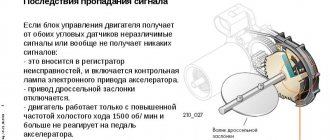
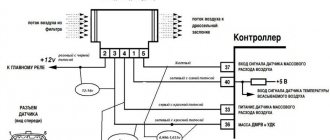
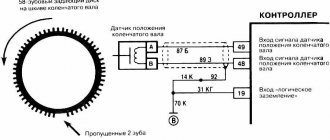
Causes of error P0101
- The mass air flow sensor sends a signal to the engine control module (ECM) that is out of range.
- The mass air flow sensor is not functioning properly due to damage or malfunction.
- Electrical wires or the MAF sensor itself are located too close to higher voltage components (such as the alternator, ignition wires, etc.) which can cause interference that affects the signal sent to the vehicle's ECM.
- The problem could also be damaged vacuum hoses, which can lead to various problems and other error codes.
- The MAF sensor must operate within a certain range to be able to send the correct signals to the vehicle's ECM, which is necessary for proper engine operation.
Description and meaning of error P0101
This diagnostic trouble code (DTC) is a generic powertrain code, which means it applies to OBD-II equipped vehicles (Nissan, Chevrolet, GMC, Mercedes, VW, Toyota, Mazda, BMW, Ford, Audi, Honda, etc.). While general, specific repair steps may vary depending on the make/model. The MAF (mass air flow) sensor is a sensor installed in the air intake path of a vehicle's engine downstream of the air filter, and is used to measure the volume and density of air being drawn into the engine. The MAF sensor itself measures only the portion of air entering and that value is used to calculate the total volume and density of the air being ingested. The powertrain control module (PCM) uses this reading along with other sensor parameters to ensure proper fuel delivery at any given time for optimal power and fuel efficiency. Basically this diagnostic trouble code (DTC) P0101 means there is a problem with the mass air flow (MAF) sensor or circuit. The PCM detects that the actual MAF sensor frequency signal is not within the specified expected MAF estimated value range. Note: Some MAF sensors also include an air temperature sensor, which is another value used by the PCM for optimal engine performance. Closely related MAF circuit trouble codes include: P0100 Ground or Tom air flow circuit Malfunction P0102 Tom Air flow Massor circuit low air flow Input P0103 Massor circuit high ground Input P0104 or Tom air flow circuit intermittent
How does a mechanic diagnose a P0101 code?
When diagnosing this error, the mechanic will do the following:
- Connects the OBD-II scanner to the vehicle's diagnostic connector and reads all stored data and error codes
- Visually inspect the engine, then clear the fault codes from the computer's memory and test drive the vehicle to see if P0101 appears again .
If the error code appears again:
- Check the electrical connector of the mass air flow sensor for looseness.
- Check the electrical wires related to the mass air flow sensor for damage
- Find out if electrical wires or the MAF sensor itself are located too close to higher voltage components
Diagnostics
There are two ways to set error codes for VAZ 2114 injector 8 valves. However, each method has unique advantages and disadvantages.
Self-diagnosis of VAZ 2114: error codes and their interpretation
The self-diagnosis method does not require the driver to have complex instruments or additional units. To complete the procedure, the car itself is enough.
The standard sequence of actions looks like this.
- Press the odometer reset button.
- Turn the ignition key to position No. 1 (turn on the on-board electrics).
- Release the mileage reset button. After this, the instrument arrows will make a full revolution and return to their place.
- Press the reset button a second time and release. The command displays the firmware version indicator.
- Repeat step No. 4 - this will display error codes on the on-board computer.
If the sequence of actions is performed correctly, all indicators will light up and the display will show a two-digit fault code.
Note!
A failure signal may be a lack of response from the indicator. In this case, it is necessary to check the circuit coming from the device.
