attached. During the procedure, you should not turn the battery over - this will prevent sludge from getting into the plates, as a result, the possibility of a short circuit.
- When draining, it can be tilted at an angle of up to 45°, which will simplify the complete pumping out of the electrolyte.
- To completely get rid of the remaining old liquid, you need to rinse the jars several times with distilled water. Slight rocking of the battery is allowed. It will not be possible to completely wash the jars - the solution will still remain in the cavities between the electrodes.
- Pour in new clean electrolyte: level is above the top edge of the electrodes.
- Let the battery sit for 5-6 hours.
- Fully charge the battery with a current of up to 0.1 A. Duration of the procedure is 18-20 hours. To fully restore capacity, you will need to perform 2-3 low-current charge cycles.
- Carry out final charging with a current of 10% of the rated capacity of the battery.
- Check the level and density of the electrolyte, if necessary, bring the values to normal.
- Install the battery on the car and connect it to the on-board network.
Adding electrolyte to the battery normalizes battery operation, allows you to restore capacity, reduces the likelihood of plate sulfation, and eliminates premature failure. You can perform the procedure yourself at home; this does not require special equipment or knowledge.