Buy tires and wheels in the PIN-AUTO online store.
8 800 222 69 80 Tires provide reliable traction between the wheels and the road. They also perform the function of shock absorption of unsprung components. They have been used in their modern form since the end of the 19th century and were gradually improved, leading to their current efficiency and reliability. At the moment, car tires have a large number of varieties, which makes it possible to more effectively select them for specific conditions.
By what criteria are tires classified?
Types of car tires are divided according to a number of parameters, which simplifies the choice. First of all, they are divided by type of transport. Tires can be designed for cars, trucks, motorcycles, and special vehicles. Truck tires also have a subdivision based on the characteristics of specific vehicles and axles. Depending on the type of vehicle, tires may have different sizes, tread, permissible loads and other parameters.
They are also divided according to acceptable road surfaces. Controllability and some other nuances depend on the right choice.
Based on the type of construction, there are several varieties that differ in the location of the cord.
It is important to differentiate by season. Tires are divided according to the possibility of use at certain times of the year. Traffic safety and the lifespan of tires depend on this.
There is also a division based on the tread. This factor affects handling, safety, and the ability to move on different surfaces. Therefore, it should be taken into account when choosing.
Low profile?
Marking of a low profile tire
Which tires are low profile? Many car enthusiasts prefer tires with a low profile, wanting to decorate the appearance of the car and slightly change its characteristics. In such products, the percentage ratio of the width and height of the tire profile should be less than 55%. You can find out the profile height of a tire from the marking, for example, in the designation 205/45R14, the number 45 indicates a low tire profile. The ratio of the width of the product to its height is 45%. The tire width is 205 mm, and the profile height is as follows: 205 * 0.45 = 92.25 mm.
The use of tires with a low profile makes it possible to:
- increase the contact patch of the wheels with the road surface;
- improve machine stability;
- improve braking;
- improve acceleration.
Disadvantages when using this type of tire:
- increased noise while driving;
- high probability of aquaplaning effect;
- increase in tire stiffness;
- the likelihood of disc deformation increases when driving on uneven road surfaces or hitting curbs.
How does a car tire work?
A car tire consists mainly of rubber, and also has a cord as its base. Rubber refers to a mixture of natural and synthetic rubbers, which make up the bulk of the tire.
Basic design elements.
- Frame. These are cord threads that give rigidity to the tire. Can be radial or diagonal.
- Breaker. Made from thick rubber or metal cord. Located between the frame and the tread.
- Tread. External part of the profile. The tread pattern is responsible for traction on the road, as well as for removing water and dirt from the contact patch.
- Board. Responsible for the firm fit of the tire on the wheel rim. In tubeless tires it is made of viscous rubber.
- Side part. Made of rubber, protects against side damage. Markings are also placed here.
- Spikes. Made from metal, they reduce the level of slipping on ice.
It is important for the driver to understand the tire design. In practice, the following options are encountered:
- Radial;
- Diagonal;
- Diagonally belted.
At the moment, radial tires are most widespread; they are marked “R”. In such tires, the cord runs along a radius from one bead to the other. In this case, all threads are placed parallel to each other. This placement protects against lateral stretching, and protects so well that it is possible to reduce the number of layers of cord. The sidewall protects against longitudinal stretching; it uses diagonal placement of threads.
Diagonal tires have a cord oriented at an angle to the radius. Also usually the layers of threads are placed at an angle to each other. This results in the need to create only an even number of layers. The main disadvantage is the release of heat during movement; the fact is that the layers are constantly shifting relative to each other, this leads to heating. Therefore, such tires are always made with a high profile.
A bias-belted tire has a belt similar to a radial tire.
There are tubed and tubeless tires. The first ones use a special rubber chamber for inflation; it is located under the tire. The main disadvantage is the rapid release of the camera when punctured.
Tubeless tires, thanks to technology, do not have a tube. It is inflated directly on the wheel, without an additional chamber. To make this possible, a sealing layer is included in the design; it also slows down the release of air in the event of damage.
