Error p0443 indicates a malfunction of the gasoline evaporative system valve circuit (in English referred to as Evaporative System Purge Control Valve Circuit Malfunction). Most often, error code p0443 occurs on cars with considerable mileage (age), and is caused by clogged pipes or the valve itself (its filter). The error itself is not critical, and if it occurs, the car can be used, but still, at the slightest opportunity, it is better to get rid of it, especially since this is not at all difficult to do. In most cases, you will only need to clean the elements of the gasoline vapor recovery system.
Open circuit of the Kalina adsorber
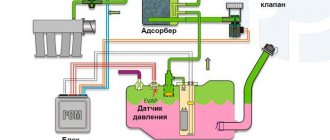
According to the requirements of new environmental standards that limit the content of harmful substances in exhaust gases, vehicles must be equipped with an EVAP system. This equipment prevents harmful fuel fumes from entering the atmosphere. The main function in the fuel vapor recovery system is performed by the adsorber. Some people underestimate the importance of this element in the operation of a car. However, a malfunction of this seemingly minor component can lead to damage to the fuel pump and affect the operation of the entire engine. Therefore, experts recommend checking the adsorber valve when signs of engine malfunction appear.
Purpose and principle of operation of the adsorber purge valve
The EVAP system is installed on gasoline internal combustion engines to prevent fuel vapors from entering the atmosphere. The canister purge solenoid valve is an element of this system. Therefore, to find out what the canister valve is for and how it works, it is important to understand the operating principle of the entire system. The design of the adsorber is a container filled with an adsorbent, most often activated carbon. The device is connected to the fuel tank and the control valve of the vehicle using special tubes.
The canister valve is installed between the intake manifold and the canister and performs the function of ventilation.
Gasoline vapors formed in the fuel tank penetrate the separator, where they condense and are discharged back into the tank. Some of the vapor does not have time to condense in the separator and enters the adsorber through the steam line. In the filter system, they are absorbed by activated carbon, accumulated and then supplied to the intake manifold when the engine starts. The process of absorption of fuel vapors takes place only when the engine is turned off. When the car is running, the electronic control unit opens the canister purge solenoid valve, through which air enters and thus ventilation occurs. In this case, the accumulated condensate along with air is sucked out of the adsorber and again enters the engine, where it is burned out. The canister valve provides ventilation to the entire mechanism and directs fuel condensate back to the engine.
Possible causes of error code p0443
There are a number of typical reasons due to which the so-called absorber error occurs, as error p0443 is sometimes called. Among them:
Valve circuit open
- Complete or partial failure of the electro-pneumatic valve of the gasoline vapor recovery system.
- A break or short circuit (to “+” or “ground”) of the wire connecting the terminals of the electro-pneumatic valve and the electronic engine control unit (ECU).
- A break (or damage to the insulation) of the wire between the control unit and the ground, which is responsible for transmitting the signal to the solenoid valve.
- Broken (or damaged insulation) wire between the main relay and the terminal on the evaporative emission system solenoid valve.
- Mechanical damage to the purge valve. For example, it is stuck in the fully open or fully closed position.
- Damage to the connectors, the so-called “chips”. They will be different for each car model; it is necessary to check those contacts that are responsible for controlling both the gasoline vapor recovery system in general and for controlling its solenoid valve in particular.
- Incorrect operation of the ECU. This is a fairly rare reason, however, there have been cases where, after its flashing or mechanical damage (for example, damage to the electronic track), so-called “glitches” occurred. However, in this case, as a rule, not one, but several errors occur, often unrelated to each other.
However, most often errors associated with incorrect operation of the fuel evaporation recovery system (including 0443) occur due to clogging of the filter and tubes or other elements that make up the specified system. For example, a common reason is that the foam in the adsorber rots and crumbles over time, causing coal to enter the system, clogging it. The valve also becomes clogged, as a result of which it stops working correctly, causing corresponding errors. Rotting occurs for banal reasons - old age, constant wetting from condensation, temperature changes, and so on. Often, if the EVAP system valve is clogged and the front windows are open, you can smell a distinct smell of gasoline in the cabin. This is especially true for the warm season.