The most common error codes for the VAZ 2114 panel, occurring in 90% of cases:
- 1 – microprocessor failure, flashing required;
- 2 – error code 2 VAZ 2114 indicates that there is an interruption or disruption in the wiring of the float sensor inside the gas tank;
- 4 – electrical wiring short circuit, voltage limit exceeded;
- 8 – error code 8 on the VAZ 2114 indicates a drop in voltage in the network, the battery may have run out;
- 12 – in the VAZ 2114, error code 12 indicates that the warning lamp is not functioning properly;
- 13 – open circuit of the oxygen sensor;
- 14 – error code 14 on the VAZ 2114 warns the driver that the engine has overheated or the antifreeze temperature sensor has shorted;
- 15 – short circuit or DTOZh has failed;
- 16 – exceeding the permissible voltage limit of the on-board network;
- 17 – BS voltage has dropped critically, battery discharge is allowed;
- 19 – DPKV does not respond or there is a short circuit on the line;
- 21-22 – incorrect response of the TPS, possible short circuit or wiring break;
- 23/25 – short circuit of the throttle position sensor;
- 24 – speedometer failure, power cords may be broken;
- 27/28 – CO sensor worn out or broken;
- 33/34 – problems with the mass air flow sensor, possible power loss or short circuit;
- 35 – IAC sensor has failed, can only be treated by complete replacement;
- 41 – incorrect phase distribution covered or shorted;
- 42 – the circuit has failed or the wires of the electronic ignition unit have been broken;
- 43 – mixture detonation sensor is faulty;
- 44/45 – there is a violation of the fuel supply to the engine, the system may trip, jerks appear during acceleration, and it picks up speed poorly;
- 51 – ROM is acting up;
- 52 – similar for RAM;
- 53 – potentiometer failure;
- 54 – break in wiring for octane corrector;
- 55 – excessive leanness of the mixture during acceleration;
- 61 – interruptions in the operation of the lambda probe.
In some cases, errors may be superimposed on each other if the failure is similar. For example, if errors 1 and 4 intersect, the panel will indicate "5".
It is important to know that after viewing, VAZ 2114/2115 error codes do not disappear on their own after repairs are performed. They need to be forced reset. To complete the work you will need a simple sequence of actions:
- turn on the car ignition;
- remove the terminals from the battery;
- wait 20-30 seconds;
- return the clamps to their place.
This also needs to be done if you are planning a trip to a service station. Having discovered the instructions from the on-board computer, the technicians will correct these problems, which will definitely be more expensive.
The disadvantages of an independent procedure include the low accuracy of the data. On-board diagnostics only show the general direction vector where the fault should be looked for.
Check using diagnostic equipment
You can identify error codes for VAZ 2115 and 2114 using a laptop with a special program. The tool is connected to the vehicle's test socket through a set of adapters. The wizard configures the software, and after diagnostics, one or more faults will be displayed on the computer screen in the form of a five-digit code.
The first part is the letter:
- B – damage to body panels;
- C – chassis or suspension malfunction;
- P – electrical, engine or transmission disorder;
- U – damage to the terminal for information exchange.
The second part is a single digit:
- 0 – typical indicator according to the SAE standard;
- 1/2 – conveyor failure code;
- 3 – reserve.
The next element is the breakdown group indicator:
- 1/2 – defect in the fuel/air line;
- 3 – ignition and related elements;
- 4 – catalyst;
- 5 – XO of the power plant;
- 6 – ECM and related wiring;
- 7/8 – transmission blocks.
The final two numbers point directly to the problem itself.
Common mistakes when diagnosing code P0101
- The most common mistake when diagnosing a P0101 is to hastily replace the MAF sensor without first checking the associated electrical wires and connector for damage.
- It is also a mistake to neglect to check the mass air flow sensor for excessive carbon buildup before replacing it. Sometimes the problem can be solved by cleaning the sensor using a special cleaner designed for mass air flow sensors.
- Another mistake is neglecting to check the vacuum hoses for wear and damage.
Basic error codes for VAZ 2114 injector: decoding
Note!
The table is also relevant for version 2115.
Exhaust system – 0000
- 30 – open circuit of the oxygen sensor heater to the catalytic converter;
- 31 – also with a short circuit to the car body;
- 32 – similar with a short circuit to 12V;
- 36-38 – the same value as 30 only for the output sensor.