Flat technology
Attempts to solve this problem led to the emergence of so-called “puncture-free” tires, also known as Run Flat tires.
There are two run flat technologies used on cars. The first of them is strengthening the sidewalls. Due to the increase in the rigidity of the sidewalls, when air is released, the weight of the car begins to be supported by the sidewalls. Thanks to this technology, a wheel without air can travel up to 100 km at a relatively good speed of up to 80 km/h.
Run flat technology
The second technology is the use of a support ring. This ring, made of high-strength plastic or metal, is installed and fixed on the rim inside the tire. In the event of a tire puncture, when the air is released, the wheel begins to rest on the ring, which allows you to continue driving without possible damage to the disc. Despite the fact that the ring is made of hard materials, the noise when driving does not increase much, since there is always a layer of rubber between the road and the ring.
Run flat technology really solves the problem of punctures. But in the case of wheels that have reinforced sidewalls, they will not help if the sidewall is severely cut. But wheels with a support ring are expensive and require specialized equipment for maintenance.
It is worth noting that Run Flat is a general designation for puncture-free tire technology. Manufacturers often use their own designation for such rubber, which creates some confusion.
What vehicles are there tires for?
Drivers often wonder how truck tires differ from passenger tires. In fact, there are few differences, and they all relate to technical features of operation.
First of all, it is worth remembering that truck tires can often withstand high loads. Therefore, special vehicles and truck tires always use reinforced cords. Also, such cars are rarely driven at high speeds, which makes it possible to use a diagonal design.
Also, tires for heavy trucks are often divided into steering and driving. Drivers get a shallow tread with almost no sipes. This ensures optimal load distribution and improves vehicle handling. The leading ones have a more serious tread, which guarantees effective grip on the road.
Passenger cars do not have this division.
For special vehicles, tires with the deepest tread are often used. This ensures optimal performance in all conditions.
The vehicle manufacturer describes the tire requirements well. Be sure to read the recommendations.
Non-flat tires
Puncture-free tires called Run Flat are very popular. In such products, manufacturers strengthen the sidewall of tires: they apply a special viscous substance to the inside of the tire, which seals the puncture hole while driving without reducing the pressure inside the tire. This technology makes it possible to travel about 150 kilometers at a speed of 80 km/hour without tire deformation. Many giant automobile factories make the basic equipment of well-known car models with puncture-free tires.
Purpose of tires by type of road surface
Based on the road surface, tires are divided into:
- road;
- off-road;
- universal;
- winter.
Often, road and winter ones are classified as the same type, but we will look at them separately. Technically they are somewhat different.
Road tires usually have a classic tread and are designed for road use. All the main differences between tires of this type are the features of the tread, as well as the ability to maintain control over the car on wet asphalt. They are distinguished by a straight pattern with virtually no lamellas.
Off-road vehicles are designed for use on any surface. Thanks to the large tread, sipes and other features, such tires allow you to drive effectively on any surface without fear of problems.
Universal tires combine the qualities of road and off-road tires. But, according to many experts, they are inferior to specialized tires.
If you drive most of the time in the city and on country roads, it is better to take regular road tires
Load Index
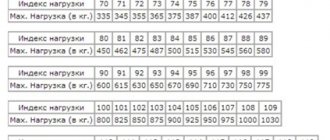
Tire load index is a digital designation that is located after the standard sizes. The parameter tells you what maximum load the rubber can withstand at the maximum permissible speed at a certain pressure. But this does not mean that if the indicator is slightly exceeded, the tire will burst. It contains a 20–30 percent safety margin.
Each numerical designation corresponds to an indicator in kilograms, for example, 62–265 kg, 63–272 kg, and so on up to 126, which corresponds to a wheel load of 1700 kg. The load index is the load capacity; this parameter should not be confused with the maximum pressure.
Appointment according to seasonality
Car tires are also divided by season. This classification divides tires into three groups:
- summer;
- winter;
- all-season.
It is recommended to use tires that are appropriate for the season. In addition, in some countries, operating a car with shoes that are out of season is prohibited.