There are cases where the reason for the formation of error P0443 is the absence of a fuse in the control circuit of the valve of the fuel vapor recovery system. Another option is to use a fuse with a lower trip current rating than required. For example, on the popular Chevrolet Aveo car, it was observed when installing a corresponding 10 Ampere fuse instead of the required 15 Ampere. Replacing it solved the problem.
Also, the cause of error code P0443 may be depressurization of the fuel tank cap (or hose system). For example, the rubber seal on its lid has worn out over time and does not hold the vacuum. To check this, just listen for a hissing sound when the car owner unscrews the gas tank cap. If there is sound, then most likely the system is sealed. If there is no such sound, there is a risk that it is letting air in, and this may be the direct reason for the formation of error code p0443 in the ECU.
Malfunctions of the adsorber valve and their elimination
Almost continuous operation of the fuel vapor absorption system canister can cause damage to the purge valve. A malfunction of the canister valve often leads to damage to the fuel pump. Due to poor ventilation of the adsorber, gasoline accumulates in the intake manifold, the engine loses power, and fuel consumption gradually increases. This may cause the engine to stop completely. The operation of the entire vehicle depends on how the adsorber valve works.
How to check the functionality of the canister purge valve?
Checking the absorber valve
In order to notice and correct problems in time, regular checks of the adsorber valve are necessary. In this case, a breakdown can be identified by certain indirect signs. When the engine is idling or in cold weather, the vapor absorption system makes characteristic sounds, like the canister valve clicking. Some people confuse this sound with a faulty timing belt, rollers or other parts. You can check this by sharply pressing the gas pedal. If the sound has not changed, it means the canister valve is clicking. Experts can explain what to do if the canister valve knocks too loudly. To do this, you need to tighten the adjusting screw, and first it is cleared of epoxy resin.
The absorber valve can be adjusted.
The screw turns approximately half a turn. If you tighten it too much, the controller will generate an error. This adjustment of the adsorber valve will make its operation softer and the knocking noise quieter. However, how to check the adsorber valve for damage? Valve failure can be determined using an error diagnostic system or mechanical testing. Electronic error codes are stored in the controller's memory and indicate electrical damage. To check the valve, it is recommended to pay attention to errors generated by the controller, such as “open circuit of the canister purge valve control circuit.” Signs by which a malfunction of the adsorber valve can be mechanically determined:
- The appearance of dips at idle speed of the engine.
- Very low engine thrust.
- There is no sound of valve operation when the engine is running.
- A hissing sound when the gas tank cap is opened indicates a vacuum in the system. This is a sure sign of a malfunction in the adsorber ventilation.
- The appearance of a fuel smell in the car interior. However, its appearance can also be caused by other reasons.
Troubleshooting P0443
Step 1
Using a diagnostic scanner or ELM327 adapter, command the purge valve to turn on. Listen or feel the solenoid click. It should click once, and on some vehicles it may click again.
Step 2
If there is no click when operating the scan tool, disconnect the connector and inspect it and the valve itself for damage, water, etc. Then check the voltage with a multimeter on the appropriate wire with the ignition key on.
If there is a voltage of +12 V, then use a jumper to apply minus to the second control wire of the valve and see if it clicks. If the valve clicks, the solenoid is working and there is a problem in the control circuit.
If the purge valve does not click when manually applying minus, replace it.
Do-it-yourself absorber valve replacement
If signs of malfunction are detected, the valve will need to be repaired or replaced. The adsorber valve is inexpensive and easy to replace. To dismantle you need to have a pair of Phillips screwdrivers and know where the canister purge valve is located. Operating procedure:
The markings on the old and new valves must match.
- Open the hood and find a cylindrical device - an adsorber.
- Remove the negative terminal from the battery.