Air line defects – 0100
- 102/103 – Mass air flow sensor open circuit or signal violation;
- 112/113 – sensor lines t˚ overboard, impulse violation;
- 116 – engine overheating;
- 117/118 – damage to the DTOZH circuit;
- 122/123 – TPS line, short circuit or insulation failure;
- 130 – failure of the oxygen sensor in front of the catalyst;
- 131/132 – similar element, signal level violation;
- 133 – slow response of DK1 to commands;
- 134 – break in the power cable DK1;
- 136 – DK2 is broken;
- 137/138 – short circuit or violation of wiring DK2;
- 140 – fuse DK2 burned out;
- 141 – the heater of the same device is broken or damaged;
- 171/172 – excessively lean or enriched fuel mixture.
Error codes VAZ 2114 1.6 liters related to fuel supply - 0200
- 201/204 – break in the injector control line for all injectors in series;
- 217 – motor overheating;
- 230 – the fuel pump has failed or the corresponding relay has burned out;
- 261/264/267/270 – short circuit of the injector control circuit at +12 V, respectively, for each insert;
- 263/266/269/272 – failure or defect of the injector driver for each in series;
- 262/265/268/271 – Short circuit of highways to the car body.
Error codes on the VAZ 2114 on-board computer indicating a breakdown in the ignition system - 0300
- 300 – there are misfires;
- 301-304 – similarly for each cylinder, respectively;
- 326-328 – DDS is broken or there is no signal;
- 335-338 – failure, short circuit or interruption of the DPKV wiring;
- 342/343/346 – malfunction of the phase distribution sensor;
- 351-354 – open circuit for all pistons in series;
- 363 – the mixture in the cylinders does not ignite, emergency fuel supply cut-off.
Additional attachment that does not have a direct effect on the motor – 0400
- 422 – the catalyst may have clogged or the exhaust gas flow rate has dropped critically;
- 441 – failure of power supply to the adsorber purge valve;
- 444 – power failure above the specified element;
- 445 – short circuit of the gearbox to the car body;
- 480 – power wires to the main radiator cooler are damaged;
- 481 – failure of the coolant fan control circuit No. 2.
Failure, malfunctions in the SU speed control system – 0500
- 500 – speedometer sensor is broken;
- 506/507 – low or high speed of the vehicle;
- 511 – XX regulator – lines from the relay and ECU are interrupted;
- 560 – the battery is low or the power cable is broken.
- 562/563 – Short circuit on on-board wiring.
On-board network of auxiliary or main equipment – 0600
- 601 – ECM, ROM error;
- 615 – secondary starter relay, wiring damage;
- 616/617 – also with short circuit to ground or 12V;
- 627 – fuel pump control relay, possible line break;
- 628/629 – similar with a short circuit to the body or on-board system;
- 645-647 – compressor clutch, damage to the wiring with contact with the housing or other cables;
- 650 – the “Check Engine” lamp is broken, check the engine, there may be damage to the wiring;
- 654 – tachometer failed;
- 685-687 – malfunction of the main engine control relay, complete replacement of the part is required;
- 691/692 – problems with the main cooling fan relay.
Auxiliary systems – 1000
- 102 – breakdown of heater DK1;
- 115 – failure or malfunction of the above device;
- 123/124 – violation, too rich/lean mixture at idle;
- 127/128 – similar, only for partial load on the internal combustion engine;
- 135 – rupture of heating line DK1;
- 136/137 – incorrect fuel supply at low engine load, the throttle drive may be malfunctioning;
- 140 – discrepancy between measured and actual load;
- 141 – failure of heater DK2;
- 171/172 – incorrect information comes from the potentiometer;
- 301-304 – the ignition in the cylinder does not work correctly, consistently for all combustion chambers;
- 386 – incorrect sequence of testing the detonation channel;
- 410/425/426 – wiring of the canister purge flap, short circuit or line damage;
- 500 – the fuel pump relay line is damaged;
- 501/502 – similarly with a short circuit to the body or wiring;
- 509/513/514 – control center of the XX regulator, open or short circuit on board or 12V;
- 541 – damage to the wire of the BN relay, possible oxidation of the terminal;
- 570 – break in immobilizer control cables;
- 602 – no power to the ECM, oxidation of the pads is allowed;
- 606 – the bump sensor is broken, the part needs to be replaced;
- 616/617 – similarly with a change in signal level, there may be a short circuit inside the device;
- 2301/2303/2305/2307 - the ignition coils are shorted to 12 volts, in series for each piston.