Summer tires are made from hard rubber compounds. This allows the tires to operate more efficiently at high temperatures. In such conditions, it is possible to combine a low level of wear (due to rigidity) and good handling. All models of such rubber have a well-developed heat dissipation system and usually have a large contact area.
At low temperatures, summer tires become hard and practically lose their ability to grip the asphalt. They should not be used at temperatures below +5°.
Winter tires, on the contrary, are made from soft varieties and mixtures of rubber, which allows them to maintain driving performance at low temperatures. It can have a simple protector (Velcro) with lamellas or be equipped with spikes.
The spike performs well on ice and snow. On asphalt, this type is less effective and also damages the coating. Modern Velcro is not inferior in quality of grip to spikes, but is more versatile.
Winter tires are also divided into types based on tread:
- Scandinavian;
- European.
The first type has a more developed tread, which allows you to successfully drive on snow and ice. European winter tires perform better on slush and wet roads. Winter tires are marked with an asterisk icon, or the designation “W-winter”.
There is also an intermediate option, these are the so-called all-season tires. They are softer than regular summer tires and stiffer than winter tires. But, in any case, they are significantly inferior to specialized tires. At temperatures below -10° they freeze, and at high temperatures they soften excessively. Marked M+S, AS or 4S.
It is recommended to use all-season tires only in areas with mild winters. In other cases, savings may backfire.
Speed index
The speed index is the letter that comes after the load index. These indicators are interrelated. Each letter corresponds to a specific speed limit. To ensure safe operation, it is recommended to install models with an index higher than the maximum speed of the vehicle. For example, if the last mark on the speedometer is 210 km/h, then the best tire in this case is marked “V”, which corresponds to 240 km/h.
Types of tread
When dealing with the question of what types of tires there are, it is worth considering the tread. In practice, the following drawing options are used:
- Symmetrical non-directional. The simplest and cheapest option. The tread is approximately the same throughout the entire profile, there are no installation requirements.
- Symmetrical directional. It has a clear direction of movement, which is marked with an arrow. In this case, maximum vehicle controllability is achieved.
- Asymmetrical non-directional. Designed for use in unstable weather conditions. One half of the profile is designed for dry weather, the other for rain.
- Asymmetrical directional. Also has a “double” profile. But, at the same time, the tread has a certain direction.
According to many drivers, tires with an asymmetric pattern last less. They should not be interchanged to reduce wear.
Knowing what types of tires there are, you can easily choose the best option. Try to take into account all the parameters when choosing tires for your car.
For SUVs and crossovers
There is also a classification of tires by purpose.
Various additional inscriptions may indicate this. For example, the letter P indicates that it belongs to passenger vehicles, T indicates tires for trucks. This classification allows you to find the best car or truck tires. And kits for SUVs or crossovers are identified by the letters AT (All Terrain). When choosing shoes, carefully look at the maximum speed index. The value in km/h is indicated by a Latin letter next to the maximum load index. A special table will help you understand the definition.
Source
Main components
A modern bicycle includes two wheels, usually of the same diameter. The rear wheel is usually the drive wheel and is driven by a bicycle chain.
A wheel consists of a hub, spokes, rim, tube and tire. Sometimes the tube and tire are one unit, that is, a tubeless tire.
The hub is connected to the wheel rim using spokes, the number of which ranges from 12 to 48. Prestigious models of bicycles with a frame made of composite materials are often equipped with wheels whose spokes are made of carbon.
The size of a bicycle wheel is traditionally determined by the outer diameter of the tire in inches - from 14 to 29 (1 inch = 2.54 cm). A mountain bike usually comes with 26-inch wheels, while a hybrid or touring bike has 28-inch wheels.
The rear wheels of sports bicycles do not contain spokes, so they consist of a solid disk. This design increases wheel rigidity and reduces oncoming air resistance at high speeds. The only drawback is the increased windage, which adds trouble to cyclists in crosswinds.
Rim
Material
In the manufacture of bicycle wheel rims, steel or aluminum alloys are used in most cases. Steel rims are cheaper, but heavier and more susceptible to corrosion. In recent years, lighter composite materials have been increasingly used: carbon and plastic.