- Disconnect the wire block by pressing the latch and pulling it towards you.
- Loosen the valve.
- Remove the fittings under the latch and disconnect the hoses.
- Remove the valve together with the bracket from the adsorber.
- The new valve is installed in the reverse order.
Thus, even such a small element as the adsorber valve performs important functions and its malfunction can seriously disrupt the operation of the entire engine. Therefore, it is important to monitor the condition of your car and carry out diagnostics on time.
I once went to the city of Samara on business, the last time I was there was around mid-autumn 2015, but when I drove into the city the day before yesterday I was simply shocked, where are the roads? no roads! melted. Having driven through them, the Check engine error came out, I was not much scared, I thought everything, soon I’ll get up somewhere and won’t start)) But having completed my business, I went home, the car did not behave adequately, when I pressed the gas pedal, all the agility of the car disappeared, as if It’s about to stall, but thank God I got home, took an OBD adapter from my father and did some diagnostics and this is what happened
I bit off all the wires completely, took a soldering iron, cleaned it, tinned it and soldered everything back, and threw more cambrics on top.
We do diagnostics, erase old errors, restart the computer (who doesn’t know what’s better to do on a stalled engine), but the key must be in position 1... That’s it, there are no more errors, Check is gone! HOORAY! I almost forgot, the valve itself is located under the air filter!
And here's something else I did the other day, changing the style of the taillights.
I did this both to change the style and so that the turn signals could be seen better, especially when you need to say thank you! I also ordered and the LED reverse lights have already arrived.
Reg.: 12/06/2004 Threads / Messages: 628 / 51730
The computer started giving an undocumented error 441 at startup, if you reset it, then until you turn off the car the error does not appear again, the error does not appear at every startup. computer Navigator.
Added after 2 hours 1 minute 44 seconds:
On the chiptuner website they write this:
Reg.: 07.28.2005 Threads / Messages: 1 / 2646 From: Ivanovo Age: 43 Car: Nivka2121. g.v. worn-out 1.9i and other minor tuning Murzik MV 300TD 1993
0441 gasoline vapor recovery system incorrect air flow through the canister purge valve. Check the canister valve for air leakage through its hoses and fitting in the throttle pipe
Added after 1 minute 34 seconds:
In general, the error is documented, it’s just that it’s only in euro 3
Reg.: 12.12.2004 Threads / Messages: 5 / 1412 From: Moscow Age: 54 Car: VAZ 21214. 2004.
Reg.: 09/11/2007 Messages: 41 From: Moscow, Perovo Age: 54 Car: 21214, nautilus, M7.9.7+, March 2007
Why the check light is on on the Lada Kalina: causes and methods of troubleshooting
Many Lada Kalina owners have encountered such a common effect as “Check Engine”. The very concept of this indicator means that there are problems in the engine. But these are the ones that are not always clear to the average car enthusiast.
"Check Engine" - the show of intuition begins
Many Kalinovites, when the check signal comes on, begin to panic and immediately go to a car service center. But not everything is as bad as it seems at first glance, and the reason may lie on the surface. So, let's look at why the check engine light is on on the Lada Kalina and the reasons for the mysterious effect:
- Failure of one of the power unit sensors.
- Throttle.
- Injectors.
- Fuel pump and filter.
- Air filter.
- Spark plugs and high-voltage wires.
- Petrol.
- ECU.
Troubleshooting methods
Now that all the causes have been identified, we can begin to consider troubleshooting.
But, before we begin, it is worth noting that a car enthusiast needs to have an idea of the design features of the engine if he wants to fix the problem himself.
Otherwise, go directly to a car service center, in order to avoid other problems that, due to lack of experience, car enthusiasts usually create for themselves.
Sensors
Often, the reason why the check light on Kalina may come on is the failure of one of the sensors. Possible ones that are worth checking right away include: mass air flow sensor, idle speed control, crankshaft position sensor, oxygen sensor and coolant temperature sensor.