Important!
Only the most popular error codes for the dashboard of the VAZ 2114 and similar models are listed here. There are other indices, but due to their low prevalence they are not mentioned.
How serious is P0101?
- When the P0101 , there are usually no serious problems with the vehicle's drivability, however, if this code is detected, it is recommended that you contact a qualified technician as soon as possible to diagnose and repair the error.
- Under certain circumstances, damage or failure of the mass air flow sensor can lead to increased fuel consumption, unstable engine operation, and problems starting the engine. In some cases, damage to internal engine components may occur.
- Often, if the Check Engine Light comes on immediately after starting the engine, the OBD-II system can be reset and the vehicle will continue to operate normally.
Common Problems Causing Code P0101 on Different Vehicles
In some GM and Chevrolet cars and trucks, code P0101 can be caused by a clogged catalytic converter. A clogged catalytic converter can be checked by measuring intake vacuum and exhaust backpressure. Associated symptoms may include misfire with codes P0300 to P0308, lack of traction under heavy load or during acceleration, and overheating of the catalyst.
Another problem in some GM vehicles is leaking intake manifold gaskets. One of the symptoms of a leaking gasket is rough idle when cold.
On vehicles with an oil-soaked air filter, oil from the filter can contaminate the air flow sensor element, causing a P0101 code or other MAF-related codes.
In some Volvo vehicles, the P0101 code can be caused by a dirty throttle body or vacuum leaks in the positive crankcase ventilation system (such as the vacuum line to the oil separator). A dirty throttle body will need to be cleaned and the intake manifold will need to be checked for air leaks.
The repair technical bulletin for some 2011-2012 Nissan Altima, Maxima and Sentra models recommends reprogramming the ECU if the P0101 code persists and there are no drivability problems.
What repairs can fix the P0101 code?
To resolve error P0101, you may need to:
- Check for the presence of the error code using a scan tool, clear the code from the computer's memory, and test drive the vehicle to see if the P0101 again
If the error code appears again:
- Reconnecting, Repairing, or Replacing the Mass Air Flow Sensor Electrical Connector
- Repair or replacement of electrical wires related to the mass air flow sensor
- Replacing worn or damaged vacuum hoses
Which cars are more susceptible to the P0101 error code?
Code P0101 can occur in any vehicle, even diesel. At the same time, there are statistical data that indicate on which car brands the error occurs more often. These include:
- Audi A8;
- BMW (BMW X5, 2 18);
- Chevrolet (Chevrolet Aveo, Captiva);
- Citroen Jumper;
- Fiat (Fiat Doblo, Fremont);
- Ford (Ford Transit, Kuga);
- Honda Civic;
- Hyundai (Hyundai Tucson, Getz);
- Kia (Kia Sorento, Sid, Bong);
- Mazda (Mazda 3, 5);
- Mercedes (Mercedes SL600, w203, Vito, Sprinter);
- Nissan (Nissan Patrol, Qashqai, Tiana);
- Opel (Opel Vectra, Astra);
- Peugeot (Peugeot Partner, Boxer);
- Renault (Renault Logan, Master);
- Toyota (Toyota Camry, Corolla, Venza);
- VW (Volkswagen Touareg, Tiguan, Passat);
- VAZ 2114;
- Lada (Lada Granta, Priora, Kalina);
- UAZ Patriot.
There are other problems that occur along with the P0101 trouble code. These include:
- P0106;
- P0107;
- P0171;
- P0300;
- P0430;
- P2004;
- P2180.
If error P0101 is detected, it is recommended to contact specialists at a service station to carry out a full diagnostic with OBD. This will prevent possible engine problems and extend the life of the vehicle.