New technologies make it possible to spray ceramics onto the braking surface of rims. This not only shortens the braking distance of the bicycle in wet weather, but also extends the service life of the wheel.
Bicycle wheel spoke
A very vulnerable element. In addition to the load from the weight of the cyclist, it is subject to impacts on uneven roads. Using a nipple, the spoke is fixed in the rim. The most common knitting needles are made of steel or aluminum.
The spoke consists of four parts:
- Head. The head is fixed to the sleeve.
- Body.
- Thread. A nipple is screwed onto the thread.
- Nipple. The nipple attaches the spoke to the rim.
The nipple must be made of the same material as the spoke.
To evenly distribute the load and avoid rim distortion, the tension of the spokes should be the same. This corresponds to an optimal balance between structural elements. Types of knitting needles:
- Rolled knitting needles are a budget option.
- A drawn knitting needle is lighter in weight, but more expensive.
- The flat knitting needle is the most expensive, significantly superior to other types both in weight and in resistance to oncoming air flow.
Spitsovka
Spoking is the order in which the hub, spokes and rim are mutually attached. There are two main types of wheel spokes: “radial” and “cross”.
In the “Radial” view, the spoke does not intersect with the others. When assembling with a “cross”, the knitting needle crosses with the other knitting needles several times, depending on the chosen knitting method. On widely used 26-inch wheels, three-cross spokes are more often used.
Types of rear bicycle hubs, their differences from each other
The hub is the base of the wheel.
The hub is located in the center of the wheel and rotates on bearings. As bearings, collapsible balls or factory-made universal sealed bearings are used. The bearing bears all the pressure of the bicycle when riding, so its quality must be high.
The hub is connected to the wheel rim through spokes. Outdated models of “Torpedo” type hubs contain a brake drum inside the structure, with the help of which the cyclist brakes by reverse rotation of the pedals.
A modern bicycle rear hub includes a ratchet mechanism and a cassette with chainrings that fits onto the drum. On a freewheel hub, the bearings are located closer to the center, so the load is not distributed evenly. Hubs of this type are installed on teenage or budget adult bicycles.
The cassette hub is another popular type of rear hub. It has slots on which the cassette with stars is mounted and secured with the cassette nut. These hubs are more reliable, the bearings are located further from the center of the hub, so the bike can support up to 120 kg.
The third type of rear hubs is a hub with a planetary gear shift system. It combines the functions of a hub and a bicycle gear shift mechanism.
The entire mechanism is located inside the bushing and is protected from dust and moisture. The chain on a bicycle with such a bushing lasts longer, as it does not change its position. The planetary bushing has a high degree of reliability.
The design of the SRAM 3-speed planetary hub is very simple. But it’s better not to disassemble the 5 and 7 speed ones. Planetary gears are installed in a special position - this requires a special tool.
What does a wheel consist of?
About sound insulation of car wheel arches
Components such as wheels are presented in the form of a high-strength and lightweight structure. Their movement is possible due to holding the frame in a vertical state during the rotational process. As a rule, a 2-wheeled vehicle is characterized by rear-wheel drive, in which the wheel at the rear of the device acts as a pusher, and the role of the weighty and controlling wheel is performed by the front wheel.
The main parts that make up a bicycle wheel are bushings, rims, tires and a tire.
The bushing consists of an axle, bearings and washers. The task of this part is to set and maintain the rotational state. Also, the rear wheel bushings are a place for attaching sprockets. If the bicycle is a road model, then a brake mechanism is installed inside the rear wheel hub.
The role of the rim, presented in the form of a round ring attached to the bushing, is aimed at making the wheels resistant to various impacts and loads.
The tire composition consists of tubes and tires. The appearance of the tube resembles a hollow rubber product, through the nipple of which air is pumped into the inner part of the tire element. The external component of a tire is the tire, which consists of beads, sidewalls and tread. The purpose of the bicycle is influenced by the type of tire used.
The reflector, presented in the form of an orange insert on the spokes, helps to make the wheels visible.