You can determine the cause by going through each sensor separately and using a tester to check their functionality.
But, there is a simpler and more effective way to determine the malfunction of a particular sensor, namely connecting to the electronic engine control unit. Here you can look at the errors and, by deciphering them, determine where the problem is.
Throttle
A clogged throttle valve can often cause the check engine light to come on because not enough air is supplied to the power unit. The solution to the problem is cleaning. This process can be carried out using carburetor cleaning fluid or VD-40 fluid.
The part is removed from the car and cleaned, after which it is installed in place. It is also recommended to check the throttle position sensor, which may have failed.
Injectors
One of the common reasons for the “check” icon to appear on the dashboard is a malfunction of one or more injectors that do not spray the fuel mixture properly. So, it is worth dismantling all the elements and checking them using a special stand.
If there is none, then you can use the traditional method by pouring flushing fluid into the fuel supply pipes and activating the injectors using the battery. This way it will be clear which injector is not working well. But, experienced auto mechanics recommend cleaning and checking the nozzles on a stand, since the effectiveness of the procedure is higher.
Fuel pump and filter
Another cause of the malfunction may be a malfunction of the gasoline pump or its filter. Lack of power or contamination of the filter elements leads to the fact that an insufficient amount of fuel will enter the power unit to form an air-fuel mixture.
This can also cause such a well-known automotive effect as engine tripping.
The malfunction can be cured by checking the functionality of the gasoline pump, as well as by replacing the filter inside the gasoline pump. It is also worth looking at the fuel filter, which could become clogged when pouring low-quality gasoline.
Air filter
A clogged air filter can cause insufficient air in the combustion chambers. So, to check this element, it must be dismantled, which is done quite simply. By inspecting the filter element, you can find out how dirty it is and whether the product needs to be replaced. So, after replacement, the check signal from the dashboard may disappear.
Spark plugs and high voltage wires
Wiring is also often the reason why the check icon lights up on the panel. This happens when the spark plug is inoperative or there is a breakdown in one of the high-voltage wires.
It is recommended to check spark plugs on a special spark plug stand. But, if there is none, then you can use the generally accepted “old-fashioned” methods. But high-voltage wires are checked using a conventional multimeter, where the resistance along each wire should be about 5 ohms. If a broken part is found, it must be replaced.
Petrol
But, in addition to the above reasons, the problem may lie on the surface. Thus, ordinary low-quality gasoline can cause the “Check Engine” icon to appear on the car’s dashboard.
To eliminate the breakdown, it is necessary to drain the low-quality fuel and flush the fuel supply system.
But, if you drive for a long time on such fuel, the batteries may fail, which should also be checked when flushing.
ECU
The last reason is the accumulation of errors or “failed” firmware of the electronic engine control unit. To fix this problem, it is recommended to contact a professional car service center. Also, with the help of “brain” errors, you can determine why the check engine light came on. But where can I get the codes deciphered? Let's look at what code that means:
- 0102 Low signal level of the mass air flow sensor
- 0103 High signal level of the mass air flow sensor
- 0112 Low level of intake air temperature sensor
- 0113 Intake air temperature sensor high level
- 0115 Incorrect coolant temperature sensor signal
- 0116 Incorrect coolant temperature sensor signal
- 0117 Coolant temperature sensor signal low
- 0118 High signal level of the coolant temperature sensor
- 0122 Low signal level of the throttle position sensor
- 0123 Throttle position sensor signal high
- 0130 Incorrect signal from oxygen sensor 1
- 0131 Low signal level of oxygen sensor 1
- 0132 Crankshaft sensor 1 signal high
- 0133 Slow response of oxygen sensor 1
- 0134 No signal from oxygen sensor 1
- 0135 Oxygen sensor 1 heater fault
- 0136 Oxygen sensor 2 short to ground
- 0137 Low signal level of oxygen sensor 2
- 0138 High signal level of oxygen sensor 2
- 0140 Oxygen sensor 2 break
- 0141 Oxygen sensor 2 heater fault
- 0171 Mixture too lean
- 0172 Mixture too rich
- 0201 Open injector 1 control circuit
- 0202 Open injector 2 control circuit
- 0203 Open injector 3 control circuit
- 0204 Open injector 4 control circuit
- 0261 Short to ground injector 1 circuit
- 0264 Short to ground injector 2 circuit
- 0267 Short to ground in injector 3 circuit
- 0270 Short to ground in injector 4 circuit
- 0262 Short circuit to +12V injector 1 circuit
- 0265 Short to +12V injector 2 circuit
- 0268 Short to +12V injector 3 circuit
- 0271 Short circuit to +12V injector 4 circuit
- 0300 Many misfires
- 0301 Misfire in cylinder 1
- 0302 Misfire in cylinder 2
- 0303 Misfire in cylinder 3
- 0304 Misfire in cylinder 4
- 0325 Open circuit of the knock sensor
- 0327 Low signal level of the knock sensor
- 0328 High signal level of the knock sensor
- 0335 Incorrect crankshaft position sensor signal
- 0336 Crankshaft position sensor signal error
- 0340 Phase sensor error
- 0342 Low phase sensor signal
- 0343 Phase sensor signal high
- 0422 Low neutralizer efficiency
- 0443 Canister purge valve circuit malfunction
- 0444 Short circuit or break in the adsorber purge valve
- 0445 Short to ground of the canister purge valve
- 0480 Cooling fan 1 circuit malfunction
- 0500 Invalid speed sensor signal
- 0501 Invalid speed sensor signal
- 0503 Speed sensor signal interruption
- 0505 Idle air control error
- 0506 Low idle speed
- 0507 High idle speed
- 0560 Incorrect on-board voltage
- 0562 Low voltage on-board network
- 0563 High voltage on-board network
- 0601 ROM error
- 0603 External RAM error
- 0604 Internal RAM error
- 0607 Detonation channel malfunction
- 1102 Oxygen sensor heater resistance low
- 1115 Faulty oxygen sensor heating circuit
- 1123 Rich mixture at idle
- 1124 Lean mixture at idle
- 1127 Rich mixture in Partial Load mode
- 1128 Lean mixture in Partial Load mode
- 1135 Oxygen sensor heater circuit 1 open, short circuit
- 1136 Rich mixture in Light Load mode
- 1137 Lean mixture in Low Load mode
- 1140 Measured load differs from calculation
- 1171 Low level CO potentiometer
- 1172 High level CO potentiometer
- 1386 Detonation channel test error
- 1410 Canister purge valve control circuit short circuit to +12V
- 1425 Canister purge valve control circuit short circuit to ground
- 1426 Canister purge valve control circuit open
- 1500 Open circuit in the fuel pump relay control circuit
- 1501 Short circuit to ground of the fuel pump relay control circuit
- 1502 Short circuit to +12V fuel pump relay control circuit
- 1509 Overload of the idle speed regulator control circuit
- 1513 Idle air control circuit short circuit to ground
- 1514 Idle air control circuit short circuit to +12V, open
- 1541 Fuel pump relay control circuit open
- 1570 Invalid APS signal
- 1600 No connection with APS
- 1602 Loss of on-board voltage to the ECU
- 1603 EEPROM error
- 1606 Rough road sensor incorrect signal
- 1616 Rough road sensor low signal
- 1612 ECU reset error
- 1617 Rough road sensor high signal
- 1620 EPROM error
- 1621 RAM error
- 1622 EEPROM error
- 1640 EEPROM Test Error
- 1689 Invalid error codes
- 0337 Crankshaft position sensor, short to ground
- 0338 Crankshaft position sensor, open circuit
- 0441 Air flow through the valve is incorrect
- 0481 Cooling fan 2 circuit malfunction
- 0615 Starter relay circuit open
- 0616 Starter relay circuit short circuit to ground
- 0617 Starter relay circuit short circuit to +12V
- 1141 Faulty oxygen sensor heater 1 after the converter
- 230 Fuel pump relay circuit malfunction
- 263 Injector driver fault 1
- 266 Faulty injector driver 2
- 269 Injector 3 driver fault
- 272 Faulty injector driver 4
- 650 Check Engine Lamp Circuit Malfunction
How to check the adsorber valve using the Lada Kalina as an example
The gas tank of any car always contains vapors formed due to a decrease in atmospheric pressure or heating of the fuel. In order to prevent the leakage of fuel vapors into the vehicle, a special gasoline vapor recovery system (VPSU) is installed. Thanks to it, the vapors retained by the adsorber (essentially activated carbon) enter the intake manifold and burn in the engine cylinders. To regulate the amount of gasoline vapor coming from the adsorber to the manifold, a special solenoid valve is used.
How does the Lada Kalina gasoline vapor recovery system work?
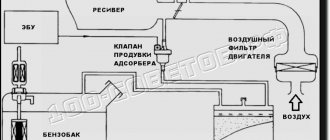
The EVAP system in question was created to prevent the release of harmful gasoline vapors into the surrounding atmosphere resulting from fuel evaporation; it includes:
- fuel shut-off valve;
- adsorber;
- solenoid valve for purging the absorbent element;
- connecting pipelines.
The most important component in the system is the adsorber (also called a carbon filter), the basis of which is activated non-edible carbon, enclosed in a plastic housing.
The resulting gasoline vapors are absorbed by the carbon of the absorbent element, gradually accumulating in it.
When the engine starts, the canister purge valve (KPA) is turned on, and due to the vacuum, all accumulated vapors enter the intake manifold and then burn out.
On the Lada Kalina, the adsorber is located in the gas tank area, and getting to it is very difficult.
To dismantle this EVAP element, it is necessary to remove the fuel tank, but the control unit is located in an accessible place - the valve is located in the engine compartment, in close proximity to the battery, on the rear wall of the air filter housing.
It should be noted that for turbocharged engines, a vacuum is not created in the intake manifold, and in order to force the vapors in the desired direction, an additional two-way valve is included in the circuit.
Design of the VAZ Kalina adsorber purge valve
KPA is present on all modern injection internal combustion engines, and Lada Kalina is also no exception.
The purge valve (another name is Evap-Solenoid) is connected on one side to the carbon filter, on the other to the intake manifold, when there is no electrical signal to the control unit, the pipeline channel is closed, and vacuum is not created in the system.
When an electrical signal is supplied while the engine is running, the valve is activated, the channel opens, and gasoline vapors freely pass from the adsorber into the intake manifold.
Malfunctions in the fuel vapor recovery system Lada Kalina
Since the solenoid valve itself is not a complex device, it has few malfunctions as such - it may not open or close when necessary, or may freeze in a certain position. But the culprit of the breakdown may not only be Evap-Solenoid; the gasoline vapor recovery system does not work correctly for other reasons:
- connecting pipes are pinched or clogged;
- normal vacuum is not created in the system;
- due to an open circuit, there is no voltage on the valve;
- the carbon filter is completely clogged (which is rare);
- The control unit malfunctions.
If the CPA is stuck in the open position and does not block the channel, the following defects may occur:
- the fuel mixture becomes richer, causing “blackness” to appear on the electrodes of the spark plugs;
- the engine begins to operate unstably, this is especially noticeable at idle;
- gasoline consumption increases;
- The throttle response of the internal combustion engine decreases.
When the EVAP channel is constantly blocked by the purge valve, excess vapor pressure is created in the gas tank, due to this:
- there is a risk of fuel pump failure;
- The fuel level sensor may fail.
It should be noted that purge occurs in a certain mode after starting the engine, the program is executed depending on the crankshaft speed, and the system does not work at idle. An impulse arrives at the CPA if:
- the coolant has heated to a temperature of at least 75 degrees Celsius;
- the throttle valve is open at least 4%;
- the car is moving at a speed of more than 10 km/h (but this is not a necessary condition).
Problems in the electrical part of the EVAP are detected by the control unit, and the Check Engine warning lamp lights up on the instrument panel. The fault code can be determined using a special diagnostic scanner or a computer with a program installed; the most common errors in the vapor recovery system detected by the diagnostic device are P0441 and P0455.
Replacing the adsorber purge valve on Kalina
If the check shows that the Evap-Solenoid is faulty, the part must be replaced (catalog number - 11181164200). There is no point in repairing the device:
- the price of the valve is in the range of 400-800 rubles;
- You can buy the device in almost any store that sells VAZ spare parts;
- changing the KPA is very easy and simple.
But before making a replacement, it would be a good idea to check the control circuit; quite often the valve does not work due to a break in the wires going to it. To complete the work, you will not need a pit or a lift, and the procedure itself will take no more than one to two hours, even if the operation is performed by an inexperienced worker without metalworking skills.
We change the valve as follows:
- turn off the ignition, raise the hood;
- we find Evap-Solenoid, it is located just below the air duct, on the air filter housing (indicated by an arrow in the figure below):
- just in case, disconnect the negative terminal from the battery;
- move the plug tab to the side and disconnect the wires;
- so that the air flow sensor does not interfere, use a Phillips screwdriver to loosen the clamp securing the air duct, and move the pipe to the side. For convenience, the air flow sensor can be removed;
- Now access to the valve is free, all that remains is to gently pull it up to pull it out of the grooves;
- but that’s not all - since the tube on the valve itself is sealed, we do not touch this connection for now, it is necessary to release the other end of the hose, to do this we remove the latch and pull the pipe out of the connection;
- We dismantle the valve together with the tube, and the disassembly is almost complete.
Replacing the purge valve could be considered a very simple task, if not for one “but” - it is very difficult to remove the plastic tube from the CPA without damaging it, and it does not come with the new valve. There are two options here:
- try to carefully heat the connection with a hairdryer and pull off the pipe;
- cut the tube at the connections, and instead buy an ordinary fuel hose with a diameter of 8 mm and two clamps.
We install everything in place, start the engine, and test the car on the move.
The adsorber valve is knocking on Kalina
Many owners of Lada Kalina cars are faced with a problem - while the engine is running, an incomprehensible clattering sound is heard from under the hood; when identifying the cause of the noise, it turns out that the sound comes from the purge valve. Although the knocking does not affect the operation of the car in any way, some car owners are annoyed by it, and car owners want to get rid of it. You can “overcome” the unpleasant clattering sound; you just need to do the following:
- remove the valve and inspect it carefully;
- Find the adjusting screw on the side; it will be filled with epoxy resin on top;
- pick out the epoxy, tighten the screw half or three-quarters of a turn;
- install the valve in place, check for changes in the operation of the internal combustion engine.
Principle of operation
The adsorber itself allows fuel vapors to accumulate in a special place - the separator. As a result, gasoline turns into condensate and goes back to the tank. Vapors that have not undergone treatment go through double valves of the system, one of which prevents fuel from spilling out during an emergency (for example, a coup), and the second “is engaged” in regulating the pressure in the tank. The adsorber purge valve is located under the hood, and the adsorber itself is located on the tank. The control unit ensures the normal operation of the entire system: it ventilates and removes condensation.
What does a vapor recovery system consist of?
The management system in Kalina consists of the following elements:
- fuel outlet and return lines;
- separator;
- adsorber;
- canister purge valve.
As you can see, the system is quite simple. Let's consider the purpose of each of its elements separately.
As for fuel lines, these are simply tubes through which gasoline vapors leave the tank, and also through which fuel returns back to it. The separator is used to collect fuel vapors and condense them. The adsorber is designed to capture those vapors that did not have time to turn into a liquid state. The adsorber purge valve (“Kalina”) is necessary to direct gasoline vapors to the intake manifold receiver.
Design and operation of the adsorber purge valve
The KPA is an electromagnetic locking device that operates from the vehicle’s on-board network. The valve consists of:
- plastic case;
- valve with spring;
- windings;
- metal core;
- connector
When the vehicle's engine is turned off, no voltage is supplied to the valve and it remains in the closed position. That is, on the motor side, the system that captures vapors is blocked. At the same time, the adsorber begins to “collect” vapors. When the power unit starts, voltage is applied to the valve, causing it to open and fuel vapors to enter the intake manifold. As soon as the ignition is turned off, the control unit is de-energized and the pipeline is closed: no vapors enter the receiver.
Cars of a high price category have a more complex evaporation system. Such machines have special sensors that can “calculate” the amount of air and vapor as a percentage. This allows you to more accurately control the supply of gasoline to the injector.
Additional errors
Often, an adsorber error is accompanied by other, parallel errors, which indicate problems with adjacent elements of the system. So, frequent “companions” of this problem are errors with codes:
P0444 . This error indicates that there is a short to power supply or an open circuit in the control circuit of the canister purge valve. Also, to generate an error with code p0444, the following prerequisites must be met (they may differ for different car models; the popular Hyundai Solaris is taken as an example):
- intact (not broken or damaged) electrical wiring, in particular from the ECU to the EVAP system solenoid valve;
- the value of the constant voltage on the battery and in general in the electrical system of the machine is in the range from 10.7 to 16 Volts;
- long diagnostic time;
- The Check Engine light on the instrument panel is activated after three driving cycles.
In the mentioned Hyundai Solaris car, the resistance value of the EVAP system valve winding is exactly 16 Ohms at a temperature of +20°C.
P0447 . The error code indicates that the evaporative control valve control circuit is open (broken). As a rule, the reason for the formation of this error is the “rotting” of the control wiring going to the solenoid valve. This problem often occurs on cars in which the valve is located in the rear of the body, for example, near one of the rear wheels. In this case, the wiring is affected by moisture, dirt, and reagents from the road surface. All this over time can damage the protective insulation of the wiring and, as a result, cause an error with the mentioned code. As a repair, we can only recommend replacing the wiring, and maybe the entire valve.
Conclusion
Error code p0443 is not critical, and when it occurs, you can use the car without worrying too much about its technical condition. However, the malfunctions that caused it still have a negative impact on the environment, and in critical cases can lead to poisoning of the driver or passengers with gasoline fumes. Also, in an enclosed area, large amounts of evaporated gasoline can lead to an increased risk of explosion and/or fire. Therefore, at the slightest opportunity, it is still better to get rid of error p0443 by correcting the faults that caused the conditions for its formation.
Signs of a malfunction of the control unit
First, start the engine: at idle or in cold weather, you will hear a characteristic, barely audible chirping sound. It indicates that the valve is working properly. In order not to confuse this sound with the noise from a working timing belt, sharply press the gas. The character of the chatter should not change. The following signs indicate a malfunction of the control unit:
- lighting of the CHECK signal on the instrument panel;
- determination of error PO441 during testing;
- increased gasoline consumption;
- unstable operation of the power unit when driving;
- unstable idle;
- increase in CO2 content;
- a hissing sound when unscrewing the tank lid (a vacuum has appeared);
- the appearance of a fuel smell in the cabin.
Valve check on site
You will need a tester (voltmeter, multimeter) and a screwdriver. The KPA itself is installed on the radiator frame. The device can be recognized by seeing two tubes approaching it, through which the evaporation moves. Further:
- disconnect the electrical connector from the control unit by releasing the block lock;
- using a multimeter, check for the presence of voltage by touching the negative (black) probe of the device to ground, and the red probe to “A” (the letter on the block connector);
- turn on the ignition: the multimeter should show the vehicle's on-board voltage. If not, check the wiring.